前言
Java是一种可以撰写跨平台应用软件的面向对象的程序设计语言。Java 技术具有卓越的通用性、高效性、平台移植性和安全性,广泛应用于PC、数据中心、游戏控制台、科学超级计算机、移动电话和互联网,同时拥有全球最大的开发者专业社群。
Java数组详解
数组的定义
-
数组是相同类型数据的有序集合。
-
数组描述的是相同类型的若干个数据,按照一定的先后次序排列组合而成。
-
其中,每一个数据称作一个数组元素,每个数组元素可以通过一个下标来访问它们。
数组声明创建
首先必须声明数组变量,才能在程序中使用数组。下面是声明数组变量的语法:
dataType[] arrayRefVar; //首选的方法
//或
dataType arrayRefVar[]; //效果相同,但不是首选方法
Java语言使用new操作符来创建数组,语法如下:
dataType[] arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraysize];
数组的元素是通过索引访问的,数组索引从0开始。
获取数组长度: arrays.length
三种初始化
静态初始化:
int[] a = {1,2,3};
Man[] mans = {new Man(1,1), new Man(2,2)};
动态初始化:
int [] a = new int[2];
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 2;
数组的默认初始化:
- 数组是引用类型,它的元素相当于类的实例变量,因此数组一经分配空间,其中的每个元素也被按照实例变量同样的方式被隐式初始化。
下标越界及小结
数组的四个基本特点:
- 其长度是确定的。数组一旦被创建,它的大小就是不可以改变的。其元素必须是相同类型,不允许出现混合类型。
- 数组中的元素可以是任何数据类型,包括基本类型和引用类型。
- 数组变量属引用类型,数组也可以看成是对象,数组中的每个元素相当于该对象的成员变量。数组本身就是对象,Java中对象是在堆中的,因此数组无论保存原始类型还是其他对象类型, 数组对象本身是在堆中的 。
数组边界:
-
下标的合法区间:[0, length-1],如果越界就会报错;
-
ArraylndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常!
小结:
- 数组是相同数据类型(数据类型可以为任意类型)的有序集合
- 数组也是对象。数组元素相当于对象的成员变量
- 数组长度的确定的,不可变的。如果越界,则报:ArraylndexOutofBounds
数组的使用
-
普通for循环
-
for-each循环
int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5};
for(int array : arrays){
System.out.println(array);
}
数组作方法入参
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5};
printArray(arrays);
}
//打印数组元素
public static void printArray(int[] arrays){
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arrays[i] + " ");
}
}
}
数组作返回值
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrays = {1,2,3,4,5};
// printArray(arrays);
int[] result = reverse(arrays);
printArray(result);
}
//反转数组
public static int[] reverse(int[] arrays){
int[] result = new int[arrays.length];
for( int i = 0, j = arrays.length-1 ; i< arrays.length ; i++ , j--){
result[j] = arrays[i];
}
return result;
}
//打印数组元素
public static void printArray(int[] arrays){
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arrays[i] + " ");
}
}
}
多维数组
- 多维数组可以看成是数组的数组,比如二维数组就是一个特殊的一维数组,其每一个元素都是一个一维数组。【参考文档】
- 二维数组
int[][] a = new int[2][5];
解析:以上二维数组a可以看成一个两行五列的数组。
public class erweiArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arrays = {{1,2},{2,3},{3,4},{4,5}};
//遍历二维数组
for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrays[i].length; j++) {
System.out.println(arrays[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
Arrays类
-
数组的工具类
java.util.Arrays -
由于数组对象本身并没有什么方法可以供我们调用,但API中提供了一个工具类Arrays供我们使用,从而可以对数据对象进行一些基本的操作。
-
查看JDK帮助文档
-
Arrays类中的方法都是static修饰的静态方法,在使用的时候可以直接使用类名进行调用布"不用"使用对象来调用(注意:是"不用”而不是"不能")
具有以下常用功能:
-
给数组赋值:通过
fill方法。 -
对数组排序:通过
sort方法,按升序。 -
比较数组:通过
equals方法比较数组中元素值是否相等。 -
查找数组元素:通过
binarySearch方法能对排序好的数组进行二分查找法操作。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArraysLei {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,12345,43,12342,98,1243};
Arrays.sort(a); //数组排序:升序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); //打印数组元素
Arrays.fill(a,2,4,0); //数组填充
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
冒泡排序
- 冒泡排序无疑是最为出名的排序算法之一,总共有八大排序!
 冒泡的代码还是相当简单的,两层循环,外层冒泡轮数,里层依次比较,江湖中人人尽皆知。我们看到嵌套循环,应该立马就可以得出这个算法的 时间复杂度为O(n2) 。
冒泡的代码还是相当简单的,两层循环,外层冒泡轮数,里层依次比较,江湖中人人尽皆知。我们看到嵌套循环,应该立马就可以得出这个算法的 时间复杂度为O(n2) 。
import java.util.Arrays;
//冒泡排序:
//1.比较数组中,两个相邻的元素,如果第一个数比第二个数大,我们就交换他们的位置;
//2.每一次比较,都会产生出一个最大,或者最小的数字;
//3. 下一轮则可以少一次排序!
//4. 依次循环,直到结束!
public class maopaopaixu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,4,5,72,2,2,2,25,6,7};
int[] sort = sort(a); //调用完我们自己写的排序方法以后,返回一个排序后的数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort));
}
public static int[] sort(int[] array){
//临时变量
int temp = 0;
//外层循环,判断我们这个要走多少次;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
//内层循环,比较判断两个数,如果第一个数,比第二个数大,则交换位置
for (int j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++) {
if (array[j+1]<array[j]){
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
}
Java对象数组的概述和使用
1 public class Student
2 {
3 // 成员变量
4 private String name;
5 private int age;
6
7 // 构造方法
8 public Student()
9 {
10 super();
11 }
12
13 public Student(String name, int age)
14 {
15 super();
16 this.name = name;
17 this.age = age;
18 }
19
20 // 成员方法
21 // getXxx()/setXxx()
22 public String getName()
23 {
24 return name;
25 }
26
27 public void setName(String name)
28 {
29 this.name = name;
30 }
31
32 public int getAge()
33 {
34 return age;
35 }
36
37 public void setAge(int age)
38 {
39 this.age = age;
40 }
41
42 @Override
43 public String toString()
44 {
45 return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
46 }
47 }
1 /**
2 把5个学生的信息存储到数组中,并遍历数组,获取得到每一个学生信息。
3 * 学生:Student
4 * 成员变量:name,age
5 * 构造方法:无参,带参
6 * 成员方法:getXxx()/setXxx()
7 * 分析:
8 * A:创建学生类。
9 * B:创建学生数组(对象数组)。
10 * C:创建5个学生对象,并赋值。
11 * D:把C步骤的元素,放到数组中。
12 * E:遍历学生数组。
13 * */
14
15 public class Practice
16 {
17 public static void main(String[] args)
18 {
19 // 创建学生数组(对象数组)。
20 Student[] students = new Student[5];
21 // for (int x = 0; x < students.length; x++)
22 // {
23 // System.out.println(students[x]);
24 // }
25 // System.out.println("---------------------");
26
27 // 创建5个学生对象,并赋值。
28 Student s1 = new Student("小明", 27);
29 Student s2 = new Student("小红", 30);
30 Student s3 = new Student("小强", 30);
31 Student s4 = new Student("旺财", 12);
32 Student s5 = new Student("张三", 35);
33
34 // 将对象放到数组中。
35 students[0] = s1;
36 students[1] = s2;
37 students[2] = s3;
38 students[3] = s4;
39 students[4] = s5;
40
41 // 遍历
42 for (int x = 0; x < students.length; x++)
43 {
44 //System.out.println(students[x]);
45 Student s = students[x];
46 System.out.println(s.getName()+"---"+s.getAge());
47 }
48 }
49 }
对象数组的内存图解
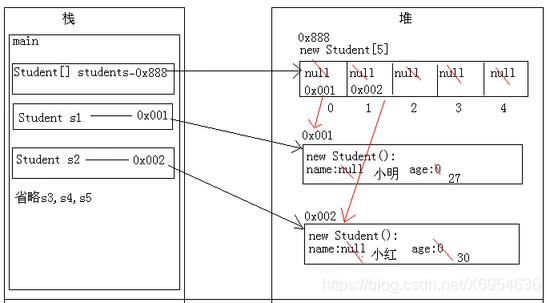
集合的由来及与数组的区别
集合类的由来:面向对象语言对事物的体现都是以对象的形式,所以为了方便对多个对象的操作,Java就提供了集合类。
数组和集合类同的区别:
数组可以存储同一种类型的基本数据也可以存储同一种类型的对象,但长度是固定的
集合只可以存储不同类型的对象,长度是可变的
集合类的特点:集合只用于存储对象,集合长度是可变的,集合可以存储不同类型的对象。
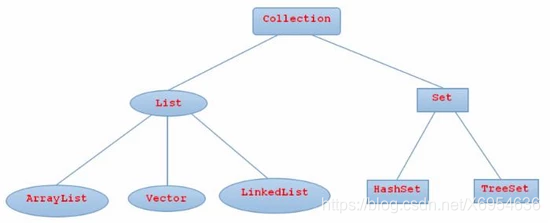
集合的继承体系图解
集合容器因为内部的数据结构不同,有多种具体容器,根据共性内容不断的向上抽取,就形成了集合框架。
框架的顶层Collection接口
Collection集合的功能概述
Collection 层次结构中的根接口。Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。一些 collection 允许有重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。JDK 不提供此接口的任何直接实现:它提供更具体的子接口(如 Set 和 List)实现。此接口通常用来传递 collection,并在需要最大普遍性的地方操作这些 collection。
最后,感谢大家的观看,谢谢大家的支持,能三连最好啦!
