【问题描述】
用 JAVA 语言设计如下界面的石头剪刀布游戏。游戏的一方点击界面上石头、剪刀、布按钮,游戏的 另一方计算机随机选择,然后给出游戏结果。
2.2【基本要求】
按照下面给出的步骤设计石头剪刀布游戏,并完成以下工作:
1. 在“//”后给出必要的注释;
2. 为程序添加菜单;至少 2 个菜单:结果显示方式和关于游戏;结果显示方式菜单有 3 个菜单项:文本
? 显示、图形显示、结束游戏;实现菜单中的功能,自行搜索能体现石头、剪刀、布的图形或图片,用
? 这些图形或图片显示游戏结果。
第一步,引用需要的包或类;
第二步,定义一个窗口类,并实现 ActionListener 接口,把需要的组件定义放到类里;
第三步,设置窗体。
? ?
import java.awt.*; //引入抽象窗口工具类包; import java.awt.event.*; //
import javax.swing.*; //
//定义一个窗口类,该类实现 ActionListener 接口;
public class work11 extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
JButton jiandao,shitou,bu,clear; JPanel pane12,panel1;
JLabel label;
//定义 JButton 对象; //
//
public work11() {
setTitle("窗体"); //设置窗体标题,修改标题为“石头剪刀布游戏”; setLocation(250,250); //设置窗体左上顶点坐标;
-3-
setSize(300,300); //设置窗体大小,修改窗体大小为:350×350; 第四步,根据需求建立对象,这里只需要 4 个 JButton 对象,2 个 JPanel 对象,1 个 JLabel 对象;
panel1 =new JPanel(); // panel1.setBackground(Color.yellow); // shitou = new JButton("石头"); // jiandao =new JButton("剪刀"); // bu = new JButton("布"); // clear = new JButton("清空"); // pane12=new JPanel(); // pane12.setBackground(Color.green); //
label =new JLabel("选择剪刀、石头、布开始游戏"); //
第五步,给所有 JButton 对象注册事件监听器;
第六步,把所有新添加的对象都逐次放进窗体中,例如下面,先放进面板里面,然后再把面板放进窗体中, 放置位置可以自定义;
shitou.addActionListener(this); //给 shitou 添加事件监听器; bu.addActionListener(this); // jiandao.addActionListener(this); // clear.addActionListener(this); //
panel1.add(shitou); panel1.add(jiandao); panel1.add(bu); panel1.add(clear); pane12.add(label);
//把 shitou 放进 panel1 中; //
//
//
//
add(panel1,BorderLayout.NORTH); // add(pane12,BorderLayout.CENTER); // }
第七步,实现 ActionListener 接口方法,使得按下按钮后执行方法里的代码;
//实现 ActionListener 接口方法,当按下按钮就会调用该方法,可以称为事件响应器;
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(e.getSource()==shitou) { //如果你按下的是 shitou 按键时,就会执行以下操作; inti=((int)(Math.random()*10))%3; //定义一个int型变量i,利用Math.random()函数获取 随机数,因为*10 所以随机数区间为[0,10),最后强制转换为 int 型,再除 3 取余,最后的赋值给 i; switch(i) //i 为 0 时就执行 case 0 操作,以此类推;
{
case 0 :label.setText("你出石头,电脑出石头,平局!");break; 操作,到 break 结束;(必须要添加 break,不然会一直执行下去);
case 1 :label.setText("你出石头,电脑出剪子,恭喜你赢了!");break; 同理;
//当 i=0 时,执行后续 //当 i=1 时,与上
-4-
case 2 :label.setText("你出石头,电脑出布,很遗憾你输了!");break; 同理;
}}
else if (e.getSource()==bu) { //如果你按下的是 bu 按键时,与上同理; int i=((int)(Math.random()*10))%3;
switch(i)
{
case 0 :label.setText("你出布,电脑出布,平局!");break;
case 1 :label.setText("你出布,电脑出石头,恭喜你赢了!");break; case 2 :label.setText("你出布,电脑出剪刀,很遗憾你输了!");break;
//当 i=2 时,与上
}}
else if (e.getSource()==jiandao) { //当你按下 jiandao 按键时,与上同理;
int i=((int)(Math.random()*10))%3;
switch(i)
{
case 0 :label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出剪刀,平局!");break;
case 1 :label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出布,恭喜你赢了!");break; case 2 :label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出石头,很遗憾你输了!");break; }}
else if(e.getSource()==clear)//当你按下 clear 按键时,直接输出 label.setText(); { label.setText("选择剪刀、石头、布开始游戏"); }
}
第八步,添加主方法,进行测试;
}


?
package 实习;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class MainFrame {
public static JFrame frame =new JFrame();
private static JPanel panel=null;
public MainFrame(){
frame=new JFrame("剪刀石头布游戏");
frame.setBounds(250,250,350,350);
frame.getContentPane().setLayout(null);
frame.setResizable(false);
JMenuBar mbr =new JMenuBar();
frame.setJMenuBar(mbr);
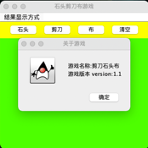
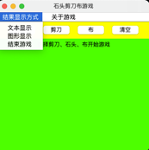
JMenu m1=new JMenu("结果显示方式");
JMenuItem m2=new JMenuItem("关于游戏");
mbr.add(m1);
mbr.add(m2);
JMenuItem m11=new JMenuItem("文本显示");
JMenuItem m12=new JMenuItem("图形显示");
JMenuItem m13=new JMenuItem("结束游戏");
m1.add(m11);
m1.add(m12);
m1.add(m13);
JPanel p3=new JPanel();
JLabel l3=new JLabel();
m11.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
firstView();
firstView().setVisible(true);
}
});
m12.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
scendView().setVisible(true);
}
});
m13.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
m2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(
frame,
"游戏名称:剪刀石头布\n游戏版本 version:1.1",
"关于游戏",
JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE
);
}
});
}
public static JFrame returnJFrame(){
return frame;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MainFrame();
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static Frame firstView() //定义一个窗口类,该类实现 ActionListener 接口;
{
JFrame frame= new JFrame("剪刀石头布游戏");
JButton jiandao, shitou, bu, clear; //定义 JButton 对象;
JPanel pane12, panel1,panel3; //定义 Jpanel 对象;
JLabel label; //定义 JLabel 对象;
frame.setBounds(250,250,350,350);
// 第四步,根据需求建立对象,这里只需要 4 个 JButton 对象,2 个 JPanel 对象,1 个 JLabel 对象;
panel1 = new JPanel(); // 建立Jpanel对象
panel1.setBackground(Color.yellow); // 给Jpanel对象创建背景
shitou = new JButton("石头"); // 建立JButton对象
jiandao = new JButton("剪刀"); //建立JButton对象
bu = new JButton("布"); // 建立JButton对象
clear = new JButton("清空"); // 建立JButton对象
pane12 = new JPanel(); // 建立Jpanel对象
pane12.setBackground(Color.green); // 给JPanel对象建立背景
label = new JLabel("选择剪刀、石头、布开始游戏"); // 建立JLabel对象
jiandao.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int i = ((int) (Math.random() * 10)) % 3;
switch (i) {
case 0:
label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出剪刀,平局!");
break;
case 1:
label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出布,恭喜你赢了!");
break;
case 2:
label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出石头,很遗憾你输了!");
break;
}
}
});
shitou.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int i = ((int) (Math.random() * 10)) % 3; //定义一个int型变量i,利用Math.random()函数获取 随机数,因为*10 所以随机数区间为[0,10),最后强制转换为 int 型,再除 3 取余,最后的赋值给 i;
switch (i) //i 为 0 时就执行 case 0 操作,以此类推;
{
case 0: //当 i=0 时,执行后续
label.setText("你出石头,电脑出石头,平局!");
break;
case 1: //当 i=1 时,与上
label.setText("你出石头,电脑出剪子,恭喜你赢了!");
break;
case 2: //当 i=2 时,与上
label.setText("你出石头,电脑出布,很遗憾你输了!");
break;
}
}
});
bu.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int i = ((int) (Math.random() * 10)) % 3;
switch (i) {
case 0:
label.setText("你出布,电脑出布,平局!");
break;
case 1:
label.setText("你出布,电脑出石头,恭喜你赢了!");
break;
case 2:
label.setText("你出布,电脑出剪刀,很遗憾你输了!");
break;
}
}
});
clear.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
label.setText("选择剪刀、石头、布开始游戏");
}
});
// 把所有的新添加的对象都放进去窗体里面,先放进组件类,再放进窗体类
panel1.add(shitou); //把 shitou 放进 panel1 中; //
panel1.add(jiandao); //把 jiandao 放进 panel1 中; //
panel1.add(bu); //把 bu 放进 panel1 中; //
panel1.add(clear); //把 clear 放进 panel1 中; //
pane12.add(label); //把 label 放进 pane12 中; //
frame.add(panel1, BorderLayout.NORTH); // 把面板Panel1放到窗口中
frame.add(pane12, BorderLayout.CENTER); // 把面板pane12放到窗口中
return frame;
}
public Frame scendView() //定义一个窗口类,该类实现 ActionListener 接口;
{
JFrame frame= new JFrame("剪刀石头布游戏");
JButton jiandao, shitou, bu, clear; //定义 JButton 对象;
JPanel pane12, panel1,panel3; //定义 Jpanel 对象;
JLabel label,label1,label2; //定义 JLabel 对象;
frame.setBounds(250,250,350,350);
// 第四步,根据需求建立对象,这里只需要 4 个 JButton 对象,2 个 JPanel 对象,1 个 JLabel 对象;
panel1 = new JPanel(); // 建立Jpanel对象
panel1.setBackground(Color.yellow); // 给Jpanel对象创建背景
shitou = new JButton("石头"); // 建立JButton对象
jiandao = new JButton("剪刀"); //建立JButton对象
bu = new JButton("布"); // 建立JButton对象
clear = new JButton("清空"); // 建立JButton对象
pane12 = new JPanel(); // 建立Jpanel对象
pane12.setBackground(Color.green); // 给JPanel对象建立背景
label = new JLabel("选择剪刀、石头、布开始游戏"); // 建立JLabel对象
label1=new JLabel();
label2=new JLabel();
jiandao.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int i = ((int) (Math.random() * 10)) % 3;
label1.setIcon(new ImageIcon("剪刀.jpg"));
switch (i) {
case 0:
label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出剪刀,平局!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("剪刀.jpg"));
break;
case 1:
label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出布,恭喜你赢了!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("布.jpg"));
break;
case 2:
label.setText("你出剪刀,电脑出石头,很遗憾你输了!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("石头.jpg"));
break;
}
}
});
shitou.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int i = ((int) (Math.random() * 10)) % 3; //定义一个int型变量i,利用Math.random()函数获取 随机数,因为*10 所以随机数区间为[0,10),最后强制转换为 int 型,再除 3 取余,最后的赋值给 i;
label1.setIcon(new ImageIcon("石头.jpg"));
switch (i) //i 为 0 时就执行 case 0 操作,以此类推;
{
case 0: //当 i=0 时,执行后续
label.setText("你出石头,电脑出石头,平局!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("石头.jpg"));
break;
case 1: //当 i=1 时,与上
label.setText("你出石头,电脑出剪子,恭喜你赢了!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("剪刀.jpg"));
break;
case 2: //当 i=2 时,与上
label.setText("你出石头,电脑出布,很遗憾你输了!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("布.jpg"));
break;
}
}
});
bu.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int i = ((int) (Math.random() * 10)) % 3;
label1.setIcon(new ImageIcon("布.jpg"));
switch (i) {
case 0:
label.setText("你出布,电脑出布,平局!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("布.jpg"));
break;
case 1:
label.setText("你出布,电脑出石头,恭喜你赢了!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("石头.jpg"));
break;
case 2:
label.setText("你出布,电脑出剪刀,很遗憾你输了!");
label2.setIcon(new ImageIcon("剪刀.jpg"));
break;
}
}
});
clear.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
label.setText("选择剪刀、石头、布开始游戏");
}
});
// 把所有的新添加的对象都放进去窗体里面,先放进组件类,再放进窗体类
panel1.add(shitou); //把 shitou 放进 panel1 中; //
panel1.add(jiandao); //把 jiandao 放进 panel1 中; //
panel1.add(bu); //把 bu 放进 panel1 中; //
panel1.add(clear); //把 clear 放进 panel1 中; //
pane12.add(label); //把 label 放进 pane12 中; //
pane12.add(label1);
pane12.add(label2);
frame.add(panel1, BorderLayout.NORTH); // 把面板Panel1放到窗口中
frame.add(pane12, BorderLayout.CENTER); // 把面板pane12放到窗口中
return frame;
}
}