目录

🍯1.5?extern "C"
🥝1. 静态库与动态库的概念
通过1.4节的简单分析,我们知道了函数重载的原理,但在这里我们再拓展一下有关“链接”的内容,首先我们来了解一下动态库与静态库。
Q1:什么是静态库?
A1:静态库是指在我们的应用中,有一些公共代码是需要反复使用,就把这些代码编译为“库”文件;在链接步骤中,连接器将从库文件取得所需的代码,复制到生成的可执行文件中的这种库。
Q2:动态库与静态库的区别是什么?
A2:静态库和动态库是两种共享程序代码的方式,它们的区别是:静态库在程序的链接阶段被复制到了程序中,和程序运行的时候没有关系;动态库在链接阶段没有被复制到程序中,而是程序在运行时由系统动态加载到内存中供程序调用。使用动态库的优点是系统只需载入一次动态库,不同的程序可以得到内存中相同的动态库的副本,因此节省了很多内存。
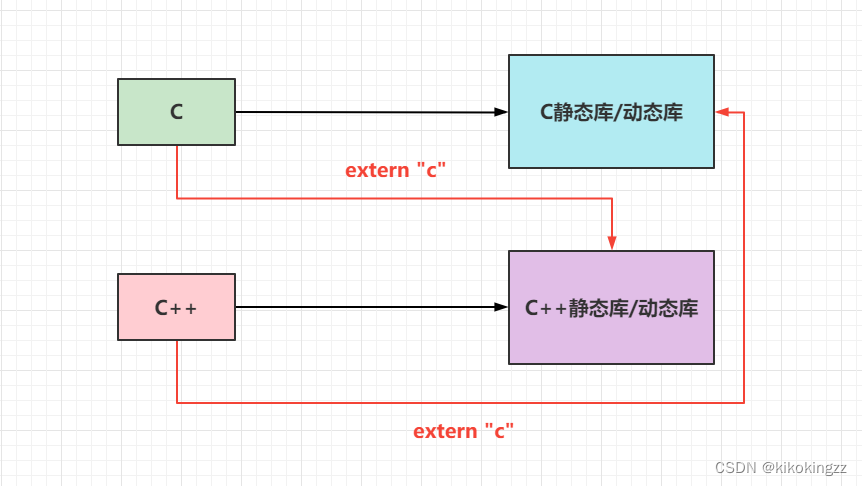
🥝2. C与C++的库调用
C与C++都可以互相调用对应的库,即C可以调用C和C++的静态库/动态库;相对地,C++也可以调用C++和C的静态库/动态库。但是由于C和C++编译器对函数名字修饰规则不同(如下例所示),在混合模式下开发,可能会导致链接失败。
int Add(int a, int b) { return a + b; } 使用C语言编译器编译:00000000004004ed<Add>: /*这里的函数名为Add*/ 使用C++编译器编译: 00000000004004ed<_Z3Addii>: /*函数名为_Z3Addii*/为了可以在C++工程中使用C语言库,C工程中使用C++的库,我们就可以在函数前加extern "C",意思是告诉编译器,将函数按照C语言规则来编译。
🥝3. 在C++里调用C的静态库
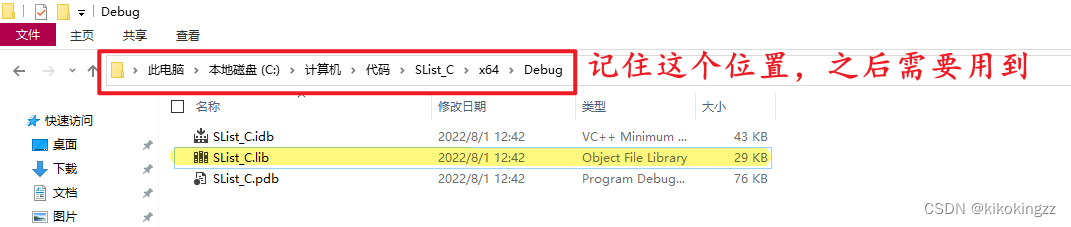
在使用extern "C"之前,我们首先需要自己创建一个静态库,我们可以新建一个项目,在这个项目中我们用C语言来编写一些函数,下例中我写了一个单链表的头文件以及单链表的函数文件,并将该项目设置为静态库.lib类型。
然后为其生成解决方案,并从文件夹中找到对应的SList_C.lib文件的位置。
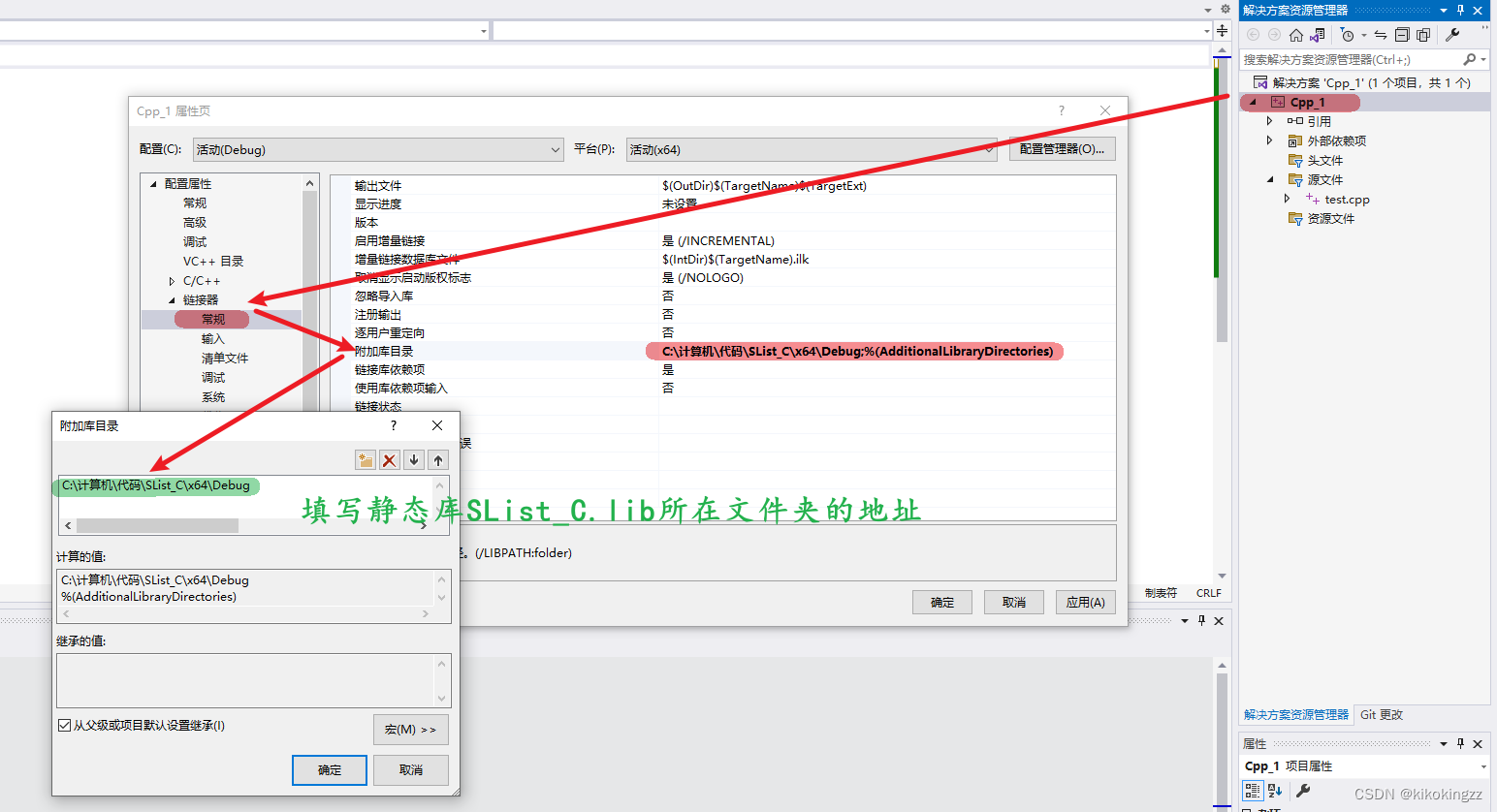
接下来,我们再建立一个C++项目,我们将会在C++项目中调用C语言的静态库,但是在此之前我们需要对C++的项目进行一定的配置操作:
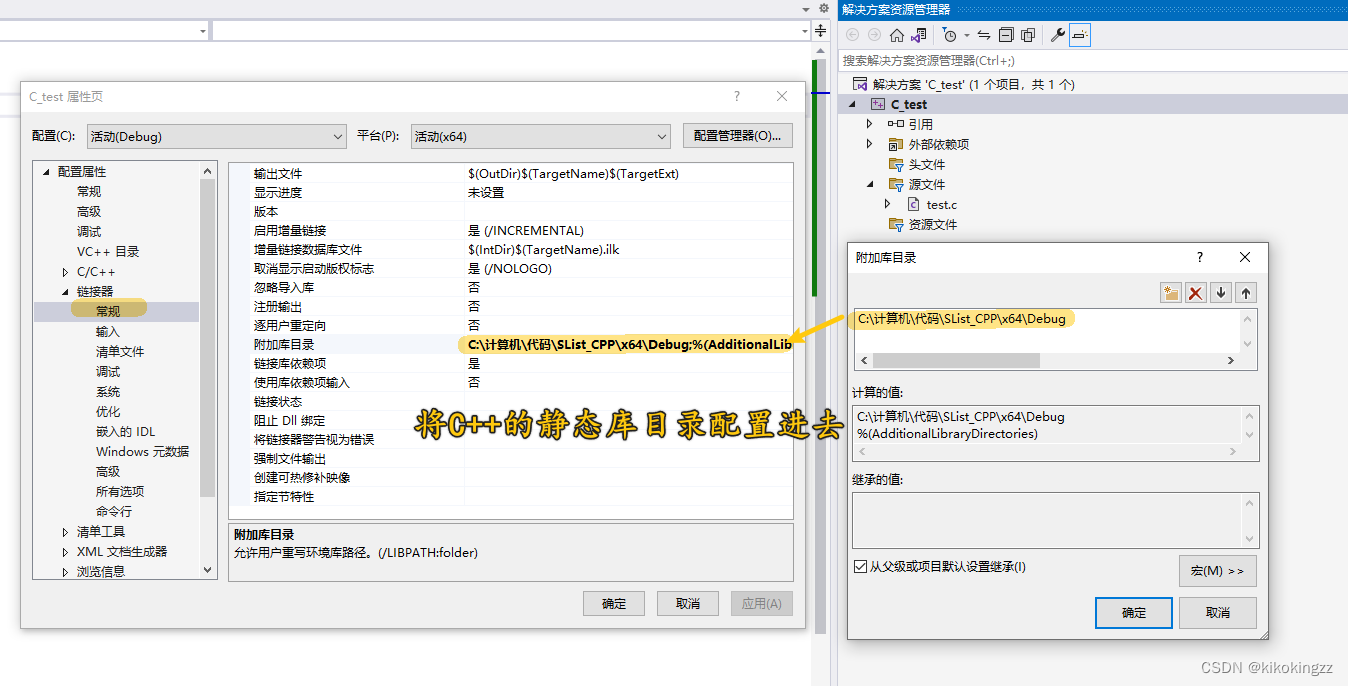
- 首先我们需要在附加库目录中添加SList_C.lib所在的这个文件的目录。
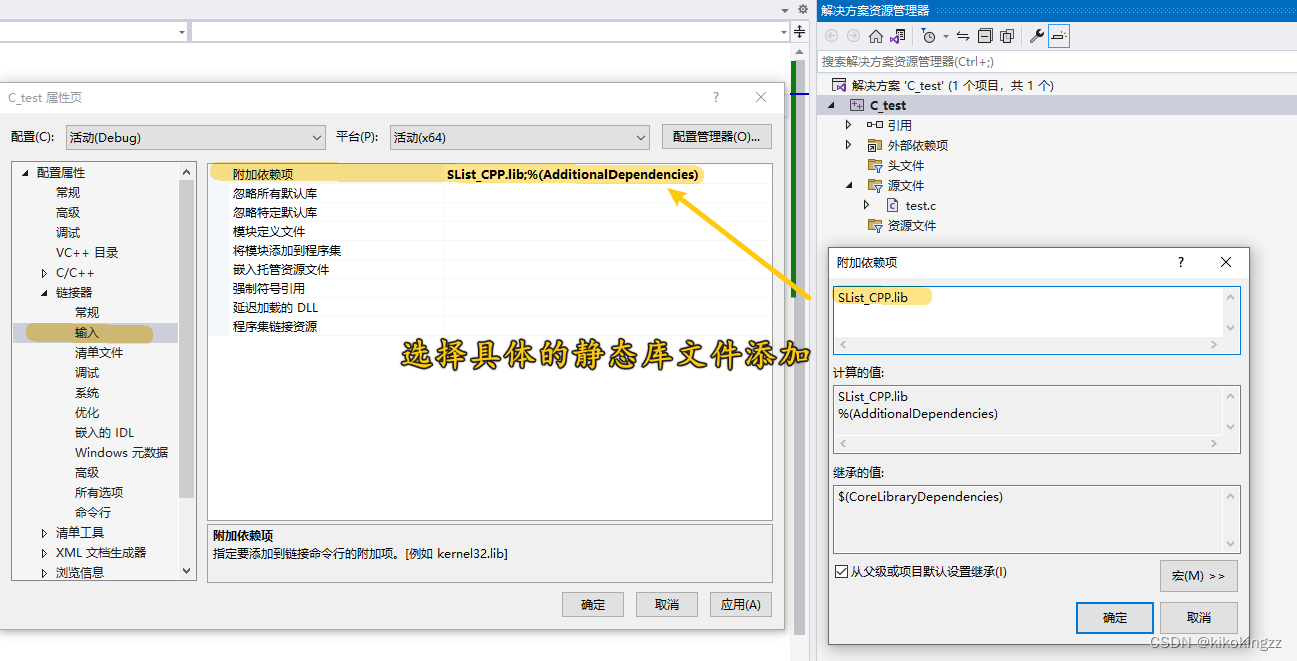
- 然后我们需要在【附加依赖项】中填入静态库的名称。
完成上述配置操作后,我们就到达了最后一步,使用extern "C"将引头文件的这句话扩住,其相关代码如下:
extern "C" //告诉编译器,extern C声明的函数是C库,要用C的方式去链接调用 { #include"../../SList_C/SList_C/SList.h" //引单链表的头文件 } int main() { SListNode* slist = NULL; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { SListPushBack(&slist, i); } SListPrint(slist); }
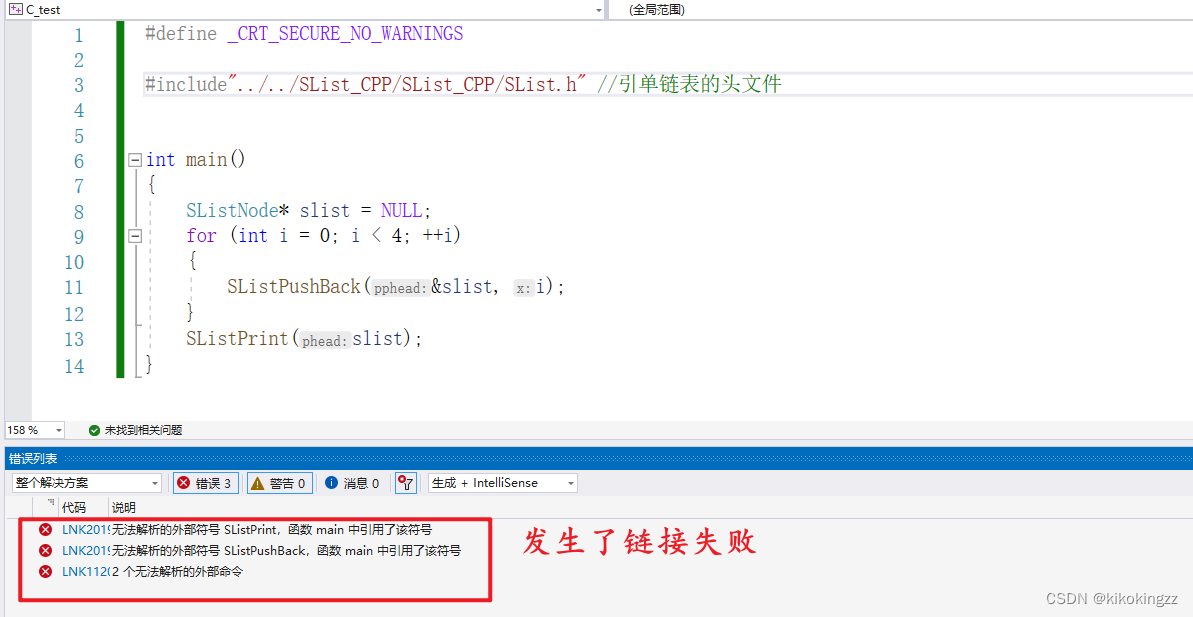
如果此时我们不添加extern "C"这条语句的话,就会出现链接不到静态库的报错:
🥝4. 在C里调用C++的静态库
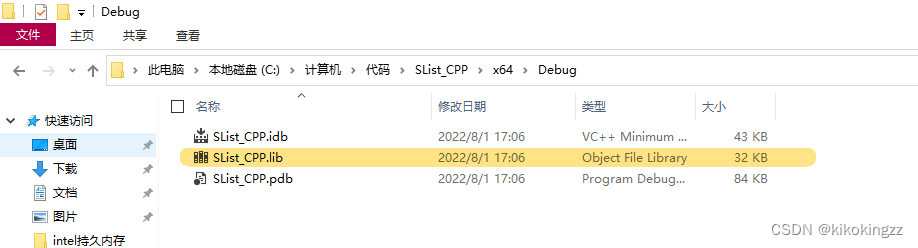
通过上面的操作,我们成功实现了在C++中调用C的静态库的操作,现在我们来尝试一下能否在C中调用C++的静态库,我们同样先创建一个C++的项目,并为其添加单链表文件(因为上面写过一遍了,这里我们只需要将SList.c与SList.h的文件拷贝到这个项目中即可,但是要将SList.c的后缀改为SList.cpp),将其设置为静态库类型SList_CPP.lib。
这时我们就可以在文件中找到这个生成后的SList_CPP.lib文件了。
完成上述操作后,我们建立一个新的C项目,我们将在C中去调用C++的静态库,这时我们同样需要将C++的静态库配置给C。
通过完成上述操作后,我们就先尝试执行一下代码,值得注意的是,C语言是不认识extern "C"的,因此我们不能添加这一句代码:
#include"../../SList_C/SList_C/SList.h" //引单链表的头文件 int main() { ?? ?SListNode* slist = NULL; ?? ?for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) ?? ?{ ?? ??? ?SListPushBack(&slist, i); ?? ?} ?? ?SListPrint(slist); }
此时会发生链接失败,这是因为链接的是C++的静态库,C++中对于每一个函数名的修饰都与C不同,因此C在C++这个静态库中是找不到名字为SListPushBack这个函数的,因此为了能让C语言可以读懂C++中的函数名,我们需要对C++静态库中的函数进行限制,在每一个函数名前设置extern "C",让C++的静态库用C的方式去链接调用,即将程序代码进行如下修饰:
#ifdef __cplusplus //如果在C++的环境中 #define EXTERN_C extern "C" //将EXTERN_C 宏替换为extern "C",让C++理解 #else //如果不在C++的环境中 #define EXTERN_C //将EXTERN_C 替换为空白 #endif EXTERN_C void SListPrint(SListNode * phead); EXTERN_C void SListPushBack(SListNode** pphead, DataType x); EXTERN_C void SListPushFront(SListNode** pphead, DataType x); EXTERN_C void SListPopBack(SListNode** pphead); EXTERN_C void SListPopFront(SListNode** pphead); EXTERN_C SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* phead, DataType x); EXTERN_C void SListInsertBefore(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos, DataType x); //在pos位置前面插入 EXTERN_C void SListInsertAfter(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos, DataType x); //在pos位置前面插入 EXTERN_C void SListErase(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos); //删除指定的pos位置 EXTERN_C void SListDestroy(SListNode** pphead);当然,我们也可以对上面的这种方式进行简化操作,修改后的代码如下:
#ifdef __cplusplus //如果是C++环境 extern "C" { #endif void SListPrint(SListNode* phead); void SListPushBack(SListNode** pphead, DataType x); void SListPushFront(SListNode** pphead, DataType x); void SListPopBack(SListNode** pphead); void SListPopFront(SListNode** pphead); SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* phead, DataType x); void SListInsertBefore(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos, DataType x); //在pos位置前面插入 void SListInsertAfter(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos, DataType x); //在pos位置前面插入 void SListErase(SListNode** pphead, SListNode* pos); //删除指定的pos位置 void SListDestroy(SListNode** pphead); #ifdef __cplusplus //如果是C++环境 } #endifQ1:为什么要使用条件编译+宏?
A1:这是因为虽然使用了extern "C"使得C++的编译器明白在调用函数时按照C的方式去链接调用,但是C在调用这个C++的头文件时,并不认识extern "C",因此使用条件编译的方式。
Q2:当C调用C++的库时,C++的库中可以函数重载嘛?
A2:这时不可以,因为这时C++的库中会使用extern "C",即按照C的方式去链接调用,这时函数重载就会导致这两个函数名字相同,导致命名冲突。
#ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif void SListPrint(SListNode* phead); //函数重载 void SListPrint(int n); #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif