1、基本简介
queryString请求方式
/request?username=admin&password=123456&age=20
rest风格请求
/request/admin/123456/20
MatrixVariable矩阵变量
/request;username=admin;password=123456;age=20
上述是最常见的三种请求方式;而矩阵变量请求是今天的主角一种新的请求风格,严格来说矩阵变量的请求需要用到rest风格但是又不同于rest.
2、MatrixVariable注解
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MatrixVariable {
// 1. 用于绑定请求路径中的参数
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
// 2. 同上
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
// 3. 当多级目录同时出现同参数名的参数,用于绑定路径来区分
String pathVar() default ValueConstants.DEFAULT_NONE;
// 4. 设置当前这一路径是否必须
boolean required() default true;
// 5. 给出路径的默认值,前提是required=true
String defaultValue() default ValueConstants.DEFAULT_NONE;
}
-
首先可以知道这个注解是一个修饰在参数上的注解,并且可以在运行时被JVM虚拟机加载到。
-
value 和 name属性是两个相同的属性,用于绑定获取到请求的参数。
-
pathvar是一个比较重要的属性,当多级路径中出现了相同的参数可以用pathvar指定绑定哪一级路径,然后在获取该级下的参数。
-
required属性主要是修饰当前这个矩阵变量是否是必须的;true表示必须,false表示非必须。
-
defaultValue属性当required属性值为false时,提交请求的矩阵变量中没有给定该参数的值可以使用默认值替代。
3、使用细节
由于SpringBoot中默认并没有开启矩阵变量的支持,直接关闭了矩阵变量。因此在使用的时候我们需要对SpringBoot自动装配的Bean对象进行手动的配置更改。
3.1、WebMvcAutoConfiguration自动装配
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
@Import({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class, WebProperties.class})
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware {
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
if (this.mvcProperties.getPathmatch().getMatchingStrategy() == MatchingStrategy.PATH_PATTERN_PARSER) {
configurer.setPatternParser(new PathPatternParser());
}
configurer.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(this.mvcProperties.getPathmatch().isUseSuffixPattern());
configurer.setUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.mvcProperties.getPathmatch().isUseRegisteredSuffixPattern());
this.dispatcherServletPath.ifAvailable((dispatcherPath) -> {
String servletUrlMapping = dispatcherPath.getServletUrlMapping();
if (servletUrlMapping.equals("/") && this.singleDispatcherServlet()) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper(); //关闭矩阵变量
urlPathHelper.setAlwaysUseFullPath(true);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
});
}
}
}
-
WebMvcAutoConfiguration自动装配类由SpringBoot启动时自动装配;
-
内部类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter适配器实现了WebMvcConfigurer接口中的所有方法。
-
WebMvcConfigurer接口中的所有方法都是有默认实现的,JDK8的新特性。
3.2、UrlPathHelper类
public class UrlPathHelper {
private boolean removeSemicolonContent = true;
public void setRemoveSemicolonContent(boolean removeSemicolonContent) {
checkReadOnly();
this.removeSemicolonContent = removeSemicolonContent;
}
}
-
真正使得无法使用矩阵变量的原因是UrlPathHelper类中的removeSemicolonContent默认为true,移除分号内容。
-
由于MatrixVariable矩阵变量是根据分号进行区分的,而底层默认是移除的也就是说不生效。
3.3、configurePathMatch方法
-
为了开启矩阵变量的使用必须实现WebMvcConfigurer接口,完成对configurePathMatch方法的手动实现。
-
而WebMvcConfigurer接口中所有的方法都是default的默认方法,因此可以使用适配器模式单独对该方法进行重写。
-
所以可以在配置类中手动向IOC容器中配置一个Bean对象,该对象只对这一个方法进行重写实现即可。
@Configuration
public class WebConfig {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){
return new WebMvcConfigurer() { //适配器模式
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper helper = new UrlPathHelper();
helper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(helper);
}
//其他方法依然采用默认实现
};
}
}
4、测试使用
-
首先必须手动配置对矩阵变量的支持
-
其次矩阵变量是放在rest路径中
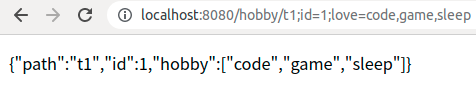
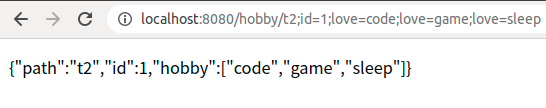
4.1、测试一
<a href="/hobby/t1;id=1;love=code,game,sleep">@MatrixVariable测试案例(1)</a>
<br/><br/>
<a href="/hobby/t2;id=1;love=code;love=game;love=sleep">@MatrixVariable测试案例(2)</a>
<br/><br/>
@RequestMapping("/hobby/{path}")
@ResponseBody
public Map MatrixVariableTest1(@MatrixVariable("id") Integer id,
@MatrixVariable("love") List<String> list,
@PathVariable("path") String path){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println(list.toString());
System.out.println(id);
map.put("hobby", list);
map.put("id", id);
map.put("path", path);
return map;
}
上述两种路径都会使用同一个Controller进行处理,path拿到的就是 / 到第一个 ; 号之间的路径。
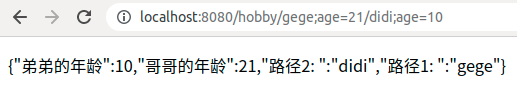
4.2、测试二
<a href="/hobby/gege;age=21/didi;age=10">@MatrixVariable测试案例(3)</a>
<br/><br/>
@RequestMapping("/hobby/{gege}/{didi}")
@ResponseBody
public Map MatrixVariableTest2(@MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "gege") Integer Gage,
@MatrixVariable(value = "age", pathVar = "didi") Integer Dage,
@PathVariable("gege") String path1,
@PathVariable("didi") String path2){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("哥哥的年龄", Gage);
map.put("弟弟的年龄", Dage);
map.put("路径1: ", path1);
map.put("路径2: ", path2);
return map;
}
Gage绑定{gege}中的age参数,Dage绑定{didi}中的age;这样就能准确的区分出到底获取哪个age。
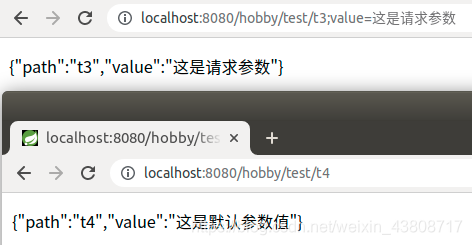
4.3、测试三
<a href="/hobby/test/t3;value=这是请求参数">@MatrixVariable测试案例(4)</a>
<br/><br/>
<a href="/hobby/test/t4">@MatrixVariable测试案例(5)</a>
<br/><br/>
@RequestMapping("/hobby/test/{path}")
@ResponseBody
public Map MatrixVariableTest3(@MatrixVariable(value = "value", required = false, defaultValue = "这是默认参数值") String value,
@PathVariable("path") String path){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value", value);
map.put("path", path);
return map;
}
当