又是两周一次的C++实验时间,最近事可真是太多了
问题一
1、检查下面的程序,找出其中的错误,并改正之。然后上机调试,使之能正常运行。
题目一
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
void A(int i=0){m=i;}
void show(){cout<<m;}
void ~A(){}
private:
int m;
};
int main()
{
A a(5);
a.m+=10;
a.show();
return 0;
}
我的方案
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A(int i = 0) { m = i; };
void show() { cout << m; }
~A(){};
int m;
private:
};
int main()
{
A a(5);
a.m += 10;
a.show();
return 0;
}
效果如下

题目二
class X
{ private:
int a=0;
int &b;
const int c;
void setA(int i){a=i;}
X(int i){ a=i;}
public:
int X(){ a=b=0;}
X(int i, int j, int k){ a=i; b=j; c=k; }
setC(int k) const { c=c+k;}
};
int main()
{
X x1;
X x2(2) ;
X x3(1,2,3) ;
x1.setA(3) ;
return 0 ;
}
想不出来
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class X
{
private:
int a = 0;
int& b;
const int c;
void setA(int i) { a = i; }
X(int i) : b(b),c()
{ a = i; }
public:
X():b(a),c()
{ a = 0; }
X(int i, int j, int k):b(j),c(k)
{ a = i; }
};
int main()
{
X x1;
X x3(1, 2, 3);
return 0;
}
问题二
2、分析下面的程序,写出其运行时的输出结果。上机运行该程序,观察运行结果是否与你的分析相同。如有不同,试分析原因。
题目一
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A();
A(int i,int j);
void print( );
private:
int a,b;
};
A::A( )
{
a=b=0;
cout<<”Default constructor called.\n”;
}
A::A(int i,int j)
{
a=i;
b=j;
cout<<”Constructor called.\n”;
}
void A::print()
{
cout<<”a=”<<a<<”,b=”<<b<<endl;
}
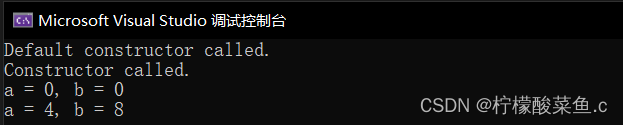
void main()
{
A m,n(4,8);
m.print();
n.print();
}
效果如下
题目二
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{public:
Date(int,int,int);
Date(int,int);
Date(int);
Date( );
void display( );
private:
int month;
int day;
int year;
};
Date::Date(int m,int d,int y):month(m),day(d),year(y){ }
Date::Date(int m,int d):month(m),day(d) {year=2005;}
Date::Date(int m):month(m)
{ day=1;
year=2005;
}
Date::Date( )
{ month=1;
day=1;
year=2005;
}
void Date::display( )
{cout<<month<<"/"<<day<<"/"<<year<<endl;}
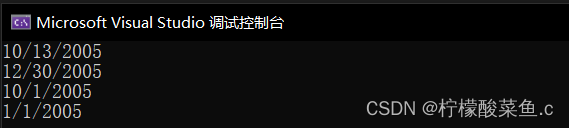
int main( )
{ Date d1(10,13,2005);
Date d2(12,30);
Date d3(10);
Date d4;
d1.display( );
d2.display( );
d3.display( );
d4.display( );
return 0;
}
效果如下
题目三
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class test
{
public:
test();
int getint() { return num; }
float getfloat() { return fl; }
~test();
private:
int num;
float fl;
};
test::test()
{
cout << "Initalizing default" << endl;
num = 0;
fl = 0.0;
}
test::~test()
{
cout << "Destructor is active" << endl;
}
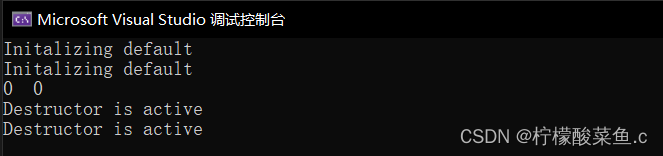
int main()
{
test array[2];
cout << array[1].getint() << " " << array[1].getfloat() << endl;
return 0;
}
效果如下
题目四
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
class X
{
public:
X(int x1, char* x2, float x3) :a(x1), c(x3)
{
b = new char[sizeof(x2) + 1];
strcpy(b, x2);
}
X() :a(0), b("X::X()"), c(10) { }
X(int x1, char* x2 = "X::X(....)", int x3 = 10) :a(x1), b(x2), c(x3) {}
X(const X& other)
{
a = other.a;
b = "X::X(const X &other)";
c = other.c;
}
void print()
{
cout << "a=" << a << "\t" << "b=" << b << "\t" << "c=" << c << endl;
}
private:
int a;
char* b;
float c;
};
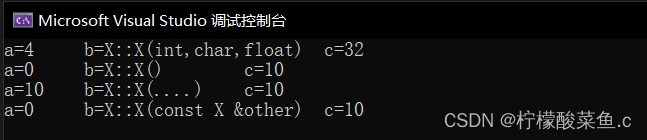
int main() {
X* A = new X(4, "X::X(int,char,float)", 32);
X B, C(10), D(B);
A->print();
B.print();
C.print();
D.print();
return 0;
}
我的垃圾代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
class X
{
public:
X(int x1, const char* x2, float x3) :a(x1), c(x3)
{
b = new char[sizeof(x2) + 1];
b = x2;
}
X() :a(0), b("X::X()"), c(10) { }
X(int x1, const char* x2 = "X::X(....)", int x3 = 10) :a(x1), b(x2), c(x3) {}
X(const X& other)
{
a = other.a;
b = "X::X(const X &other)";
c = other.c;
}
void print()
{
cout << "a=" << a << "\t" << "b=" << b << "\t" << "c=" << c << endl;
}
private:
int a;
const char* b;
float c;
};
int main() {
X* A = new X(4, "X::X(int,char,float)", 32);
X B, C(10), D(B);
A->print();
B.print();
C.print();
D.print();
return 0;
}
效果如下
问题三
3、某单位的职工工资包括基本工资Wage,岗位津贴Subsidy,房租Rent,水费WaterFee,电费ElecFee。设计并实现工资管理的类Salary,该类的形式如下:
class Salary
{public:
Salary(){初始化工资数据的各分项数据为0}
Salary(……) {初始化工资数据的各分项数据}
void setXX(double f){ XX=f; }
double getXX(){ return XX; }
double RealSalary(){ …… }//计算实发工资
……
Private:
Bouble Wage, Subsidy, Rent, WaterFee, ElecFee;
};
其中,成员函数setXX()用于设置工资的各分项数据,成员函数getXX()用于获取工资的各分项数据,XX代表Wage、Subsidy等数据成员,如Wage对应的成员函数则为setWage()和getWage()。
实发工资=Wage+Subsidy-Rent-WaterFee-ElecFee
编程完善该类的设计,并在主函数中测试该类的各成员函数。
/*某单位的职工工资包括基本工资Wage,岗位津贴Subsidy,房租Rent,水费WaterFee,电费ElecFee。
设计并实现工资管理的类Salary,该类的形式如下:
class Salary
{
public:
Salary() { 初始化工资数据的各分项数据为0 }
Salary(……) { 初始化工资数据的各分项数据 }
void setXX(double f) { XX = f; }
double getXX() { return XX; }
double RealSalary() { …… }//计算实发工资
……
Private :
Bouble Wage, Subsidy, Rent, WaterFee, ElecFee;
};
其中,成员函数setXX()用于设置工资的各分项数据,
成员函数getXX()用于获取工资的各分项数据,
XX代表Wage、Subsidy等数据成员,
如Wage对应的成员函数则为setWage()和getWage()。
实发工资 = Wage + Subsidy - Rent - WaterFee - ElecFee
编程完善该类的设计,并在主函数中测试该类的各成员函数。*/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
class Salary
{
public:
Salary() {
Subsidy = 0;//岗位津贴
Rent = 0;//房租
WaterFee = 0;//水费
ElecFee = 0;//电费
Wage = 0;//基本工资
}
Salary(double a,double b,double c,double d,double e) {
Subsidy = a;//岗位津贴
Rent = b;//房租
WaterFee = c;//水费
ElecFee = d;//电费
Wage = e;//基本工资
}
void setSubsidy(double f) {
Subsidy = f;
}
void setRent(double f) {
Rent = f;
}
void setWaterFee(double f) {
WaterFee = f;
}
void setElecFee(double f) {
ElecFee = f;
}
void setWage(double f) {
Wage = f;
}
double getSubsidy() {
cout << "岗位津贴是多少:" ;
cin >> Subsidy;
return Subsidy;
}
double getRent() {
cout << "房租是多少:" ;
cin >> Rent;
return Rent;
}
double getWaterFee() {
cout << "水费是多少:" ;
cin >> WaterFee;
return WaterFee;
}
double getElecFee() {
cout << "电费是多少:";
cin >> ElecFee;
return ElecFee;
}
double getWage() {
cout << "基本工资是多少:" ;
cin >> Wage;
return Wage;
}
double RealSalary() {
cout << "RealSalary = " << Wage + Subsidy - Rent - WaterFee - ElecFee << endl;
return 0;
}//计算实发工资
private:
double Subsidy;//岗位津贴
double Rent;//房租
double WaterFee;//水费
double ElecFee;//电费
double Wage;//基本工资
};
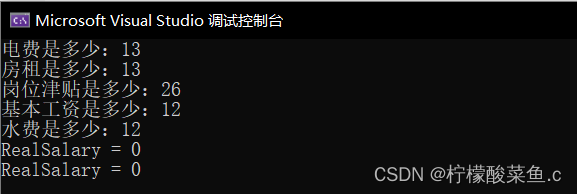
int main()
{
Salary John;
Salary();
double a = John.getElecFee();
double b = John.getRent();
double c = John.getSubsidy();
double d = John.getWage();
double e = John.getWaterFee();
Salary(a, b, c, d, e);
John.RealSalary();
John.setElecFee(a);
John.setRent(b);
John.setSubsidy(c);
John.setWage(d);
John.setWaterFee(e);
John.RealSalary();
}
效果如下
问题四
4、设计一个时钟类Clock。数据成员包括hour(小时)、minute(分钟)、second(秒)。要求用成员函数实现以下功能:
(1)创建具有指定时钟(小时、分钟、秒)的Clock对象,默认时钟为00:00:00。
(2)动态地设置时、分、秒。
(3)在屏幕上按“时:分:秒”的格式显示时钟。
(4)在主函数中测试该类。
/*设计一个时钟类Clock。
数据成员包括hour(小时)、minute(分钟)、second(秒)。
要求用成员函数实现以下功能:
(1)创建具有指定时钟(小时、分钟、秒)的Clock对象,默认时钟为00 : 00 : 00。
(2)动态地设置时、分、秒。
(3)在屏幕上按“时 : 分:秒”的格式显示时钟。
(4)在主函数中测试该类。*/
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<Windows.h>
using namespace std;
class Clock
{
public:
Clock() {};
void SetTime(int newH = 0, int newM = 0, int newS = 0);
void ShowTime();
void Run(); //Run()控制计时
private:
int hour, minute, second;
};
void Clock::SetTime(int newH, int newM, int newS) //设置时间
{
hour = newH;
minute = newM;
second = newS;
}
void Clock::ShowTime() //显示时间,在显示时间前进行判断,如果时间设置不合适,则提示错误
{
if (hour > 24 || hour < 0 || minute>60 || minute < 0 || second>60 || second < 0)
{
cout << "输入有误!" << endl;
exit(0);
}
else
{
cout << setw(2) << setfill('0') << hour << ":" << setw(2) << setfill('0') //<<setw(2)<<setfill('0')设置域宽为2 不够的话用字符‘0’填充
<< minute << ":" << setw(2) << setfill('0') << second << endl;
}
}
void Clock::Run() //实现计时功能
{
while (1)
{
second += 1;
if (second >= 60)
{
second -= 60;
minute += 1;
}
if (minute >= 60)
{
minute -= 60;
hour += 1;
}
if (hour >= 24)
{
hour -= 24;
}
system("cls");
ShowTime();
Sleep(1000);
}
}
int main()
{
Clock myClock; //定义时钟类对象
myClock.SetTime(23, 59, 55);
myClock.ShowTime();
myClock.Run();
return 0;
}
效果如下

问题五
5、需要求3个三角形的体积,请编写一个基于对象的程序。数据成员包括三角形的三边长a、b、c。要求用成员函数实现以下功能:
(1) 定义构造函数完成三角形的初始化;
(2) 求三角形的周长;
(3) 求三角形的面积;
(4) 输出三角形信息。
/*需要求3个三角形的体积,请编写一个基于对象的程序。
数据成员包括三角形的三边长a、b、c。
要求用成员函数实现以下功能:
(1) 定义构造函数完成三角形的初始化;
(2) 求三角形的周长;
(3) 求三角形的面积;
(4) 输出三角形信息。*/
//面向对象的程序设计求三角形面积及周长
#include <iostream>
#include <Cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Ctriangle //定义三角形类
{
private:
double S1, S2, S3;//三角形的三条边
double l;
double a;
public:
Ctriangle(int x = 0, int y = 0, int z = 0)//边长初始化
{
this->S1 = x;
this->S2 = y;
this->S3 = z;
}
double Girth(); //三角形周长
bool Istriangle(); //判断是否是三角形
double Area(); //三角形面积
void init_triangle();//输入三角形边长
void print_tri();
};
bool Ctriangle::Istriangle() //判断是否是三角形
{
if ((S1 + S2) > S3 && (S2 + S3) > S1 && (S1 + S3) > S2)//使用两边之和大于第三边判断
{
return true;
}
else
{
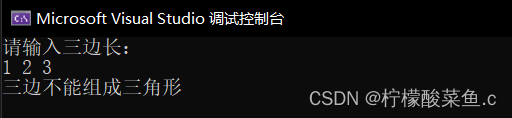
cout << "三边不能组成三角形" << endl;
return false;
}
}
void Ctriangle::init_triangle() //输入三角形边长
{
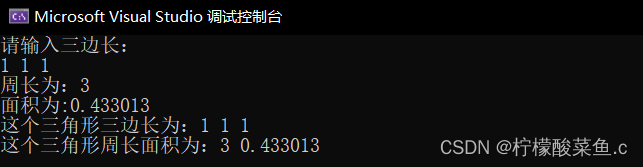
cout << "请输入三边长:" << endl;
cin >> S1 >> S2 >> S3;
}
void Ctriangle::print_tri () //输入三角形边长
{
cout << "这个三角形三边长为:"<< S1<<" " << S2<<" " << S3 << endl;
cout << "这个三角形周长面积为:" << l << " " << a << endl;
}
double Ctriangle::Girth() //求周长
{
l = S1 + S2 + S3;
cout << "周长为:" << l<< endl;
return 0;
}
double Ctriangle::Area() //求面积
{
double x;
x = (S1 + S2 + S3) / 2;
a = sqrt(x * (x - S1) * (x - S2) * (x - S3));
cout << "面积为:" << a << endl;
return 0;//使用海伦公式
}
int main()
{
Ctriangle t;
t.init_triangle();
if (t.Istriangle())
{
t.Girth();
t.Area();
t.print_tri();
}
return 0;
}
效果如下
问题六
建立一个对象数组,内放5个学生的数据(学号、成绩),设立一个函数max,用指向对象的指针作函数参数,在max函数中找出5个学生中成绩最高者,并输出其学号、成绩。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class student
{
public:
student(int n, string na, int m) : num(n), name(na), mark(m) {}
int num;
string name;
int mark;
};
void max(student* p, int n)
{
student* pt, t(0, "", 0);
int max = p->mark;
for (pt = p; pt < p + n; pt++)
{
if (pt->mark > max)
{
max = pt->mark;
t = *pt;
}
}
cout << t.mark;
}
int main()
{
student stu[5] = {
student(1001, "Mark", 57),
student(1002, "Tony", 76),
student(1003, "Tim", 80),
student(1004, "Tom", 77),
student(1005, "Hork", 81) };
max(stu, 5);
return 0;
}
效果如下
问题七
7.设计一个点类Point,再设计一个矩形类,矩形类使用Point类的两个坐标点作为矩形的对角顶点。并可以输出4个坐标值和面积。使用测试程序验证程序。
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
class Point;
class Rectangle
{
private:
double x1, y1, x2, y2, s;
public:
Rectangle();
void peak1(Point&);
void peak2(Point&);
void area();
};
class Point
{
private:
double x1, y1;
public:
Point();
Point(double m_x1, double m_y1) :x1(m_x1), y1(m_y1) {}
friend void Rectangle::peak1(Point&);
friend void Rectangle::peak2(Point&);
};
Point::Point()
{
x1 = y1 = 0;
}
Rectangle::Rectangle()
{
s = x1 = x2 = y1 = y2 = 0;
}
void Rectangle::peak1(Point& t1)
{
x1 = t1.x1;
y1 = t1.y1;
}
void Rectangle::peak2(Point& t2)
{
x2 = t2.x1;
y2 = t2.y1;
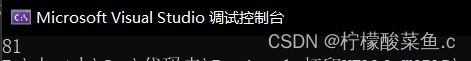
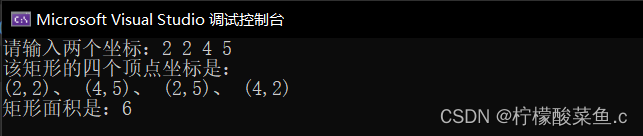
cout << "该矩形的四个顶点坐标是:" << endl;
cout << "(" << x1 << "," << y1 << ")";
cout << "、 (" << x2 << "," << y2 << ")";
cout << "、 (" << x1 << "," << y2 << ")";
cout << "、 (" << x2 << "," << y1 << ")" << endl;
}
void Rectangle::area()
{
s = fabs(x2 - x1) * fabs(y2 - y1);
cout << "矩形面积是:" << s << endl;
}
void main()
{
double x1, y1, x2, y2;
cout << "请输入两个坐标:";
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
Point a(x1, y1);
Point b(x2, y2);
Rectangle c;
c.peak1(a);
c.peak2(b);
c.area();
}
效果如下
问题八
8、下面是一个整型数组类intArray的声明,请给出该类所有数据成员的类外定义。
class intArray
{public:
intArray(int size);//构造函数
intArray(const intArray &x);//复制构造函数
~intArray();//析构函数
bool Set(int i, int elem);//设置第i个数组元素的值,设置成功返回true,失败返回false
bool Get(int i, int &elem); //获取第i个数组元素的值,获取成功返回true,失败返回false
int Length( ) const;//获取数组的长度
void ReSize ( int size ); //重置数组
void Print();//输出数组
private:
int *element; //指向动态数组的指针
int arraysize; //数组的当前长度
};
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class intArray
{
friend istream& operator>>(istream& cin, intArray&);//数组的整体输入
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, intArray&);//数组的整体输出
public:
intArray() {}
intArray(int size);//构造函数
intArray(const intArray& x);//复制构造函数
~intArray();//析构函数
bool Set(int i, int elem)//设置第i个数组元素的值,设置成功返回true,失败返回false
{
if (i >= 0 && i < this->arraysize)
{
this->element[i] = elem;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
int Get(int i)//获取第i个数组元素的值
{
if (i > 0 && i < this->arraysize)
{
return this->element[i];
}
}
int Length() {//获取数组长度
return arraysize;
}
void ReSize(int size);//重置数组的长度
intArray& operator=(const intArray& other);//赋值运算符“=”重载函数
intArray operator+(const intArray& other);//加运算符“+”重载函数
intArray operator-(const intArray& other);//减运算符“-”重载函数
private:
int* element;//指向动态数组的指针
int arraysize;//数组的当前长度
};
intArray::~intArray() {
delete element;
element = NULL;
}
intArray::intArray(const intArray& x) {
this->arraysize = x.arraysize;
this->element = new int[arraysize];
for (int i = 0; i < arraysize; i++)
{
this->element[i] = x.element[i];
}
}
intArray::intArray(int size) {
this->arraysize = size;
this->element = new int[size];
}
/*
对数组对象进行输入
*/
istream& operator>>(istream& cin, intArray& arr) {
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.arraysize; i++)
{
cin >> temp;
arr.element[i] = temp;
}
return cin;
}
/*
对数组对象进行输出
*/
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, intArray& arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.arraysize; i++)
{
cout << arr.element[i] << endl;
}
return cout;
}
intArray& intArray::operator=(const intArray& other)//赋值运算符“=”重载函数
{
if (this->element != NULL)
{
delete this->element;
this->element = NULL;
}
this->arraysize = other.arraysize;
this->element = new int[arraysize];
for (int i = 0; i < arraysize; i++)
{
this->element[i] = other.element[i];
}
return *this;
}
intArray intArray:: operator+(const intArray& other)//加运算符“+”重载函数
{
intArray temp(this->arraysize);
for (int i = 0; i < this->arraysize; i++)
{
temp.element[i] = this->element[i] + other.element[i];
}
return temp;
}
intArray intArray:: operator-(const intArray& other)//减运算符“-”重载函数
{
intArray temp(this->arraysize);
for (int i = 0; i < this->arraysize; i++)
{
temp.element[i] = this->element[i] - other.element[i];
}
return temp;
}
void intArray::ReSize(int size) {
this->arraysize = size;
if (this->element != NULL)
{
delete this->element;
}
this->element = new int[size];
}
intArray& testA() {
int size = 0;
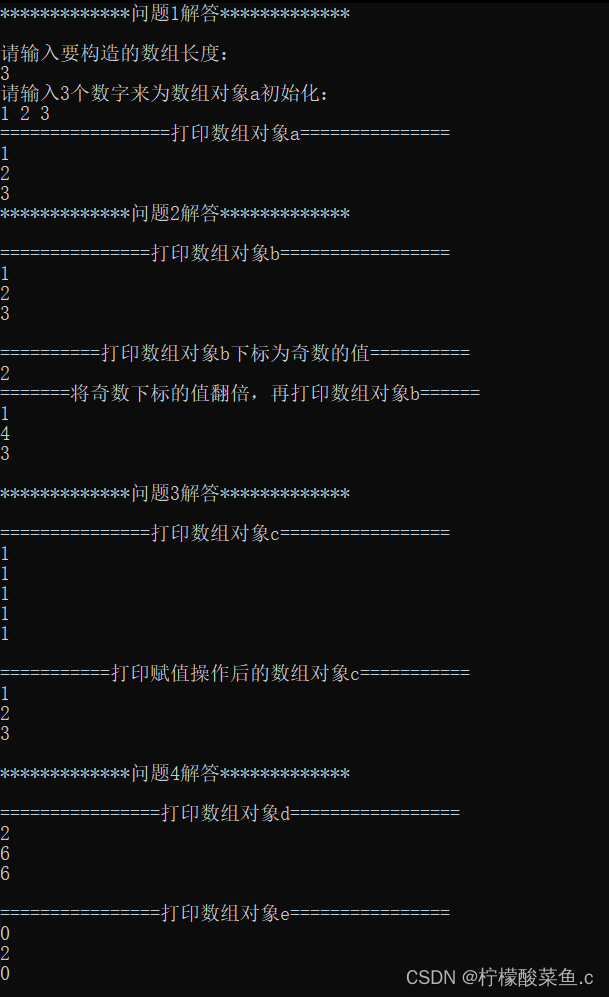
cout << "请输入要构造的数组长度:" << endl;
cin >> size;
intArray* a = new intArray(size);
cout << "请输入" << size << "个数字来为数组对象a初始化:" << endl;
cin >> *a;
cout << "=================打印数组对象a===============" << endl;
cout << *a;
return *a;
}
intArray& testB(intArray& a) {
//拷贝构造数组b
intArray* b = new intArray(a);
int size = a.Length();//获取数组长度
cout << "===============打印数组对象b=================" << endl;
cout << *b << endl;
cout << "==========打印数组对象b下标为奇数的值==========" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < size; i += 2)
{
cout << (*b).Get(i) << endl;
}
cout << "=======将奇数下标的值翻倍,再打印数组对象b======" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < size; i += 2)
{
(*b).Set(i, (*b).Get(i) * 2);
}
cout << *b << endl;
return *b;
}
intArray& testC(intArray& a) {
//构造数组对象c
intArray* c = new intArray(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
(*c).Set(i, 1);
}
cout << "===============打印数组对象c=================" << endl;
cout << *c << endl;
(*c).ReSize(10);
(*c) = a;
cout << "===========打印赋值操作后的数组对象c===========" << endl;
cout << *c << endl;
return *c;
}
void testD(intArray& b, intArray& c) {
intArray d = b + c;
intArray e = b - c;
cout << "================打印数组对象d=================" << endl;
cout << d << endl;
cout << "================打印数组对象e================" << endl;
cout << e << endl;
}
void test() {
cout << "*************问题1解答*************" << endl << endl;
intArray a = testA();
cout << "*************问题2解答*************" << endl << endl;
intArray b = testB(a);
cout << "*************问题3解答*************" << endl << endl;
intArray c = testC(a);
cout << "*************问题4解答*************" << endl << endl;
testD(b, c);
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
效果如下
问题九
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class complex
{
private:
double sb, xb;
public:
complex(double a = 0, double b = 0)
{
sb = a; xb = b;
}
friend complex add(complex& x, complex& y);
void Show()
{
cout << "(" << sb << "," << xb << ")" << endl;
}
};
complex add(complex& x, complex& y)
{
complex z;
z.sb = y.sb + x.sb;
z.xb = y.xb + x.xb;
return z;
}
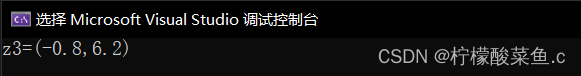
int main() //主函数
{
complex z1(1.5, 2.8), z2(-2.3, 3.4), z3; //声明复数类的对象
z3 = add(z1, z2);//友元函数调用
cout << "z3=";
z3.Show();
return 0;
}
效果如下