目录
二、Mybatis-HelloWorld(idea-maven版)
一、Mybatis是什么?
Mybatis是支持定制化SQL、存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架,它避免了几乎所有JDBC代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集,它可以使用简单的XML或注解用于配置和原始映射,将接口和Java的POJO(普通的java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。
二、Mybatis-HelloWorld(idea-maven版)
1.创建Mybatis全局配置文件
<!--configuration核心配置文件
mybatis可以使用properties来引入外部properties配置文件内容
resource:引入类下面的资源
url:引入网络路径或磁盘路径下的资源
-->
<configuration>
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"></properties>
<!--
environments:环境们,mybatis可以配置多种环境,default指定使用某种环境,可以达到快速切换环境
environment:配置一个具体的环境信息,必须有两个标签,id代表当前环境的唯一表示
transactionManager:事务管理器,type里是事务管理器类型,有JDBC和MANAGED两类,可以自定义事务管理器
dataSource:数据源,type里是数据源类型:UNPOOLED、POOLED、JNDI,自定义数据源实现DataSourceFactory接口
-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- databaseIdProvider标签:支持多数据库厂商的
type="DB_VENDOR":VendorDatabaseIdProvider
作用就是得到数据库厂商的表示(驱动getDatabaseProductName()),mybatis就能
根据数据库厂商标识来执行不同的sql
-->
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<!--为不同的数据库厂商起别名-->
<property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="oracle"/>
</databaseIdProvider>
<!--将我们写好的sql映射文件(EmpMapping.xml)一定要注册到(mybatis-config.xml)中-->
<!--
注册接口 Class:引用(注册)接口
1.有sql映射文件,映射文件名必须和接口同名,并且放在与接口同一目录下
2.没有sql映射文件,所有的sql都是利用注解写在接口上
推荐:比较重要的复杂的Dao接口我们来写sql映射文件,不重要的简单的Dao接口未为了开发速度可以使用注解
-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="EmpMapping.xml"/>
<!--<mapper class=""></mapper>-->
<!--批量注册-->
<!--这种方式要求SQL映射文件名必须和接口名相同并且在同一目录下-->
<!--<package name="com.atguigu.dao"/> 是通过class注册的方式对包下所有进行注册-->
</mappers>
</configuration>注意:Mybatis核心配置文件声明标签是由顺序的,否则报错,顺序如下:
configuration (properties?, settings?, typeAliases?, typeHandlers?, objectFactory?, objectWrapperFactory?, reflectorFactory?, plugins?, environments?, databaseIdProvider?, mappers?)jdbc.properties:
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=1234562.创建SQL映射文件
<!--namespace:绑定一个对应的Dao/Mapper接口-->
<mapper namespace="com.atguigu.dao.EmployeeMapping">
<!--id对应dao接口的方法-->
<!--databseId标签指明我们要连接的数据库的别名-->
<!--id:绑定那个方法使用这个select resultType:表示返回值类型-->
<select id="getEmpList" resultType="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee" databaseId="mysql">
select id,last_name lastName,gender,email from t_emp
</select>
</mapper>3.创建SqlSession对象
(1)因为SqlSession对象会创建的很频繁,所以我们先写一个获取(getSqlSession)的工具类方法
public class MybatisUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
static{
try {
//使用Mybatis第一步:获取sqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
* 既然有了SqlSessionFactory,顾名思义,我们就可以从中获得SqlSession的实例了
* SqlSession完全包含了面向数据库执行SQL命令所需要的所有方法
* */
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
return sqlSession;
}
}(2)测试
* 1、接口式编程
* 原生: Dao ===> DaoImpl
* mybatis Dao ===> xxMapper.xml
* 2、SqlSession代表和数据库的一次会话,用完必须关闭
* 3、SqlSession和Collection一样都是非线程安全的,每次使用都应该去获取新的对象
* 4、mapper(以前的xxxDao接口)接口没有实现类,但将接口和xml进行绑定mybatis会为这个接口生成一个代理对象(getMapper)
* 5、两个重要的配置文件
* ①mybatis的全局配置文件:包含数据库连接信息,事务管理信息等系统运行环境
* ②sql映射文件:保存了每一个sql语句的映射信息;将sql抽取出来(如EmpMapping.xml)
* */
public class EmployeeMappingTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
try{
//第一步:获取SqlSession对象
// sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//方式一:getMapper
EmployeeMapping mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapping.class);
List<Employee> empList = mapper.getEmpList();
//方式二:不推荐使用
// sqlSession.selectList("com.atguigu.dao.EmployeeMapping.getEmpList");
for (Employee employee : empList) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
}finally{
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
注意:SqlSession的实例是非线程安全的,因此不能被共享,sqlSession用完一定要关闭,一个sqlSession对象代表和数据库的一次会话。
4.映射文件xxxMapper.xml
(1)参数传递:
①单个参数:可以接受基本类型、对象类型、集合类型的值。这种情况Mybatis可以直接使用这个参数,不需要进行任何处理。
②多个参数:任意多个参数,都会被Mybatis重新包装成为一个Map传入。Map的key是param1,param2...或0,1...,值就是参数的值。
③命名参数:为参数使用@Param起一个名字,Mybatis就会将这些参数封装进map中,key就是我们自己制定的名字。
④#{key}获取参数的值预编译到sql语句中,安全。${key}获取的参数拼接到sql中会有sql注入问题
(2)resultMap:定义结果集映射规则 resultMap="自定义resultMap的id值"
<!--自定义某个javaBean的封装规则
type:自定义规则的java类型
id:唯一id方便引用
-->
<resultMap type="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee" id="MyEmpPlus">
<!--指定主键列的封装规则
id:定义主键会底层有优化
colum:指定那一列
property:指定对应的javaBean属性
result:定义普通列封装规则
-->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="last_name" property="lastName"/>
<!--其他列名和javaBean属性名一样可以不写,自动封装,但建议把全部都写上-->
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
</resultMap>
<!--resultMap:定义结果集映射规则-->
<select id="getEmpById" resultMap="MyEmpPlus">
select * from t_emp where id=#{id}
</select>三、动态SQL
1.什么是动态SQL?
动态SQL是Mybatis强大特征之一,极大的简化了我们拼装SQL的操作。动态SQL元素和使用JSTL或其他类似基于XML的文件处理器相似。Mybatis采用功能强大的基于OGNL的表达式来简化操作。
2.OGNL表达式
(1)if:
<select id="getEmpsByConditionIf" resultType="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee">
select * from t_emp where 1=1
/*test:判断表达式(OGNL)
OGNL参照PPT或者官方文档 c:if test 从参数中取值进行判断
遇见特殊符号应该去屑转义字符
*/
<if test="id!=null">and id=#{id}</if>
<if test="last_name!=null and last_name!=''">
and last_name like #{lastName}
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">and gender=#{gender}</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=''">and email=#{email}</if>
</select>注意:查询的时候如果有些条件没带可能SQL拼装会有问题,如上:如果参数没带id就会出现where and last_name like...。解决方法:
①给where后面加上1=1,以后的条件都为and xxx
②mybatis使用where标签来将所有的查询条件包括在内,mybatis就会将where标签多出来的第一个and去掉。
(2)trim(where/set)
<select id="getEmpsByConditionTrim" resultType="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee">
select id,last_name lastName,gender,email from t_emp
/*后面多出的and或者or where 标签不能解决
prefix 前缀:trim标签体中是整个字符串拼串的结果,prefix给拼串后的整个字符
串加一个前缀
prefixOverrides:前缀覆盖,去掉整个字符串前面多余的字符
suffix suffixOverrides
*/
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and">
<if test="id!=null">id=#{id} and</if>
<if test="lastName!=null and lastName!=''">
last_name like #{lastName} and
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">gender=#{gender} and</if>
<if test="email!=null and email.trim()!=''">email=#{email}</if>
</trim>
</select><update id="updateEmp">
update t_emp
/*第一种使用set去掉多余逗号的写法*/
<!--<set>
<if test="lastName!=null">last_name=#{lastName},</if>
<if test="gender!=null">gender=#{gender},</if>
<if test="email!=null">email=#{email}</if>
</set>-->
/*第二种使用trim标签*/
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="lastName!=null">last_name=#{lastName},</if>
<if test="gender!=null">gender=#{gender},</if>
<if test="email!=null">email=#{email}</if>
</trim>
</update>(3)choose:只会拼接when中的一个条件,例:传进来有id和lastName则只会拼接where id=?
<select id="getEmpsByConditionChoose" resultType="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee">
select * from t_emp
<where>
<choose>
<when test="id!=null">id=#{id}</when>
<when test="lastName!=null">last_name like #{lastName}</when>
<when test="email!=null">email=#{email}</when>
<otherwise>gender="女"</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>(4)foreach:
<select id="getEmpsByConditionForeach" resultType="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee">
select * from t_emp <!--wher id in(1,2,3..) Arrays.asList(1,2,3)-->
<!--collection:指定要遍历的集合,单个list传进来最好给他加个别名@param(ids);
list类型的参数会特殊处理封装在map中,map的key就叫list
item:将当前遍历出的元素赋值给指定的变量。separator:每个元素之间的分隔符
open:遍历出所有结果拼接一个开始的字符。close:遍历出所有结果拼接一个结束的字符
index:索引。遍历list的时候index就是索引,item就是当前值
遍历map的时候index就是map的key,item就是map的值
#{变量名}就能取出变量的值也就是当前遍历出的元素
-->
<foreach collection="ids" item="item_id" separator=","
open="where id in(" close=")">
#{item_id} <!--遍历出传入的list集合里的值1,2,3-->
</foreach>
</select>?(5) 批量保存
<!--批量保存,可以foreach遍历,mysql支持values(),(),()语法-->
<select id="addEmps">
insert into t_emp(last_name,gender,email,d_id) values
<foreach collection="add" item="emp" separator=",">
(#{emp.lastName},#{emp.gender},#{emp.email},#{emp.dept.id})
</foreach>
</select>
<!--方式二:这种方式需要数据库连接属性allowMultiQuery=true-->
<!-- <select id="addEmps">
<foreach collection="add" item="emp" separator=";">
insert into t_emp(last_name,gender,email,d_id) values
(#{emp.lastName},#{emp.gender},#{emp.email},#{emp.dept.id})
</foreach>
</select>-->?(6)?两个内置参数
<!--两个内置参数:不只是方法传递过来的参数可以被用来判断,取值
mybatis默认还有两个内置参数:_parameter:代表整个参数
单个参数:_parameter就是这个参数 多个参数:参数就会被封装为一个map,就代表这个map
_parameter:如果配置了databaseIdProvider标签,
_databaseId就是代表当前数据的别名mysql或oracle
-->
<select id="getEmpsInnerParameter" resultType="com.atguigu.pojo.Employee">
<!-- bind:可以将ODNL表达式的值绑定到一个变量中,方便后来引用这个变量的值 -->
<bind name="_lastName" value="'%' + lastName + '%'"></bind>
<if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">
select * from t_emp
<if test="_parameter!=null">
where last_name like #{lastName}
</if>
</if>
<if test="_databaseId=='oracle'">
<!--oracle的sql语句-->
</if>
</select>?(7) sql标签抽取可重用的sql语句
<!--sql标签可以抽取可重用的sql片段。方便后面引用
1.sql抽取:经常将要查询的列名,或者插入用的列名抽取出来方便引用
2.include来引用已经抽取的sql <include refid=""></include> refid的值就是sql的id值
3.include还可以自定义一些property,sql标签内部就能使用自定义的属性(不常用)
${prop},#{不能使用这种方式}
-->
<sql id="insertColumn">
<if test="_databaseId=='mysql'">
last_name lastName,gender,email,d_id dId
</if>
<if test="_databaseId=='oracle'">
<!--oracle的sql语句-->
</if>
</sql>注意:xml中特殊字符如:",>,<等这些都需要转义字符
四、Mybatis-缓存机制
1.简介
Mybatis包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。缓存可以极大的提升查询速率。Mybatis中定义了两级缓存:一级缓存 和二级缓存;
(1)默认情况下,只有一级缓存(SqlSession级别的缓存,也称为本地缓存)开启
(2)二级缓存需要手动开启和配置,他是基于namespace级别的缓存
(3)为了提高扩展性。Mybatis定义了缓存接口Cache。我们可以通过实现接口Cache来定义缓存
2.一级缓存
(1)简介:
①即本地缓存,作用域为SqlSession,即同一次数据库会话中。当SqlSession关闭或者Session flush,该SqlSession所有Cache将被清空。
②本地缓存不能被关闭,但可以调用clearCache()来清空本地缓存,或者改变缓存的作用域
③在mybaits3.1之后,可以配置本地缓存的作用域,在mybaits.xml中配置
(2)本地缓存失效的四种情况
①不同的SqlSession对应不同的一级缓存
②同一个SqlSession但是查询条件不一样
③同一个SqlSession两次查询之间执行了任意一个增删改操作
④同一个SqlSession两只查询之间手动情况了缓存(clearCache())
3.二级缓存
(1)简介:
①二级缓存,全局作用缓存域,二级缓存默认不开启,需要手动在Mybatis核心xml文件中配置
<setting name= "cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
②Mybaits提供二级缓存的接口以及实现,缓存实现要求POJO实现Serializable接口
public class Employee implements Serializable
③二级缓存存在SqlSession关闭或提交后才会生效,作用于namespace中的所有增删改查。
注意:当在某一个作用域(一级缓存、二级缓存)进行了CUD操作后,默认该作用域下所有select中的缓存将被clear
五、逆向工程
1.简介
Mybatis Generator:简称MBG,是一个专门为Mybaits框架使用者定制的代码生成器,可以快速的根据表生成对应的映射文件,接口以及bean类。支持基本的增删改查,以及QBC风格的条件查询,但是表连接,存储过程等这些复杂的sql的定义需要我们手工编写。
2.MBG的使用
(1)引入相关依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator</artifactId>
<version>1.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.49</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>(2)编写MBG的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd">
<generatorConfiguration>
<context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<commentGenerator>
<!-- 是否去除自动生成的注释 true:是 : false:否 -->
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="true" />
</commentGenerator>
<!--①配置数据库连接信息-->
<jdbcConnection
driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mbg?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8"
userId="root"
password="123456">
</jdbcConnection>
<!--javaBean(pojo)的生成策略-->
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.xxx.pojo"
targetProject=".\src\main\java">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false"/>
<property name="trimStrings" value="true"/>
</javaModelGenerator>
<!--映射文件的生成策略-->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="mybatis.mapper" targetProject=".\src\main\resources">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/>
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!--dao接口java文件的生成策略-->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="com.xxx.dao"
targetProject=".\src\main\java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/>
</javaClientGenerator>
<!--数据表与javaBean的映射-->
<!--配置下列Example=false表示不生成Example的方法-->
<table tableName="t_user" domainObjectName="User"
enableCountByExample="false"
enableUpdateByExample="false"
enableDeleteByExample="false"
enableSelectByExample="false"
selectByExampleQueryId="false"
></table>
<table tableName="t_book" domainObjectName="Book"
enableCountByExample="false"
enableUpdateByExample="false"
enableDeleteByExample="false"
enableSelectByExample="false"
selectByExampleQueryId="false"
></table>
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>注意:Context标签
①targetRuntime=''Mybatis3''可以生成带条件的增删改查
②targetRuntime="Mybatis3Simple"可以生成基本的增删改查,如果再次生成,建议将之前生成的数据删除,避免xml向后追加内容出现问题。
(3)在测试中编写生成器代码
@Test
public void test(){
List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<String>();
boolean overwrite = true;
File configFile = new File("mbgxml配置文件");
ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);
DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);
MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config,
callback, warnings);
myBatisGenerator.generate(null);
}六、Mybatis-工作原理
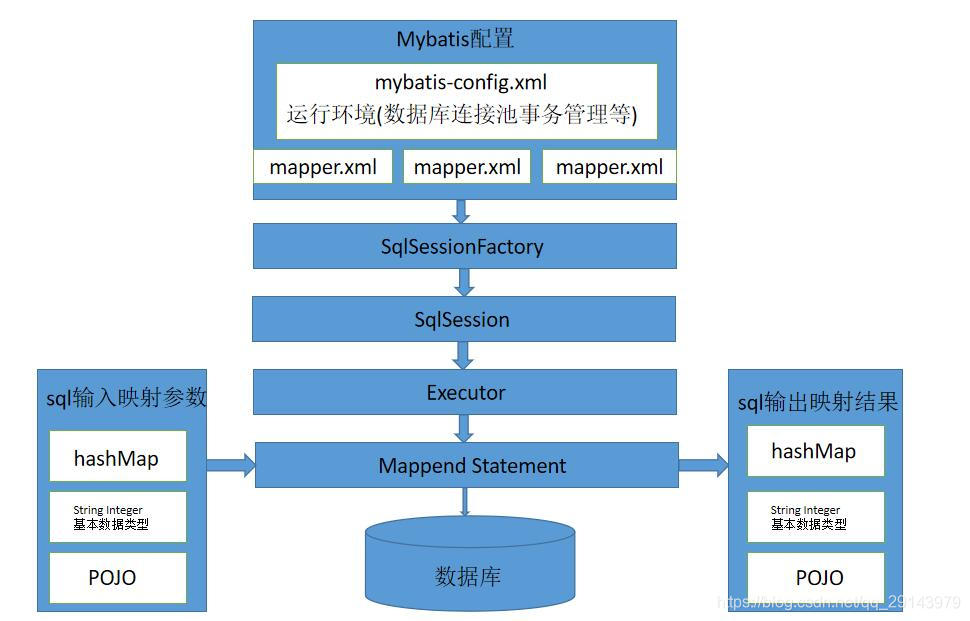
?七、Mybatis-插件开发
(1)简介
①Mybatis在四大对象创建的过程中,都会有插件进行介入。插件可以利用动态代理机制一层层的包装目标对象,从而实现在目标对象执行目标方法之前进行拦截的效果。
②Mybatis允许在已映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用
③默认情况下,Mybatis允许使用插件来拦截的方法调用包括:
* Executor? ? ? ? * ParameterHandler? ? ? ? * ResultSetHandler? ? ? ? * StatementHandler
(2)编写插件开发步骤
①编写插件实现interceptor接口,并使用@Intercepts注解完成插件签名
/*
*完成插件签名:告诉Mybatis当前插件用来拦截哪个对象的哪个方法
* */
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class,
method = "parameterize",args =java.sql.Statement.class)
})
public class MyFirstPlugin implements Interceptor {
/*
* interceptor:拦截:拦截目标对象的目标方法的执行
* */
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
//动态的改变了一下sql运行的参数,以前1号员工,实际从数据库查询3号员工
Object target = invocation.getTarget();//target拦截到的对象
System.out.println("拦截器拦截到的对象:" + target);
//拿到StatementHandler===>ParameterHandler===>parameterObject
//拿到target的元数据
MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(target);
System.out.println("target里面的元数据是:" + metaObject);
//获取参数
Object value = metaObject.getValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject");
System.out.println("获取传入的参数为:" + value);
//设置参数(占位符里的值)
metaObject.setValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject",3);
//执行目标方法,放行拦截到的target方法
//为拦截到的对象放行,如果不调用invocation.proceed()这个对象就不会被执行了
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
return proceed;
}
//plugin:包装目标对象的:包装:为目标对象创建一个代理对象
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
//我们可以借助plugin的wrap方法来实现当前Interceptor包装我们目标对象,代理对象
Object wrap = Plugin.wrap(target, this);
//返回为当前target创建的动态代理
return wrap;
}
//setProperties:将插件注册时的property属性设置进来
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}②在全局配置文件中注册插件
<!--plugins:注册插件-->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.atguigu.pojo.MyFirstPlugin">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>? (3) 插件原理
①按照插件注解声明,按照插件配置顺序调用插件plugin方法,生成被拦截对象的动态代理。
②多个插入依次生成目标对象的代理对象,层层包裹,先声明的先包裹,形成代理链。
③目标方法执行时,依次从外到内执行插件的intercept方法。
④多个插件情况下,我们往往需要在某个插件中分离出目标对象。可以借助Mybaits提供的SystemMetaObject类来进行获取最后一层的h以及target属性的值。
(4)扩展-Mybatis使用场景(插件)
①PageHelper插件进行分页:Page是Mybatis中非常方便的第三方分页插件。
②使用步骤:
* 导入相关jar包
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.2.1</version>* 在Mybaits全局配置文件中配置分页插件
<!--注册pageHelper分页插件-->
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
</plugin>
</plugins>* 使用PageHelper提供的方法进行分页
* 可以使用更强大的PageInfo封装返回结果
/*
pageHelper分页插件的使用
1.导入pageHelper依赖
2.在mybatis配置xml拦截器plugin插件
3.调用PageHelper.startPage
注意:第三步一定要放在得到数据结果集之前
* */
public class EmployeeMappingTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
try{
//第一步:获取SqlSession对象
// sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//方式一:getMapper
EmployeeMapping mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapping.class);
Page<Object> page = PageHelper.startPage(1, 2);
List<Employee> empList = mapper.getEmpList();
//第二个参数可以设置要连续显示几页
PageInfo<Employee> info = new PageInfo<>(empList,2);
// System.out.println("当前页码:" + page.getPageNum());
// System.out.println("当前页数据数:" + page.getPageSize());
// System.out.println("总的数据数:" + page.getTotal());
// System.out.println("总页码:" + page.getPages());
System.out.println("当前页码:" + info.getPageNum());
System.out.println("当前页数据数:" + info.getPageSize());
System.out.println("总的数据数:" + info.getTotal());
System.out.println("总页码:" + info.getPages());
System.out.println("是否是第一页:" + info.isIsFirstPage());
System.out.println("连续显示的页码");
int[] nums = info.getNavigatepageNums();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
System.out.print(nums[i] + ",");
}
//方式二:不推荐使用
// sqlSession.selectList("com.atguigu.dao.EmployeeMapping.getEmpList");
for (Employee employee : empList) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
}finally{
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
}(5)批量操作
/*
* 批量插入:
* 可以在创建SqlSession的时候,在SqlSessionFactory.openSession()的参数设置为ExecutorType.BATCH
* */
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
try{
EmployeeMapping mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapping.class);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
mapper.addEmp(new Employee(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(1,5),"男","123@qq.com"));
}
sqlSession.commit();
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}