C和C++的 区别
1、C 是面向过程的语言,而C++是面向对象的语言
2、C和 C++动态管理内存的方法不一样,C是 使用 malloc/free 函数,而 C++ 除此之外还有new/delete函数
3、C++ 对 C 的 struct 进行了扩展 ,C++中 struct 默认是public的 ,class中默认是private的
?
?
extern
?
C
??举例说明,项目文件夹下有多个文件,main.c、hello1.c、hello1.h、hello2.c、hello2.h,现在希望 声明一个整型变量在hello1.c中定义,但是 hello2,c 和 main.c 中都可以使用,就可以在hello1.c 中定义一个 int key ,在hello2.c 和 main.c 中用 extern 声明 key 是一个外部变量即可。
?
?
C++
??C++是向下兼容 C的,所以extern关键字C中有的功能 ,C++中也有,对于多个文件,main.cpp 、static1.cpp、static1.h、static2.cpp、static2.h,如果在static1.cpp中有一个全局变量 ( 注意,不要把 全局变量以及全局方法的定义放在头文件中 ) a,在 static2.cpp 中我也想使用这个全局变量 a,那么要在static2.cpp中先用 extern 声明 a 为外部变量。这样static2.cpp 就可以使用这个全局变量了
?
main.cpp
#include "static1.h"
#include "static2.h"
using namespace std;
extern int a;
int main(){
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
func2();
funcA();
return 0;
}
?
static1.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "static1.h"
int a=3;
void func1(){
cout << "func1" << endl;
}
??
static1.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func1();
?
static2.cpp
#include "static2.h"
using namespace std;
extern int a; //声明a为外部变量
void func2(){
cout << "func2" << endl;
}
void funcA(){
cout << "funcA" <<endl;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
}
?
static2.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void func2();
void funcA();
?
?
?
static
?
??前面说到 C 和 C++ 中都可以使用 extern 来声明外部变量在本文件夹中使用,但是一旦变量被 static 关键字修饰,那么这个变量就只能在本文件下使用,对于 其他文件就是隐藏了,static的主要作用 是
1、未加 static 关键字的变量和函数都具有全局可见性
2、static 的作用可以保持变量的持久
3、对于函数来说,static 的作用仅限于隐藏,而对于变量来说,static还有另外两个作用,就是保持内容的持久和默认初始化为0,因为全局变量存储在静态数据区,在静态数据区,内存中所有的字节默认都是 0x00;
?
?
?
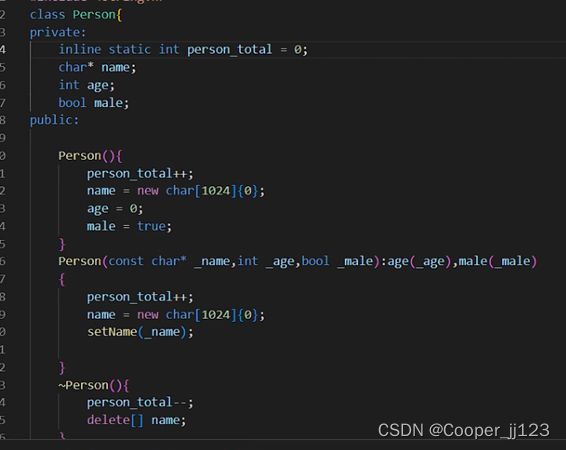
??在C++中,类的静态成员必须在类内声明,在类外初始化
#include "../Algorithm/includes.h"
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
A(){}
A(int a):_a(a){}
// static int b = 1; //只能在类的内部定义,在类的外部进行声明
static int b;
static const int c = 34;
static void func(){
cout << "func" << endl;
}
private:
int _a;
};
int A::b ;
int main(){
A a;
cout << a.b << endl;
cout << a.c << endl;
A::func();
return 0;
}
??
??为什么这样,因为静态成员属于整个类,而不属于某个对象,如果在类内初始化,会导致每个对象都包含该静态成员,这是矛盾的。
??????
??
??但为什么 static const int 就可以在类里面初始化呢?
??因为静态常量成员是常量,不允许修改。
??可以直接访问 func静态函数是因为
??静态成员函数是跟着类走的,还没有创建对象的时候,就已经存在于内存的静态区中了,在没有创建对象之前我们就可以访问类中的静态成员变量和静态成员函数了
??
??
C++17 的标准中 static 前面加上 inline 就可以直接在类中进行初始化了