获取客户端 / 服务端信息
| 方法 | 注释 |
|---|---|
| getMethod( ) | 获取客户端请求方式 |
| getScheme( ) | 获取请求协议;(当前链接使用的协议) |
| getProtocol( ) | 获取http协议名称 |
| getRemoteAddr( ) | 获取发出请求的客户端的IP地址 |
| getServerName( ) | 获取服务器主机名(ip或域名) |
| getServerPort( ) | 获取服务器端口 |
| getRemotePort( ) | 获取远程端口,即客户端端口 |
| getRemoteUser( ) | 获取远程用户名 |
| getHeader(String s) | 获取指定参数名的请求头 |
| getHeaderNames( ) | 获取请求头的所有名字;返回类型为集合 |
| getLocalAddr( ) | 获取本地IP地址,即服务器IP |
| getLocalName( ) | 获取本地名称,即服务器名称 |
| getLocalPort( ) | 获取本地端口号,即Tomcat端口号 |
| getLocale( ) | 获取用户的语言环境 |
| getContextPath( ) | 获取绝对路径(根目录) |
| getContentType( ) | 获取请求数据类型 |
| getContentLength( ) | 获取请求数据长度 |
| getQueryString( ) | 查询字符串 |
| getRequestedSessionId( ) | 获取客户端的Session的ID |
| getRequestURI() | 获取用户请求的URL |
| getServletPath( ) | 获取Servlet路径 |
案例:在LoginServlet类中的都Post方法中,输出部分获取客户端/服务端信息的方法;
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
//无参构造的实例化方式,默认存在;
//初始化方法 init ,默认调用父类的;
//service方法,可调用父类中的; 在父类中会判断请求方式 ; get对应doGet方法; post对应doPost 方法.
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//设置数据解码格式;(字符过滤)
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//接收请求中传递的数据;(请求行,请求头)
System.out.println("请求方法为 " + req.getMethod());
System.out.println("客户端IP为 " + req.getRemoteAddr());
System.out.println("服务器主机名 " + req.getServerName());
System.out.println("服务器端口为 " + req.getServerPort());
System.out.println("当前链接使用的协议 " + req.getScheme());
System.out.println("协议名称为 " + req.getProtocol());
System.out.println("请求数据类型为 "+req.getContentType());
System.out.println("请求数据长度为 "+req.getContentLength());
System.out.println("绝对路径为 "+req.getContextPath());
System.out.println("获得指定参数名称的请求头(host) "+req.getHeader("Host"));
System.out.println("=========获取所有请求头的名字===================");
Enumeration<String> headerNames = req.getHeaderNames();
//遍历判断是否还有元素;
while(headerNames.hasMoreElements()){
//获取下一个元素;
String s = headerNames.nextElement();
System.out.println(s+"==>"+req.getHeader(s));
}
}
//销毁方法 destory 默认调用父类的;
}
表单页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>初识JavaWeb</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="login" method="post">
账号:<input type="text" name="account"/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
启动服务器,提交表单,查看打印信息;
请求方法为 POST
客户端IP为 127.0.0.1
服务器主机名 127.0.0.1
服务器端口为 8080
当前链接使用的协议 http
协议名称为 HTTP/1.1
请求数据类型为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded
请求数据长度为 114
绝对路径为 /xaiozhi
获得指定参数名称的请求头(host) 127.0.0.1:8080
=========获取所有请求头的名字===================
host==>127.0.0.1:8080
connection==>keep-alive
content-length==>114
cache-control==>max-age=0
sec-ch-ua==>"Chromium";v="92", " Not A;Brand";v="99", "Google Chrome";v="92"
sec-ch-ua-mobile==>?0
upgrade-insecure-requests==>1
origin==>http://127.0.0.1:8080
content-type==>application/x-www-form-urlencoded
user-agent==>Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.107 Safari/537.36
accept==>text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9
sec-fetch-site==>same-origin
sec-fetch-mode==>navigate
sec-fetch-user==>?1
sec-fetch-dest==>document
referer==>http://127.0.0.1:8080/
accept-encoding==>gzip, deflate, br
accept-language==>zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
cookie==>JSESSIONID=8D86ABC72A38FF7457B22020E89A1429
HTTP 响应
http响应代表服务器向客户端回送的数据,
它包括三部分:响应行,响应头,响应体。
响应行里包含了http协议版本,以及用于描述服务器对请求的处理结果。
案例:HTTP/1.1 (协议版本) 200(状态码) OK(对于状态码的描述)
状态码(HTTP Status Code):服务器和浏览器用于确定状态的固定数字号码
当浏览者访问一个网页时,浏览者的浏览器会向网页所在服务器发出请求。当浏览器接收并显示网页前,此网页所在的服务器会返回一个包含HTTP状态码的信息头(server header)用以响应浏览器的请求。
常用状态码:
| 状态码 | 英文 | 注释 |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | Continue | 继续。客户端继续其请求 |
| 101 | Switching Protocols | 切换协议。服务器根据客户端的请求切换协议。只能切换到更高级的协议,例如,切换到HTTP的新版本协议 |
| 200 | OK | 请求成功,多用于GET与POST请求 |
| 201 | Created | 已创建。成功请求并创建了新的资源 |
| 202 | Accepted | 已接受。已经接受请求,但未处理完成 |
| 302 | Found | 请求重定向 |
| 400 | Bad Request | 语义有误,当前请求无法被服务器理解或请求参数有误 |
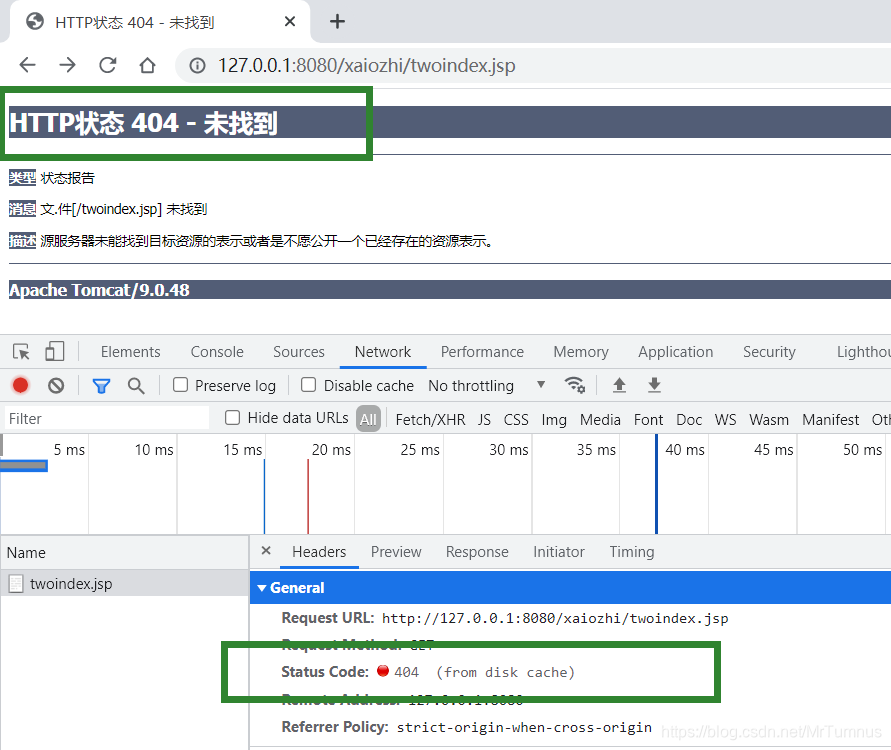
| 404 | Not Found | 请求资源不存在,通常是路径写错或者服务器资源删除.服务器无法根据客户端的请求找到资源(网页)。通过此代码,网站设计人员可设置"您所请求的资源无法找到"的个性页面 |
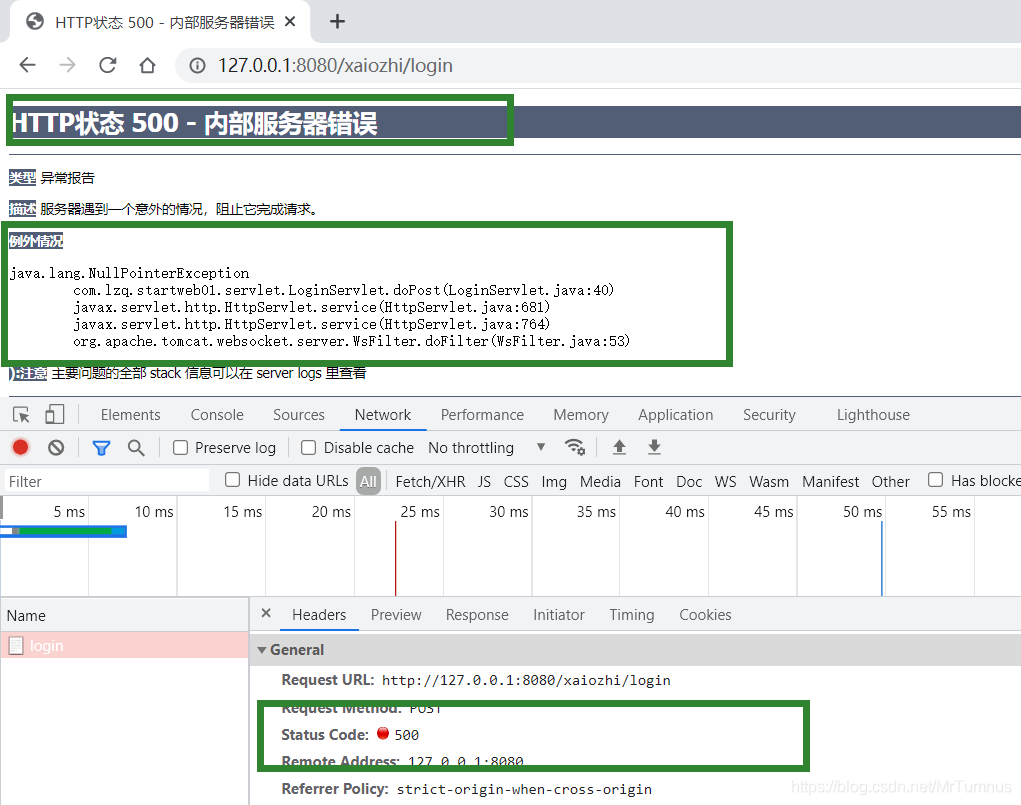
| 500 | Internal Server Error | 服务内部错误(代码异常),无法完成请求 |
404错误提示:
500错误提示
响应头用于描述服务器的基本信息,以及数据描述
案例:
HTTP/1.1 200
Content-Type: text/html;charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 21
Date: Fri, 30 Jul 2021 08:58:19 GMT
Keep-Alive: timeout=20
Connection: keep-alive
响应体代表服务器向客户端浏览器回送的正文
也就是网页内容
案例,对客户端做出模拟响应
在LoginServlet类的doPost方法中进行模拟响应(使用字符输出流).
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
//无参构造的实例化方式,默认存在;
//初始化方法 init ,默认调用父类的;
//service方法,可调用父类中的; 在父类中会判断请求方式 ; get对应doGet方法; post对应doPost 方法.
//销毁方法 destory 默认调用父类的;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//设置数据解码格式;(字符过滤)
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//接收请求中传递的数据(提交的数据)
String account = req.getParameter("account");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
//模拟数据交互(调用其他Java程序处理);
//注意设置字符编码格式,(字符过滤);
resp.setHeader("content-type", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
//向客户端做出响应;(本质上使用 IO流;字符输出流)
PrintWriter out= resp.getWriter();
if (account.equals("张三") && password.equals("123456")) {
out.print("<h2>欢迎登入</h2>");
}else{
out.print("<h2>失败了!</h2>");
}
}
}
前端网页文件为
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Servlet学习</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="login" method="post">
账号:<input type="text" name="account"/><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="登录"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
启动服务器;输入对应的账号,密码

如果在响应客户端之前,没有进行字符过滤,会出现中文乱码
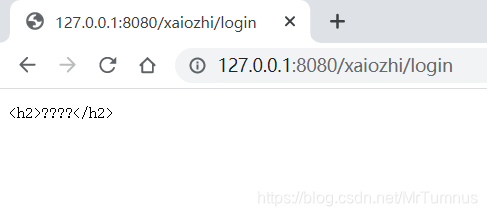
用getWriter()获得一个PrintWriter字符输出流输出数据response会默认以ISO8859-1将需要输出到浏览器的字符进行解码,如果输出的字符在ISO8859-1中不存在,就会导致乱码问题。
注意在响应客户端之前首先进行字符过滤;避免中文乱码
有两种方式
- response.setContentType(“text/html;charset=utf-8”);
- response.setHeader(“content-type”, “text/html;charset=utf-8”);
关于输出流在打印时使用print与writer区别
| 输出方法 | 区别 |
|---|---|
response.getWriter().print() | 打印输出文本格式的(包括html标签);也能让一个对象以默认的编码方式转换为二进制字节输出 |
response.getWriter().writer() | 打印输出文本格式的(包括html标签),不能打印对象。 |
HttpServletReponse
- HttpServletResponse
是ServletResponse的子接口;封装了响应信息 - Web服务器收到客户端的http请求,会针对每一次请求,分别创建一个代表响应的HttpServletResponse对象。