Day04-Java
1、数组
数组的引用传递
public class TestDemo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
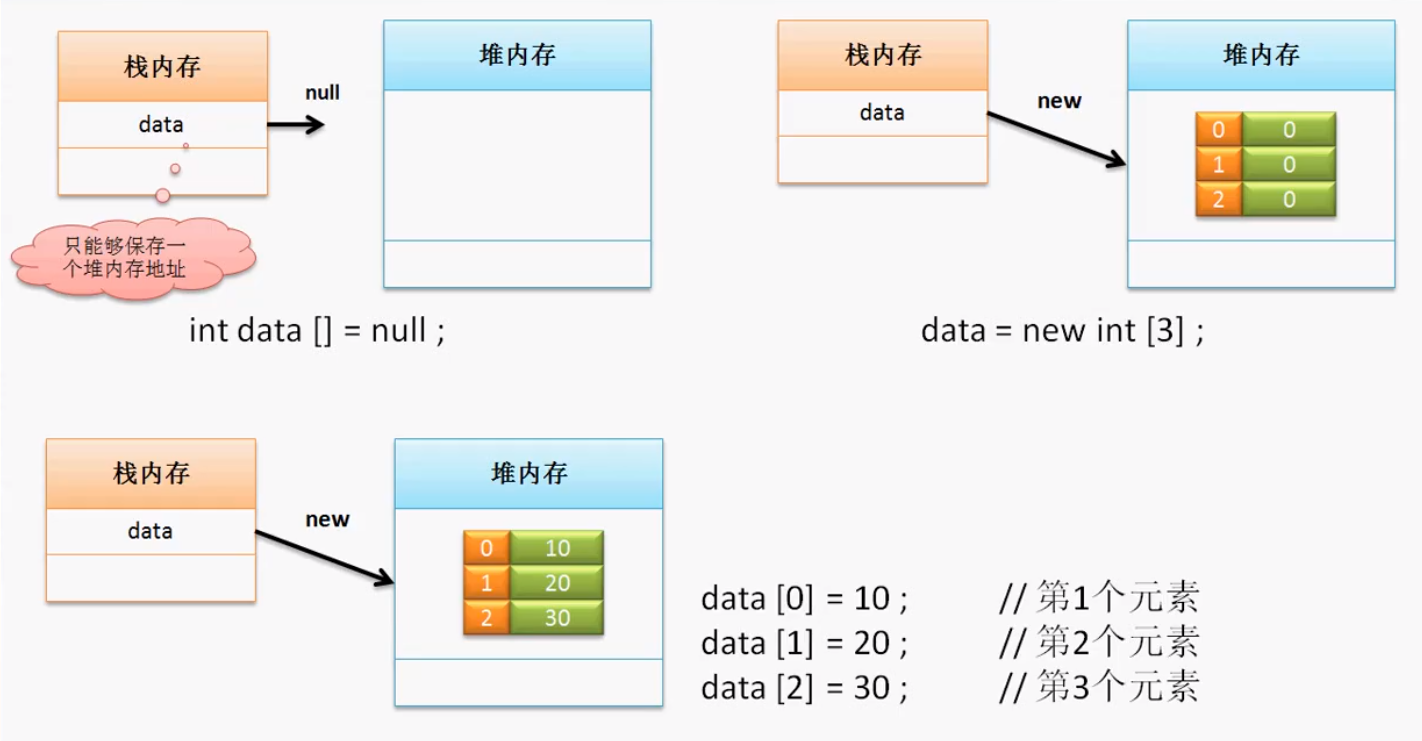
int data[] = null;
data = new int [3];
data[0] = 10; //第一个元素
data[1] = 20; //第二个元素
data[2] = 30; //第三个元素
}
}
public class TestDemo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
int data[] = null;
int temp[] = null;
data = new int [3];
data[0] = 10; //第一个元素
data[1] = 20; //第二个元素
data[2] = 30; //第三个元素
temp = data;
temp[0] = 99;
for(int i=0 ;i < temp.length ; i++){
System.out.println(temp[i]);
}
}
}
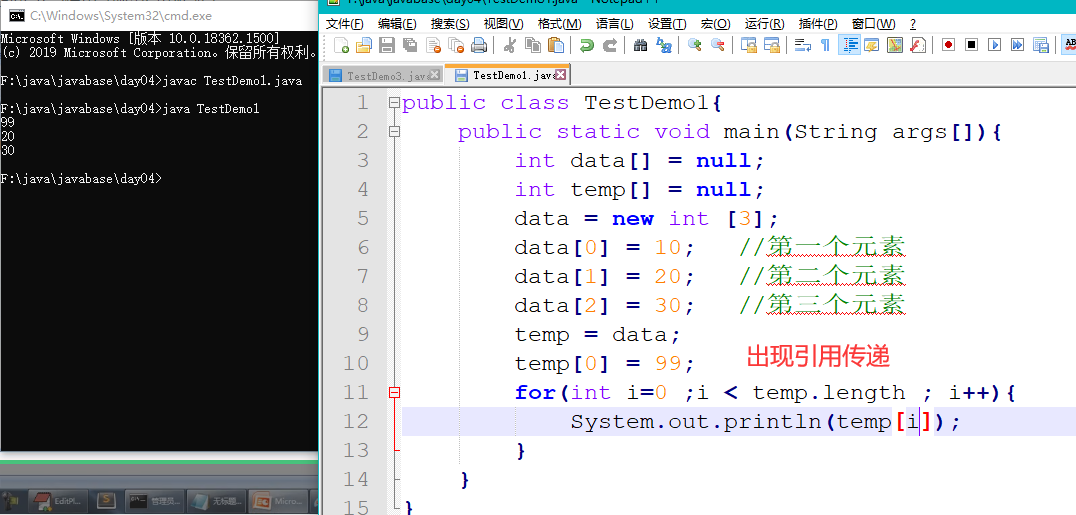
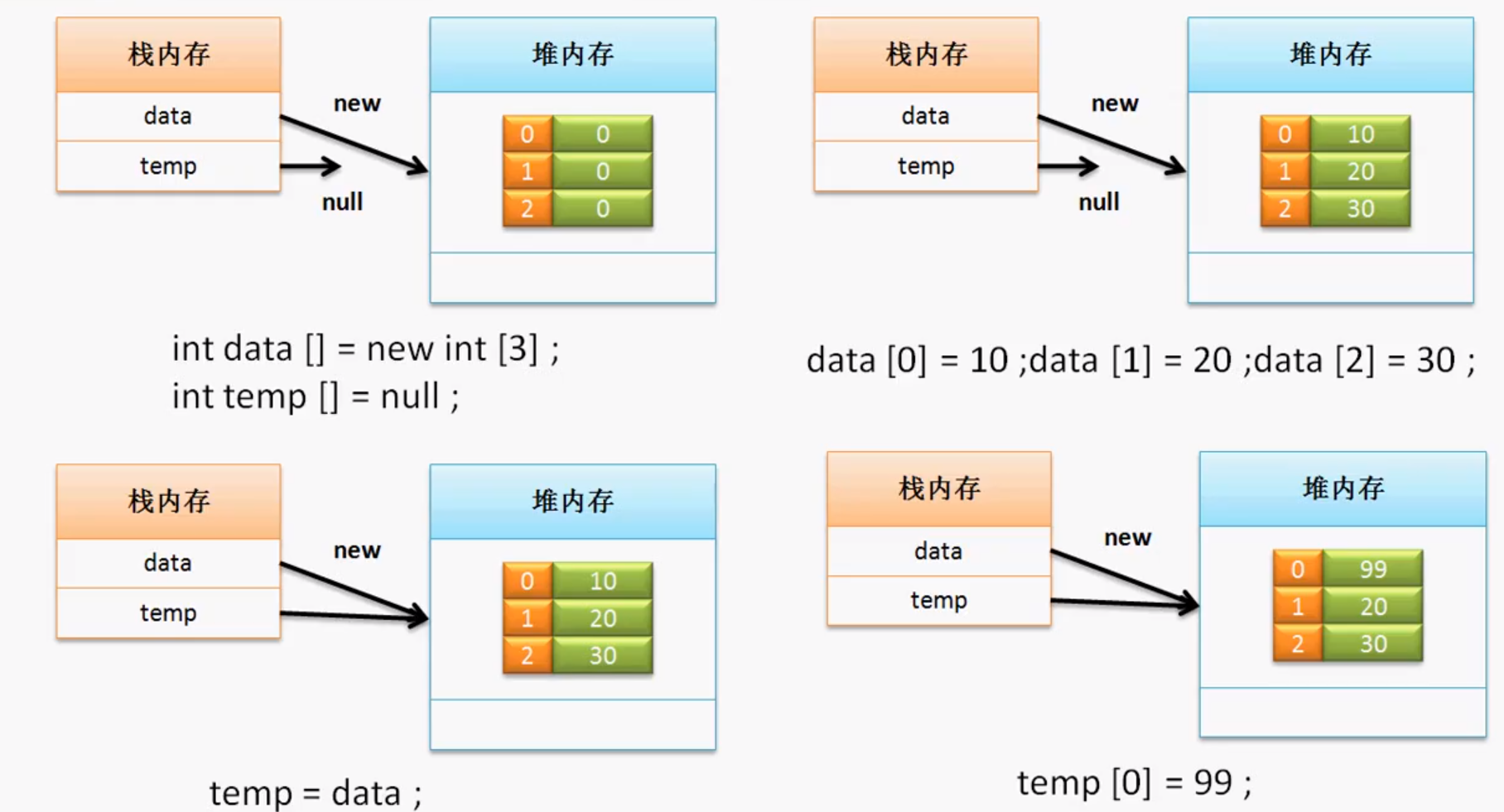
引用传递分析都是一个套路,不同的堆被同一个栈内存所指向。
数组的静态初始化
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String args[]){
//数组静态初始化的两种方式
//简化格式
int data [] = {1,2,3};
//完整格式
int data [] = new int []{1,2,3};
}
}
数组的最大缺点:长度固定。
数组与方法的调用
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [] = new int []{1,2,3,4,5};
printfArray(data); //int temp [] = data;
}
//定义一个专门用于数组输出的方法
public static void printfArray(int temp[]){
for(int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++){
System.out.println(temp[i] + "、");
}
}
}
方法返回数组
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [] = init(); //接受数组
printfArray(data); //int temp [] = data;
}
//此时的方法希望可以返回一个数组类型,所以
//返回值类型定义为整型数组
public static int[] init(){
return new int []{1,2,3,4,5};
}
//定义一个专门用于数组输出的方法
public static void printfArray(int temp[]){
for(int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++){
System.out.println(temp[i] + "、");
}
}
}
扩大数组的内容
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [] = init(); //接受数组
inc(data); //扩大数组的内容
printfArray(data); //int temp [] = data;
}
//此时的方法希望可以返回一个数组类型,所以
//返回值类型定义为整型数组
public static int[] init(){
return new int []{1,2,3,4,5};
}
public static void inc(int arr[]){ //没有返回值
for(int i = 0 ; i<arr.length ; i++){
arr[i] *= 2;
}
}
//定义一个专门用于数组输出的方法
public static void printfArray(int temp[]){
for(int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++){
System.out.println(temp[i] + "、");
}
}
}
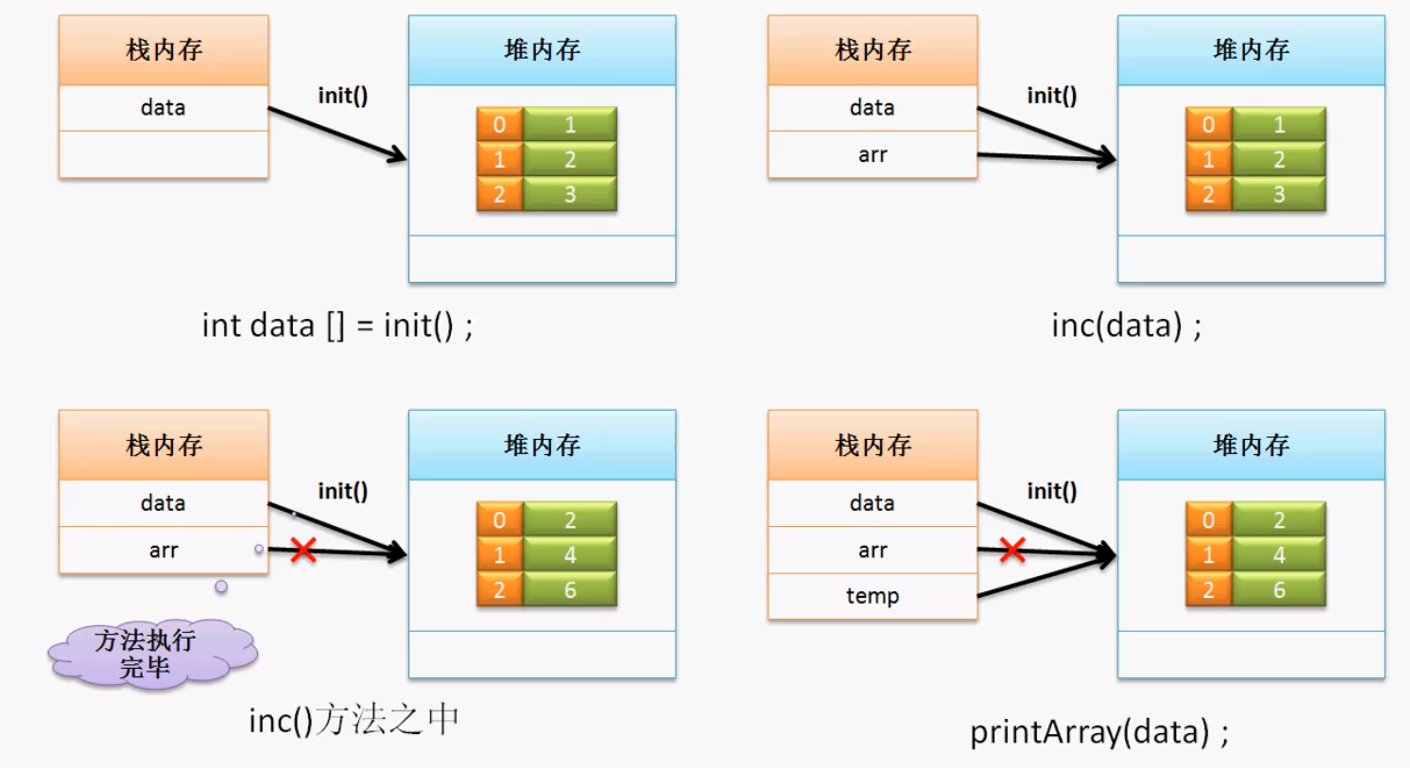
Java对数组的支持
在java本身的类库中也提供有对于数组相关的方法。
1、数组的排序:java.util.Arrays.sort(数组名称)
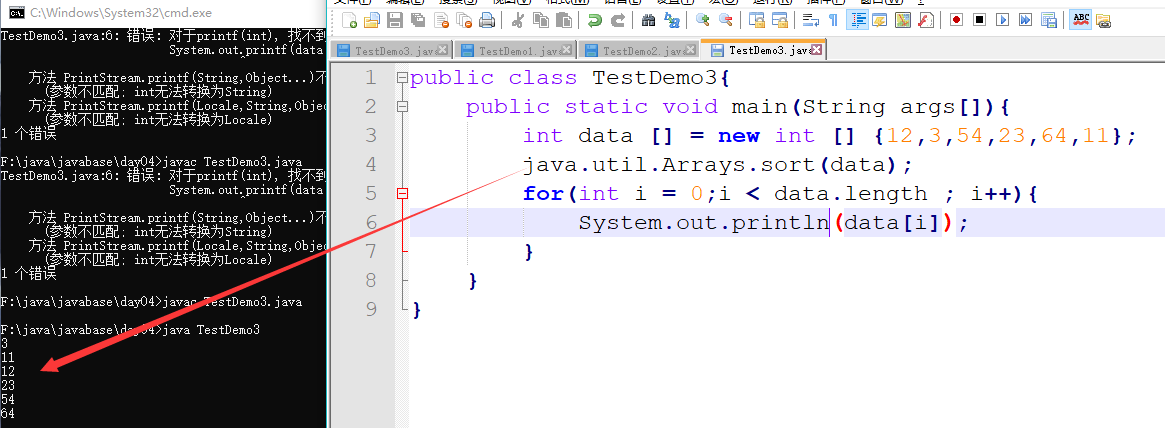
public class TestDemo3{
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [] = new int [] {12,3,54,23,64,11};
java.util.Arrays.sort(data);
for(int i = 0;i < data.length ; i++){
System.out.println(data[i]);
}
}
}
2、数组的拷贝:指的是将一个数组的部分内容替换掉另一个数组的部分内容
方法:System.arraycopy(源数组名称,源数组开始,目标数组名称,目标数组开始点,拷贝长度);
数组的数据分析
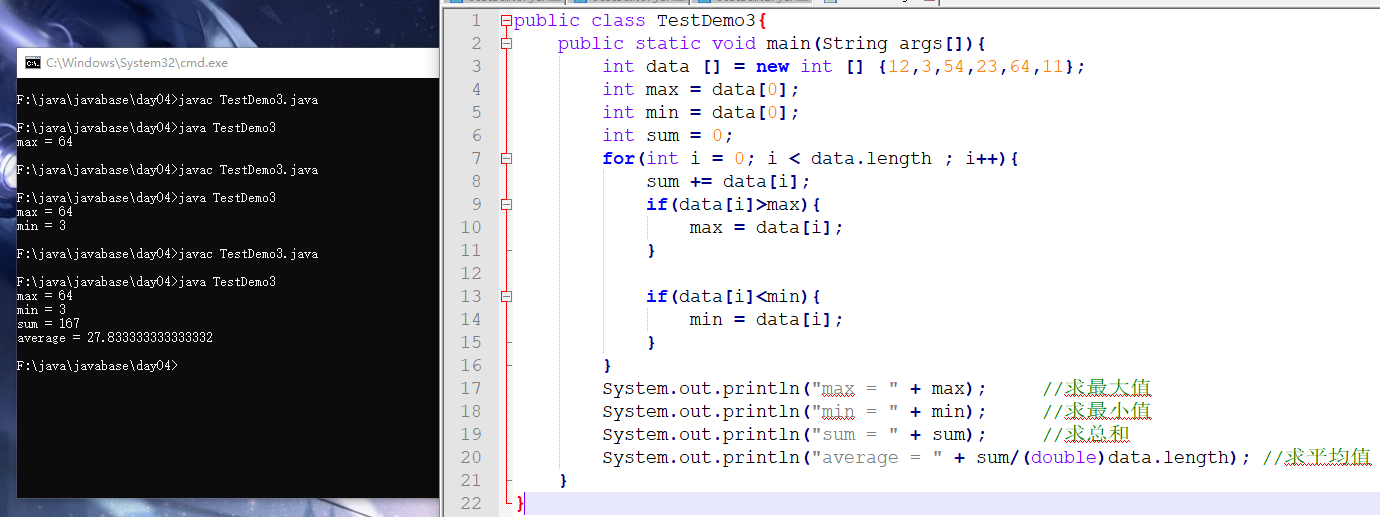
public class TestDemo3{
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [] = new int [] {12,3,54,23,64,11};
int max = data[0];
int min = data[0];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < data.length ; i++){
sum += data[i];
if(data[i]>max){
max = data[i];
}
if(data[i]<min){
min = data[i];
}
}
System.out.println("max = " + max); //求最大值
System.out.println("min = " + min); //求最小值
System.out.println("sum = " + sum); //求总和
System.out.println("average = " + sum/(double)data.length); //求平均值
}
}
数组排序
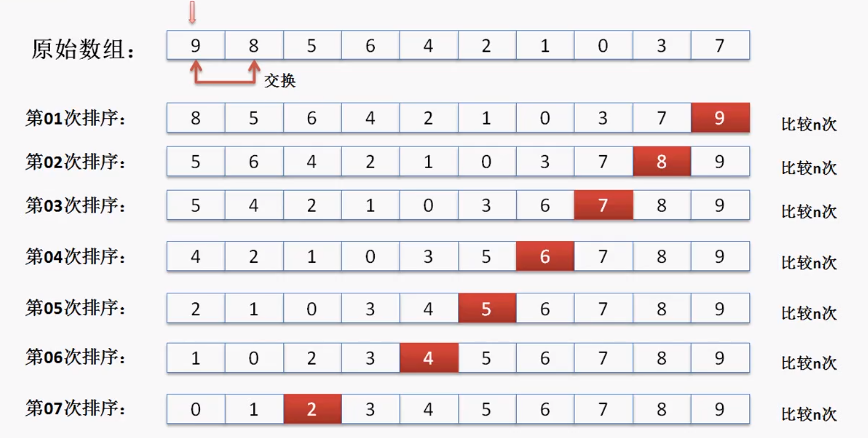
发现最终要进行循环的次数就是N^(n-1),时间复杂度高。
public class TestDemo4{
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [] = new int [] {9,8,5,6,4,2,1,0,3,7};
sort(data);
printfArray(data);
}
public static void sort(int arr[]){//实现数组的升序排序
for(int i = 0 ;i < arr.length - 1 ; i++){
//控制循环的次数
for(int j = 0 ; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
//定义一个专门用于数组输出的方法
public static void printfArray(int temp[]){
for(int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++){
System.out.println(temp[i] + "、");
}
}
}
数组的转置
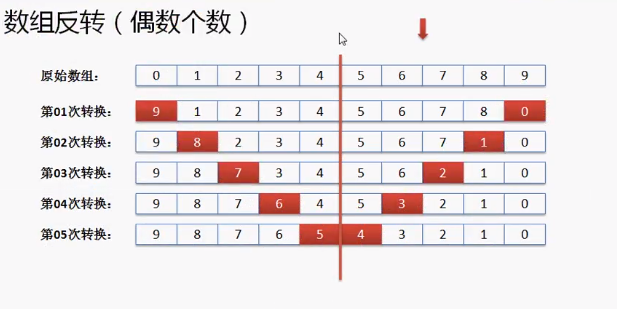
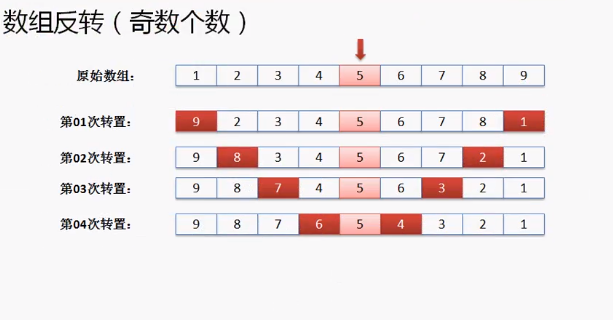
public class TestDemo4{
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [] = new int [] {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
reverse(data);
printfArray(data);
}
public static void reverse(int arr[]){
int center = arr.length / 2; //转换次数
int head = 0; //头部索引
int tail = arr.length - 1; //尾部索引
for(int i = 0 ; i < center ; i++){
int temp = arr[head];
arr[head] = arr[tail];
arr[tail] = temp;
head ++;tail --;
}
}
//定义一个专门用于数组输出的方法
public static void printfArray(int temp[]){
for(int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++){
System.out.print(temp[i] + "、");
}
}
}
public class TestDemo5{
//二维数组转置
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [][] = new int [][] {{9,8,7},{6,5,4},{3,2,1}};
reverse(data);
printfArray(data);
}
public static void reverse(int arr[][]){
int count = arr.length; //转换次数
System.out.println(count);
for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++){
for(int j = i; j < arr.length; j++){
if(i != j){
int temp = arr[i][j];
arr[i][j] = arr[j][i];
arr[j][i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
//定义一个专门用于数组输出的方法
public static void printfArray(int temp[][]){
for(int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < temp[i].length ; j++){
System.out.print(temp[i][j] + "、");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
数组的二分查找法
要求你在一个指定的数组之中查询一个数据的位置。
普通的查找的时间复杂度是n.
public class TestDemo6{
//二分查找
public static void main(String args[]){
int data [] = new int [] {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int search = 9;
System.out.println(binarySearch(data, 0 , data.length-1, search));
}
public static int binarySearch(int arr[],int form, int to, int key){
if(form < to){
int mid = (form / 2) + (to / 2); //确定中间位置索引
if(arr[mid] == key){
return mid;
}else if(key > arr[mid]){
return binarySearch(arr, mid+1 , to , key);
}else if(key < arr[mid]){
return binarySearch(arr, form, mid-1, key);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
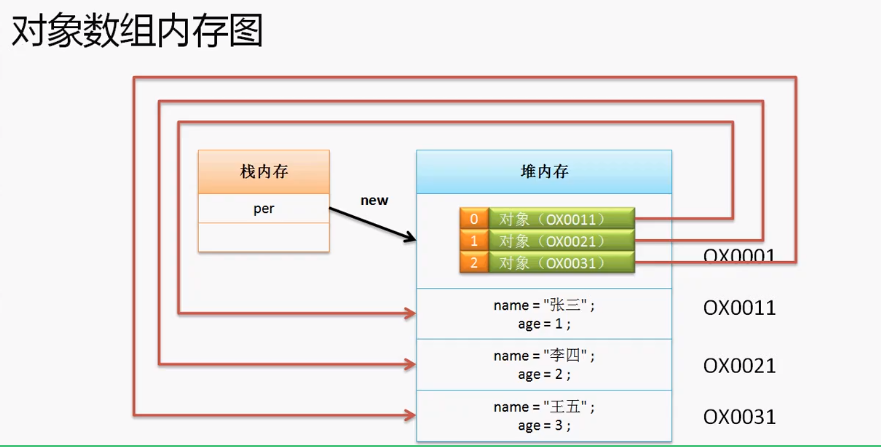
对象数组
之前所接触的都是基本数据类型的数据,那么对象也可以将其定义为数组,这样操作形式叫做对象数组。对象数组往往是引用数据类型为主的定义,例如类、接口,而且对象数组分为两种定义格式。
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String n, int a){
name = n;
age = a;
}
public void setName(String n){
name = n;
}
public void setAge(int a){
age = a;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "name = " + name + ",age = " + age;
}
}
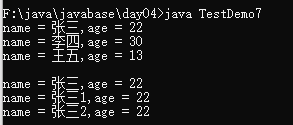
public class TestDemo7{
//对象数组
public static void main(String args[]){
Person per [] = new Person [3]; //动态初始化
Person per1 [] = new Person [] {
new Person("张三",22),
new Person("张三1",22),
new Person("张三2",22)
}; //静态初始化
per[0] = new Person("张三",22);
per[1] = new Person("李四",30);
per[2] = new Person("王五",13);
for(int i = 0;i < per.length ; i++){
System.out.println(per[i].getInfo());
}
System.out.println();
for(int i = 0;i < per.length ; i++){
System.out.println(per1[i].getInfo());
}
}
}