Day06-Java
1、this关键字
首先需要提醒的是,在整个Java之中,this是最麻烦的一个关键字,只要是代码开发,几乎都离不开this。在Java中this可以完成三件事情:表示本类属性、表示本类方法、表示当前对象(只介绍概念)。
1.1 “this.属性”表示本类属性
在讲解着一操作之前首先观察如下程序:
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String n,int a){
name = n;
age = a;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "姓名:"+name+","+"年龄:"+age;
}
}
public class ThisText{
public static void main(String args[]){
Person per = new Person("张三",20);
System.out.println(per.getInfo());
}
}
这个时候的构造方法的两额参数的目的是为了类中的name和age两额属性初始化,可是这个方法上的两个参数一个是字母n一个是字母a,什么意思?那么最好的做法,既然构造方法的两个参数是为了类中name和age初始化使用,那么最好将其参数名称也定义为name和age才最为直观。
public Person(String name,int age){
name = name;
age = age;
}
此时构造方法中参数的名称变得有意义了,但是这样一来就出现问题了,发现属性没有内容了!因为在程序之中是采用“{}”作为分界,采用就近的取用原则,所以现在为了明确指定要操作的是类中属性的话,那么应该采用“this.属性”的形式完成,代码应该变为:
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name = name; //this.name 表示类中的属性name
this.age = age;
}
提示:在日后的所有开发过程之中,如果要调用类中属性的话,都要使用“this.属性”的方式来调用。
1.2“this”表示调用本类方法
对于一个类之中的方法分为两种:
1、普通方法:之前强调过,如果现在要调用的是本类之中的方法,则可以使用“this.方法()”调用。
2、构造方法:调用其他构造使用“this ()”调用。
例如:现在一个类之中存在了三个构造方法(无参、有一个参数、有两个参数),但是不管使用何种构造方法,都要求在实例化对象产生的时候输出一行提示信息:“欢迎光临”。
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){
System.out.println("-----欢迎光临-----");
}
public Person(String name){
System.out.println("-----欢迎光临-----");
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name,int age){
System.out.println("-----欢迎光临-----");
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "姓名:"+name+","+"年龄:"+age;
}
}
public class ThisText1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Person per = new Person();
System.out.println(per.getInfo());
}
}
不过,遗憾的是按照之前的知识来讲,此时的程序之中会出现大量的重复代码,而这样的方法不是最优的。
这种情况下就可以利用this()来完成
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){
System.out.println("-----欢迎光临-----");
}
public Person(String name){
this(); //调用无参构造方法
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name,int age){
this(name); //调用有一个参数的构造方法
this.age = age;
}
public String getInfo(){
return "姓名:"+name+","+"年龄:"+age;
}
public class ThisText1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Person per = new Person();
System.out.println(per.getInfo());
}
}
使用this()就完成了构造方法之间的互相调用。
**注意:**在使用this()调用构造方法的时候有以下问题:
1、所有的构造方法实在对象实例化的时候被默认调用,而且是在调用普通方法之前调用,所以使用“this()”调用构造方法的操作,一定要放在构造方法的首行;
2、如果一个类之中存在了多种构造方法的话,并且这些构造方法都使用this()相互调用,那么至少要保证一个构造方法没有调用其他构造,以作程序的出口。
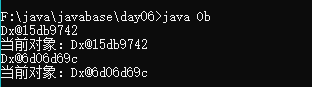
1.3“this”表示当前对象
class Dx{
public void fun(){
System.out.println("当前对象:" + this);
}
}
public class Ob{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dx dx = new Dx();
System.out.println(dx);
dx.fun();
Dx dx1 = new Dx();
System.out.println(dx1);
dx1.fun();
}
}
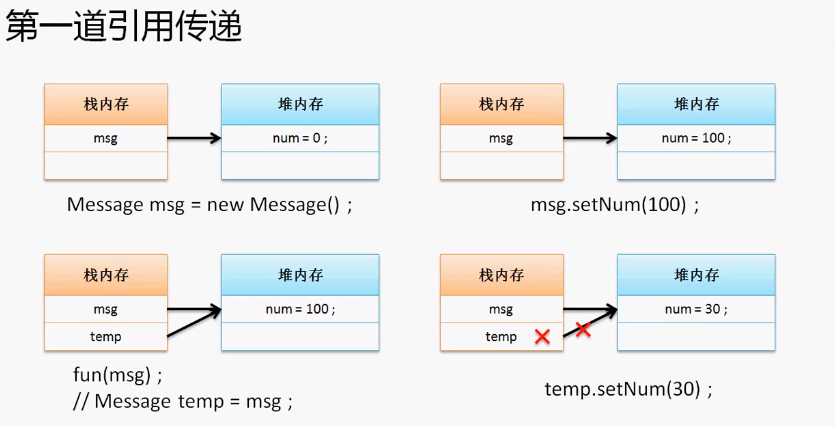
1.4引用传递进阶分析
程序一
class Message{
private String num;
public void setNum(String num){
this.num = num;
}
public String getNum(){
return num;
}
}
public class TestDemo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Message message = new Message();
message.setNum("100");
fun(message);
//30
System.out.println(message.getNum());
}
public static void fun(Message temp){ //引用传递
temp.setNum("30");
}
}
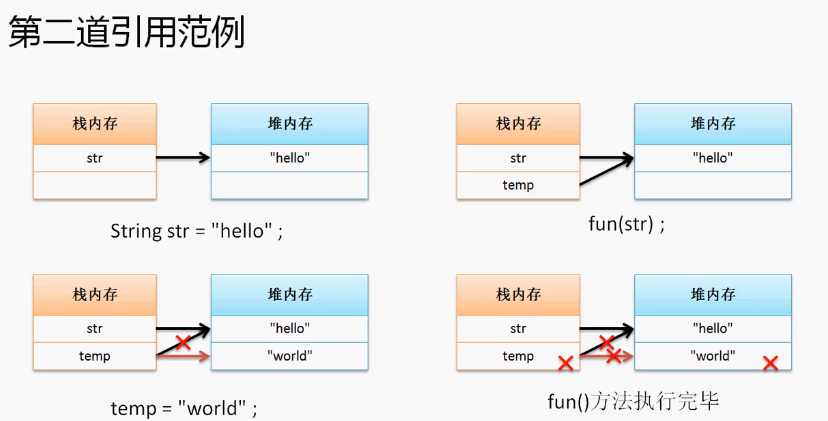
程序二
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "hello";
fun(str);
//hello
System.out.println(str);
}
public static void fun(String temp){
temp = "world";
}
}
本程序的关键是:String的内容一旦声明则不可改变,改变的是内存的地址指向。
1.5对象比较
对象的比较实际就是对象属性的比较。
class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public int getAge(){
return this.age;
}
}
public class TestDemo3{
public static void main(String args[]){
Person per1 = new Person("张三",20);
Person per2 = new Person("张三",20);
//false
System.out.println(per1==per2); //比较两个对象的地址
//是同一个对象
if(per1.getName().equals(per2.getName())&&per1.getAge() == per2.getAge()){
System.out.println("是同一个对象");
}
else{
System.out.println("不是同一个对象");
}
}
}
对象比较的操作一定是一个类自己本身所具备的功能,而且对象比较的操作特点:
1 本类接收自己的引用,而后与本类当前对象(this)进行比较;
2 为了避免NullPointerException的产生,应该增加一个null的判断;
3 为了防止浪费性能的情况出现,可以增加地址数值的判断,相同的对象地址相同;
4之后与属性依次进行比较,如果属性全部相同,则返回true,否则返回false。
1.6引用传递实际应用
//电脑
class Computer{
private View [];
private Host;
}
//显示器
class View{
}
//主机
class Host{
private Board;
}
//主板
class Board{
private Cpu [];
private Memory[];
private Disk[];
}
//CPU
class Cpu{
}
//内存
class Memory{
}
//硬盘
class Disk{
}
public class TestDemo3{
public static void main(String args[]){
}
}
重点
1.7数据表与简单Java类(一对多)
利用此关系模型,表示出emp和dept的关系,使用字段:
? **emp表:**empno、ename、job、sal、comm、mgr、deptno;
? **dept表:**deptno、dname、loc。
第一步 编写实体类
class Emp{
private int empno;
private String ename;
private String job;
private double sal;
private double comm;
public Emp(int empno,String ename,String job,double sal,double comm){
this.empno = empno;
this.ename = ename;
this.job = job;
this.sal = sal;
this.comm = comm;
}
public String getEmpInfo(){
return "【Emp】 empno = " + this.empno +
",ename = " + this.ename +
",job; = " + this.job +
",sal = " + this.sal +
",comm = " + this.comm;
}
}
class Dept{
private int deptno;
private String dname;
private String loc;
public Dept(int deptno, String dname, String loc){
this.deptno = deptno;
this.dname = dname;
this.loc = loc;
}
public String getDept(){
return "deptno = " + this.deptno +
",dname = " + this.dname +
",loc = " + this.loc;
}
}
public class Exam1_7{
public static void main(String args[]){
}
}
第二步 进行关系设计
一个雇员属于一个部门,需要追加部门引用
一个雇员有一个领导,领导一定是自身关联
一个部门有一个雇员,需要一个对象数组来描述多个雇员信息
class Emp{
private int empno;
private String ename;
private String job;
private double sal;
private double comm;
private Emp mgr; //描述雇员的领导
private Dept dept; //描述雇员的部门
public Emp(int empno,String ename,String job,double sal,double comm){
this.empno = empno;
this.ename = ename;
this.job = job;
this.sal = sal;
this.comm = comm;
}
public void setMgr(Emp mgr){
this.mgr = mgr;
}
public Emp getMgr(){
return this.mgr;
}
public void setDept(Dept dept){
this.dept = dept;
}
public Dept getDept(){
return this.dept;
}
public String getEmpInfo(){
return "【Emp】 empno = " + this.empno +
",ename = " + this.ename +
",job; = " + this.job +
",sal = " + this.sal +
",comm = " + this.comm;
}
}
class Dept{
private int deptno;
private String dname;
private String loc;
private Emp [] emps; //一个部门有多个雇员
public Dept(int deptno, String dname, String loc){
this.deptno = deptno;
this.dname = dname;
this.loc = loc;
}
public void setEmps(Emp [] emps){
this.emps = emps;
}
public Emp [] getEmps(){
return this.emps;
}
public String getDept(){
return "deptno = " + this.deptno +
",dname = " + this.dname +
",loc = " + this.loc;
}
}
public class Exam1_7{
public static void main(String args[]){
}
}
此时基本类定义完成。
第三步 开发需求
主函数main
public class Exam1_7{
public static void main(String args[]){
//第一步、设置类对象的关系
//1.分别创建各自对象实例化
Dept dept = new Dept(10,"市场部","New York");
Emp ea = new Emp(7345,"Rock","CLERK",800.0,0);
Emp eb = new Emp(7567,"Joker","MANAGER",3050.0,0);
Emp ec = new Emp(7825,"Ben","PRESIDENT",10000.0,0);
//2.设置雇员和领导的关系
ea.setMgr(eb);
eb.setMgr(ec); //ec没有领导 自己就是最大的领导
//3.设置雇员和部门的关系
ea.setDept(dept);
eb.setDept(dept);
ec.setDept(dept);
//4.设置部门的雇员
dept.setEmps(new Emp[]{ea, eb, ec});
//第二步、进行数据的取得
//一个部门有多个雇员
/*
【Emp】 empno = 7345,ename = Rock,job = CLERK,sal = 800.0,comm = 0.0
【Emp】 empno = 7567,ename = Joker,job = MANAGER,sal = 3050.0,comm = 0.0
【Emp】 empno = 7825,ename = Ben,job = PRESIDENT,sal = 10000.0,comm = 0.0
*/
for(int i = 0; i < dept.getEmps().length; i++){
System.out.println(dept.getEmps()[i].getEmpInfo());
}
System.out.println();
//一个雇员有一个领导
//【Emp】 empno = 7567,ename = Joker,job = MANAGER,sal = 3050.0,comm = 0.0
System.out.println(ea.getMgr().getEmpInfo());
//【Emp】 empno = 7825,ename = Ben,job = PRESIDENT,sal = 10000.0,comm = 0.0
System.out.println(eb.getMgr().getEmpInfo());
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
//没有设置关系 所以自己是老板 显示空指针异常
//System.out.println(ec.getMgr().getEmpInfo());
System.out.println();
//一个雇员属于同个部门
//deptno = 10,dname = 市场部,loc = New York
System.out.println(ea.getDept().getDeptInfo());
//deptno = 10,dname = 市场部,loc = New York
System.out.println(eb.getDept().getDeptInfo());
//deptno = 10,dname = 市场部,loc = New York
System.out.println(ec.getDept().getDeptInfo());
}
}
在上面的代码基础上进行改进
//一个部门有多个雇员,一个雇员有一个领导,一个雇员属于同个部门
/*
【Emp】 empno = 7345,ename = Rock,job = CLERK,sal = 800.0,comm = 0.0
该雇员所属的领导【Emp】 empno = 7567,ename = Joker,job = MANAGER,sal = 3050.0,comm = 0.0
该雇员所属的部门deptno = 10,dname = 市场部,loc = New York
------------------------------------------------------------------
【Emp】 empno = 7567,ename = Joker,job = MANAGER,sal = 3050.0,comm = 0.0
该雇员所属的领导【Emp】 empno = 7825,ename = Ben,job = PRESIDENT,sal = 10000.0,comm = 0.0
该雇员所属的部门deptno = 10,dname = 市场部,loc = New York
------------------------------------------------------------------
【Emp】 empno = 7825,ename = Ben,job = PRESIDENT,sal = 10000.0,comm = 0.0
自己就是领导
------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
for(int i = 0; i < dept.getEmps().length; i++){
System.out.println(dept.getEmps()[i].getEmpInfo());
if(dept.getEmps()[i].getMgr() != null){
System.out.println("该雇员所属的领导" +
dept.getEmps()[i].getMgr().getEmpInfo());
System.out.println("该雇员所属的部门" +
dept.getEmps()[i].getDept().getDeptInfo());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
else{
System.out.println("自己就是领导");
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
}
1.8数据表与简单Java类(多对多)
利用此关系模型,表示出student和course的关系,使用字段:
? **student表:**stuid、name、age。
? **course表:**cid、name、credit。
? 关系表:学生编号、课程编号、成绩
要求:
可以找到一门课程,参加此次课程的所有学生信息和成绩
可以根据一个学生,找到所参加的所有课程和没门课程的一个成绩
第一步 编写实体类
class Student{
private int stuid;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(int stuid, String name, int age){
this.stuid = stuid;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getStuInfo(){
return "【Student】stuid = " + this.stuid +
",name = " + this.name +
",age = " +this.age ;
}
}
class Course{
private int cid;
private String name;
private double credit;
public Course(int cid, String name, double credit){
this.cid = cid;
this.name = name;
this.credit = credit;
}
public String getCouInfo(){
return "【Course】cid = " + this.cid +
",name = " + this.name +
",credit = " + this.credit;
}
}
class StudentCourse{//学生选课
private Student student;
private Course course;
private double score;
public StudentCourse(Student student, Course course, double score){
this.student =student;
this.course = course;
this.score = score;
}
public Student getStudent(){
return this.student;
}
public Course getCrouse(){
return this.course;
}
public double getScore(){
return this.score;
}
}
第二步 进行关系设计
class Student{
private int stuid;
private String name;
private int age;
private StudentCourse studentCourses [];
public Student(int stuid, String name, int age){
this.stuid = stuid;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setStudentCourses(StudentCourse []studentCourses){
this.studentCourses = studentCourses;
}
public StudentCourse[] getStudentCourses(){
return this.studentCourses;
}
public String getStuInfo(){
return "【Student】stuid = " + this.stuid +
",name = " + this.name +
",age = " +this.age ;
}
}
class Course{
private int cid;
private String name;
private double credit;
private StudentCourse studentCourses[];
public Course(int cid, String name, double credit){
this.cid = cid;
this.name = name;
this.credit = credit;
}
public void setStudentCourses(StudentCourse []studentCourses){
this.studentCourses = studentCourses;
}
public StudentCourse[] getstudentCourses(){
return this.studentCourses;
}
public String getCouInfo(){
return "【Course】cid = " + this.cid +
",name = " + this.name +
",credit = " + this.credit;
}
}
class StudentCourse{//学生选课
private Student student;
private Course course;
private double score;
public StudentCourse(Student student, Course course, double score){
this.student =student;
this.course = course;
this.score = score;
}
public Student getStudent(){
return this.student;
}
public Course getCrouse(){
return this.course;
}
public double getScore(){
return this.score;
}
}
第三步 开发需求
主函数main
public class Exam1_8{
public static void main(String args[]){
//第一步、设置类对象的关系
//1.分别创建各自对象实例化
Student stu1 = new Student(107,"Rock",13);
Student stu2 = new Student(108,"Joker",18);
Student stu3 = new Student(109,"Perke",22);
Course ca = new Course(1,"数据结构",4.0);
Course cb = new Course(2,"计算机操作系统",2.0);
Course cc = new Course(3,"SSM框架集合",3.0);
//2.设置学生和课程的关系
stu1.setStudentCourses(new StudentCourse[]{
new StudentCourse(stu1,ca,78.0),
});
stu2.setStudentCourses(new StudentCourse[]{
new StudentCourse(stu2,ca,87.0),
new StudentCourse(stu2,cb,79.0)
});
stu3.setStudentCourses(new StudentCourse[]{
new StudentCourse(stu3,ca,90.0),
new StudentCourse(stu3,cb,95.0),
new StudentCourse(stu3,cc,99.0)
});
//3.设置课程和学生的关系
ca.setStudentCourses(new StudentCourse[]{
new StudentCourse(stu1,ca,78.0),
new StudentCourse(stu2,ca,87.0),
new StudentCourse(stu3,ca,90.0)
});
cb.setStudentCourses(new StudentCourse[]{
new StudentCourse(stu2,cb,79.0),
new StudentCourse(stu3,ca,90.0)
});
cc.setStudentCourses(new StudentCourse[]{
new StudentCourse(stu3,cc,99.0)
});
//第二步、进行数据的取得
//可以找到一门课程,参加此次课程的所有学生信息和成绩
/*
【Course】cid = 1,name = 数据结构,credit = 4.0
学生名单:【Student】stuid = 107,name = Rock,age = 13,成绩:78.0
学生名单:【Student】stuid = 108,name = Joker,age = 18,成绩:87.0
学生名单:【Student】stuid = 109,name = Perke,age = 22,成绩:90.0
*/
System.out.println(ca.getCouInfo());
for(int i = 0 ;i < ca.getStudentCourses().length ; i++){
System.out.print("学生名单:"+ ca.getStudentCourses()[i].getStudent().getStuInfo());
System.out.println(",score = "+ ca.getStudentCourses()[i].getScore());
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------------------------------");
//可以根据一个学生,找到所参加的所有课程和没门课程的一个成绩
/*
【Student】stuid = 109,name = Perke,age = 22
选课列表:【Course】cid = 1,name = 数据结构,credit = 4.0,score = 90.0
选课列表:【Course】cid = 2,name = 计算机操作系统,credit = 2.0,score = 95.0
选课列表:【Course】cid = 3,name = SSM框架集合,credit = 3.0,score = 99.0
*/
System.out.println(stu3.getStuInfo());
for(int i = 0; i < stu3.getStudentCourses().length ; i++){
System.out.print("选课列表:" + stu3.getStudentCourses()[i].getCourse().getCouInfo());
System.out.println(",score = "+ stu3.getStudentCourses()[i].getScore());
}
}
}