文章目录
- Set特点
- Set集合去重
- TreeSet
?
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、Set
1.set特点
? ? ?①.不可重复?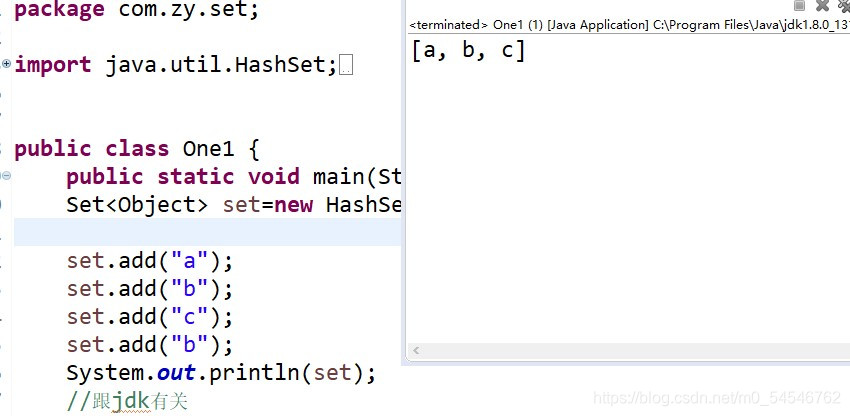
②无序(每一次运行的结果都会不一样)
?
2.遍历方式 (与list相比 少一种遍历方式 for)
代码如下(示例):
①.foreach
set.add(new stu("小白", 12));
set.add(new stu("小黑", 15));
set.add(new stu("小薛", 18));
for (Object ob : set) {
System.out.println(ob);
}代码如下(示例):
②。Iterator(迭代器)
Iterator<Object> it=set.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}二、Set集合去重
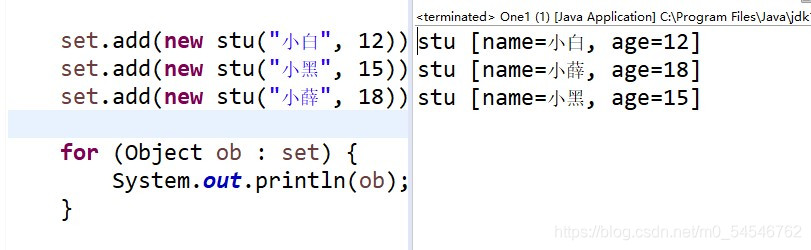
1.hashset 底层数据结构是哈希表
2.优先会调用hashcode方法对比地址
??然后调用equals方法对比值
代码如下(示例):
public static void main(String[] args) {
?? ?Set<Object> set=new HashSet<>();
?? ?
?? ?set.add(new stu("小白", 12));
?? ?set.add(new stu("小黑", 15));
?? ?set.add(new stu("小薛", 18));
?? ?set.add(new stu("小黑", 15));
?? ?
?? ?for (Object ob : set) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println(ob);
?? ?}
?? ??? ??? ?
?? ?}
}
class stu{
?? ?private String name;
?? ?private int age;
?? ?public String getName() {
?? ??? ?return name;
?? ?}
?? ?public void setName(String name) {
?? ??? ?this.name = name;
?? ?}
?? ?public int getAge() {
?? ??? ?return age;
?? ?}
?? ?public void setAge(int age) {
?? ??? ?this.age = age;
?? ?}
?? ?public stu() {
?? ??? ?// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
?? ?}
?? ?public stu(String name, int age) {
?? ??? ?super();
?? ??? ?this.name = name;
?? ??? ?this.age = age;
?? ?}
?? ?@Override
?? ?public String toString() {
?? ??? ?return "stu [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
?? ?}
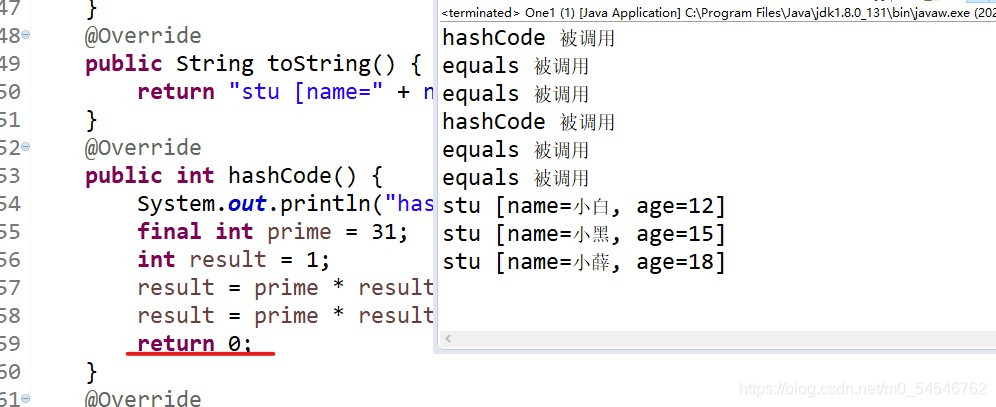
?? ?@Override
?? ?public int hashCode() {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("hashCode 被调用");
?? ??? ?final int prime = 31;
?? ??? ?int result = 1;
?? ??? ?result = prime * result + age;
?? ??? ?result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
?? ??? ?return result;
?? ?}
?? ?@Override
?? ?public boolean equals(Object obj) {
?? ??? ?System.out.println("equals 被调用");
?? ??? ?if (this == obj)
?? ??? ??? ?return true;
?? ??? ?if (obj == null)
?? ??? ??? ?return false;
?? ??? ?if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
?? ??? ??? ?return false;
?? ??? ?stu other = (stu) obj;
?? ??? ?if (age != other.age)
?? ??? ??? ?return false;
?? ??? ?if (name == null) {
?? ??? ??? ?if (other.name != null)
?? ??? ??? ??? ?return false;
?? ??? ?} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
?? ??? ??? ?return false;
?? ??? ?return true;
?? ?}
?? ?
?? ?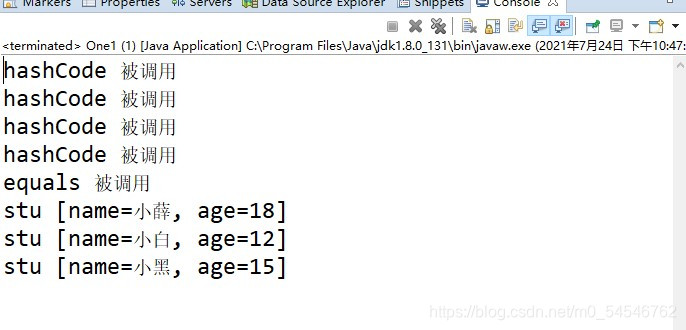
?2.当HashCode相同时会增加equals的调用次数
?
三、TreeSet
1.自然排序
自然排序对象需要实现自然排序接口如果没实现会报类转换异常 user不能转换成Comparable接口
(Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: com.zy.set.user cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable)
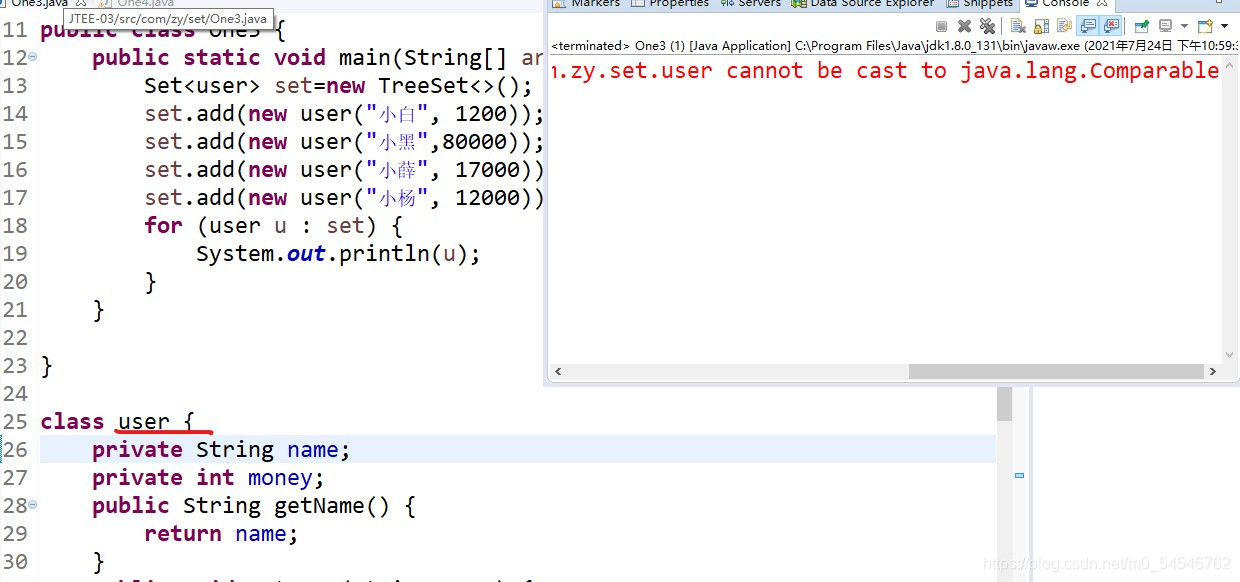
正确写法代码如下(示例):
public class One3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<user> set=new TreeSet<>();
set.add(new user("小白", 1200));
set.add(new user("小黑",80000));
set.add(new user("小薛", 17000));
set.add(new user("小杨", 12000));
for (user u : set) {
System.out.println(u);
}
}
}
class user implements Comparable{
private String name;
private int money;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public user() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public user(String name, int money) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "user [name=" + name + ", money=" + money + "]";
}
public int compareTo(Object ob) {
//ob 是对比的那个值
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
user u=(user)ob;
return this.money - u.money;
}
运行结果会根据money来升序
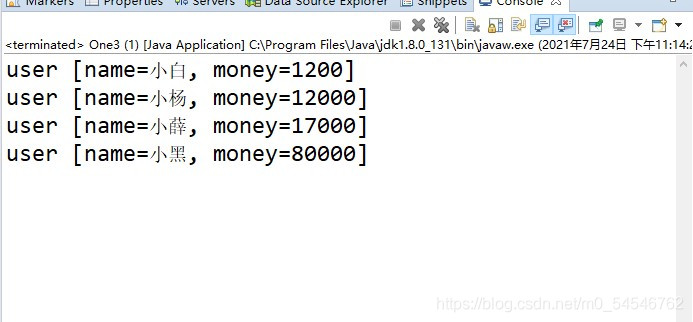
?这样写有弊端(因为自然排序是写死了的,不灵活),因为不同的模块有不同的需求,对于一张表会有不同的排序规则,这个时候我们就要用到比较器排序
2.比较器排序
代码如下(示例):
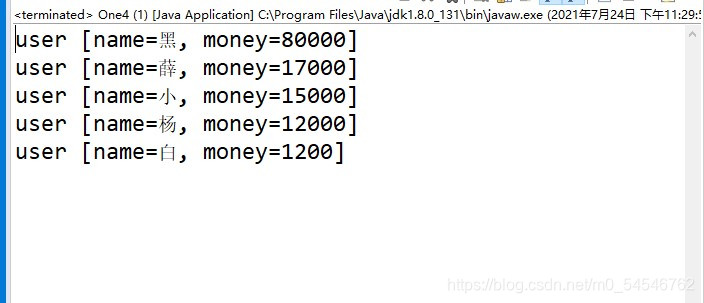
根据money降序
public class One4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<user> set=new TreeSet<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return ((user)o2).getMoney() -((user)o1).getMoney();
}
});
set.add(new user("小", 15000));
set.add(new user("白", 1200));
set.add(new user("黑",80000));
set.add(new user("薛", 17000));
set.add(new user("杨", 12000));
for (user u : set) {
System.out.println(u);
}
}
}
class user {
private String name;
private int money;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public user() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public user(String name, int money) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "user [name=" + name + ", money=" + money + "]";
}
}
?
代码如下(示例):
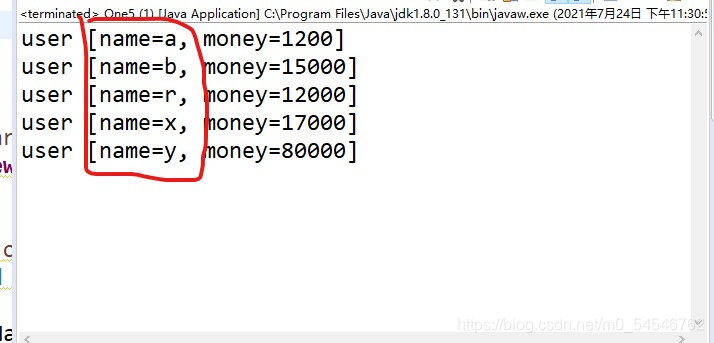
根据name的首字母进行排序
public class One5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<user> set=new TreeSet<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return ((user)o1).getName().compareTo(((user)o2).getName());
}
});
set.add(new user("b", 15000));
set.add(new user("a", 1200));
set.add(new user("y",80000));
set.add(new user("x", 17000));
set.add(new user("r", 12000));
for (user u : set) {
System.out.println(u);
}
}
}
?