🏆个人主页:企鹅不叫的博客
? 🌈专栏
?? 博主码云gitee链接:代码仓库地址
?若有帮助可以【关注+点赞+收藏】,大家一起进步!
💙系列文章💙
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第二篇:C&&C++互相调用(创建静态库)并保护加密源文件
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第三篇:类和对象上(类和this指针)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第四篇:类和对象中(类的六个默认成员函数)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第五篇:类和对象下(构造+static+友元+内部类
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第六篇:C&C++内存管理(动态内存分布+内存管理+new&delete)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第七篇:模板初阶(泛型编程+函数模板+类模板+模板特化+模板分离编译)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第八篇:string类(标准库string类+string类模拟实现)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第九篇:vector(vector接口介绍+vector模拟实现+vector迭代器区间构造/拷贝构造/赋值)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第十篇:list(list接口介绍和使用+list模拟实现+反向迭代器和迭代器适配)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第十一篇:stack+queue+priority_queue+deque(仿函数)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第十二篇:模板进阶(函数模板特化+类模板特化+模板分离编译)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第十三篇:继承(菱形继承+菱形虚拟继承+组合)
【初阶与进阶C++详解】第十四篇:多态(虚函数+重写(覆盖)+抽象类+单继承和多继承)
文章目录
💎一、二叉搜索树概念
二叉搜索树中序遍历是有序的
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于于根节点的值
它的左右子树都是二叉搜索树
这棵树中没有重复的元素
💎二、二叉搜索树操作实现
🏆1.基本框架
构建一个树的节点结构
template<class K> struct BSTreeNode { public: BSTreeNode* _left; BSTreeNode* _right; K _key; BSTreeNode(K key) :_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key) {} };定义一个根节点,默认值是空
template<class K> class BSTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; private: //成员变量 Node* _root=nullptr; };
🏆2.插入
步骤
首先判断root是否为空,如果为空直接插入数据即可,然后结束
如果root非空则定义==cur(当前节点)和parent(父亲节点)==两个指针遍历,要插入的值比当前节点值小,cur则往左走,要插入的值比当前节点大,cur则往右走,如果等于就返回flase,表示树已经存在这个数据,不用插入,找到正确位置后创建新节点插入即可
返回值使用bool用来判断是否成功插入
bool Insert(const K& key) { //根为空,直接创建空间插入 if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key); return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; //找到合适的插入位置 while (cur) { //比根节点大则查找右子树 if (key > cur->_key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } //比根节点小则查找左子树 else if (key < cur->_key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } //有相同元素不执行插入 else { return false; } } //创建节点进行插入 cur = new Node(key); //判断cur要插入到parent的左子树还是右子树 if (key > parent->_key) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } return true; }递归版本:
bool InsertR(const K& key)//实际调用的函数 { return _InsertR(_root, key); } //使用引用,这时候的root就是上一个节点的左右子树的别名 //修改root的同时也会修改上一个子树的左右节点 bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key) { //空代表走完了,则插入 if (root == nullptr) { Node* newNode = new Node(key); root = newNode; return true; } if (key > root->_key) { _InsertR(root->_right, key); } else if (key < root->_key) { _InsertR(root->_left, key); } else { return false;//不插入相同值 } }
🏆3.中序遍历打印
在类外面无法访问到私有成员
root,无法直接给该函数传参,可以把这个函数定义为private成员//利用子函数中序遍历 void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); } void _InOrder(Node* root) { //递归打印 if (root == nullptr) return ; _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " "; _InOrder(root->_right); }
🏆4.查找
步骤:
如果查找值key比当前节点的值小,就往左子树走
如果查找值key比当前节点的值大,就往右子树走
如果查找值key和当前节点的值相等,就返回当前节点的指针
//搜索二叉树一般不直接操作节点,不需要返回节点的指针 //Node* Find(const K& key) bool Find(const K& key) { Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { //比根节点大则查找右子树 if (key > cur->_key) { cur = cur->_right; } //比根节点小则查找左子树 else if (key < cur->_key) { cur = cur->_left; } //相同则返回 else { return true; } } //遍历完则说明查找不到,返回false return false; }递归版本:
bool FindR(const K& key)//实际调用的函数 { return _FindR(_root, key); } //递归实现 bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key) { if (root == nullptr) { return false; } //如果大于右子树 if (key > root->_key) { _FindR(root->_right, key); } //如果大于左子树 else if (key < root->_key) { _FindR(root->_left, key); } else { return true; } }
🏆5.删除(重点)
情况:
- 要删除的节点无孩子节点,比如删除节点1时,直接删除
- 要删除的节点只有左孩子节点,比如节点2,删除节点2的左孩子并且指向左孩子的右边
- 要删除的节点只有右孩子节点,比如节点7,删除节点7的右孩子并且指向右孩子的做左边
- 要删除的节点有左孩子和右孩子,比如节点3,在右子树中找到最小/在左子树中找到最大,将它的值填补到被删除的节点中
//删除去找左子树的最大节点,或者右子树的最小节点 //与需要删除的树进行交换,交换之后删除叶子节点 bool Erase(const K& key) { // 如果树为空,删除失败 if (_root == nullptr) return false; Node* prev = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { // 小于往左边走 if (key > cur->_key) { prev = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (key < cur->_key) { prev = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { // 找到了,开始删除 // 1.左右子树都为空 直接删除 可以归类为左为空 // 2.左右子树只有一边为空 左为空,父亲指向我的右,右为空,父亲指向我的左 // 3.左右子树都不为空 取左子树最大的节点或右子树最小的节点和要删除的节点交换,然后再删除 //处理只有右子树时 if (cur->_left == nullptr) { //如果当前节点为根节点,则让右子树成为新的根节点 if (cur == _root) { _root = _root->_right; } else { //判断当前节点是他父节点的哪一个子树 if (prev->_left == cur) { prev->_left = cur->_right; } else { prev->_right = cur->_right; } } delete cur; } //处理只有左子树时 else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { //如果当前节点为根节点,则让左子树成为新的根节点 if (cur == _root) { _root = _root->_left; } else { if (prev->_left == cur) { prev->_left = cur->_left; } else { prev->_right = cur->_left; } } delete cur; } //左右都有孩子 else { //将cur和右子树的最小值节点进行交换 Node* minParent = cur;//不给空放置要删除的是头节点 Node* minRight = cur->_right; //右子树找到最左边的节点 while (minRight->_left) { minParent = minRight; minRight = minRight->_left; } //替换节点 swap(minRight->_key, cur->_key); //如果要删除的是minParent的左子树,则将minParent指向左子树的右边 if (minParent->_left == minRight) { minParent->_left = minRight->_right; } //如果要删除的是minParent的右子树,则将minParent指向右子树的右边 else { minParent->_right = minRight->_right; } delete minRight; } return true; } } return false; }递归版本:
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key) { //根为空,返回false if (root == nullptr) { return false; } if (key > root->_key) { _EraseR(root->_right, key); } else if (key < root->_key) { _EraseR(root->_left, key); } else { Node* del = root;//保存变量用于删除 if (root->_left == nullptr) { //传引用的作用 //root不仅是当前递归到的节点,同时是上一个节点的左右子树的别名 //对该节点的操作会直接改变上一个节点的左右子树 root = root->_right; } else if (root->_right == nullptr) { root = root->_left; } //左右都有孩子 else { //将cur和右子树的最小值节点进行交换 Node* minRight = root->_right; while (minRight->_left) //判断的是left,不然会走到空然后交换 { minRight = minRight->_left; } swap(minRight->_key, root->_key); //转换到下一个子树中删除 return _EraseR(root->_right, key); } delete del; return true; } }
💎三、二叉搜索树应用
K模型: K模型只有key值,节点只存储key值。这里主要应用就是查找判断某个元素在不在。
KV模型: KV模型每个key值都对应着一个value,主要应用就是通过key找value,将<key, value>绑定
排序依据key来排序,而不是value
key不可以修改,但是value可以修改
在保存键值关系的同时,去重+排序
下面是修改代码(只用修改查找和插入即可),和具体应用
template <class K, class V> struct BSTNode { BSTNode<K, V>* _left; BSTNode<K, V>* _right; K _key; V _value; BSTNode(const K& key, const V& value) :_left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _key(key) ,_value(value) {} }; template <class K, class V> class BSTree //Binary Search Tree { typedef BSTNode<K, V> Node; public: ~BSTree() { Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { Erase(cur->_key); cur = _root; } } //找到了则返回地址 Node* Find(const K& key) { if (_root == nullptr) return nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { // 小于往左边走 if (key < cur->_key) cur = cur->_left; else if (key > cur->_key) cur = cur->_right; else return cur; } return nullptr; } bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value) { // 没有节点时第一个节点就是根节点 if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key, value); return true; } // 用一个父亲节点记录cur的上一个节点 Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { parent = cur; // 小于往左边走 if (key < cur->_key) cur = cur->_left; else if (key > cur->_key) cur = cur->_right; else return false;// 已有的节点不插入,此次插入失败 } cur = new Node(key, value); // 判断应该插在父节点的左边还是右边 if (cur->_key < parent->_key) { parent->_left = cur; } else { parent->_right = cur; } return true; } bool Erase(const K& key) { // 如果树为空,删除失败 if (_root == nullptr) return false; Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { // 小于往左边走 if (key < cur->_key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else if (key > cur->_key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else { // 找到了,开始删除 // 1.左右子树都为空 直接删除 可以归类为左为空 // 2.左右子树只有一边为空 左为空,父亲指向我的右,右为空,父亲指向我的左 // 3.左右子树都不为空 取左子树最大的节点或右子树最小的节点和要删除的节点交换,然后再删除 if (cur->_left == nullptr) { // 要删除节点为根节点时,直接把右子树的根节点赋值给——root // 根节点的话会导致parent为nullptr if (_root == cur) { _root = _root->_right; } else { // 左为空,父亲指向我的右 // 判断cur在父亲的左还是右 if (parent->_left == cur) // cur->_key < parent->_key parent->_left = cur->_right; else parent->_right = cur->_right; } delete cur; cur = nullptr; } else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { if (_root == cur) { _root = _root->_left; } else { // 右为空,父亲指向我的左 // 判断cur在父亲的左还是右 if (parent->_left == cur) parent->_left = cur->_left; else parent->_right = cur->_left; } delete cur; cur = nullptr; } else { // 找右子树中最小的节点 Node* rightMinParent = cur; Node* rightMin = cur->_right;// 去右子树找 while (rightMin->_left) { rightMinParent = rightMin; rightMin = rightMin->_left; } //swap(cur->_key, rightMin->_key); // 替代删除 cur->_key = rightMin->_key; // 转换成了第一种情况 左为空 if (rightMinParent->_left == rightMin) rightMinParent->_left = rightMin->_right; else rightMinParent->_right = rightMin->_right; delete rightMin; rightMin = nullptr; } return true; } } return false; } void InOrder() { // 利用子函数遍历 _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } private: void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return; _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << ":" << root->_value << endl; _InOrder(root->_right); } private: Node* _root = nullptr; }; void TestBSTree_KV1() { // 创建一个简易的字典 BSTree<string, string> dict; dict.Insert("苹果", "apple"); dict.Insert("排序", "sort"); dict.Insert("培养", "cultivate"); dict.Insert("通过", "pass"); dict.Insert("apple", "苹果"); dict.Insert("sort", "排序"); dict.Insert("cultivate", "培养"); dict.Insert("pass", "通过"); string str; while (cin >> str) { //BSTNode<string, string>* ret = dict.Find(str); aotu ret = dict.Find(str); if (ret) { cout << ret->_value << endl; } else { cout << "本字典无此词" << endl; } } void TestBSTree_KV2() { // 统计水果个数 BSTree<string, int> countTree; string strArr[] = { "香蕉","水蜜桃","西瓜","苹果","香蕉" ,"西瓜","香蕉" ,"苹果","西瓜","苹果","苹果","香蕉" ,"水蜜桃" }; for (auto e : strArr) { BSTNode<string, int>* ret = countTree.Find(e); if (ret == nullptr) { // 第一次出现则插入 countTree.Insert(e, 1); } else { //如果出现过了则增加出现次数即可 ret->_value++; } } countTree.InOrder(); }
💎四、二叉搜索树新能分析
理想情况情况(完全二叉树),二叉搜索树的插入和删除的效率都是O(logN),极端情况(一条链)会导致效率变成O(N)。
💎五、面试题
🏆1.根据二叉树创建字符串
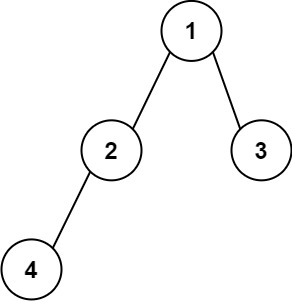
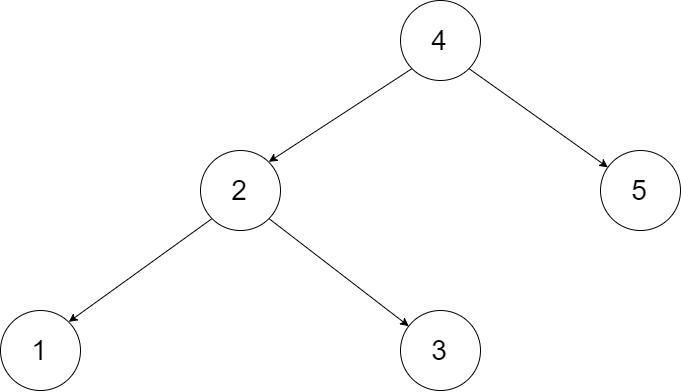
输入:root = [1,2,3,4]
输出:“1(2(4))(3)”
解释:初步转化后得到 “1(2(4)())(3()())” ,但省略所有不必要的空括号对后,字符串应该是"1(2(4))(3)" 。
思路:
? 最后是否加括号有三种情况,左右两边都是空,那么不要加括号,左边是空右边不是空,保留括号,右边是空左边不是空,不要加括号,然后递归循环即可
class Solution {
public:
//左右两边都是空,那么不用加()
//左边是空右边不是空,要加()
//右边是空左边不是空,不要加()
string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
return "";
string str;
//to_string 常量转字符串
str += to_string(root->val);
//如果左边是空,右边不是空,则直接加()
if(root->left)
{
str += '(';
str += tree2str(root->left);
str += ')';
}
else if(root->right)
{
str += "()";
}
//如果右边是空,则直接跳过
if(root->right)
{
str += '(';
str += tree2str(root->right);
str += ')';
}
return str;
}
};
🏆2.二叉树的层序遍历
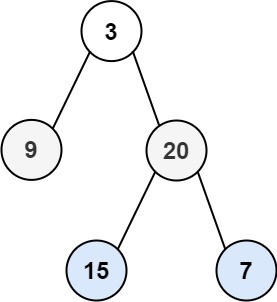
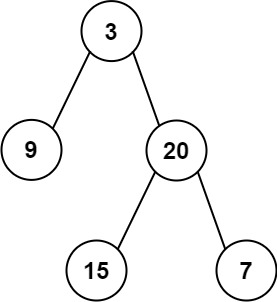
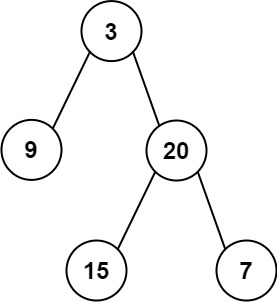
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
思路:
? 利用变量levelsize控制一层变量,然后将每一层变量放到队列q中,如果q为空则表示遍历完了
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> vv;
//为空直接返回
if(root == nullptr)
return vv;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
int levelsize = 1;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> v;
//levelsize计算每一层有多少个数据
while(levelsize--)
{
//将每一层的数据依次放到v中
TreeNode* front = q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
q.push(front->left);
if(front->right)
q.push(front->right);
}
//将v放到vv中
vv.push_back(v);
levelsize = q.size();
}
return vv;
}
};
🏆3.二叉树的层序遍历 II
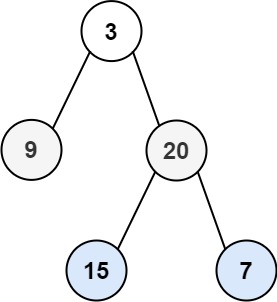
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[15,7],[9,20],[3]]
思路同第二题,最后逆置即可
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> vv;
//为空直接返回
if(root == nullptr)
return vv;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
int levelsize = 1;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> v;
//levelsize计算每一层有多少个数据
while(levelsize--)
{
//将每一层的数据依次放到v中
TreeNode* front = q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(front->val);
if(front->left)
q.push(front->left);
if(front->right)
q.push(front->right);
}
//将v放到vv中
vv.push_back(v);
levelsize = q.size();
}
reverse(vv.begin(), vv.end());
return vv;
}
};
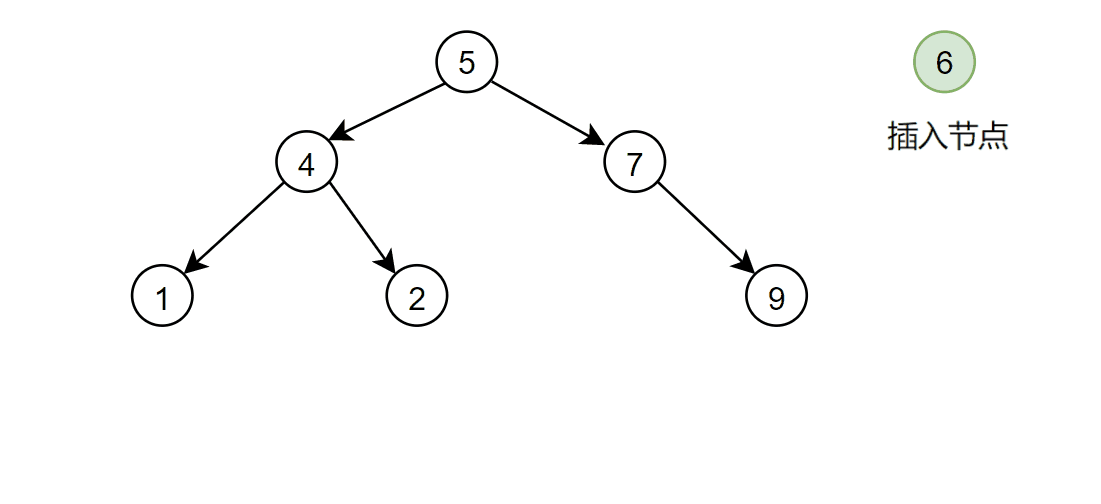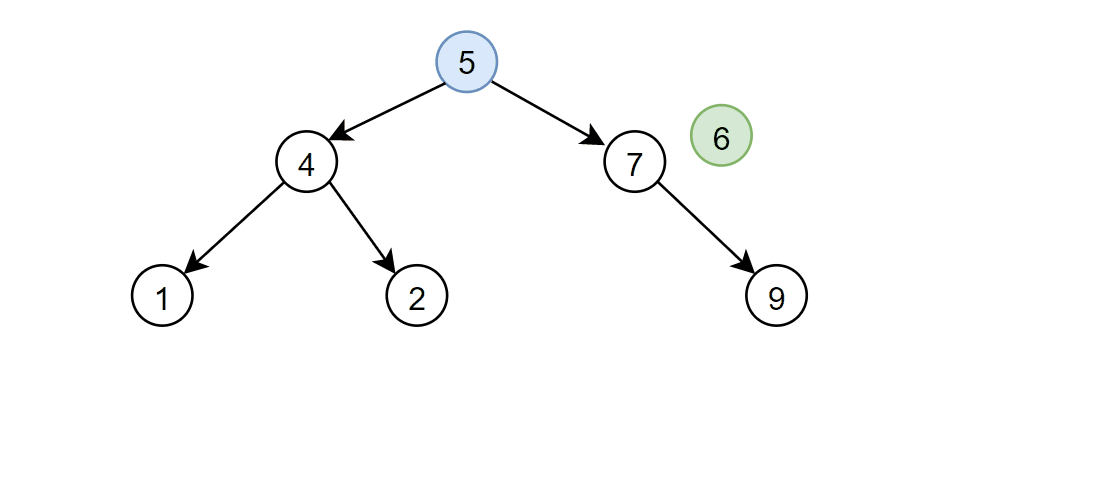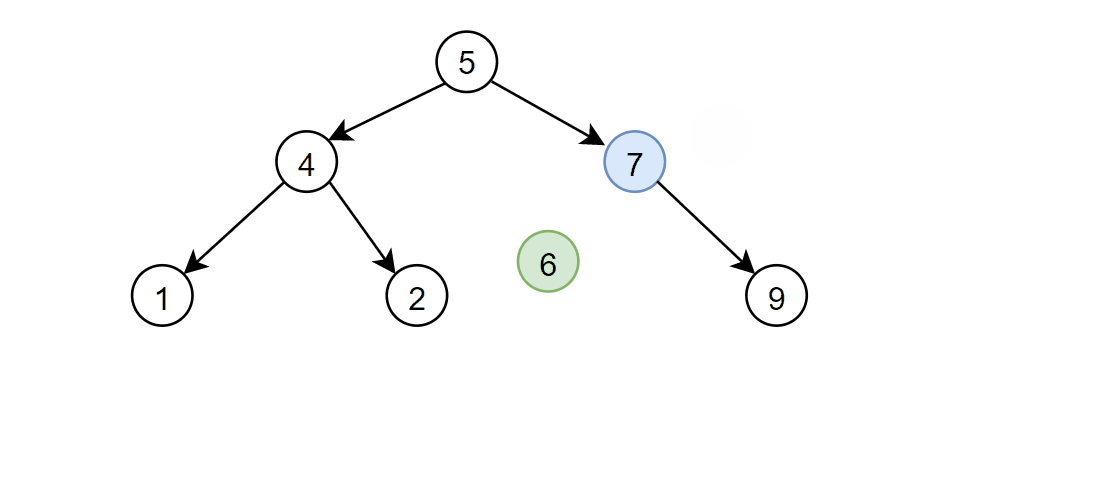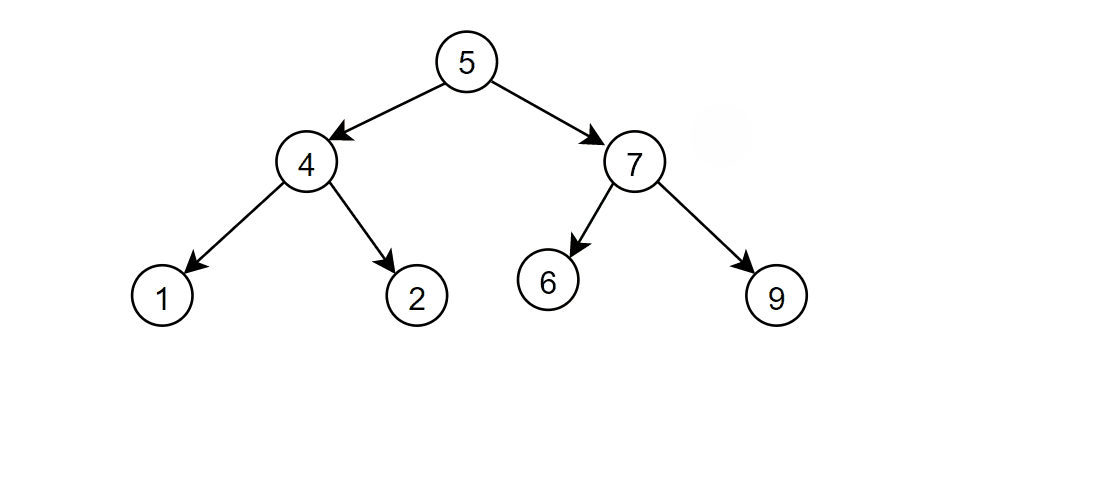
🏆4.二叉树的最近公共祖先
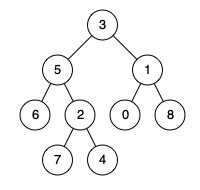
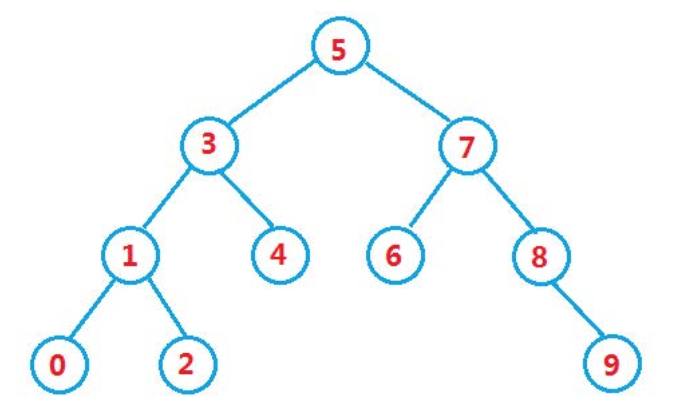
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
输出:3
解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
思路:
? 当一个节点是祖先的时候,一种情况是,pq两个点都在祖先的左右两边,另一种情况是pq两点中有一个点是祖先,如果pq两点中有一个是祖先的话,那么返回root即可,如果当前root节点不是pq的话,那么就从root的左右子树中找pq,此时我们定义一个子树中寻找节点的函数,用来寻找root子树中是否存在pq,如果pq存在root左右两边的话,那么返回root祖先,如果pq存在root同一边的话,那么将root移动到一边寻找即可
class Solution {
public:
bool IsInBinry(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x)
{
//如果为空,返回空
if(root == nullptr)
return false;
//如果根找到了就返回true
if(root == x)
return true;
//如果根没有找到就向左右子树中寻找
return IsInBinry(root->left, x)
||IsInBinry(root->right, x);
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr)
return root;
//如果p或者q是root说明找到了其中一个节点
if(p == root || q == root)
return root;
//如果在当前节点没有找到则左右分开找
bool qInleft = IsInBinry(root->left, q);
bool qInright = IsInBinry(root->right, q);
bool pInleft = IsInBinry(root->left, p);
bool pInright = IsInBinry(root->right, p);;
//如果当前pq一个在左一个在右,说明当前root是祖先
if((qInleft && pInright)||(qInright && pInleft))
return root;
//如果qp都在左那么就往左边去找
else if(qInleft && pInleft)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
else
return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
}
};
🏆5.二叉搜索树与双向链表
思路:
? 通过中序遍历,将节点左子树的右边指向节点,利用一前一后指针将每一个系欸但双向
class Solution {
public:
//使用引用,这样在不同的递归时,都不会改变
void InOrder(Node* cur, Node*& prev)
{
if(cur == nullptr) return;
InOrder(cur->left, prev);
//每次将root左子树给prev
cur->left = prev;
//当prev不为空时,将prev右指向cur
if(prev)
prev->right = cur;
//将prev移动到cur
prev = cur;
InOrder(cur->right, prev);
}
Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) {
if(root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* prev = nullptr;
InOrder(root, prev);
Node* head = root;
while(head->left)
{
head = head->left;
}
return head;
}
};
🏆6.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
思路:
? 首先通过前序遍历找到root然后通过中序遍历确定root位置,那么根据中序遍历root位置可知,在root左边是左树,右边是右树,将中序区间划分为[begini, rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1, endi],然后将root的左右树分别递归划分
class Solution {
public:
//prei修改了,防止出作用域销毁
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, int& prei, int begini, int endi)
{
//中间序列不存在说明找到空
if(begini>endi)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[prei]);
++prei;
//划分左右区间
int rooti = begini;
while(rooti<=endi)
{
if(root->val == inorder[rooti])
break;
else
rooti++;
}
//[begini, rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1, endi]
root->left = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, begini, rooti-1);
root->right = _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, rooti+1, endi);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int prei = 0, begini = 0, endi = inorder.size()-1;
return _buildTree(preorder, inorder, prei, begini, endi);
}
};
🏆7.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
思路:
思路和前序中序遍历差不多,首先从后序遍历的最后开始,找到根节点,然后从中序遍历中找到[begini, rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1, endi]区间,然后将每个区间递归遍历,注意的是,递归顺序是后序中序遍历时,递归是先右再左
class Solution {
public:
//prei修改了,防止出作用域销毁
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder, int& nexti, int begini, int endi)
{
//中间序列不存在说明找到空
if(begini>endi)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[nexti]);
nexti--;
//划分左右区间
int rooti = begini;
while(rooti<endi)
{
if(root->val == inorder[rooti])
break;
else
rooti++;
}
//[begini, rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1, endi]
root->right = _buildTree(inorder, postorder, nexti, rooti+1, endi);
root->left = _buildTree(inorder, postorder, nexti, begini, rooti-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int nexti = postorder.size()-1, begini = 0, endi = inorder.size()-1;
return _buildTree(inorder, postorder, nexti, begini, endi);
}
};
🏆8.二叉树的前序遍历
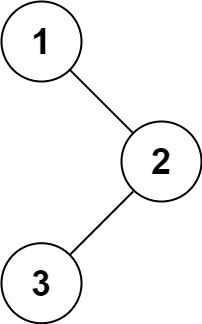
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,2,3]
思路:
? 前序遍历是根左右,所以我们要优先·访问根节点,然后递归访问左节点和右节点,其他中序遍历和后续遍历差不多
class Solution {
public:
void _preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& v)
{
if(root == nullptr)return ;
v.push_back(root->val);
_preorderTraversal(root->left, v);
_preorderTraversal(root->right, v);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> v;
_preorderTraversal(root, v);
return v;
}
};
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-LNMLsWF1-1664000420661)(C:/Users/LENOVO/AppData/Roaming/Typora/typora-user-images/image-20220922152632937.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/53e694842c3e48cabb2ac9213d8aed70.png)