SpringMVC入门第四部分
- 自定义类型对象和请求参数的数据绑定流程
- 自定义类型转换器
- annotation-driven介绍
- mvc:annotation-driven和mvc:default对动态和静态资源的影响
- 数据格式化之日期格式化
- 数据校验:只做前端校验是不安全的,在重要的数据一定要加上后端校验
- 普通表单将请求信息放在请求域中去页面获取
- 自定义国际化错误消息的显示,Hibernate Validator已经实现了默认的国际化错误消息显示格式
- 步骤1:编写国际化文件,起名要规范,放在conf资源文件夹下面
- 步骤2:编写国际化配置资源文件
- 步骤3:让SpringMVC管理国际化资源文件
- 可以通过注解上的message属性来指定错误消息,如果配置了国际化,先走国际化中配置的
- SpringMVC支持ajax
- 导入jquery的依赖
- 导入JackSon的依赖
- @JsonIgnore 输出数据的时候,不将当前数据发送给前端
- @JsonFormat与@DateTimeFormat注解的配合使用
- jQuery的each()函数补充知识点
- @ResponseBody注解将服务器端将对象以json对象形式返回,前端收到数据,显示在页面上
- @ReuqestBody获取请求体----只有Post请求才有请求体
- 将请求体中的数据直接封装为自定义类型对象---@RequestBody
- 在参数位置写HttpEntity< String>,比@RequestBody更强,可以拿到请所有请求头和请求体数据
- @ResponseBody加在方法上---》本质是将返回的数据直接塞在请求体重
- 设置方法返回类型为: ResponseEntity< T >:泛型是响应体数据的类型,可以自定义响应
- SpringMVC中提供的文件下载---较为鸡肋--->ResponseEntity方式
- SpringMVC的文件上传
- 拦截器
- 国际化
- 异常处理
- @ExceptionHandler()注解使用演示
- 里面参数可以填数组,每一个参数代表当前处理异常的方法能够处理的异常类型,返回值可以跳转到定制的错误页面
- 注意事项:
- 如果有多个@ExceptionHandler都能处理一个异常,那么精确优先
- @ControllerAdvice注解----》表明当前类是集中处理异常的类,可以全局处理异常
- 全局异常处理与本类异常处理同时存在,那么本类异常处理优先,不论精确与否
- @ResponseStatus标注在自定义异常上,返回一个服务器错误页面,省去做错误页面
- @ResponseStatus注解工作的前提是,上面没有@ExceptionHandler标注的异常处理方法能处理该异常,否则走@ExceptionHandler标注的异常处理方法
- Spring默认的异常如果没人处理,就使用默认的处理方法来进行处理---->DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
- 基于SpringMVC.xml配置的异常处理方式-----在处理异常的顺序上,优先级最低
- SpringMVC运行流程总结
- SpringMVC和Spring整合
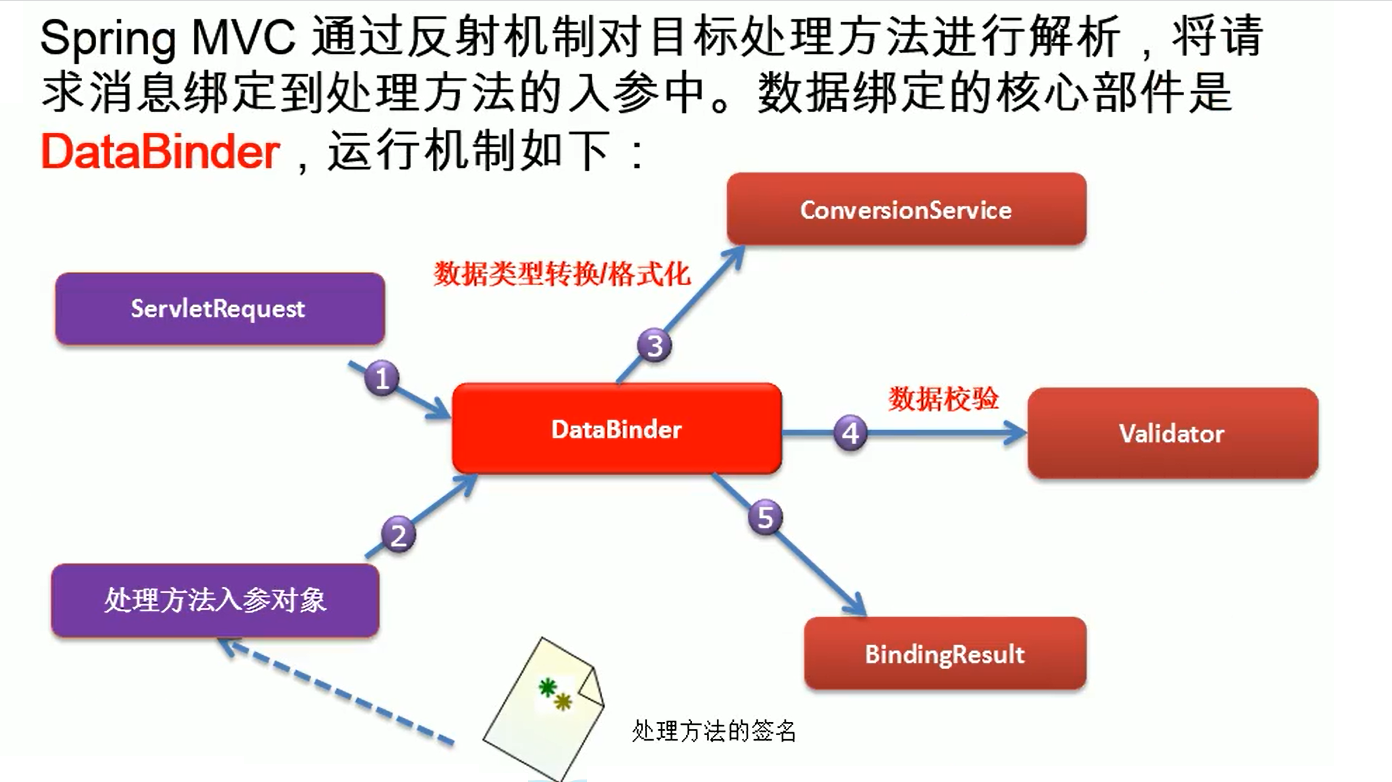
自定义类型对象和请求参数的数据绑定流程

自定义类型转换器
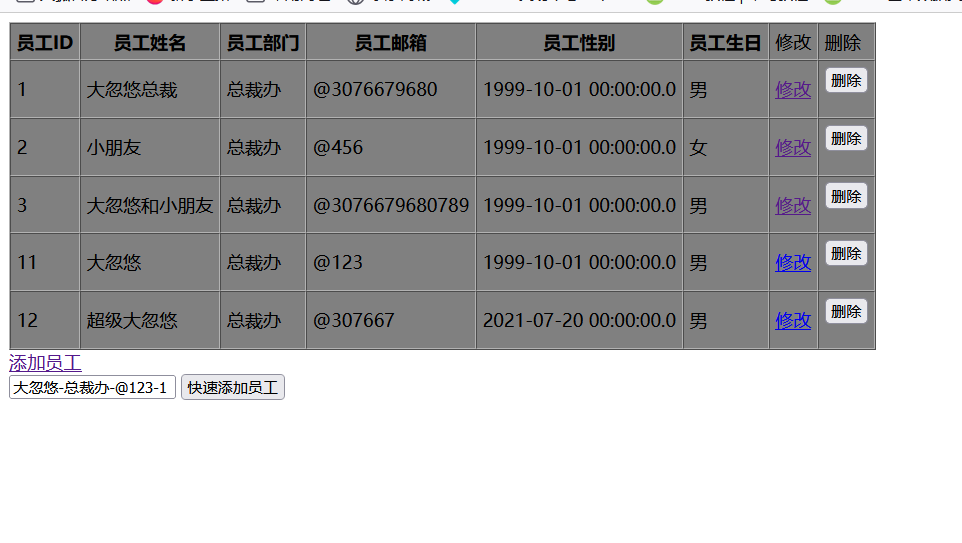
自定义类型转换器,实现String----->employee对象的转换和封装
<form action="${ctp}/quickAdd">
<%--将员工所有信息都写上,自动封装对象--%>
<input type="text" name="empInfo" value="大忽悠-总裁办-@123-1"/>
<input type="submit" value="快速添加员工"/>
</form>
快速添加员工的方法:
@RequestMapping("quickAdd")
//获取请求参数empInfo
//employee=request.getParame("empInfo")---->大忽悠-总裁办-@123-1
public String quickAdd(@RequestParam("empInfo") Employee employee)
{
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
ConversionService是一个接口,里面通过一个Converter转换器进行工作

步骤1:实现Converter接口,写一个自定义类型转换器
/*
* 两个泛型S,T
* S:source
* T:target
* 把s转换为t
* */
//自定义类型转换器
public class MyConverter implements Converter<String, Employee> {
//自定义转换规则
public Employee convert(String source) {
System.out.println("要转换的字符串:"+source);
Employee employee=new Employee();
if(source.contains("-"))
{
//大忽悠-总裁办-@123-1
String[] ret=source.split("-");
employee.setName(ret[0]);
employee.setDepartment(ret[1]);
employee.setEamil(ret[2]);
employee.setGender(Integer.parseInt(ret[3]));
}
return employee;
}
}
步骤2:Converter是ConversionService中的一个组件,我们需要把Converter放入到ConversionService中
步骤3:将WebDataBinder中的ConversionService设置成我们这个加了自定义类型ConversionService
步骤4:让SpringMVC使用我们的ConversionService
配置文件中实现步骤1:配置出ConversionService
converters在源码中是一个set集合
<!--告诉SpringMVC别用默认的ConversionService,
而是使用自定义的ConversionService
,里面有我们自定义的converter-->
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<!--在converters转换器中添加我们自定义的类型转换器-->
<property name="converters">
<set>
<bean class="com.Converter.MyConverter"/>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
<!--使用我们自己的配置的类型转换组件-->
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven>
总结三步

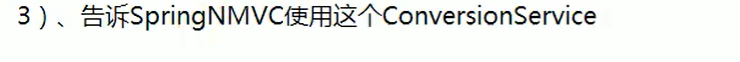
annotation-driven介绍

mvc:annotation-driven和mvc:default对动态和静态资源的影响
当mvc:annotation-driven和mvc:default-servlet-handler都没配置时,只有动态资源能够访问,静态资源访问不了

常见动态资源: @RequestMapping映射的资源,.jsp
常见的静态资源: .html , .js , .img
只加mvc:default-servlet-handler,那么静态资源能访问,动态资源不能访问


只配置mvc:annotation-driven,那么只能访问动态资源,不能访问静态资源
mvc:default-servlet-handler和mvc:annotation-driven都配置后,那么静态资源和动态资源都可以访问了
数据格式化之日期格式化
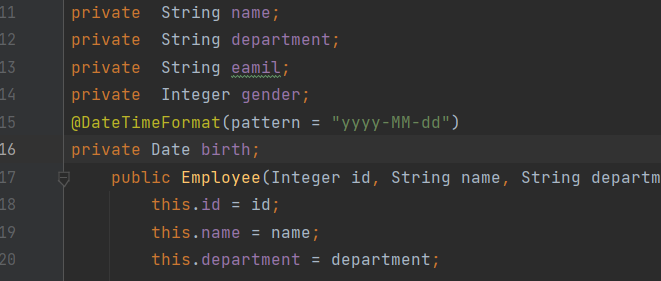
ConversionServiceFactoryBean创建的ConversionService组件是没有格式化器存在的
解决方法1:不使用自定义类型的转换器
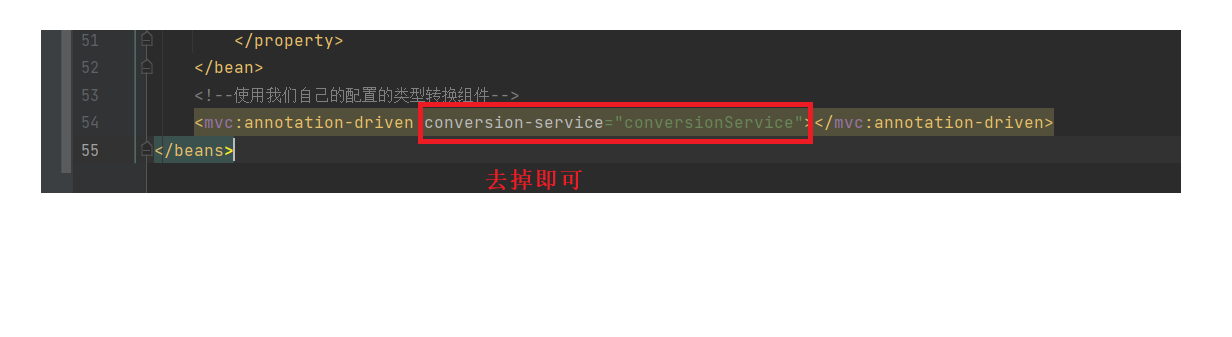
解决方法2:将自定义类型转换器注册到FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean,这样就有格式化功能了
以后写自定义数据类型转换器的时候,就使用FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean来注册自定义类型转换器,这样就既具有类型转换,又具有格式化功能
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<!--在converters转换器中添加我们自定义的类型转换器-->
<property name="converters">
<set>
<bean class="com.Converter.MyConverter"/>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
<!--使用我们自己的配置的类型转换组件-->
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven>
后端规定提交的日期格式,不对就报错
//规定提交的日期格式
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date birth;
后端规定提交的数字格式
@NumberFormat(pattern = "#,###,###.##")//类似这样的数字格式: 1,000,000.98
private double salary;
数据校验:只做前端校验是不安全的,在重要的数据一定要加上后端校验
SpingMVC可以使用JSR303来做数据校验

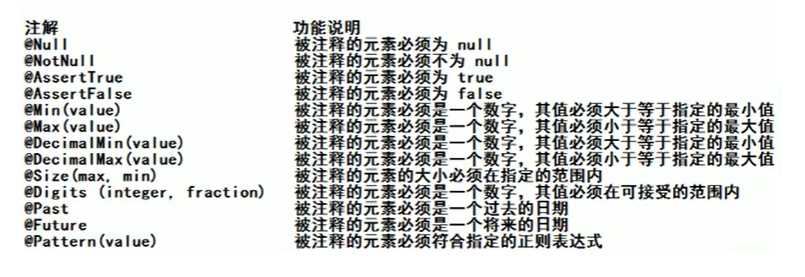
Hibernate Validator是第三方框架实现了JSR303规范

实现步骤:
1.maven管理引入springmvc注解数据校验所需jar包:
<!-- maven管理引入springmvc注解数据校验所需jar包:-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>validation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
2.只需要给javaBean的属性上加上校验注解
@NotEmpty
@Length(min=6,max=8)//至少6个字符,最多8个字符
private String name;
private String department;
@Email
private String eamil;
3.在SpringMVC封装对象的时候,告诉SpringMVC这个javaBean对象需要校验----@Valid注解
//只接收Post请求
@RequestMapping(value = "/emp",method = RequestMethod.POST)
//@Valid注解,告诉SpringMVC,封装这个javabean对象时,按照这个对象里面变量规定的校验规则进行校验
public String addEmp(@Valid Employee employee)//这里会自动赋值
{
System.out.println("要添加的员工信息:"+employee);
employeeDao.save(employee);
//返回列表页面,直接重定向到查询所有员工的请求
return "redirect:/emps";
}
4.如何知道校验结果,给需要校验的javaBean后面紧跟一个BindingResult,这个BindingResult就是封装前一个bean的校验结果
//只接收Post请求
@RequestMapping(value = "/emp",method = RequestMethod.POST)
//@Valid注解,告诉SpringMVC,封装这个javabean对象时,按照这个对象里面变量规定的校验规则进行校验
public String addEmp(@Valid Employee employee,BindingResult res)//这里会自动赋值
{
System.out.println("要添加的员工信息:"+employee);
employeeDao.save(employee);
//返回列表页面,直接重定向到查询所有员工的请求
return "redirect:/emps";
}
5.根据不同的校验结果决定怎么做
//只接收Post请求
@RequestMapping(value = "/emp",method = RequestMethod.POST)
//@Valid注解,告诉SpringMVC,封装这个javabean对象时,按照这个对象里面变量规定的校验规则进行校验
public String addEmp(@Valid Employee employee,BindingResult res)//这里会自动赋值
{
System.out.println("要添加的员工信息:"+employee);
//获取是否有校验错误
boolean hasErrors = res.hasErrors();
if(hasErrors)
{
System.out.println("有校验错误");
return "addPage";
}
else
{
employeeDao.save(employee);
//返回列表页面,直接重定向到查询所有员工的请求
return "redirect:/emps";
}
}
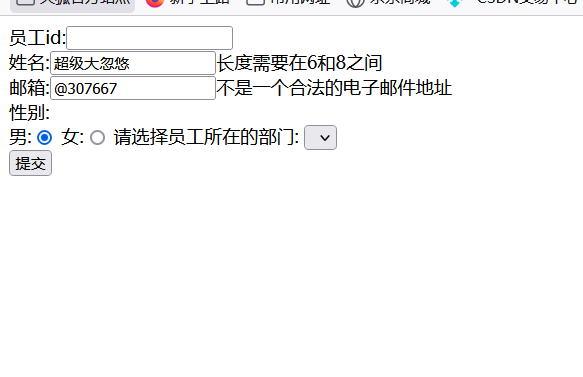
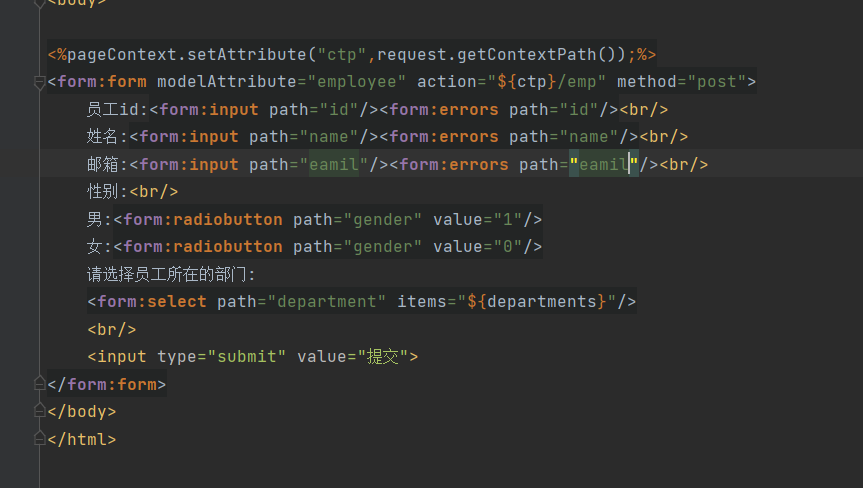
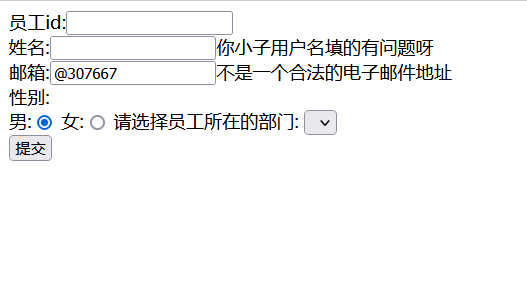
6.将错误信息回显在页面上
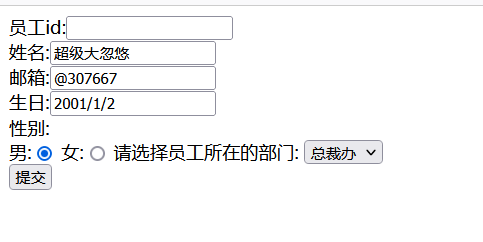
<%pageContext.setAttribute("ctp",request.getContextPath());%>
<form:form modelAttribute="employee" action="${ctp}/emp" method="post">
<%--显示错误信息,有默认的错误信息,也可也自己写显示的错误西信息--%>
员工id:<form:input path="id"/><form:errors path="id"></form:errors><br/>
姓名:<form:input path="name"/><form:errors path="name"></form:errors><br/>
邮箱:<form:input path="eamil"/><form:errors path="eamil"></form:errors><br/>
性别:<br/>
男:<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="1"/>
女:<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="0"/>
请选择员工所在的部门:
<form:select path="department" items="${departments}"/>
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form:form>
普通表单将请求信息放在请求域中去页面获取
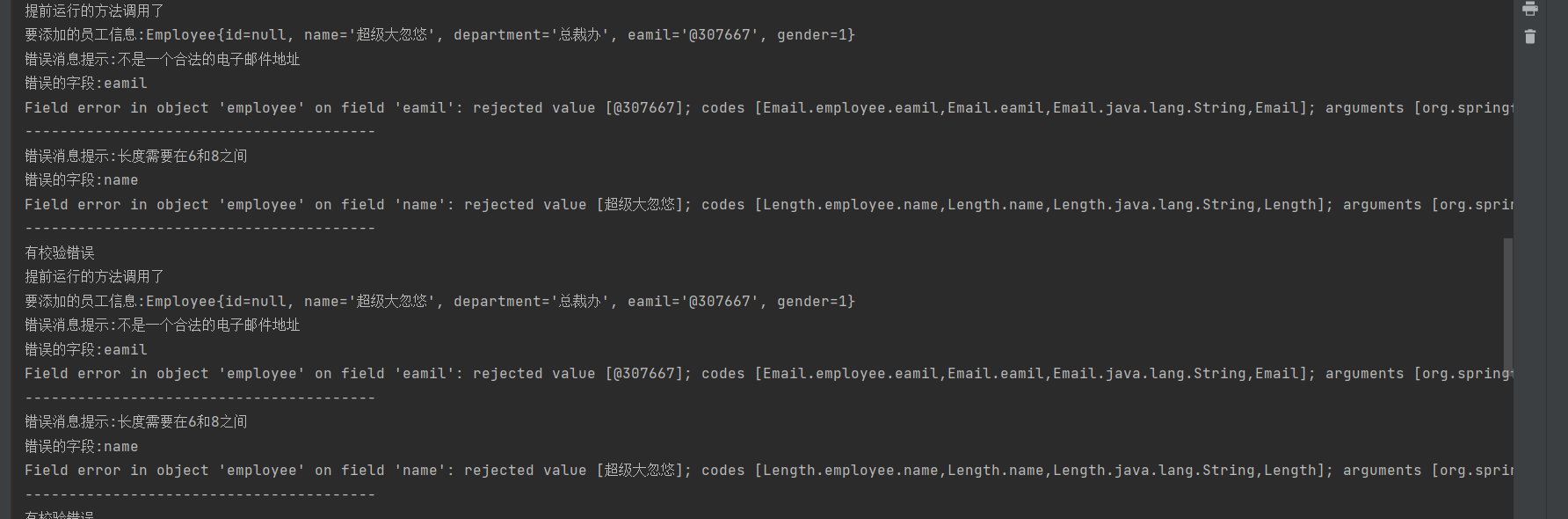
通过BindingResult的res对象的 getFieldErrors方法,可以获得当前属性值出现的全部错误,然后通过一个Model对象存储错误信息,放到隐含模型中
//只接收Post请求
@RequestMapping(value = "/emp",method = RequestMethod.POST)
//@Valid注解,告诉SpringMVC,封装这个javabean对象时,按照这个对象里面变量规定的校验规则进行校验
public String addEmp(@Valid Employee employee,BindingResult res,Model model)//这里会自动赋值
{
System.out.println("要添加的员工信息:"+employee);
//获取是否有校验错误
boolean hasErrors = res.hasErrors();
Map<String,String> errorMap=new HashMap<String, String>();
if(hasErrors)
{
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = res.getFieldErrors();
for(FieldError fieldError:fieldErrors)
{
System.out.println("错误消息提示:"+fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
System.out.println("错误的字段:"+fieldError.getField());
System.out.println(fieldError);
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
errorMap.put(fieldError.getField(),fieldError.getDefaultMessage());
}
model.addAttribute("errorInfo",errorMap);
System.out.println("有校验错误");
return "addPage";
}
else
{
employeeDao.save(employee);
//返回列表页面,直接重定向到查询所有员工的请求
return "redirect:/emps";
}
}
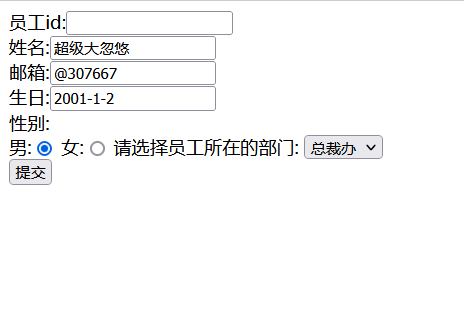
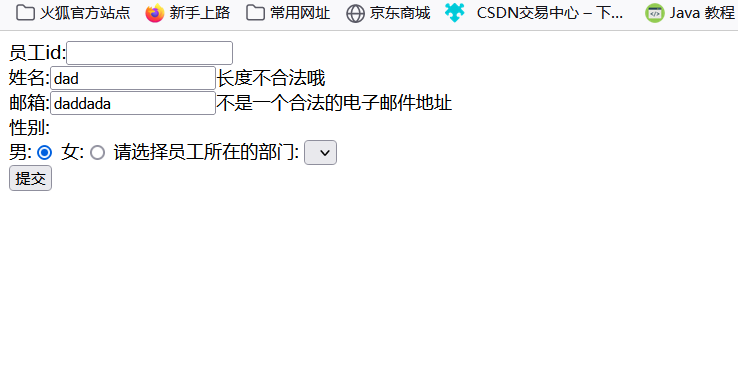
jsp页面通过${},从请求域中拿出之前存放的错误信息,显示在页面上
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>员工添加页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<%pageContext.setAttribute("ctp",request.getContextPath());%>
<form:form modelAttribute="employee" action="${ctp}/emp" method="post">
员工id:<form:input path="id"/>${errorInfo.id}<br/><%--取不出来就为空--%>
姓名:<form:input path="name"/>${errorInfo.name}<br/>
邮箱:<form:input path="eamil"/>${errorInfo.eamil}<br/>
性别:<br/>
男:<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="1"/>
女:<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="0"/>
请选择员工所在的部门:
<form:select path="department" items="${departments}"/>
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
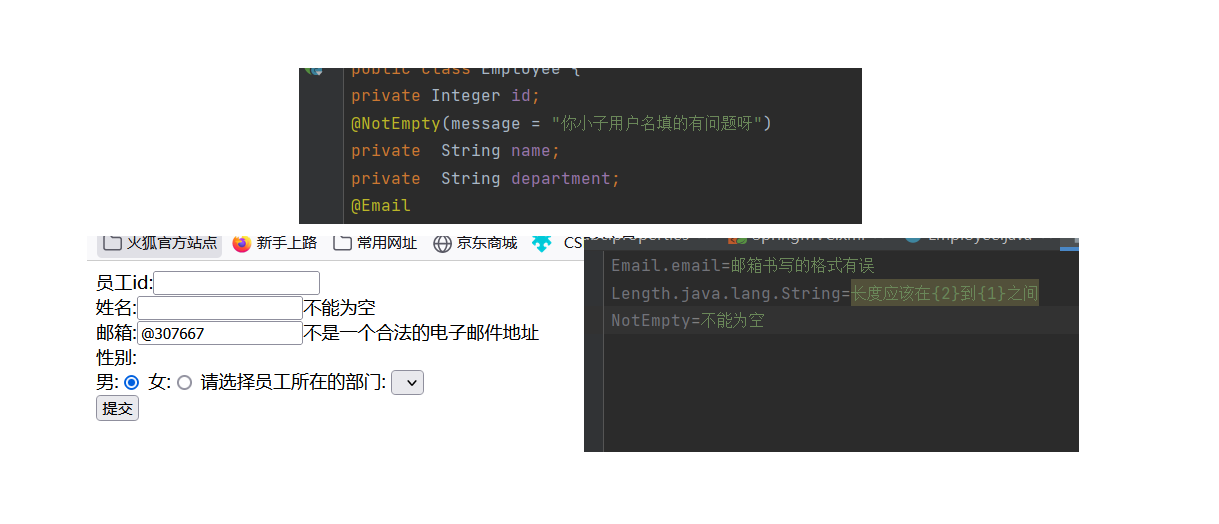
自定义国际化错误消息的显示,Hibernate Validator已经实现了默认的国际化错误消息显示格式
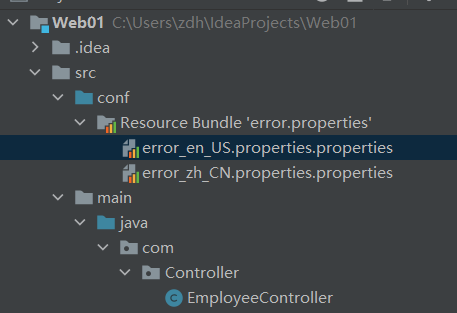
步骤1:编写国际化文件,起名要规范,放在conf资源文件夹下面
注意:国际化文件里面写的key有规定,每一个字段发生错误以后,都会有一个自己的错误代码,国际化资源文件中的错误消息的key必须对应一个错误代码
什么是错误代码:
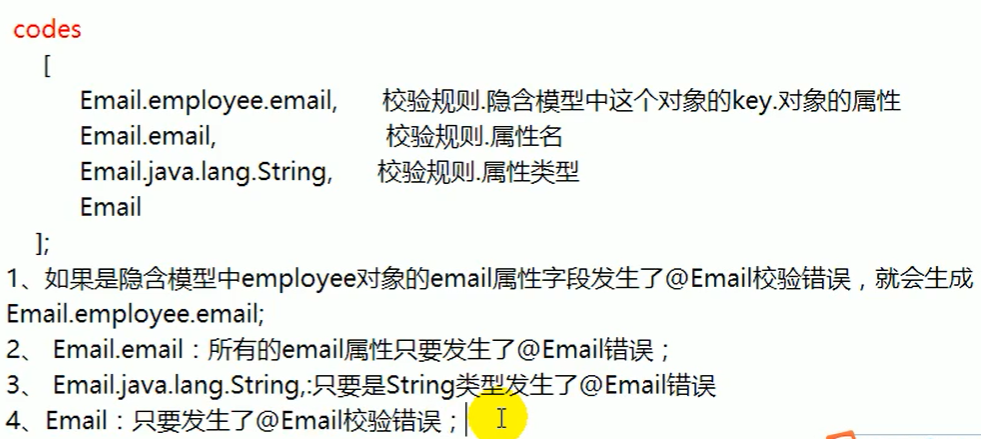
步骤2:编写国际化配置资源文件
error_en_US.properties.properties:
Email.email=email error--->
NotEmpty=not empty--->
Length.java.lang.String=type is not I want--->
error_zh_CN.properties.properties:
Email.email=邮箱书写的格式有误
NotEmpty=不能为空哦
Length.java.lang.String=长度不合法哦
步骤3:让SpringMVC管理国际化资源文件
<!--让SpringMVC管理国际化资源文件-->
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<!--basename:指定国际化资源文件的基础名-->
<property name="basename" value="error"></property>
<!-- 支持UTF-8的中文 -->
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
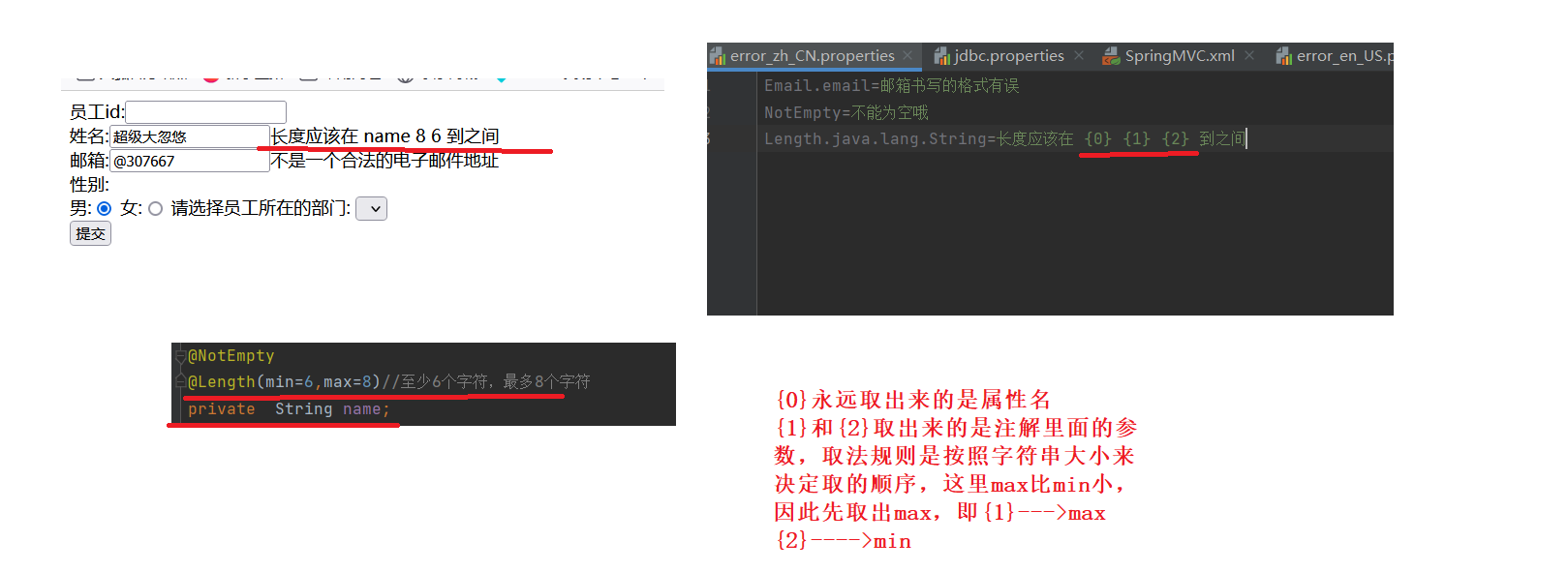
精确优先:同时写了Eamil.eamil和Eamil的错误显示信息,那么先走前者,因为前者更加精确
国际化资源文件支持从JSR-303注解中获取属性的参数值的,例如从@Length注解中,获取min和max属性的值
可以通过注解上的message属性来指定错误消息,如果配置了国际化,先走国际化中配置的
@NotEmpty(message = "你小子用户名填的有问题呀")
private String name;
SpringMVC支持ajax
导入jquery的依赖
<!--引入jquery的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1-2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
导入JackSon的依赖
<!--jackSon的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.10.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.10.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.10.0</version>
</dependency>
@JsonIgnore 输出数据的时候,不将当前数据发送给前端
@JsonIgnore//输出数据的时候,忽略id字段
private Integer id;
@JsonFormat与@DateTimeFormat注解的配合使用
@JsonFormat与@DateTimeFormat注解的使用
jQuery的each()函数补充知识点
@ResponseBody注解将服务器端将对象以json对象形式返回,前端收到数据,显示在页面上
ajaxController:
@Controller
public class ajaxController {
@Autowired
EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@ResponseBody//将返回的数据放在响应体中,如果返回的是对象,jackson自动将对象转换为json格式
@RequestMapping("/getAllAjax")
public List<Employee> getAjaxAll()
{
List<Employee> allEmployees = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
return allEmployees;
}
}
index.jsp:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<html>
<head>
<title>JQuery显示页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="${ctx}/webjars/jquery/3.3.1-2/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$("#b1").click(function (){
//1.发送ajax请求,获取所有员工
$.ajax(
{
url:"${ctx}/getAllAjax",
type:"get",
success:function (data)
{
$.each(data,function (){
var empInfo=data.name+" "+data.department;
$("div").append(empInfo);
})
}
}
)
})
</script>
<button id="b1">ajax请求发送</button>
<div>大忽悠</div>
</body>
</html>
@ReuqestBody获取请求体----只有Post请求才有请求体
ajaxController:
@Controller
public class ajaxController {
@Autowired
EmployeeDao employeeDao;
//放在视图解析器进行拼串
@ResponseBody//将返回的数据放在响应体中,如果返回的是对象,jackson自动将对象转换为json格式
@RequestMapping("/getAllAjax")
public List<Employee> getAjaxAll()
{
System.out.println("ajax方法调用");
List<Employee> allEmployees = employeeDao.getAllEmployees();
return allEmployees;
}
//获取一个请求的请求体
@RequestMapping("/Body")
public String testRequestBody(@RequestBody String Body)
{
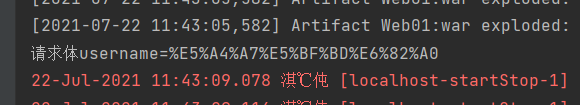
System.out.println("请求体"+Body);
return "success";
}
}
index.jsp:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<html>
<head>
<title>无标题</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="${ctx}/Body" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input name="username" value="大忽悠"/>
<input type="file" name="file"><%--文件上传--%>
<button>提交</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
将请求体中的数据直接封装为自定义类型对象—@RequestBody
@RequestBody接收json数据,封装为对象(高级用法)
@ResponseBody把对象转换为json数据,返回给浏览器(高级用法)
@RequestBody可以直接将得到的json字符串直接封装为自定义类型对象,前提是自定义对象的属性名和请求参数名一一对应,并且有get和set方法,还有无参构造器
//获取一个请求的请求体,直接封装为people对象
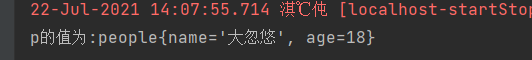
@RequestMapping("/peo")
public String getPeople(@RequestBody people p)
{
System.out.println("p的值为:"+p);
return "success";
}
index.ja
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<head>
<title>JQuery显示页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="${ctx}/webjars/jquery/3.3.1-2/jquery.js"></script>
<script>
$(function ()
{
$("#b1").click(function (){
console.log("=====");
var emp={"name":"大忽悠","age":"18"};
//打印emp的类型----》是一个json对象
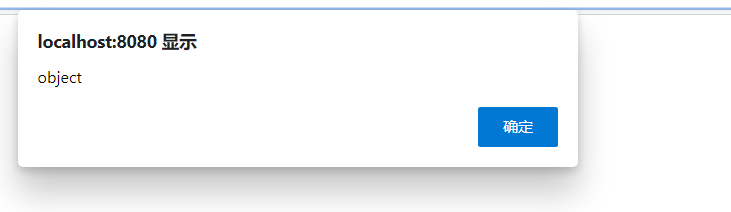
alert(typeof emp);
//将这个json对象,转换为一个json形式的字符串
var stringEmp=JSON.stringify(emp);
//打印stringEmp的类型----->字符串
alert(typeof stringEmp);
//1.发送ajax请求,获取所有员工
$.ajax(
{
url:"${ctx}/peo",
type:"post",
data:stringEmp,
//指定要提交的数据格式为json----告诉浏览器
contentType:"application/json",
success:function (data)
{
alert(data);
}
}
)
return false;
})
})
</script>
<a id="b1" href="${ctx}/peo">点击,ajax请求发送</a>
</body>
</html>
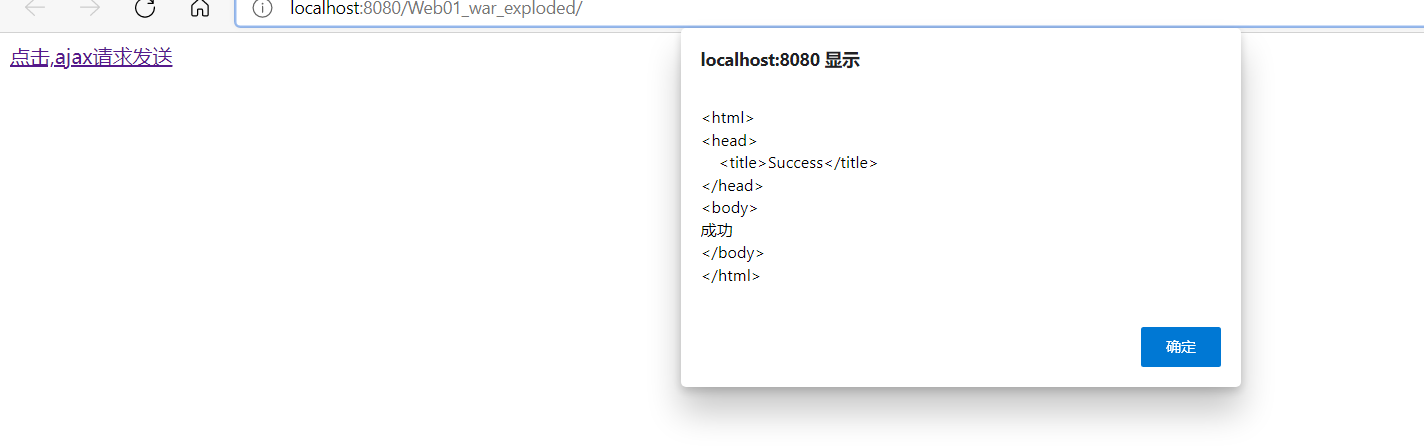
在参数位置写HttpEntity< String>,比@RequestBody更强,可以拿到请所有请求头和请求体数据
@RequestMapping("/peo")
public String getPeople(HttpEntity<String> ret)
{
System.out.println(ret);
return "success";
}


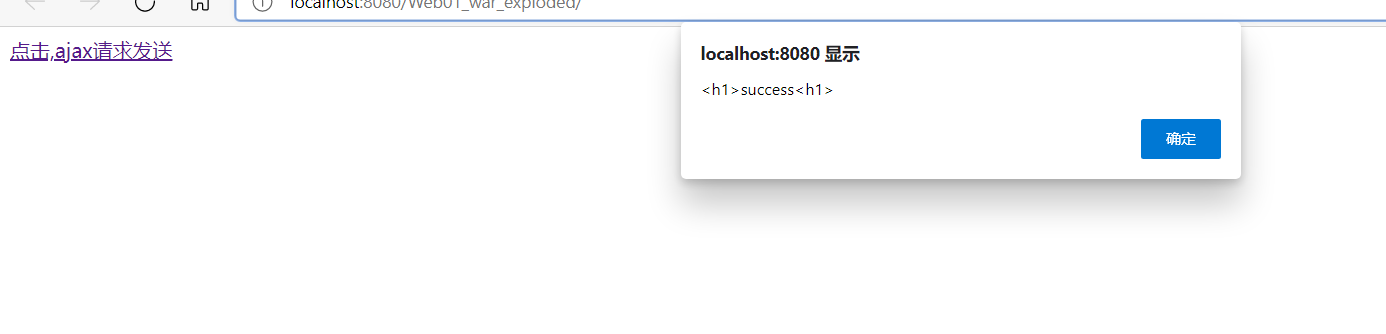
@ResponseBody加在方法上—》本质是将返回的数据直接塞在请求体重
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/peo")
public String getPeople(HttpEntity<String> ret)
{
return "<h1>success<h1>";
}
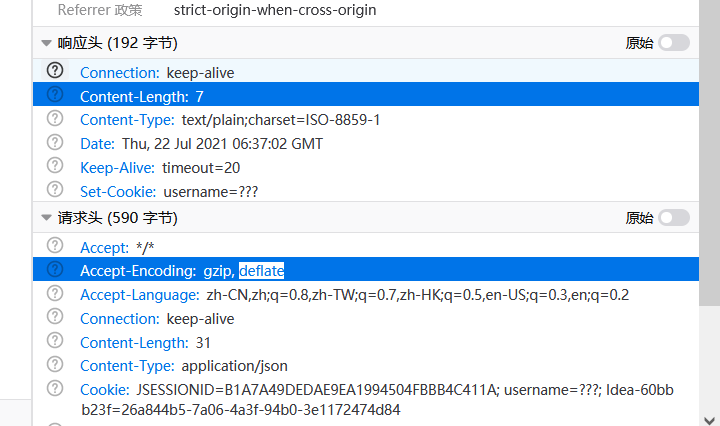
设置方法返回类型为: ResponseEntity< T >:泛型是响应体数据的类型,可以自定义响应
@RequestMapping("/peo")
public ResponseEntity<String> getPeople(HttpEntity<String> ret)
{
//三个参数: 响应体,响应头,状态码
String body="Success";
MultiValueMap<String, String> headers=new HttpHeaders();
//让浏览器保存一个cookie
headers.add("Set-Cookie","username=大忽悠");
return new ResponseEntity<String>(body,headers,HttpStatus.OK);
}
SpringMVC中提供的文件下载—较为鸡肋—>ResponseEntity方式
@RequestMapping("/peo")
public ResponseEntity<Byte[]> download(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//1.得到要下载的文件的流
//找到要下载的文件的真实路径
ServletContext context=request.getSession().getServletContext();
String realPath=context.getRealPath("C:\\Users\\zdh\\IdeaProjects\\Web01\\src\\main\\webapp\\index.jsp");
FileInputStream is=new FileInputStream(realPath);
byte[] temp=new byte[is.available()];
is.read(temp);
is.close();
//将要下载的文件流返回
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = new HttpHeaders();
httpHeaders.set("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename="+"index.jsp");
return new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(temp,httpHeaders,HttpStatus.OK);
}
总结: ResponseEntity响应数据的同时,可以自定义响应头 ,HttpEntity< String>获取响应体数据的同时,获取响应头
对于这些怪异的返回值,视图解析器就不会进行拼串了,具体工作机制,看源码
SpringMVC的文件上传
导入依赖
<!--文件上传的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
文件上传表单准备
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<head>
<title>JQuery显示页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript" src="${ctx}/webjars/jquery/3.3.1-2/jquery.js"></script>
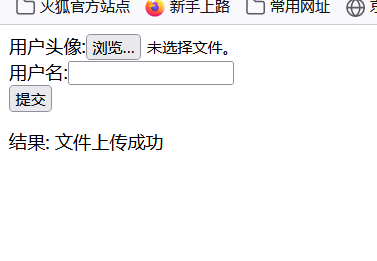
<form action="${ctx}/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
用户头像:<input type="file" name="head"/><br/>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
结果: ${msg}
</body>
</html>
SpringMVC中配置文件上传解析器
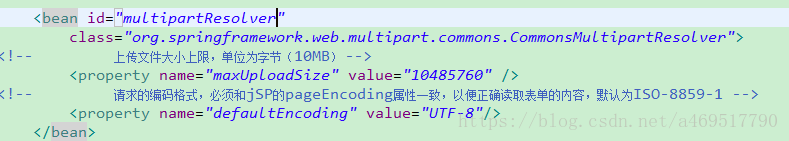
<!--文件上传解析器: id必须是multipartFile-->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!--设置文件上传最大量为5m-->
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="5242880"></property><!--spel运算符,计算最大可上传文件体积-->
<!--设置默认的编码-->
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="utf-8"></property>
</bean>
文件上传请求处理
在处理器方法上写一个 @RequestParam(“head”) MultipartFile file,封装当前文件信息,可以直接保存
@Controller
public class uploadController {
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public String upload(
@RequestParam(value = "username",required = false) String username,
@RequestParam("head") MultipartFile file
,Model model)
{
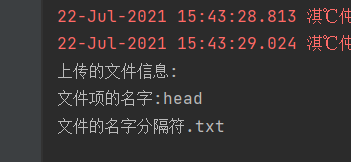
System.out.println("上传的文件信息:");
System.out.println("文件项的name:"+file.getName());
System.out.println("文件的名字"+file.getOriginalFilename());
//文件保存
try {
file.transferTo(new File("D:\\dhy\\"+file.getOriginalFilename()));
model.addAttribute("msg","文件上传成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
model.addAttribute("msg","文件上传失败");
}
return "forward:/index.jsp";
}
}
多文件上传
@Controller
public class uploadController {
@RequestMapping("/upload")
public String upload(
@RequestParam(value = "username",required = false) String username,
@RequestParam(value = "head") MultipartFile[] file1
,Model model)
{
System.out.println("上传的文件信息:");
for(MultipartFile file:file1)
{
if(!file.isEmpty())
{
try {
file.transferTo(new File("D:\\dhy\\"+file.getOriginalFilename()));
model.addAttribute("msg","文件上传成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
model.addAttribute("msg","文件上传失败");
}
}
}
return "forward:/index.jsp";
}
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<head>
<title>JQuery显示页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="${ctx}/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
用户头像:<input type="file" name="head"/><br/>
用户头像:<input type="file" name="head"/><br/>
用户头像:<input type="file" name="head"/><br/>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
结果: ${msg}
</body>
</html>

拦截器
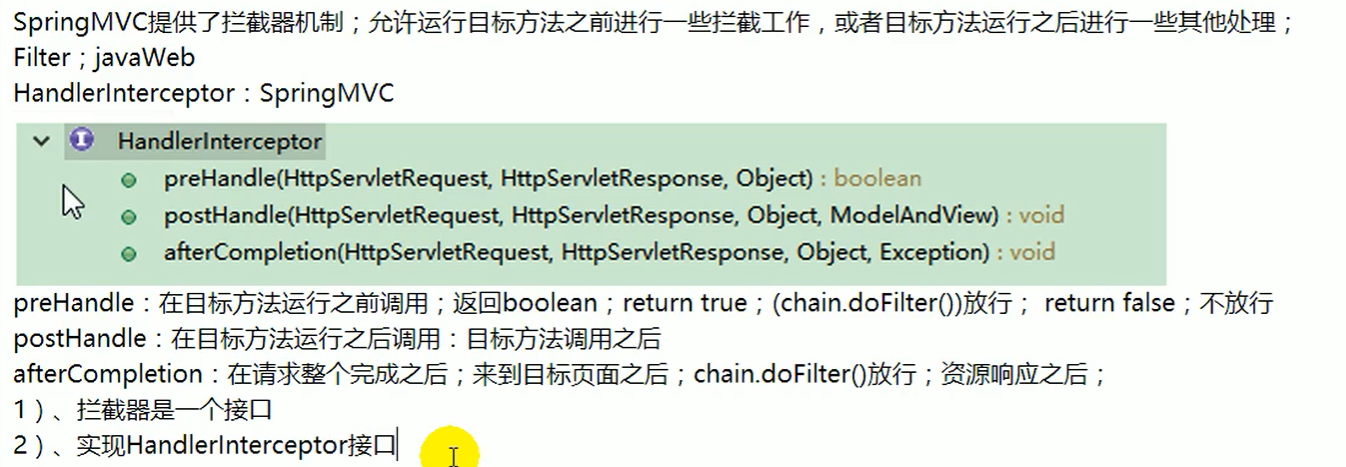
单拦截器运行流程
1.创建拦截器类
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 该方法在目标方法之前被调用.
* 若返回值为 true, 则继续调用后续的拦截器和目标方法.
* 若返回值为 false, 则不会再调用后续的拦截器和目标方法.
*
* 可以考虑做权限. 日志, 事务等.
*/
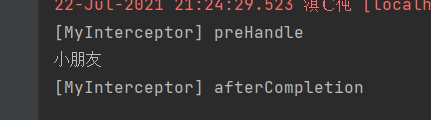
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("[MyInterceptor] preHandle");
return true;
}
/**
* 调用目标方法之后, 但渲染视图之前.
* 可以对请求域中的属性或视图做出修改.
*/
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("[MyInterceptor] postHandle");
}
/**
* 渲染视图之后被调用. 释放资源
*/
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("[MyInterceptor] afterCompletion");
}
}
2.在spingMVC的配置文件中注册这个拦截器的工作,配置这个拦截器来拦截哪些请求的方法
<!--测试拦截器-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--配置某个拦截器,默认是拦截所有请求-->
<bean class="com.Controller.MyInterceptor"/>
<!--具体配置某个拦截器-->
<!-- <mvc:interceptor>
<!–只拦截test01请求–>
<mvc:mapping path="/test01"/>
<bean class="com.Controller.MyInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>-->
</mvc:interceptors>
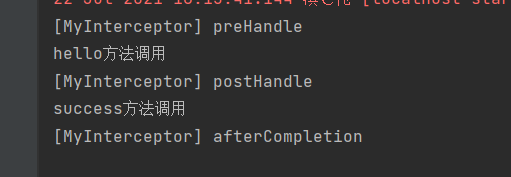
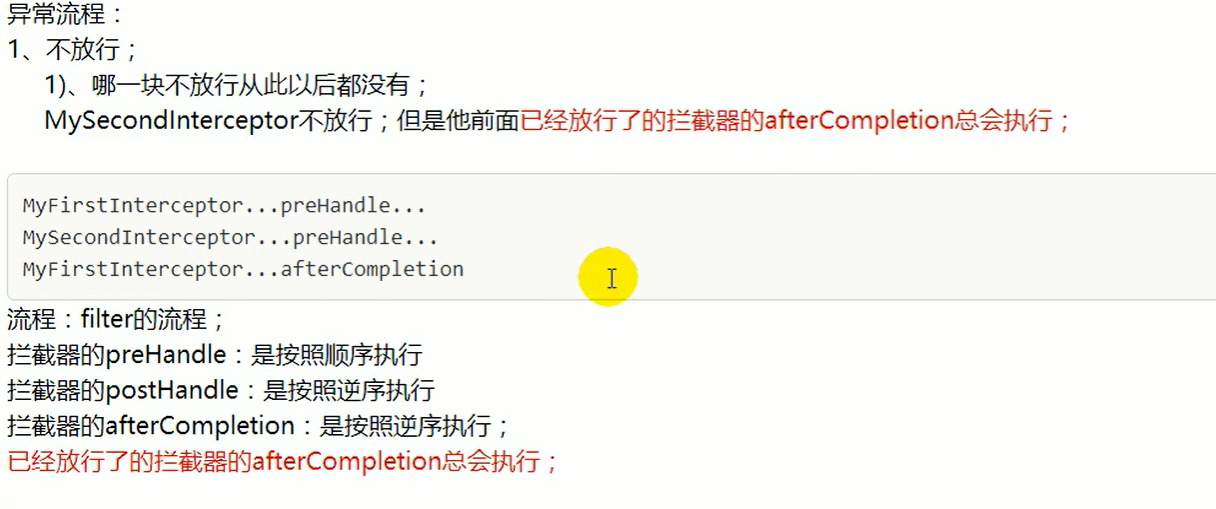
拦截器正常运行流程和其他流程


多个拦截器运行流程
<!--测试拦截器-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--配置某个拦截器,默认是拦截所有请求-->
<bean class="com.Controller.MyInterceptor"/>
<!--具体配置某个拦截器-->
<mvc:interceptor>
<!--只拦截hello请求-->
<mvc:mapping path="/hello"/>
<bean class="com.Controller.MyInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
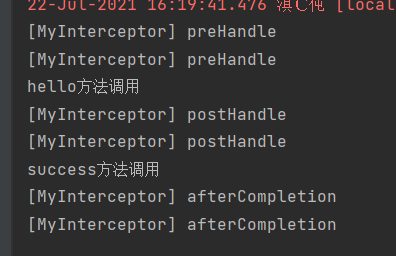
多拦截器异常运行流程
已经放行了的拦截器的afterCompletion总会执行
目标方法出现异常,postHandle不会执行
国际化
1.创建国际化资源文件夹
error_en_US.properties:
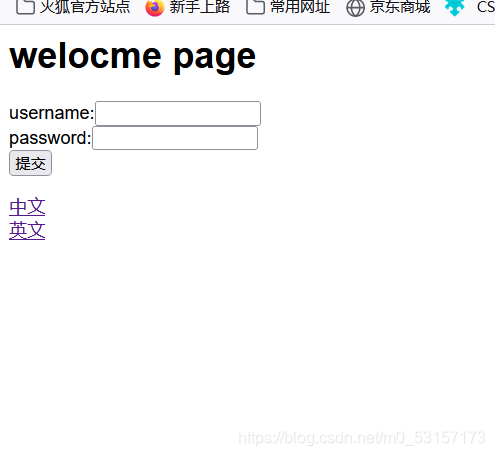
welcome=welocme page
username=username
password=password
error_zh_CN.properties:
welcome=登录界面
username=用户名
password=密码
2.配置
<!--让SpringMVC管理国际化资源文件,id不能改-->
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<!--basename:指定国际化资源文件的基础名-->
<property name="basename" value="error"></property>
<!-- 支持UTF-8的中文 -->
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
3.在页面进行内容替换
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
<head>
<h1>
<fmt:message key="welcome"/>
</h1>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<fmt:message key="username"/>:<input/><br/>
<fmt:message key="password"/>:<input/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
国际化必看注意事项

注意不能直接进入国际化的页面中,因为直接进入某个jsp页面的时候,就相当直接向Tomcat请求页面,没有经过Spring,然而Spring管理的国际化也就不会生效
SpringMVC国际化实现完整流程,详细介绍
springmvc区域信息是由区域信息解析器得到的

通过MessageSource对象,来获取国际化资源文件中对应key对应的值,也可以获取国际化资源文件中的错误信息
@Controller
public class hello {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hai(Locale locale)
{
System.out.println(locale);//打印当前区域信息
String username = messageSource.getMessage("username", null, locale);//第二个参数是占位符数组
System.out.println("用户名:"+username);
return "guojihua";
}
}
打印结果为:
zh_CN
用户名: 用户名
自定义区域信息解析器----实现点击不同超链接,切换当前页面的语言
MyLocalResolve:
/*自定义区域解析器*/
public class MyLocalResolve implements LocaleResolver {
//解析返回locale
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request)
{
String localeStr=request.getParameter("locale");
Locale l=null;
//如果带了locale参数就用参数指定的区域信息,否则就用请求头的
if(localeStr!=null&&!"".equals(localeStr))
{
l=new Locale(localeStr.split("_")[0],localeStr.split("_")[1]);
}
else{
l=request.getLocale();
}
return l;
}
//修改locale
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale)
{
}
}
国际化展示页面:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
<head>
<h1>
<fmt:message key="welcome"/>
</h1>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<fmt:message key="username"/>:<input/><br/>
<fmt:message key="password"/>:<input/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
<a href="hello?locale=zh_CN">中文</a><br/>
<a href="hello?locale=en_US">英文</a><br/>
</body>
</html>
hello页面跳转类:
@Controller
public class hello {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hai(Locale locale)
{
System.out.println(locale);//打印当前区域信息
String username = messageSource.getMessage("username", null, locale);//第二个参数是占位符数组
System.out.println("用户名:"+username);
return "guojihua";
}
}
将自定义区域解析器放到容器中,让springMVC使用
<!--配置自定义区域信息解析器 id固定-->
<bean id="localeResolver" class="com.Controller.MyLocalResolve"></bean>
演示效果
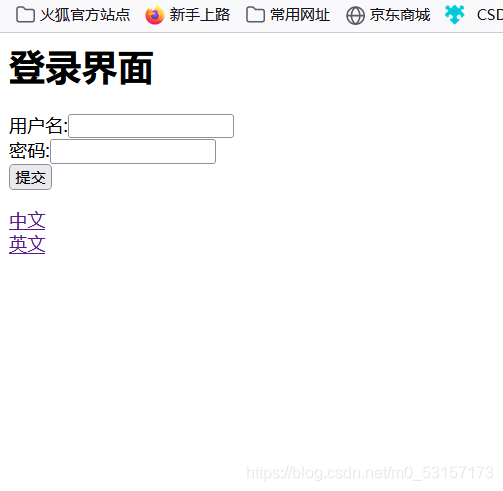
完整流程看下面这篇文章
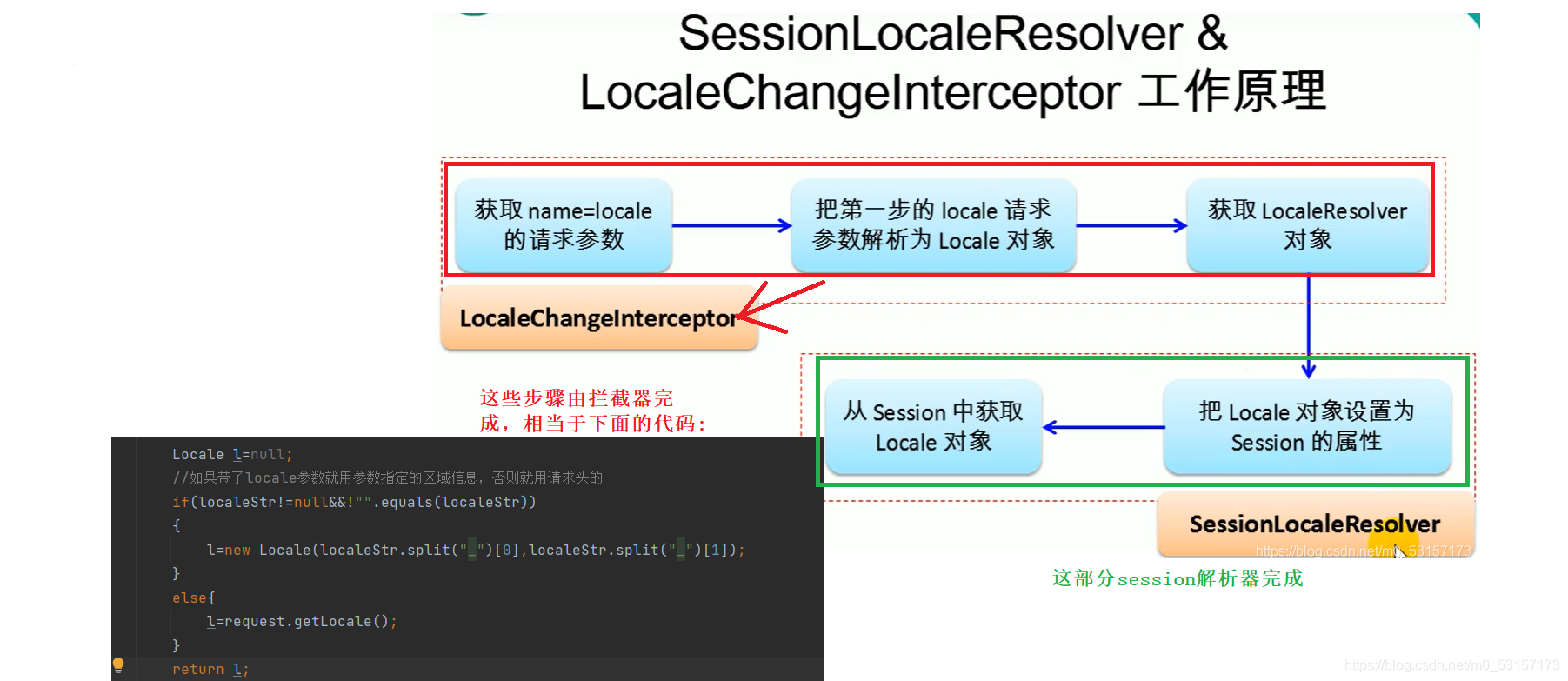
SessionLocaleResolver实现点击链接切换国际化----信息从session中获取
SessionLocaleResolver保存客户的Locale到HttpSession对象中,并且支持获取和修改
1.在配置文件中配置使用SessionLocaleResolver
<!--区域信息从session中获取-->
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver"/>
2.在跳转资源hello中获取区域信息,并防止再session域中,让SessionLocaleResolver进行国际化操作实现
@Controller
public class hello {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
@RequestMapping("/hello") //如果有请求参数locale,那么就使用,否则默认为中文
public String hai(@RequestParam(value = "locale",defaultValue = "zh_CN") String localeStr,
Locale locale,//这里locale是获取当前请求头里面的区域信息
HttpSession httpSession)
{
Locale l=null;
//如果带了locale参数就用参数指定的区域信息,否则就用请求头的
if(localeStr!=null&&!"".equals(localeStr))
{
l=new Locale(localeStr.split("_")[0],localeStr.split("_")[1]);
}
else{
l=locale;
}
httpSession.setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.class.getName()+".LOCALE",l);
return "guojihua";
}
}
guojihua.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
<head>
<h1>
<fmt:message key="welcome"/>
</h1>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<fmt:message key="username"/>:<input/><br/>
<fmt:message key="password"/>:<input/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
<a href="hello?locale=zh_CN">中文</a><br/>
<a href="hello?locale=en_US">英文</a><br/>
</body>
</html>
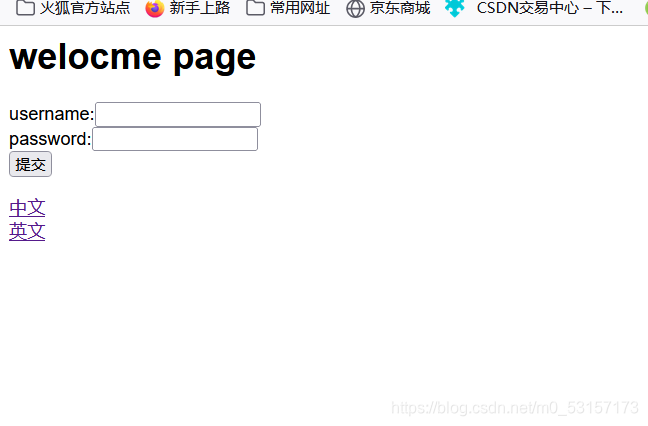
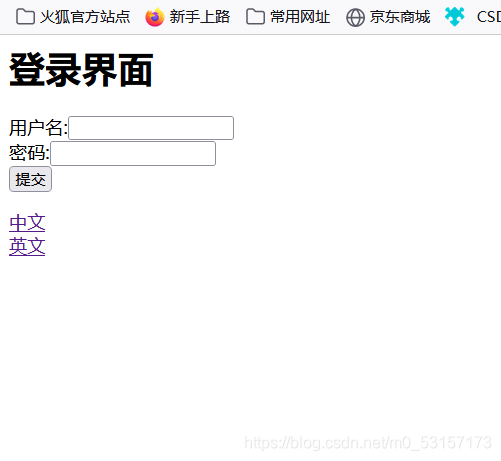
Session的区域信息解析器SessionLocaleResolver配合LocaleChangeInterceptor拦截器使用
1.配置文件中配置解析器和拦截器
<!--区域信息从session中获取-->
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver"/>
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--配置拦截器-->
<bean id="localeChangeInterceptor" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptors>
配置了解析器和拦截器后,其他操作都可以省略
跳转类:
@Controller
public class hello {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hai()
{
return "guojihua";
}
}
guojihua.jsp:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<% pageContext.setAttribute("ctx",request.getContextPath());%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
<head>
<h1>
<fmt:message key="welcome"/>
</h1>
</head>
<body>
<form action="">
<fmt:message key="username"/>:<input/><br/>
<fmt:message key="password"/>:<input/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
<a href="hello?locale=zh_CN">中文</a><br/>
<a href="hello?locale=en_US">英文</a><br/>
</body>
</html>
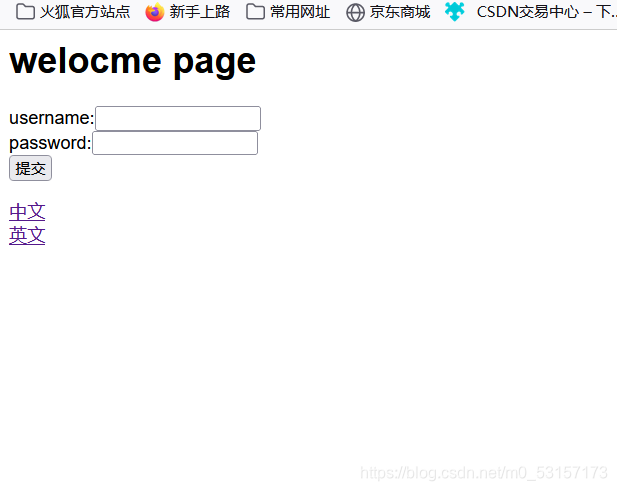
工作原理
异常处理
@ExceptionHandler()注解使用演示
里面参数可以填数组,每一个参数代表当前处理异常的方法能够处理的异常类型,返回值可以跳转到定制的错误页面
@Controller
public class exception
{
@RequestMapping("/dhy")
public String handle01(Integer i)
{
System.out.println(10/i);
return "success";
}
//里面参数可以填数组
//每一个参数代表当前处理异常的方法能够处理的异常类型,返回值可以跳转到定制的错误页面
@ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class,NullPointerException.class})
public String exceptionHandle()
{
System.out.println("发生错误");
//视图解析器拼串
return "error";
}
}
index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<a href="dhy?i=0">点我</a>
error.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
error
</body>
</html>
注意事项:

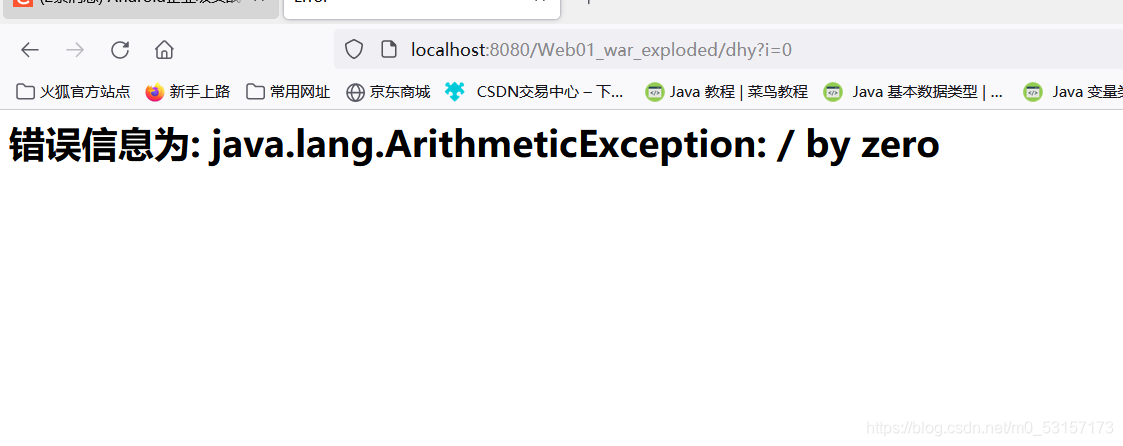
返回ModelAndView,可以将错误信息带给页面
@Controller
public class exception
{
@RequestMapping("/dhy")
public String handle01(Integer i)
{
System.out.println(10/i);
return "success";
}
//里面参数可以填数组
//每一个参数代表当前处理异常的方法能够处理的异常类型,返回值可以跳转到定制的错误页面
@ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class,NullPointerException.class})
public ModelAndView exceptionHandle(Exception exception)
{
ModelAndView m=new ModelAndView("error");//参数:设置跳转页面
m.addObject("ex",exception);//将错误信息放到隐含模型中
return m;
}
}
error页面:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>错误信息为: ${ex}</h1>
</body>
</html>
如果有多个@ExceptionHandler都能处理一个异常,那么精确优先
@ControllerAdvice注解----》表明当前类是集中处理异常的类,可以全局处理异常
@ControllerAdvice
public class exception
{
@ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class,NullPointerException.class})
public ModelAndView exceptionHandle(Exception exception)
{
ModelAndView m=new ModelAndView("error");//参数:设置跳转页面
m.addObject("ex",exception);//将错误信息放到隐含模型中
return m;
}
}
全局异常处理与本类异常处理同时存在,那么本类异常处理优先,不论精确与否
@ResponseStatus标注在自定义异常上,返回一个服务器错误页面,省去做错误页面
ex异常类:
package com.Exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
//第一个参数自定义的错误信息,第二个参数是错误显示的状态码
@ResponseStatus(reason = "用户登录异常",value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class ex extends RuntimeException{
private static final long serialVersionUID=1l;
}
hello类:
@Controller
public class hello
{
@RequestMapping("/dhy")
public String show(String name)
{
System.out.println(name);
if(!name.equals("大忽悠"))
{
throw new ex();
}
return "success";
}
}
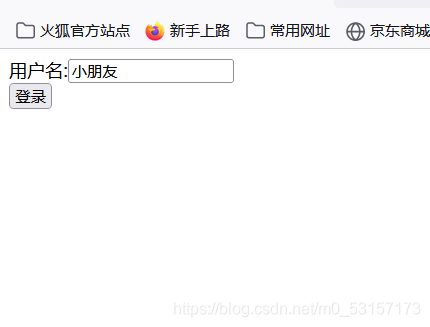
登录页面:
<form action="dhy">
用户名:<input type="text" name="name"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>
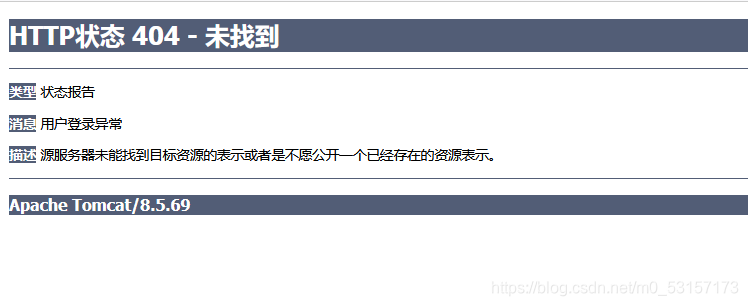
@ResponseStatus注解工作的前提是,上面没有@ExceptionHandler标注的异常处理方法能处理该异常,否则走@ExceptionHandler标注的异常处理方法
Spring默认的异常如果没人处理,就使用默认的处理方法来进行处理---->DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
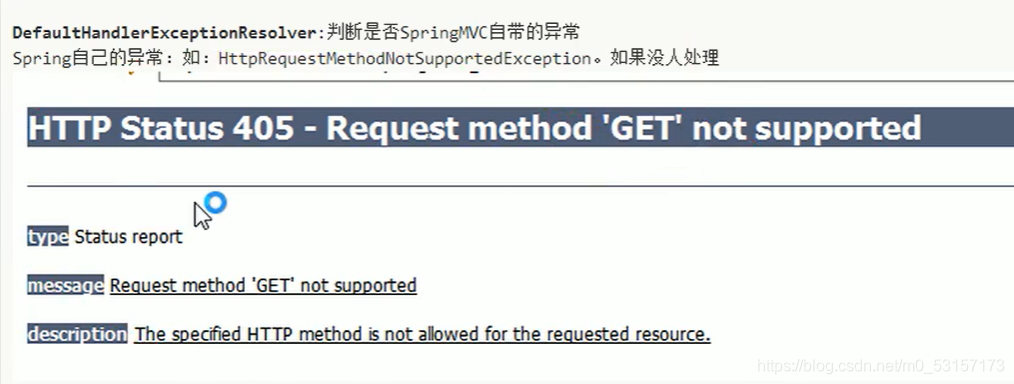
基于SpringMVC.xml配置的异常处理方式-----在处理异常的顺序上,优先级最低
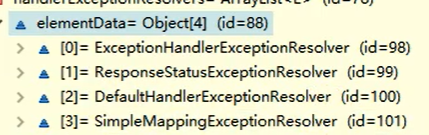
xml配置
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<!--exceptionMappings配置哪些异常区哪些页面-->
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<!--key: 异常全类名 value:要去的页面视图名-->
<prop key="java.lang.NullPointerException">error</prop>
</props>
</property>
<!--指定错误信息取出时指定的key,默认是exception-->
<property name="exceptionAttribute" value="ex"></property>
</bean>
error页面:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>错误信息为: ${ex}</h1>
</body>
</html>
Hai:
@Controller
public class Hai
{
@RequestMapping("/dhy")
public String show(String name)
{
String s=null;
s.length();//引发空指针异常
return "success";
}
}
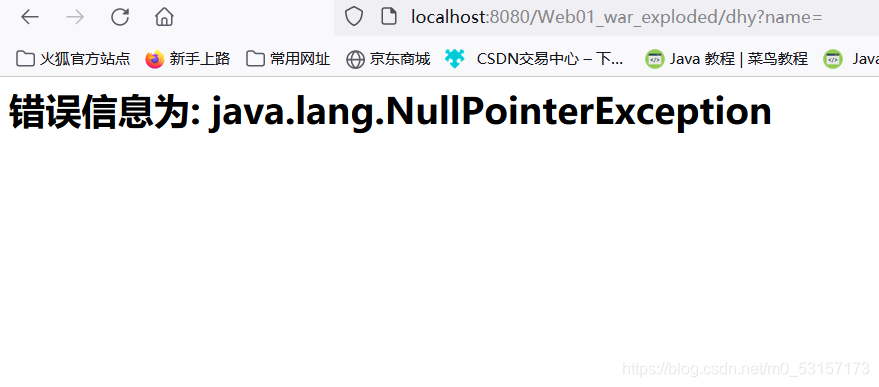
SpringMVC运行流程总结



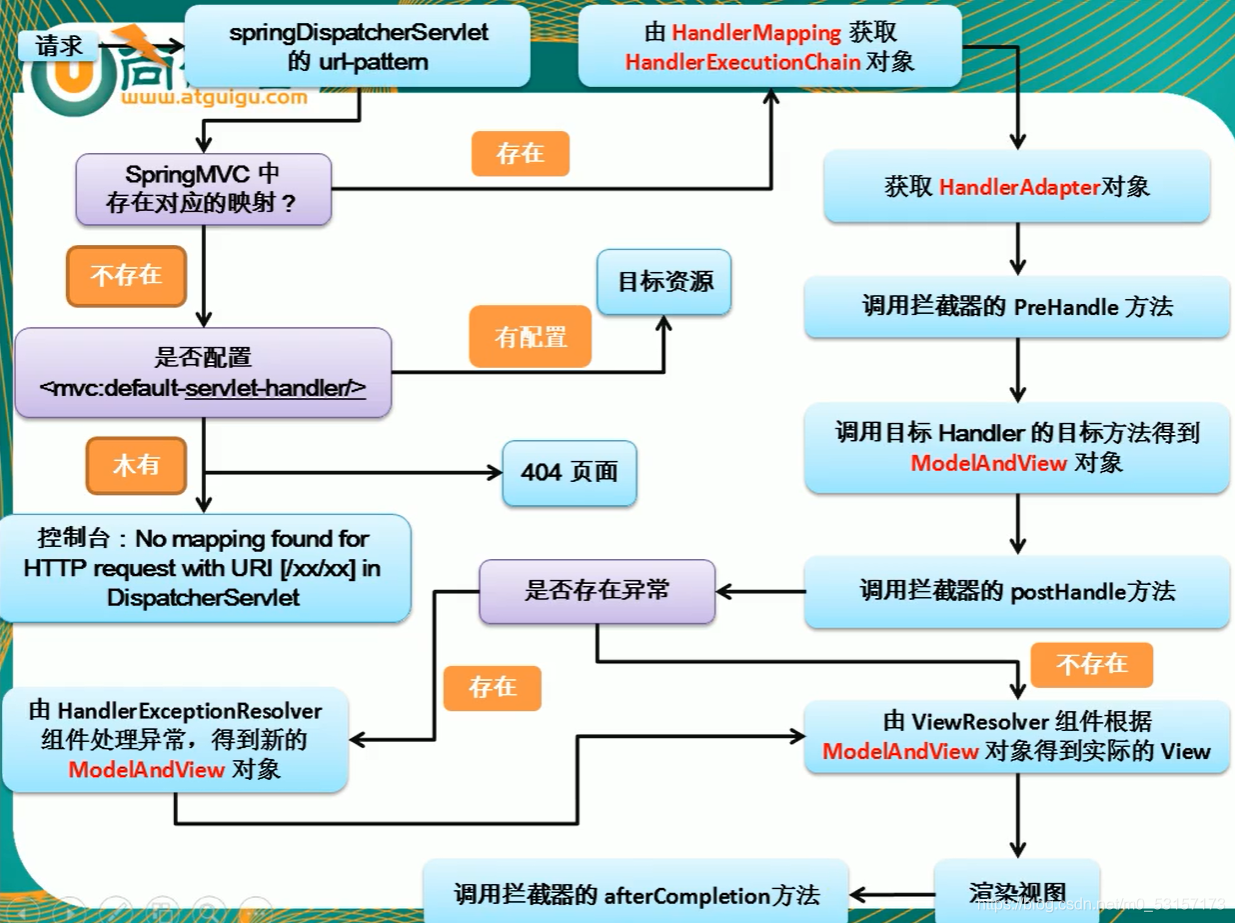
SpringMVC和Spring整合


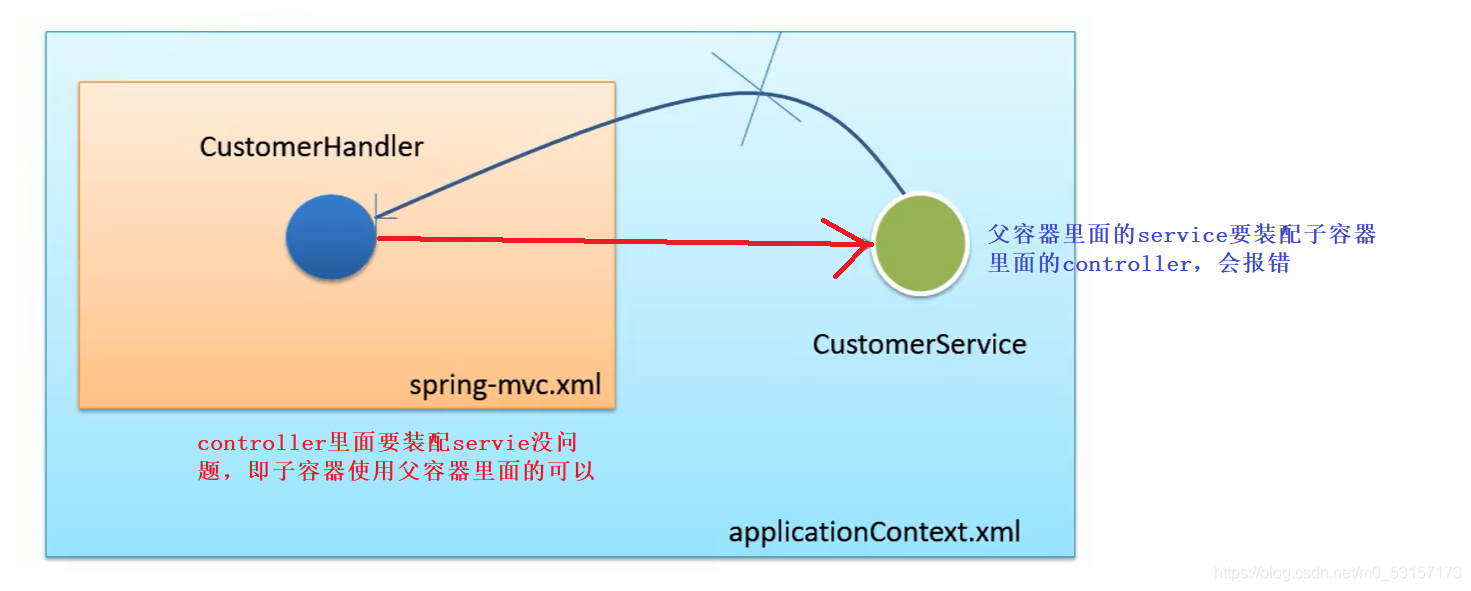
如果采用上面的合并配置文件,那么相当于系统一起动只有一个IOC容器,这样一部分报错,整个容器就凉凉
建议SpringMVC和spring分容器操作—》通过区分注解扫描范围来达到效果,各自创建自己的容器,在自己的容器中创建自己扫描到或者配置文件中配置的Bean
需要先禁止掉扫描所有包的默认行为
Spring.xml包扫描配置:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.service" use-default-filters="false">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice"/>
</context:component-scan>
SpringMVC包扫描配置:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.controller" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
<!--第二个是SpringMVC错误控制的注解-->
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice"/>
</context:component-scan>
父子容器概念: SpringMVC作为子容器,而Spring作为父容器