Web原生组件注入
使用Servlet API
@ServletComponentScan注解
在 SpringBootApplication 上使用@ServletComponentScan 注解后,Servlet、Filter、Listener 可以直接通过 @WebServlet、@WebFilter、@WebListener 注解自动注册,无需其他代码
@ServletComponentScan("com.Servlet")
@SpringBootApplication
public class CrudApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CrudApplication.class, args);
}
}
Servlet的使用
@WebServlet("/dhy")
public class Myservlet extends HttpServlet
{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("servlet请求");
}
}
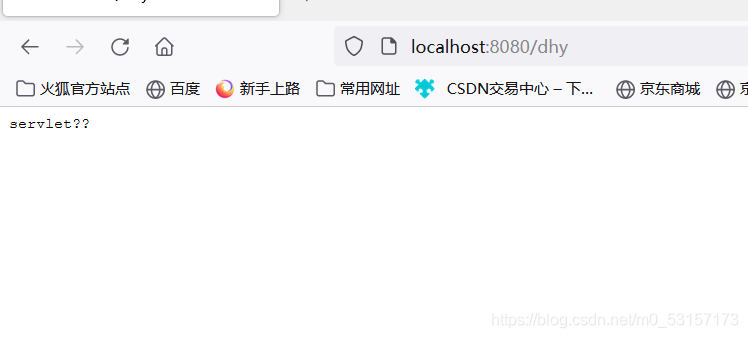
Filter的使用
@Slf4j
@WebFilter("/main.html")
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
log.info("初始化");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("放行");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("销毁");
}
}
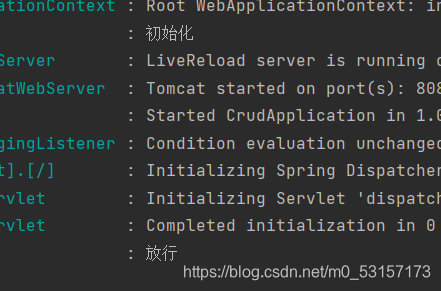
Listener的使用
@WebListener
public class MyFilter implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("项目初始化中");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("项目销毁中");
}
}
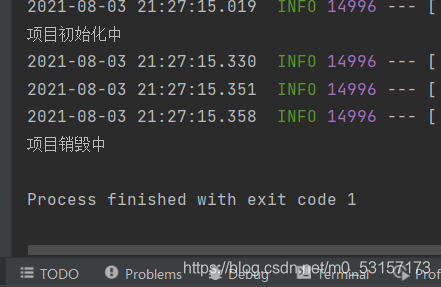
使用RegistrationBean
ServletRegistrationBean, FilterRegistrationBean, and ServletListenerRegistrationBean
@Configuration
public class MyServletConfig
{
//注册三大组件
//注册Servlet到容器中
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet()
{
ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean =
//第一个参数:注册哪一个Servlet
//第二个参数:这个Servlet映射哪些路径
new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(),"/myServlet");
return servletRegistrationBean;
}
//注册Filter到容器中
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter()
{
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean=new FilterRegistrationBean();
registrationBean.setFilter(new MyFilter());
//拦截路径
registrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/hello","/myServlet"));
return registrationBean;
}
//注册Listener到容器中
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener()
{
ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener> listener = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean<>(new MyListener());
return listener;
}
//定制嵌入式的Servlet容器相关的规则
@Bean
public WebServerFactoryCustomizer webServerFactoryCustomizer(){
return new WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>() {
//定制嵌入式的Servlet容器相关的规则
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
factory.setPort(8896);
}
};
}
}
这里需要注意一个小细节: 组件是单实例,还是多实例的,这里建议还是使用默认的单实例,防止每一次请求访问都要创建一个Servlet对象
解释为什么原生的Servlet会直接响应,没有经过spring的拦截器
SpringBoot帮我们自动启动SpirngMVC的时候,自动的注册SpringMVC的前端控制器
-
容器中自动配置了 DispatcherServlet 属性绑定到 WebMvcProperties;对应的配置文件配置项是 spring.mvc。
-
通过 ServletRegistrationBean 把 DispatcherServlet 配置进来。
-
默认拦截的是 / 路径,所有请求,包括静态资源,但不包括jsp , /*会拦截jsp
-
我们可以通过spring.mvc.servlet.path来修改SpringMVC前端控制器默认拦截的请求路径
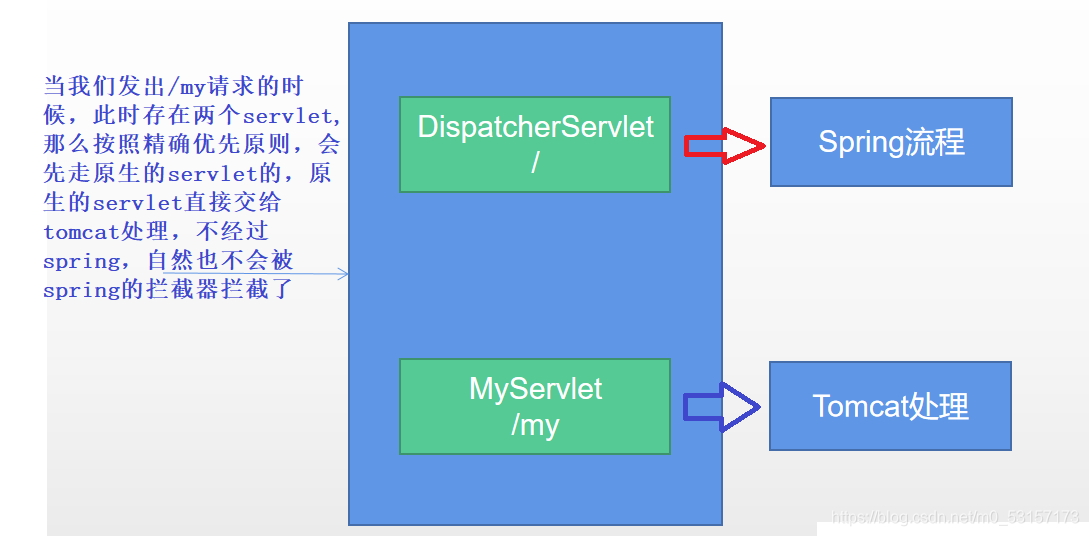
Tomcat-Servlet;
多个Servlet都能处理到同一层路径,精确优选原则
A: /my/
B: /my/1
配置spring.mvc.servlet.path 为dispatchSerlvet中拦截的路径
配置server.servlet.context-path为上下文路径(项目路径),访问的前缀
嵌入式Servlet容器
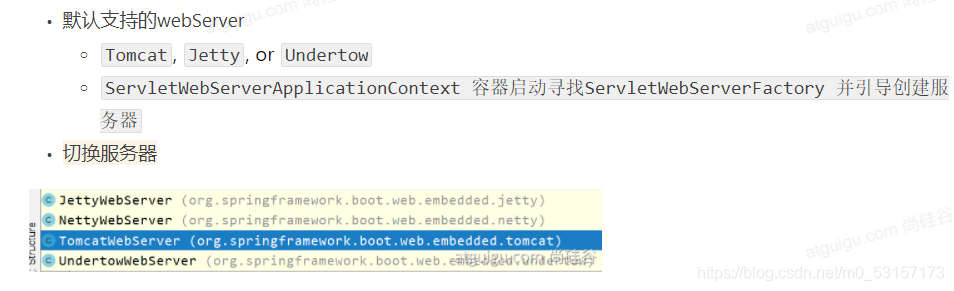
在pom.xml中排除tomcat依赖,再将要切换到的服务器的starter导入即可实现切换,
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
原理

定制Servlet容器—修改默认的属性值,例如端口号等
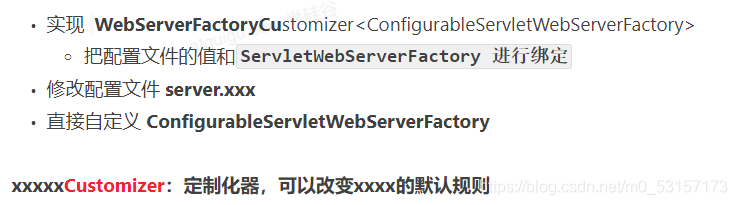
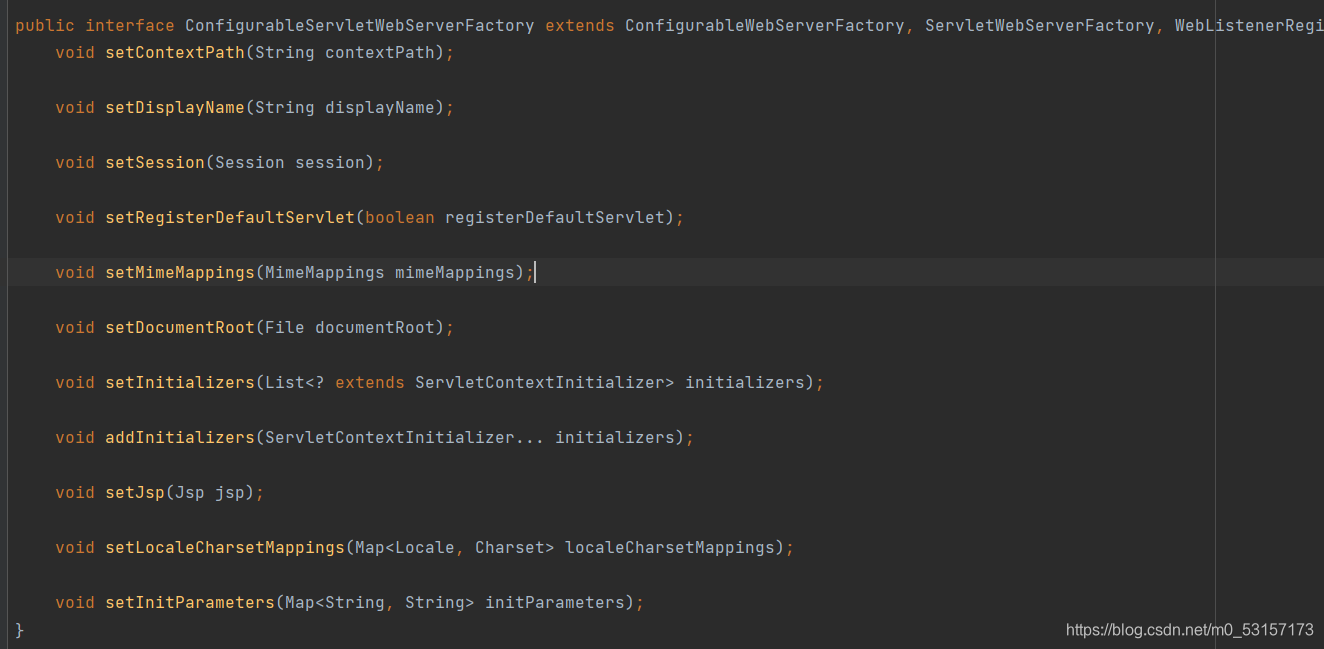
一般修改默认属性建议在全局配置文件中设置或者实现WebServerFactoryCustomizer接口,重写相关方法,并放入容器中完成
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerFactoryCustomizer;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CustomizationBean implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory> {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory server) {
server.setPort(9000);
}
}