C++/QT图形界面编程(GUI)
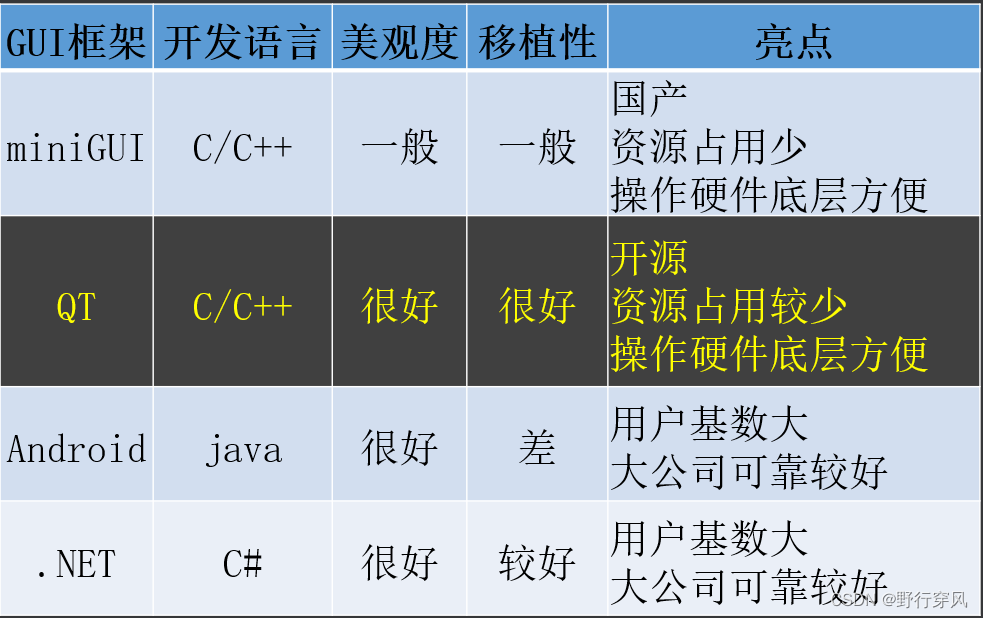
一、从C到C++
1.语法升级

(1)引用
void swp(int &a, int &b);
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 100;
int &b = a;
printf("a = %d\n", a);
printf("b = %d\n", b);
printf("addr: a = %p\n", &a);
printf("addr: b = %p\n", &b);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
/*
int swap(int a, int b)
{
a ^= b;
b ^= a;
a ^= b;
}
*/
/*
void swap(int *p, int *q)
{
*p ^= *q;
*q ^= *p;
*p ^= *q;
}
*/
int swap(int &a, int &b)
{
a ^= b;
b ^= a;
a ^= b;
}
int main()
{
int a = 100;
int b = 10;
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
// swap(&a, &b);
swap(a, b);
printf("a = %d, b = %d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}
(2)默认参数
void debug(const char *ptr=“----------”);
#include <stdio.h>
void debug(const char *ptr = "---------------")
{
printf("%s\n", ptr);
}
int main()
{
debug();
debug();
debug("hello");
debug("world");
return 0;
}
(3)函数重载
int cmp(int data1, int data2 );
int cmp(const char *str1, const char *str2);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/*
int intcmp(int a, int b)
{
return a-b;
}
int scmp(const char *str1, const char *str2)
{
return strcmp(str1, str2);
}
*/
int cmp(int a, int b)
{
return a-b;
}
int cmp(const char *str1, const char *str2)
{
return strcmp(str1, str2);
}
int main()
{
printf("%d, %d\n", cmp(1, 1), cmp(1,2));
printf("%d, %d\n", cmp("hhh", "hhh"), cmp("hhh", "aaa"));
return 0;
}
(4)堆内存
malloc(),free() -> new, delete
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
/*
char *p = (char *)malloc(10);
strcpy(p, "hello");
printf("p: %s\n", p);
free(p);
*/
int *intp = new int; //int *intp = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
*intp = 100;
printf("*intp = %d\n", *intp);
delete intp;
char *p = new char[10];
strcpy(p, "hello");
printf("p = %s\n", p);
delete [] p;
return 0;
}
2.概念升级

(1)名字空间
namespace NAME1{ };
#include <stdio.h>
namespace A{
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
};
namespace B{
int add(int a, int b)
{
return 2*a+b;
}
};
using namespace A;
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", A::add(1, 2) );
printf("%d\n", B::add(1, 2) );
printf("%d\n", add(1, 2) );
return 0;
}
(2)类:class
class 类名 {
private:
私有的数据和成员函数;
public:
公用的数据和成员函数;
protected:
保护的数据和成员函数
};
(3)面向对象编程(oop)
类、对象、封装,继承、组合等
C实现尾部插入(结构体)
test.h
#ifndef _TEST_H_
#define _TEST_H_
typedef struct arr_t{
int data[10];
int last;
}ARR;
void init(ARR *arr);
void addtail(ARR *arr, int data);
void show(ARR *arr);
#endif
test.c
#include "test.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void init(ARR *arr)
{
arr->last = -1;
}
void addtail(ARR *arr, int data)
{
arr->last++;
arr->data[arr->last] = data;
}
void show(ARR *arr)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i <= arr->last; i++)
printf("%d, ", arr->data[i]);
puts("");
}
main.c
#include "test.h"
int main()
{
ARR arr;
init(&arr);
int i = 5;
for (; i > 0; i--) {
addtail(&arr, i);
}
show(&arr);
return 0;
}
C实现尾部插入(面向对象思想、结构体、函数指针)
test.h
#ifndef _TEST_H_
#define _TEST_H_
typedef struct arr_t{
int data[10];
int last;
void (*addtail)(struct arr_t *arr, int data);
void (*show)(struct arr_t *arr);
}ARR;
void init(ARR *arr);
#endif
test.c
#include "test.h"
#include <stdio.h>
static void addtail(struct arr_t *arr, int data)
{
arr->last++;
arr->data[arr->last] = data;
}
static void show(struct arr_t *arr)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i <= arr->last; i++)
printf("%d, ", arr->data[i]);
puts("");
}
void init(ARR *arr)
{
arr->last = -1;
arr->addtail = addtail;
arr->show = show;
}
main.c
#include "test.h"
int main()
{
ARR arr;
init(&arr);
int i = 5;
for (; i > 0; i--) {
arr.addtail(&arr, i);
}
arr.show(&arr);
return 0;
}
C++实现尾部插入和倒序(面向对象编程、类、友元函数)
test.h
#ifndef _TEST_H_
#define _TEST_H_
class ARR{
public:
ARR():last(-1){
// last = -1;
}
void addtail(int data);
void show();
friend void rev(ARR &arr); //友元函数
private:
int data[10];
int last;
};
#endif
test.cpp
#include "test.h"
#include <stdio.h>
void ARR::addtail(int data)
{
this->data[++last] = data;
}
void ARR::show()
{
int i = 0;
for (; i <= last; i++)
printf("%d, ", data[i]);
puts("");
}
main.cpp
#include "test.h"
void rev(ARR &arr)
{
int i = 0;
for (; i < arr.last/2; i++) {
int temp = arr.data[i];
arr.data[i] = arr.data[arr.last-i];
arr.data[arr.last-i] = temp;
}
}
int main()
{
ARR arr;
int i = 0;
for (; i < 5; i++)
arr.addtail(i);
arr.show();
rev(arr);
arr.show();
return 0;
}
3.思维升级
二、类与对象
1.类的声明

class.cpp
类中成员数据、成员函数的声明和使用。
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A() //构造函数:在于创建对象时为对象的成员属性赋值,构造函数由编译器自动调用,无须手动调用。
{
printf("construct!\n");
a = 0;
}
A(int data) //带参构造函数
{
a = data;
}
~A() //析构函数:在于对象销毁前系统自动调用,执行一些清理工作。
{
printf("ddddddddddd\n");
}
void show()
{
printf("xxxxxxxxxxx\n");
}
void setdata(int data) //通过成员函数操作private中的变量
{
a = data;
}
int getdata(void); //类内声明,类外实现
private:
int a;
};
int A::getdata(void)
{
return a;
}
int main()
{
A x(100);
// x.a = 100;
// x.setdata(100);
printf("%d\n", x.getdata() );
x.show();
}
2.类的成员函数(类内、类外实现)

class_construct.cpp
当使用类创建新对象时的会调用的函数。
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("A()\n");
}
A(int data)
{
printf("A(int data)\n");
}
~A(){
printf("~A()\n");
}
};
int main()
{
//当创建新对象时的会调用的函数
A *p = new A(1000); //调用A(int data),没有调用~A()
A x; //调用A()、~A()
A m(100); //调用A(int data)、~A()
A y = 10; //调用A(int data)、~A()
A z = y; //调用了系统自动生成的拷贝函数、~A()
//调用系统的拷贝函数,当类A的构造函数中有开辟堆空间、析构函数会释放空间时,z和y调用析构函数释放空间时会是同一个空间,会导致double free。因此应该自己创建一个拷贝构造函数,如下class_copy.cpp
}
class_copy.cpp
使用A z = y语句时,会调用系统的拷贝函数,当类A的构造函数中有开辟堆空间、析构函数会释放空间时,z和y调用析构函数释放空间时会是同一个空间,会导致double free。因此应该自己创建一个拷贝构造函数。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
class A{
public:
A()
{
printf("A()\n");
p = new char[10];
strcpy(p, "hello");
}
A(const A &x) //拷贝构造函数
{
printf("A(const A &x)\n");
p = new char[10];
strcpy(p, x.p);
}
~A()
{
printf("~A()\n");
delete [] p;
}
private:
char *p;
};
int main()
{
A x;
A y = x;
// y = x;
}
3.常成员、常函数(C++推荐const而不用#define,mutable )

const.cpp
常成员数据、常成员函数的声明和使用。
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
A(int a = 50, int data = 1000):b(data){
// b = data; //不能通过这种方式,常成员数据通过构造函数初始化表赋值或者使用构造函数默认参数
this->a = a; //this指针
printf("AAAAAAAAA\n");
}
~A(){
printf("~~~~~~~~~\n");
}
void show(void) const //常成员函数,不能修改里面的数据
{
printf("a = %d\n", a);
printf("b = %d\n", b);
// a++;
// b++;
}
private:
int a;
const int b; //常成员数据
};
int main()
{
A x(10,10);
x.show();
A y = 100; //只能传给第1个参数,data使用构造函数默认参数
y.show();
A z; //会使用构造函数的默认参数
z.show();
}
4.静态成员(属于类不属于对象)

static.cpp
静态成员数据、静态成员函数的声明和使用。
#include <stdio.h>
class A{
public:
static void func(void) //静态成员函数
{
printf("xxxxxxxxx\n");
}
static int data; //静态成员数据
};
int A::data = 10; //通过命名空间使用时,需要初始化(静态成员函数不需要初始化)
int main()
{
A a;
a.func();
A::func(); //不需要对象也能操作类成员函数
A x;
x.data = 100;
printf("x.data = %d\n", x.data);
A::data = 1000; //不需要对象也能操作类成员数据,修改的是同一命名空间的成员数据
printf("x.data = %d\n", x.data);
}
5.友元(破坏封装)

friend.cpp
友元类、友元成员函数的声明和使用。(友元函数的使用在一、2.(3)中使用过)
#include <stdio.h>
class A;
class B{
public:
void printfA(A &c);
void show() {}
};
class A{
public:
A()
{
x = 100;
}
// friend class B; //友元类,开放类A给类B使用(包括私有成员)
friend void B::printfA(A &x); //友元成员函数,只开放类A给类B的某个函数使用(包括私有成员)
private:
int x;
};
void B::printfA(A &c)
{
printf("%d\n", c.x);
}
int main()
{
A a;
// printf("%d\n", a.x); //a.x是私有成员,不能直接操作
B b;
b.printfA(a); //必须声明友元类或者友元成员函数,类B中的方法就能访问类A的私有成员
}