文章目录
压缩原件原理
前言:
- 压缩的原理是,把文件中的字符通过特定的编码方式保存起来,将其写入到文件中。
- 解压原理:根据文件的压缩规则,读取压缩后的文件,将原来的字符还原出来
eg:
原文件内容为 abbccc
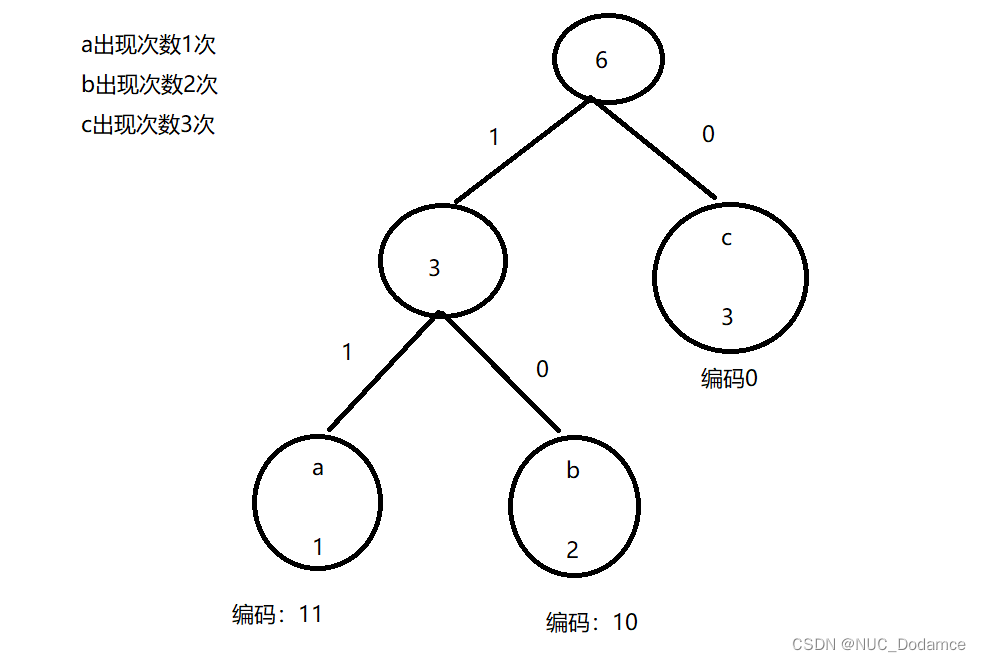
- a对应编码11
- b对应编码10
- c对应编码0
(编码的每一个数字代表一个比特位)
这样原文件内容经过压缩后变为
11101000 00000000
不足8比特的补足8比特,也就是只需要2字节就可以保存原文件的内容了
同时可以观察到,出现次数越多的字符,编码格式最好越短。
- 这样的编码方式与哈夫曼树类似,哈夫曼树权值越大的节点越靠近根。
- 哈夫曼树只有叶子节点保存数据,所以我们可以根据根节点到叶子节点的顺序对字符进行编码
eg:
abbccc
a出现次数1次
b出现次数2次
c出现次数3次
编码过程如下:
所以:我们设计压缩软件流程如下:
1编码表示数据 2 出现次数多编码短,出现次数少编码长
压缩流程
- 分析待压缩文件,获取文件中出现的字符,字符出现次数.将这些数据组织成字典
- 根据字典创建哈夫曼树(核心)
- 根据哈夫曼树获取哈夫曼编码并写入字典中
- 把哈夫曼编码写入文件中
解压过程
- 将文件中的字典读取出来,根据字典生成哈夫曼树
- 按照字节读取文件,按照二进制位分析,将对应的字符写入到解压文件
- 关闭文件
1. 利用哈夫曼树编码
项目需要的头文件及声明common.h
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<fstream>
自定义每个字符结构体charactor.h
每个字符结构体应该包括:
- 这个字符是什么
- 字符在要压缩的文件中出现次数
- 这个字符的哈夫曼编码
- 这个字符在字符字典中的位置
同时还需要一个字符字典,用于查阅每个字符对应的哈夫曼编码。同时,通过这个字典还可以找到文件中出现多少个字符。
#pragma once
#include"common.h"
//字符结构体
struct Char {
char _character;//字符
unsigned int _times;//字符出现次数
std::string _code;//哈夫曼编码
int _index;//这个字符在字符字典中的位置
Char() = default;
Char(char ch, int times, int index = -1)
:_character(ch), _times(times), _index(index)
{}
};
//字符索引,保存的是每个字符的编码,出现的字符
struct CharDict {
int _cout = 0;//出现过的字符个数,最大MAXCHAR个
std::vector<Char>_CharArray;//每个字符数组
};
创建哈夫曼树hufftree.h
思路:假设字典中又5类字符
- 首先根据找到出现次数最小的字符节点,和出现次数第二小的字符节点,这两个节点构造父节点。
- 新构造的父节点覆盖出现次数最少节点,出现次数第二小的字符节点制空,不参与下次循环。
- 之后循环上面两布,循环4次(因为字典有5类字符)
#pragma once
#include"common.h"
#include"charactor.h"
struct TreeNode {
Char _data;
TreeNode* _left = nullptr;
TreeNode* _right = nullptr;
TreeNode* _parent = nullptr;
TreeNode(const Char&msg):
_data(msg)
{}
bool _isLeaf() {
return (_left == nullptr) && (_right == nullptr);
}
};
class HufTree {
typedef TreeNode Node;
friend class Encode;
friend class UnZip;
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
public:
void creatHufTree(CharDict& dict) {
//储存所有字符节点
std::vector<Node*>NodeArray(dict._cout);
Node* node = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < dict._cout; i++) {
NodeArray[i] = new Node(dict._CharArray[i]);
//设置字符在字典中的下标
NodeArray[i]->_data._index = i;
dict._CharArray[i]._index = i;
}
//循环创建哈夫曼树节点
//如果只有一个节点
if (dict._cout == 1) {
_root = NodeArray[0];
}
else {
//找出现次数最小的和第二小的节点
for (int time = 0; time < dict._cout - 1; time++) {
int minIndex = 0;
int minSecIndex = 0;
while (NodeArray[minIndex] == nullptr) {
minIndex++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dict._cout; i++) {
//使用父节点结合两个节点,替换最小的节点,删除第二小的节点
if (NodeArray[i] != nullptr && NodeArray[i]->_data._times < NodeArray[minIndex]->_data._times) {
minIndex = i;
}
}
//找次小值
while (NodeArray[minSecIndex] == nullptr || minIndex == minSecIndex) {
minSecIndex++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dict._cout; i++) {
if (i != minIndex) {
if (NodeArray[i] != nullptr && NodeArray[i]->_data._times < NodeArray[minSecIndex]->_data._times) {
minSecIndex = i;
}
}
}
/*printf("出现次数最小的字符是%c,出现次数%d\n",NodeArray[minIndex]->_data._character, NodeArray[minIndex]->_data._times);
printf("出现次数次少的字符是%c,出现次数为%d\n", NodeArray[minSecIndex]->_data._character, NodeArray[minSecIndex]->_data._times);
printf("============\n");*/
//创建空节点
_root = new Node(Char(0, NodeArray[minIndex]->_data._times + NodeArray[minSecIndex]->_data._times));
//链接节点
NodeArray[minIndex]->_parent = _root;
NodeArray[minSecIndex]->_parent = _root;
_root->_left = NodeArray[minIndex];
_root->_right = NodeArray[minSecIndex];
//覆盖数组最小位置,第二小位置制空
NodeArray[minIndex] = _root;
NodeArray[minSecIndex] = nullptr;
}
}
}
};
利用哈夫曼树创建哈夫曼编码encoding.h
思路:
- 打开原文件,按照字节读取文件,统计文件中每个字符出现的次数
- 根据每个字符出现次数调用HufTree类的方法创建哈夫曼树
- 根据字符在树的位置,倒着遍历到根节点,创建哈夫曼编码
#pragma once
#include"common.h"
#include"charactor.h"
#include"hufftree.h"
#include"Zip.h"
class Encode {
friend class GZip;
private:
HufTree _tree;
std::string _srcFile;
CharDict _dict;
//检测字符是出现过,返回字符所在字典的位置
public:
Encode(std::string&srcFile)
:_srcFile(srcFile)
{
_anylizeFile();
_tree.creatHufTree(_dict);
_creatHuffCode();
}
private:
//测试字典是否正确
void _TestDict() {
printf("共有%d个字符\n", _dict._cout);
for (int i = 0; i < _dict._cout; i++) {
printf("字符%c出现了%d次\n", _dict._CharArray[i]._character, _dict._CharArray[i]._times);
}
}
//测试字符的哈夫曼编码
void _TestHuffCode() {
for (int i = 0; i < _dict._cout; i++) {
printf("字符%c的编码为%s\n", _dict._CharArray[i]._character,_dict._CharArray[i]._code.c_str());
}
}
int _findChar(const char ch) {
for (int i = 0; i < _dict._cout; i++) {
if (_dict._CharArray[i]._character == ch) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//分析文件
void _anylizeFile() {
FILE* fp = fopen(_srcFile.c_str(), "rb");
if (fp == nullptr) {
printf("%s文件打开失败", _srcFile.c_str());
}
assert(fp != nullptr);
//循环按字节读取文件数据
char ch = ' ';
int readNum = 0;
while (true) {
readNum = fread(&ch, 1, 1, fp);
if (readNum != 1) {//读取完毕
break;
}
//统计字符出现次数
int pos = _findChar(ch);
if (pos == -1) {
//没有出现过
_dict._cout++;
_dict._CharArray.push_back(Char(ch, 1));
}
else {
//出现过
_dict._CharArray[pos]._times++;
}
}
fclose(fp);
}
//创建哈夫曼编码,遍历哈夫曼树,遍历到叶子节点,左子树设置为1,右子树设置为0
void _setHuffCode(TreeNode* root) {
//向上走,判断其是左孩子还是右孩子,左孩子编码为1,右孩子编码为0。最后再反转一下数组即可
TreeNode* node = root;
std::string& code = root->_data._code;
while (node->_parent != nullptr) {
if (node == node->_parent->_left) {
code.push_back('1');
}
else {
code.push_back('0');
}
node = node->_parent;
}
std::reverse(code.begin(), code.end());
//修改字典值
_dict._CharArray[root->_data._index]._code = code;
}
void _creatHuffCode() {
_creatHuffCode(_tree._root);
}
void _creatHuffCode(TreeNode* root) {
if (root != nullptr) {
if (root->_isLeaf()) {
//遍历到叶子节点,设置哈夫曼编码
_setHuffCode(root);
}
else {
//遍历左子树
_creatHuffCode(root->_left);
//遍历右子树
_creatHuffCode(root->_right);
}
}
}
std::string _getHufCharCode(char ch) {
for (int i = 0; i < _dict._cout; i++) {
Char msg = _dict._CharArray[i];
if (msg._character== ch) {
return msg._code;
}
}
return "-1";
}
};
2. 编码完成后将生成的字典和原文件写入压缩文件中Zip.h
注意:
- 将编码转化为比特位是这一步的重点
- 同时写入压缩文件的字典需要自定义协议,方便解压缩读取
/*
* 压缩流程
1.分析待压缩文件,获取文件中出现的字符,字符出现次数.将这些数据组织成字典
2.根据字典创建哈夫曼树(核心)
3.根据哈夫曼树获取哈夫曼编码并写入字典中
4.把哈夫曼编码写入文件中
*/
#pragma once
#include"encoding.h"
#include"decoding.h"
class GZip {
private:
Encode _encode;
public:
GZip(std::string& srcFile)
:_encode(srcFile)
{}
//保存压缩后哈夫曼编码写到文件中
void ZipFile(const std::string& destPath) {
//将编码组合成8位的位运算,最后编码不足8位填0即可
//循环读取源文件字节,找到HuffCode,凑齐8位写入destPath文件中
std::fstream fpSrc(_encode._srcFile, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
if (!fpSrc.is_open()) {
printf("DEAD:待压缩文件丢失");
return;
}
std::ofstream fpDst(destPath, std::ios::out | std::ios::app | std::ios::binary);
if (!fpDst.is_open()) {
printf("DEAD:目标压缩路径丢失");
return;
}
//将字典写入文件中
for (int i = 0; i < _encode._dict._cout; i++) {
Char msg = _encode._dict._CharArray[i];
fpDst << msg._character << ";" << msg._code << ";" << msg._index << ";" << msg._times << ";\n";
}
fpDst << "-\n";//字典结束的标志
char ch = 0;
//判断是否读取完毕
bool isEnd = false;
//记录处理的哈夫曼编码位置
size_t indexHufCode = 0;
//记录处理到第几位了
size_t indexWrite = 0;
//记录字符的哈夫曼编码
std::string HufCode;
while (true) {
if (indexHufCode == HufCode.size()) {
fpSrc.read(&ch, 1);
//获取某个字符的哈夫曼编码
//std::cout << ch << ":" << _getHufCharCode(ch) << std::endl;
HufCode = _encode._getHufCharCode(ch);
indexHufCode = 0;
}
indexWrite = 0;
//8字节写入一次
int bite = 0;
//储存要写入的数据
char write = 0;
while (bite < 8) {
if (indexHufCode < HufCode.size()) {
if (HufCode[indexHufCode] == '0') {
//设置对应位为0
write &= ~(1 << (7 - indexWrite));
}
else if (HufCode[indexHufCode] == '1') {
//设置对应位为1
write |= (1 << (7 - indexWrite));
}
bite++;
indexWrite++;
indexHufCode++;
}
else {
//这个字符已经读取完毕了
if (fpSrc.read(&ch, 1)) {
HufCode = _encode._getHufCharCode(ch);
indexHufCode = 0;
}
else {
//文件已经读取完毕了
isEnd = true;
break;
}
}
}
fpDst << write;
//测试写入的数据是否正确,一个字节8比特位,打印每个比特位
char test_write = write;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
//0x80 :1000 0000
if ((test_write & 0x80) == 0x80) {
printf("%d", 1);
}
else {
printf("%d", 0);
}
test_write <<= 1;
}
printf("\n");
if (isEnd == true) {
break;
}
}
fpSrc.close();
fpDst.close();
}
};
3. 读取压缩文件中的字段,还原哈夫曼编码decoding.h
按照自定义的协议从文件中读取字典即可
#pragma once
#include"hufftree.h"
#include"charactor.h"
class Decode {
friend class UnZip;
public:
Decode(std::string& srcFile) {
_anylizeFile(srcFile);
_tree.creatHufTree(_dict);
}
//通过key找到对应字符
char findchar(std::string& key) {
for (int i = 0; i < _dict._cout; i++) {
if (_dict._CharArray[i]._code == key) {
return _dict._CharArray[i]._character;
}
}
return -1;
}
//返回总共的字符数
int allAlph() {
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _dict._cout; i++) {
ret += _dict._CharArray[i]._times;
}
return ret;
}
private:
CharDict _dict;
std::string _srcFile;//解压后的文件保存路径
HufTree _tree;
//分析压缩文件
void _redictDict(CharDict& dict, std::string& readLine) {
assert(readLine.size() > 0);
Char msg;
int begin = 0;
int flag = 0;//标记还原到那个属性
for (int i = 0; i < readLine.size(); i++) {
if (readLine[i] != ';') {
continue;
}
else {
if (flag == 0) {
msg._character = readLine[0];
}
else if (flag == 1) {
msg._code = readLine.substr(begin, i - begin);
}
else if (flag == 2) {
msg._index = atoi(readLine.substr(begin, i - begin).c_str());
}
else {
msg._times = atoi(readLine.substr(begin, i - begin).c_str());
}
begin = i + 1;
flag++;
}
}
_dict._CharArray.push_back(msg);
_dict._cout++;
}
void _anylizeFile(std::string& srcFile) {
_srcFile = srcFile;
std::fstream fpSrc(_srcFile, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
if (!fpSrc.is_open()) {
printf("DEAD:压缩文件丢失");
return;
}
std::string readLine;
//还原字典
while (true) {
std::getline(fpSrc, readLine);
if (readLine=="-") {
//字典已经全部读取完毕了
break;
}
_redictDict(_dict,readLine);
}
fpSrc.close();
_TestDict();
_TestHuffCode();
}
public:
//测试字典是否正确
void _TestDict() {
printf("共有%d个字符\n", _dict._cout);
for (int i = 0; i < _dict._cout; i++) {
printf("字符%c出现了%d次\n", _dict._CharArray[i]._character, _dict._CharArray[i]._times);
}
}
//测试字符的哈夫曼编码
void _TestHuffCode() {
for (int i = 0; i < _dict._cout; i++) {
printf("字符%c的编码为%s\n", _dict._CharArray[i]._character, _dict._CharArray[i]._code.c_str());
}
}
};
4. 利用还原的哈夫曼树和哈夫曼编码解压缩Zip.h
思路:
- 先统计原文件应该有多少个字符
- 定位压缩文件的内容部分,按照字节分析,如果能够走到哈夫曼树的叶子节点就可以还原这个字符。
/*
解压过程
1.将文件中的字典读取出来,根据字典生成哈夫曼树
2.按照字节读取文件,按照二进制位分析,将对应的字符写入到解压文件
3.关闭文件
*/
class UnZip {
private:
Decode _decode;
public:
UnZip(std::string& destPath)
:_decode(destPath)
{}
//解压缩文件
void UnzipFile(const std::string& destPath) {
/*_decode._anylizeFile(destPath);
_decode._TestDict();
_decode._TestHuffCode();*/
//定位到正文部分
FILE* fp = fopen(destPath.c_str(), "rb");
char ch = 0;
int readNum = 0;
while (true) {
readNum = fread(&ch, 1, 1, fp);
assert(readNum != 0);
if (ch == '-') {
break;
}
}
//把换行符读取掉
readNum = fread(&ch, 1, 1, fp);
assert(readNum == 1);
//定位到正文了,读取到正文结束
HufTree tree = _decode._tree;
TreeNode* node = tree._root;
//还原文件
FILE* redict_fp = fopen("还原文件.txt", "w");
std::string key;
bool isFinish = false;//判断是否读取完毕
int allAlph = _decode.allAlph();
while (true) {
readNum = fread(&ch, 1, 1, fp);
if (readNum == 0) {
break;
}
int num = ch;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
//获取每一位
if ((ch & 0x80) == 0x80) {
node = node->_left;
key.push_back('1');
}
else if ((ch & 0x80) == 0) {
node = node->_right;
key.push_back('0');
}
ch <<= 1;
if (node->_isLeaf()) {
char write = _decode.findchar(key);
if (write == -1) {
break;
}
fwrite(&write, 1, 1, redict_fp);
node = tree._root;
key.clear();
allAlph -= 1;
if (allAlph == 0) {
isFinish = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (isFinish == true) {
break;
}
}
fclose(redict_fp);
}
};
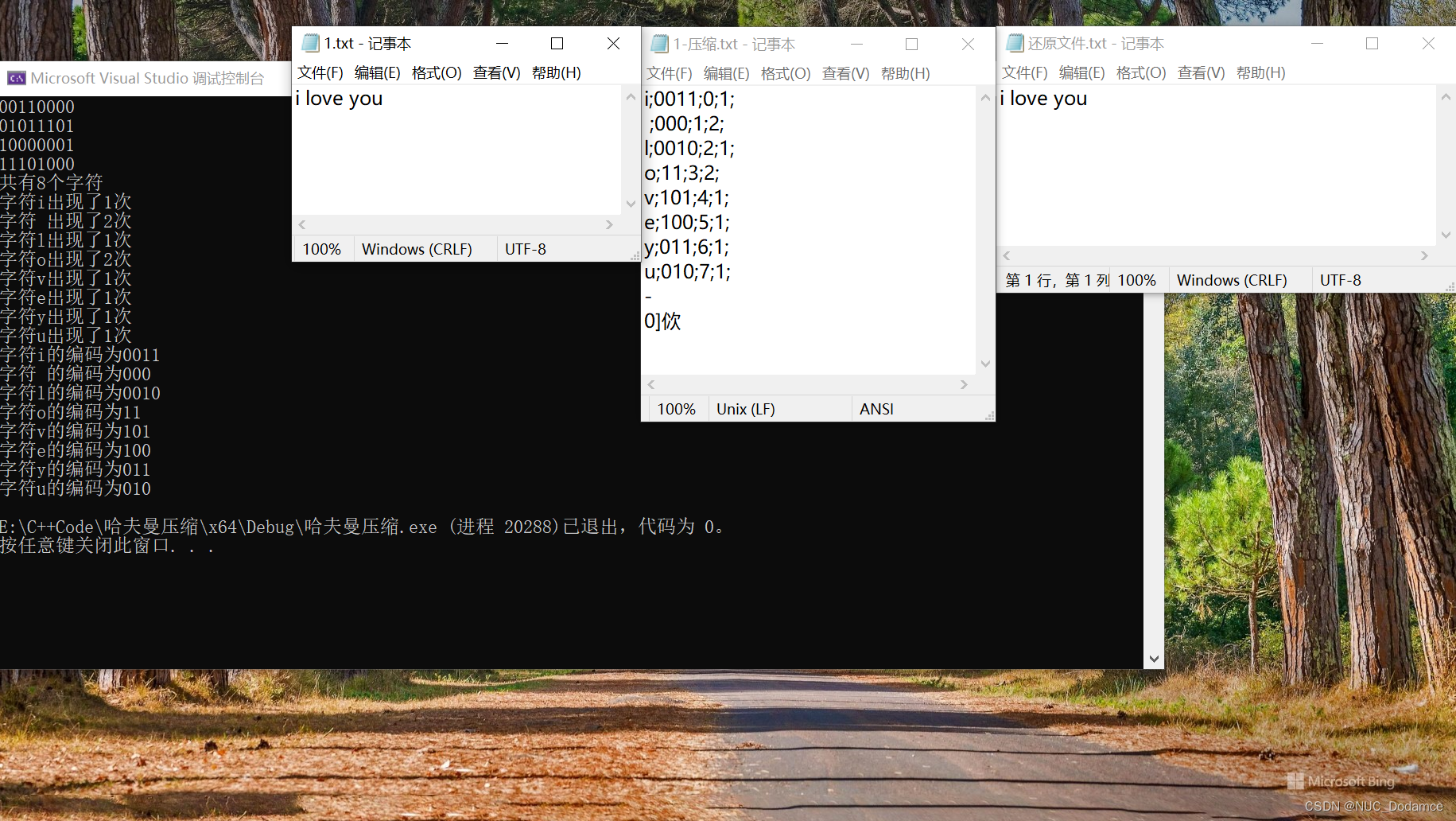
测试结果