JavaWeb-03-Servlet-05-HttpServletRequest接口
1.HttpServletRequest简介
- HttpServleRequest接口来自于Servlet规范中,存在于Tomcat中的servle-api.jar,具体位置是【javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest】。
- HttpServletRequest接口实现类由Http服务器负责提供。
- HttpServletRequest接口负责在doGet()/doPost()方法执行时读取Http请求协议包中的信息。
- 开发人员习惯将HttpServletRequest接口修饰的对象称为【请求对象】。
2.请求对象的功能
- 可以读取Http请求协议包里【请求行】中的信息。
- 可以读取保存在Http请求协议包中【请求头】或者【请求体】中的请求参数信息。
- 可以代替浏览器向Http服务器申请资源文件调用。
3.功能实现
3.1读取【请求行】中的信息
3.1.1读取请求行里的URL和Method信息
新建项目,创建一个Servlet接口实现类OneServlet,重写doGet方法。
在方法体内,通过请求对象request读取请求行内的【URL】信息和【Method】信息。
package com.tsccg.controller;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: TSCCG
* @Date: 2021/08/13 17:56
*/
public class OneServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.通过请求对象,读取【请求行】里的【URL】信息
String url = request.getRequestURL().toString();
//2.通过请求对象,读取【请求行】里的【Method】信息
String method = request.getMethod();
System.out.println("url:" + url);
System.out.println("method:" + method);
}
}
通过浏览器向服务器发送一次请求,在后台成功读取到请求的URL和Method信息。

3.1.2读取【请求行】里的URI信息
什么是URI?
URI:资源文件精准定位地址。
- 在请求行内并没有URI这个属性
- URI其实就是将URL中有关资源路径的字符串截取下来。
- URI格式:【/网站名/资源文件名】,如【/MyWeb/one】
- URI用于让Http服务器对被访问的资源文件进行定位。
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.通过请求对象,读取【请求行】里的【URL】信息
String url = request.getRequestURL().toString();
//2.通过请求对象,读取【请求行】里的【Method】信息
String method = request.getMethod();
//3.通过请求对象,读取【URI】信息
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
System.out.println("url:" + url);
System.out.println("method:" + method);
System.out.println("uri:" + uri);
}
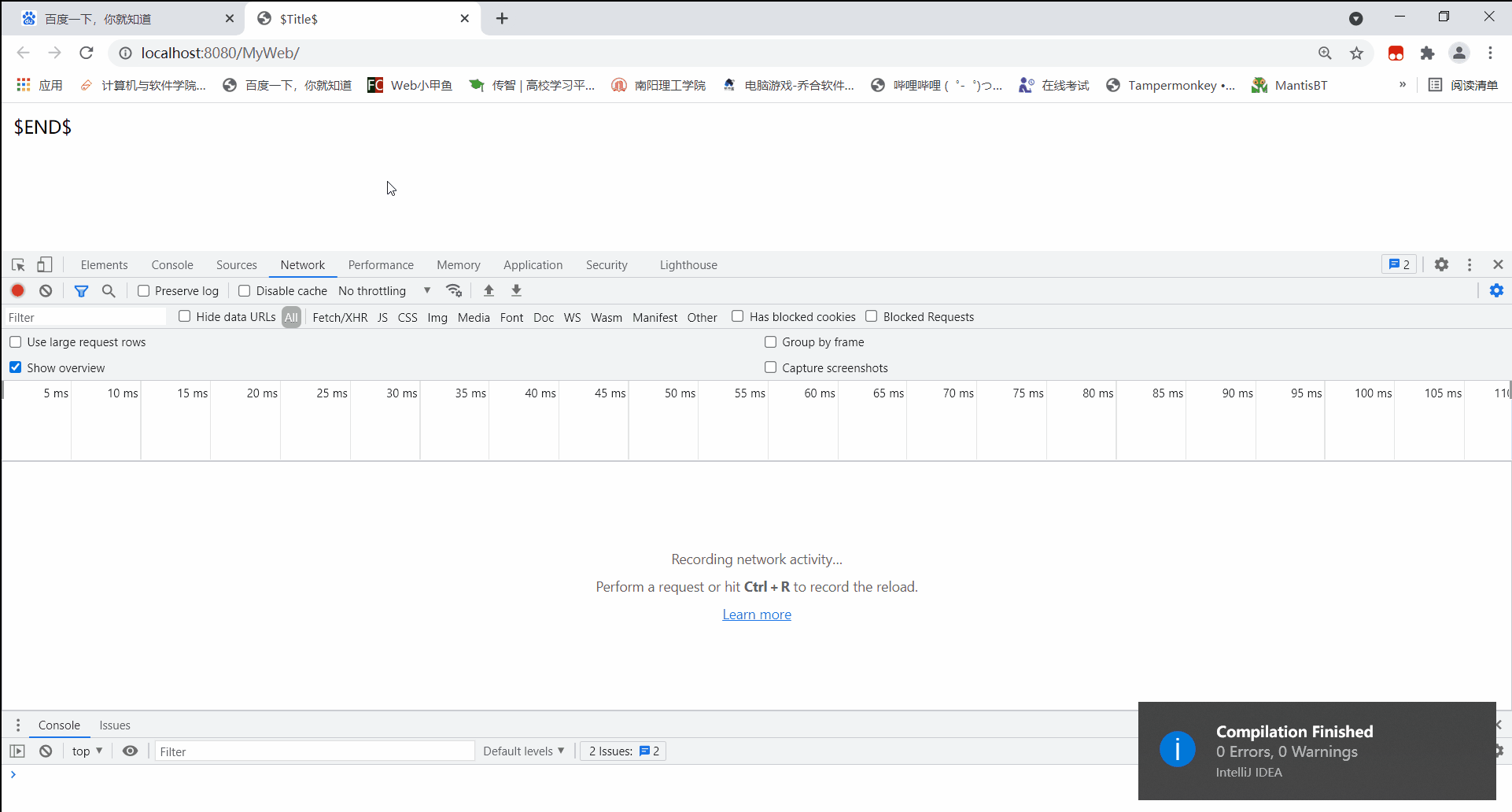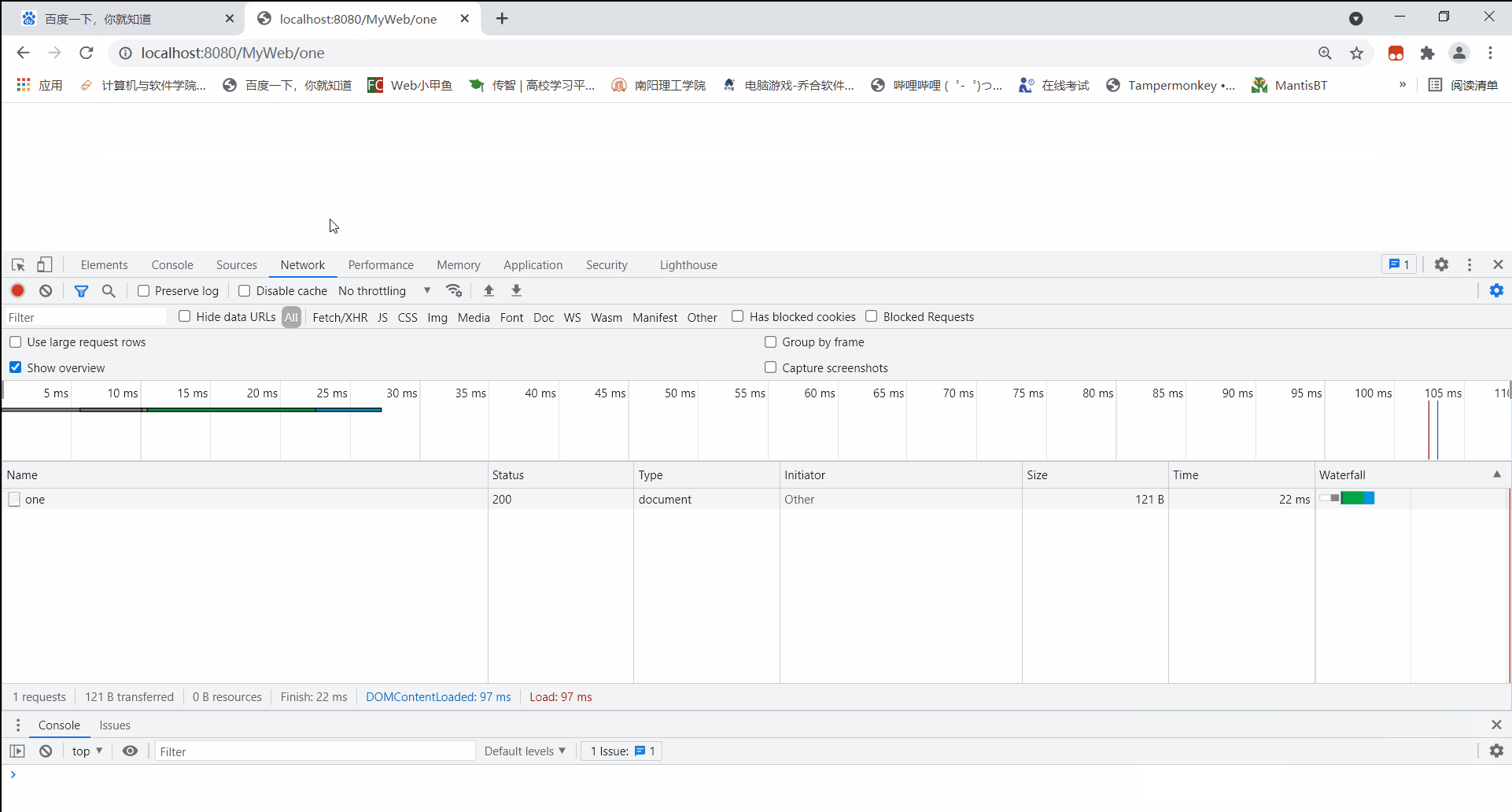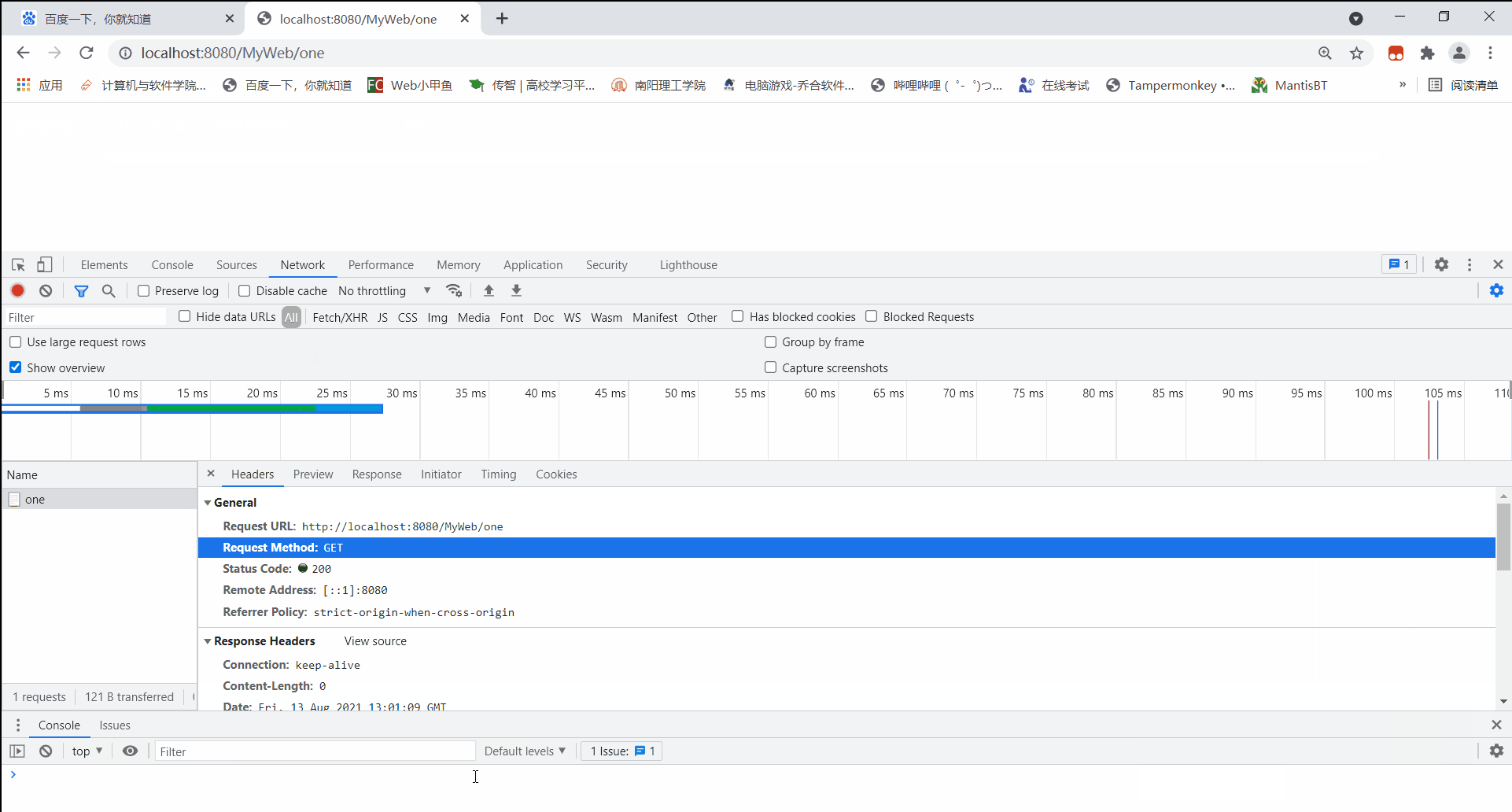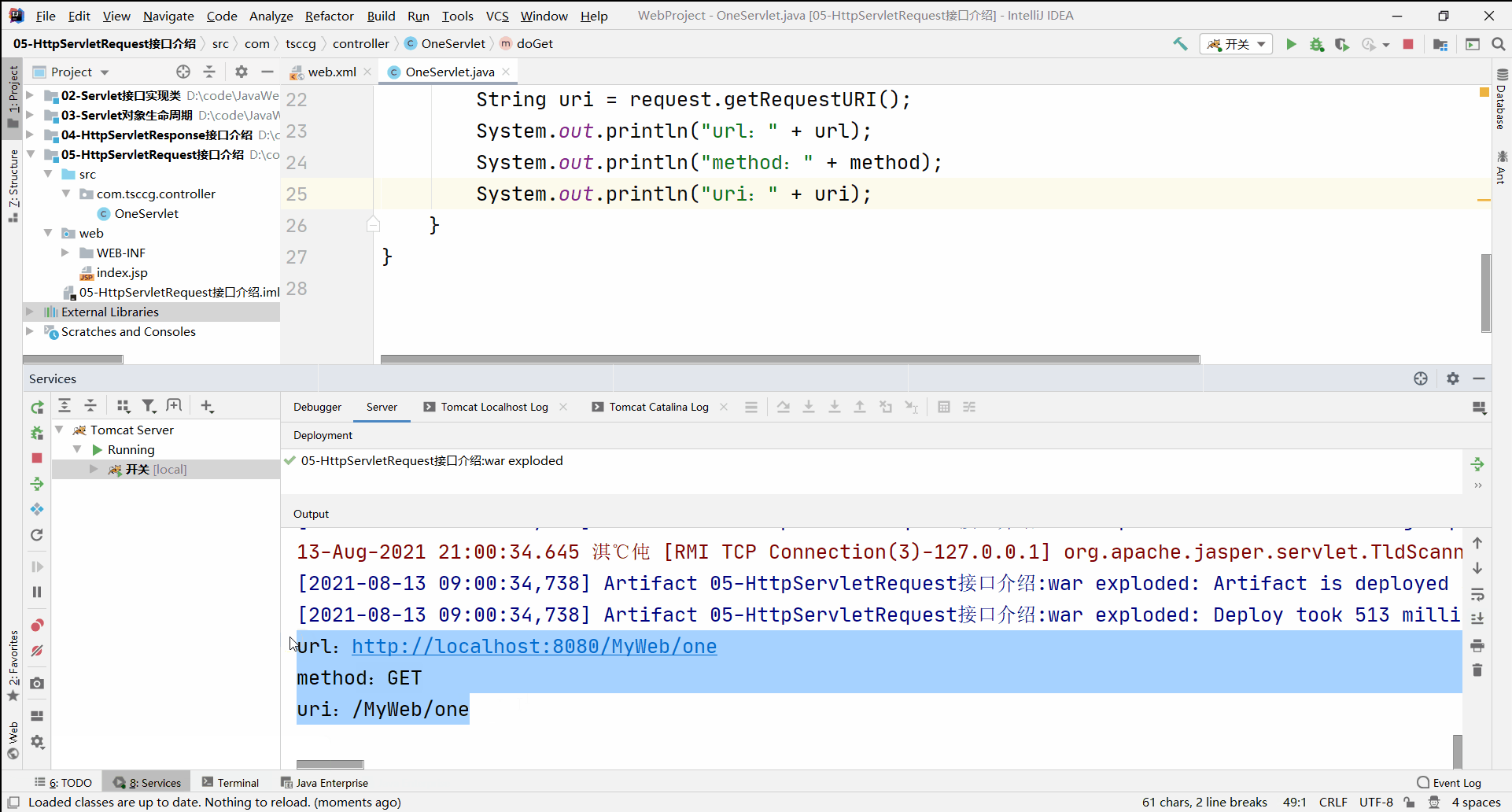
通过浏览器访问OneServlet后读取到结果:
url:http://localhost:8080/MyWeb/one
method:GET
uri:/MyWeb/one
3.2读取【请求头】或【请求体】中的请求参数信息
3.2.1读取【请求头】内的所有的请求参数信息
新建一个Servlet接口实现类TwoServlet,重写doGet方法,在方法中完成如下操作:
- 先通过请求对象,调用getParameterNames方法,返回一个枚举对象,里面存放着【请求头】中所有的【请求参数名】
- 然后使用for循环遍历该枚举对象,方法类似于迭代器
- 在循环体内通过枚举对象调用nextElement方法获取当前【请求参数名】,需要将返回结果强转为String类型
- 获取当前【请求参数名】后,通过请求对象调用getParameter方法获取【请求参数值】,该方法需要传入当前的【请求参数名】
- 将【请求参数名】和【请求参数值】打印输出。
package com.tsccg.controller;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
/**
* @Author: TSCCG
* @Date: 2021/08/13 21:40
* 通过请求对象,获取获取【请求头】或【请求体】中的【请求参数】
*/
public class TwoServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.通过请求对象,获取【请求头】中【所有请求参数名】
Enumeration paramNames = request.getParameterNames();//将所有请求参数名保存到一个枚举对象中并返回
//遍历所有请求参数名,遍历方式类似于迭代器
while (paramNames.hasMoreElements()) {
//获取当前请求参数名
String paramName = (String)paramNames.nextElement();
//2.通过请求对象,获取请求参数值,需要请求参数名
String value = request.getParameter(paramName);
System.out.println("请求参数名:" + paramName + " 请求参数值:" + value);
}
}
}
启动服务器,在浏览器地址栏内输入【请求地址】并携带【请求参数】。
http://localhost:8080/MyWeb/two?username=zhangsan&password=123
回车。
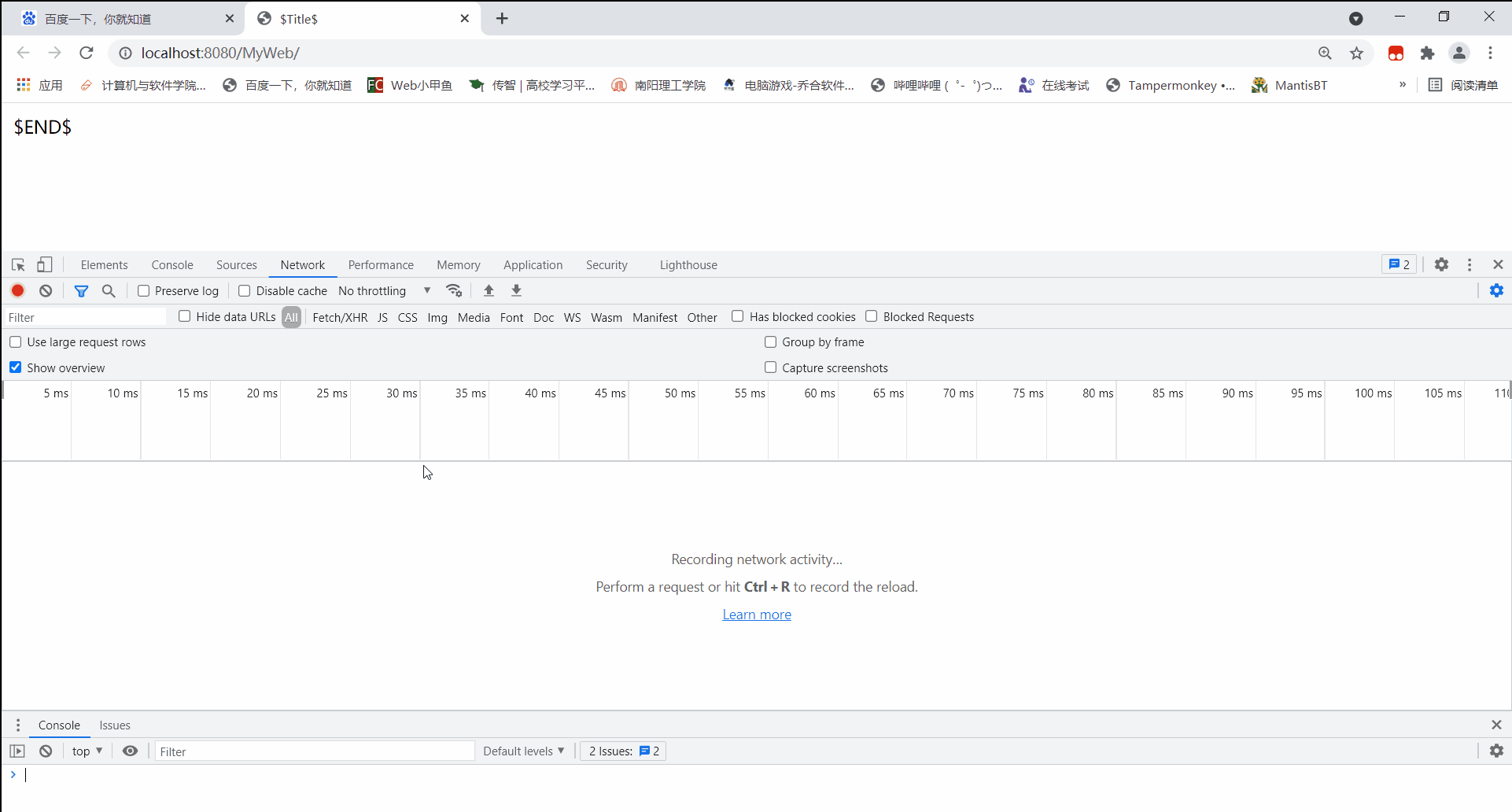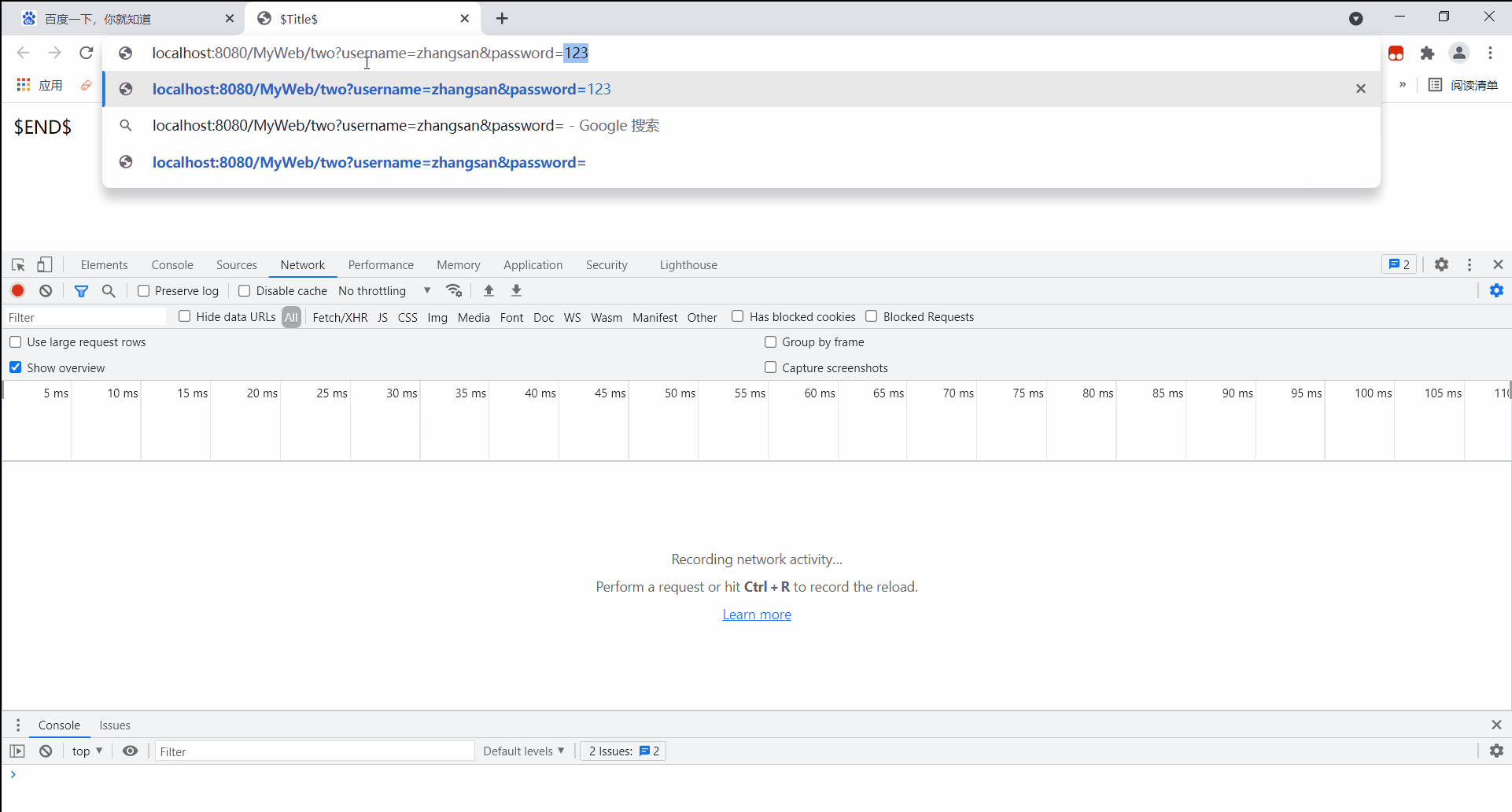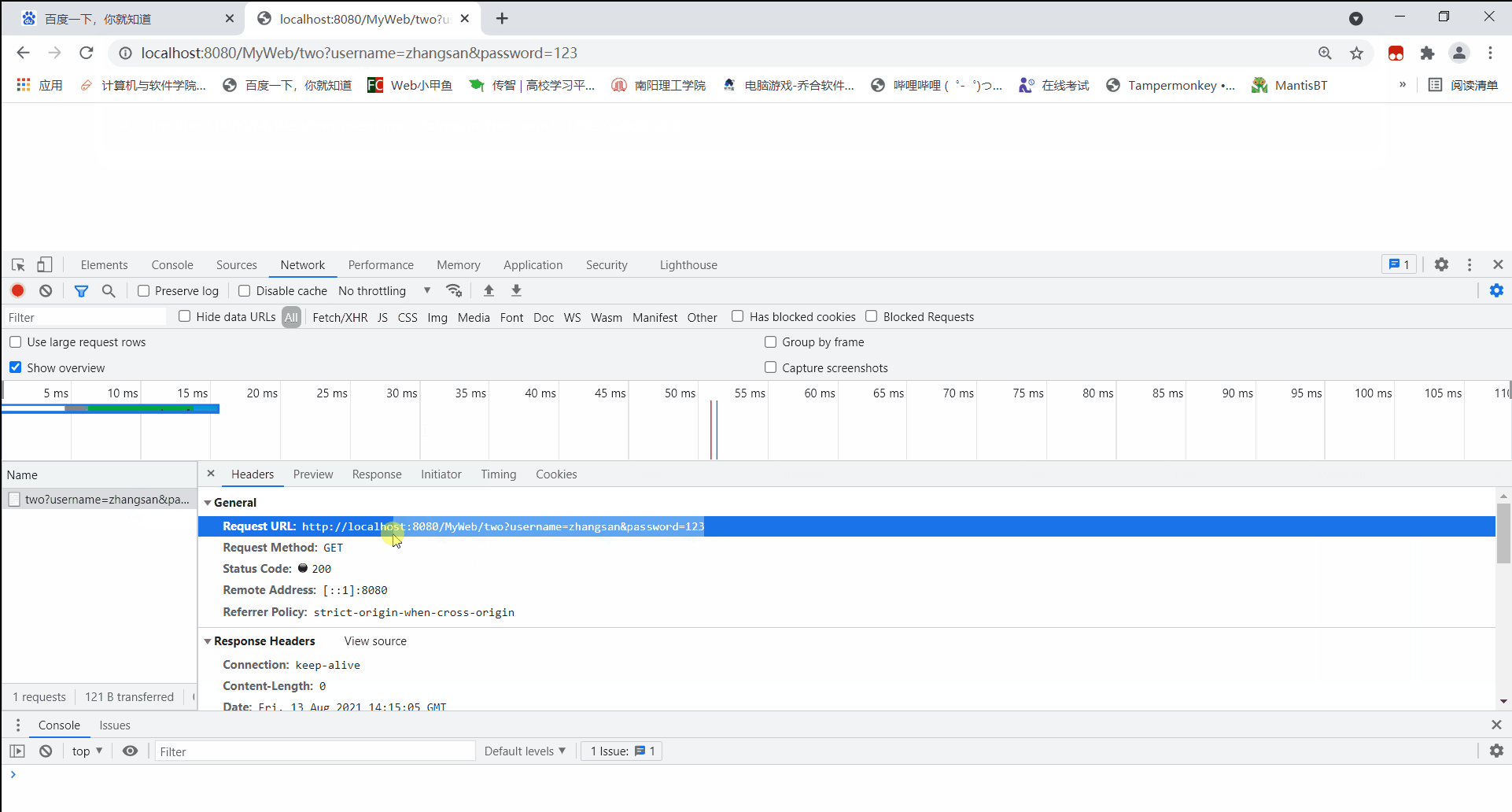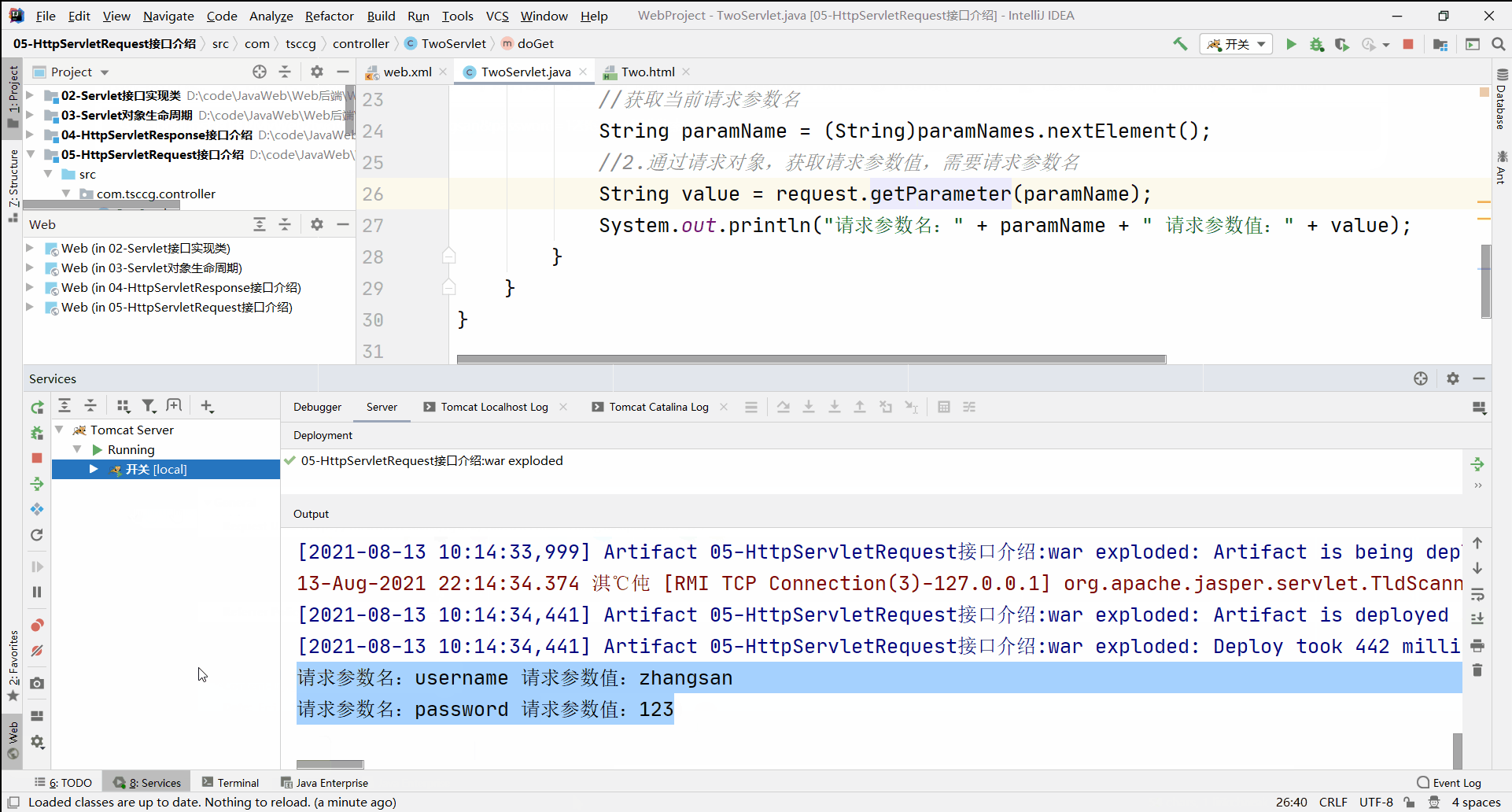
后台读取到的信息:
请求参数名:username 请求参数值:zhangsan
请求参数名:password 请求参数值:123
凡是通过浏览器地址栏发送的请求,【请求方式】都是GET,【请求参数信息】会存在【请求头】中。
3.2.2读取【请求体】内的请求参数信息
新建一个Servlet接口实现类ThreeServlet,重写doGet和doPost方法。
分别在两个方法体内读取请求参数信息:
package com.tsccg.controller;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: TSCCG
* @Date: 2021/08/13 22:29
*/
public class ThreeServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//通过请求对象,获取【请求体】里的请求参数值
String password = request.getParameter("password");
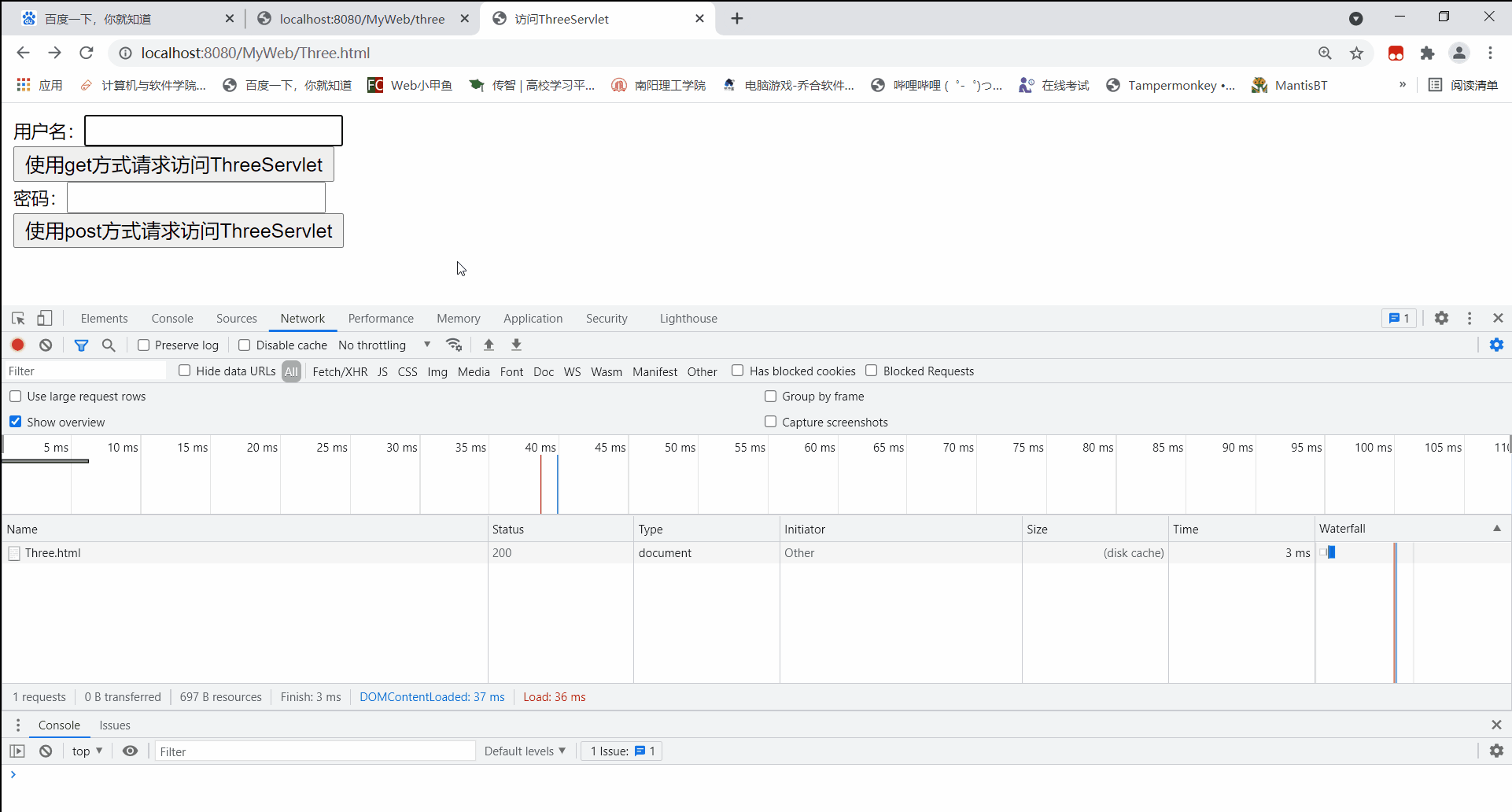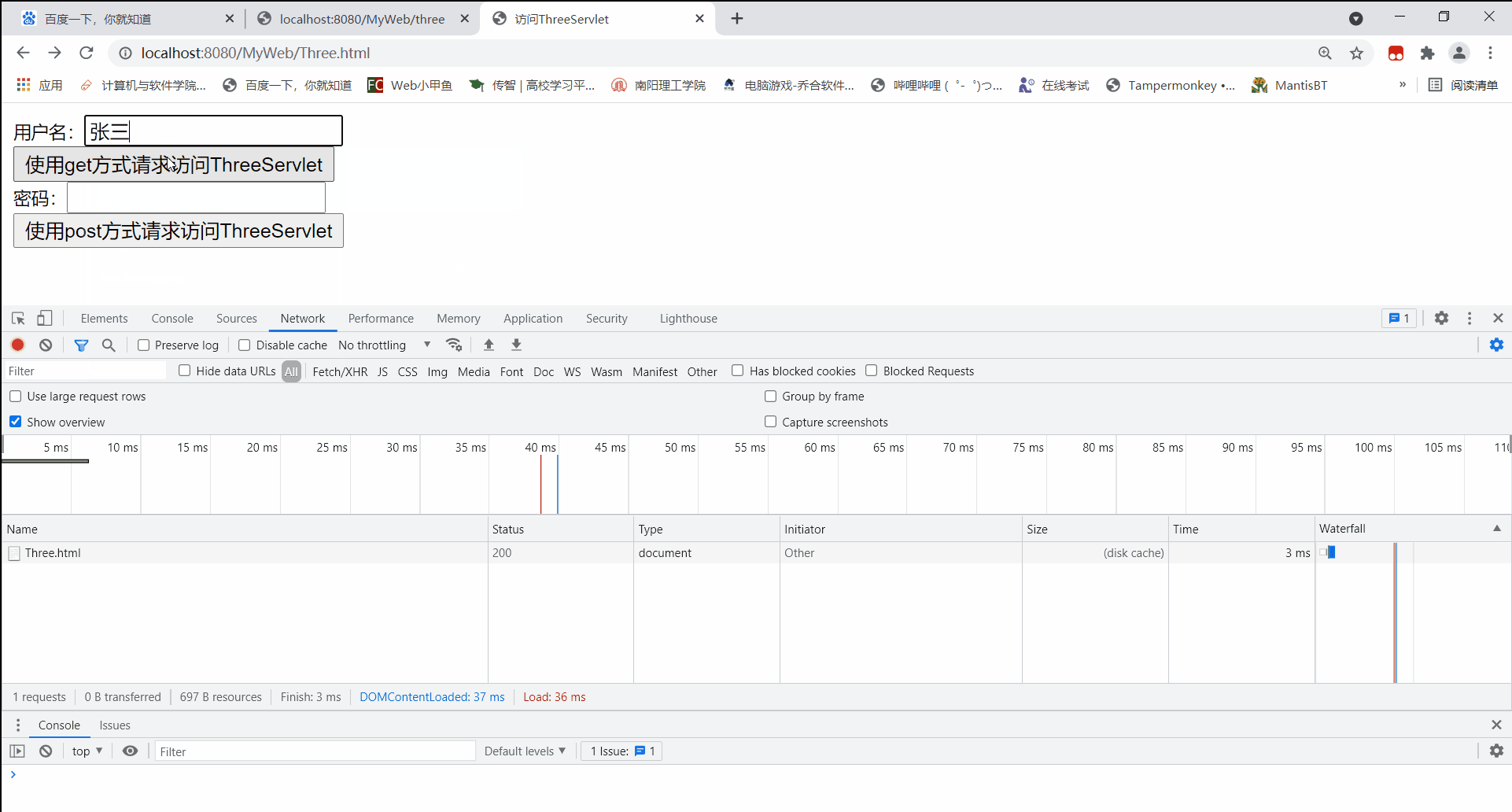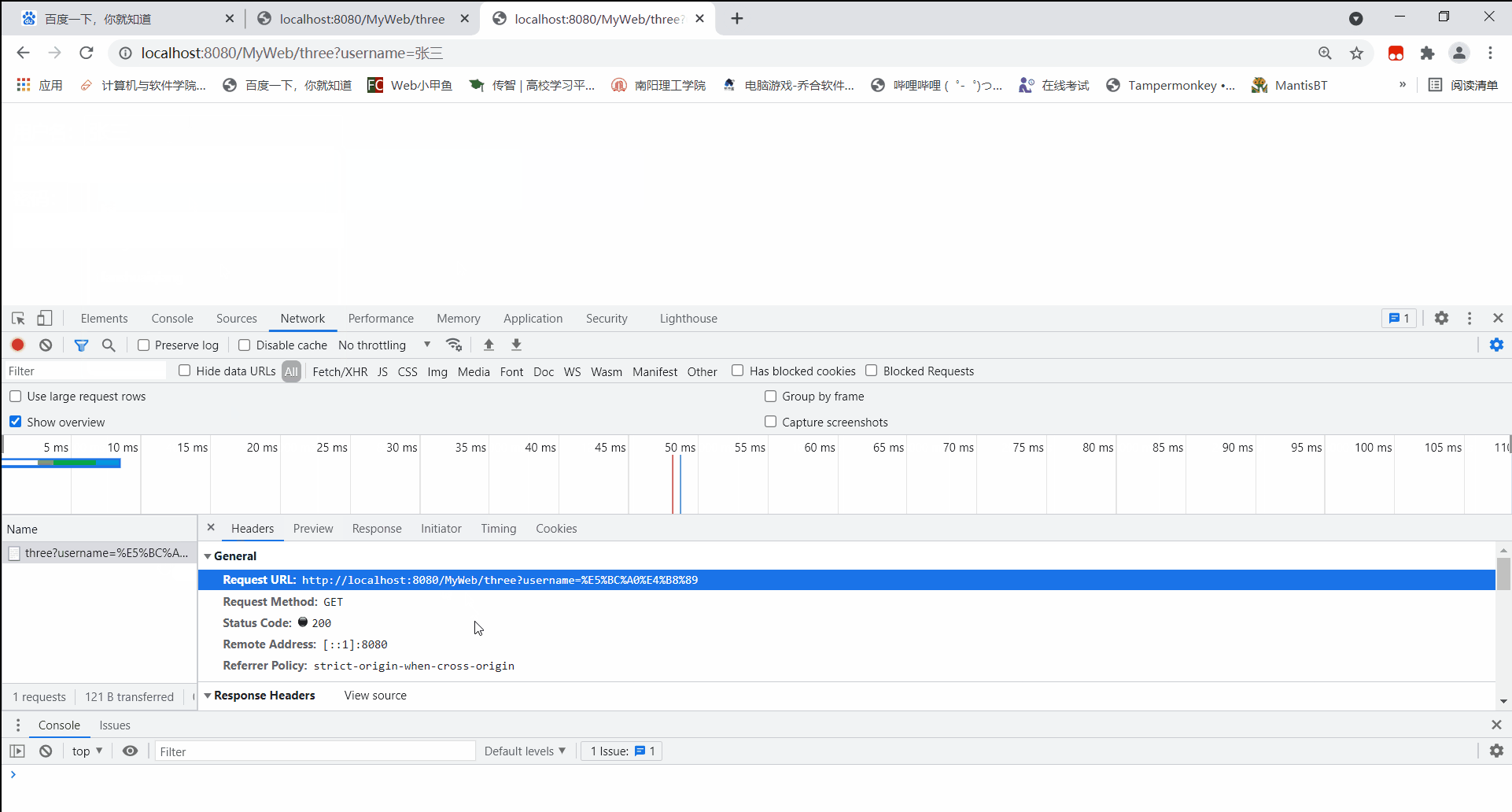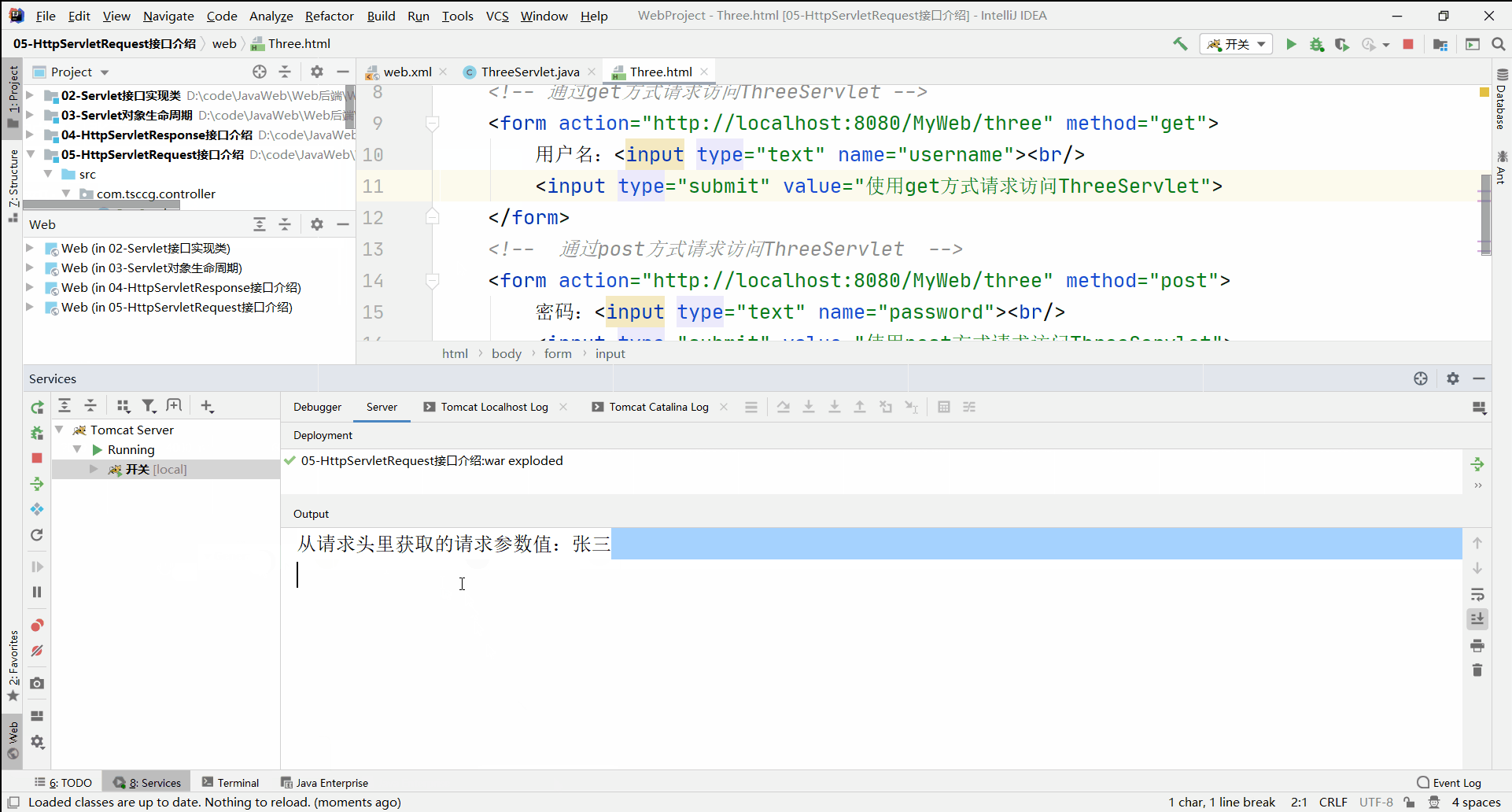
System.out.println("从请求体里获取的请求参数值:" + password);
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//通过请求对象,获取【请求头】里的请求参数值
String username = request.getParameter("username");
System.out.println("从请求头里获取的请求参数值:" + username);
}
}
目前,post方式只有通过表单设置,所以需要写一个页面。
在web目录下创建一个html文件:Three.html
编写两个表单标签,分别通过get和post方式访问ThreeServlet,且通过文本框携带请求参数信息。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>访问ThreeServlet</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 通过get方式请求访问ThreeServlet -->
<form action="http://localhost:8080/MyWeb/three" method="get">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="使用get方式请求访问ThreeServlet">
</form>
<!-- 通过post方式请求访问ThreeServlet -->
<form action="http://localhost:8080/MyWeb/three" method="post">
密码:<input type="text" name="password"><br/>
<input type="submit" value="使用post方式请求访问ThreeServlet">
</form>
</body>
</html>
开启服务器,通过浏览器访问Three.html页面。
先使用get方式访问:
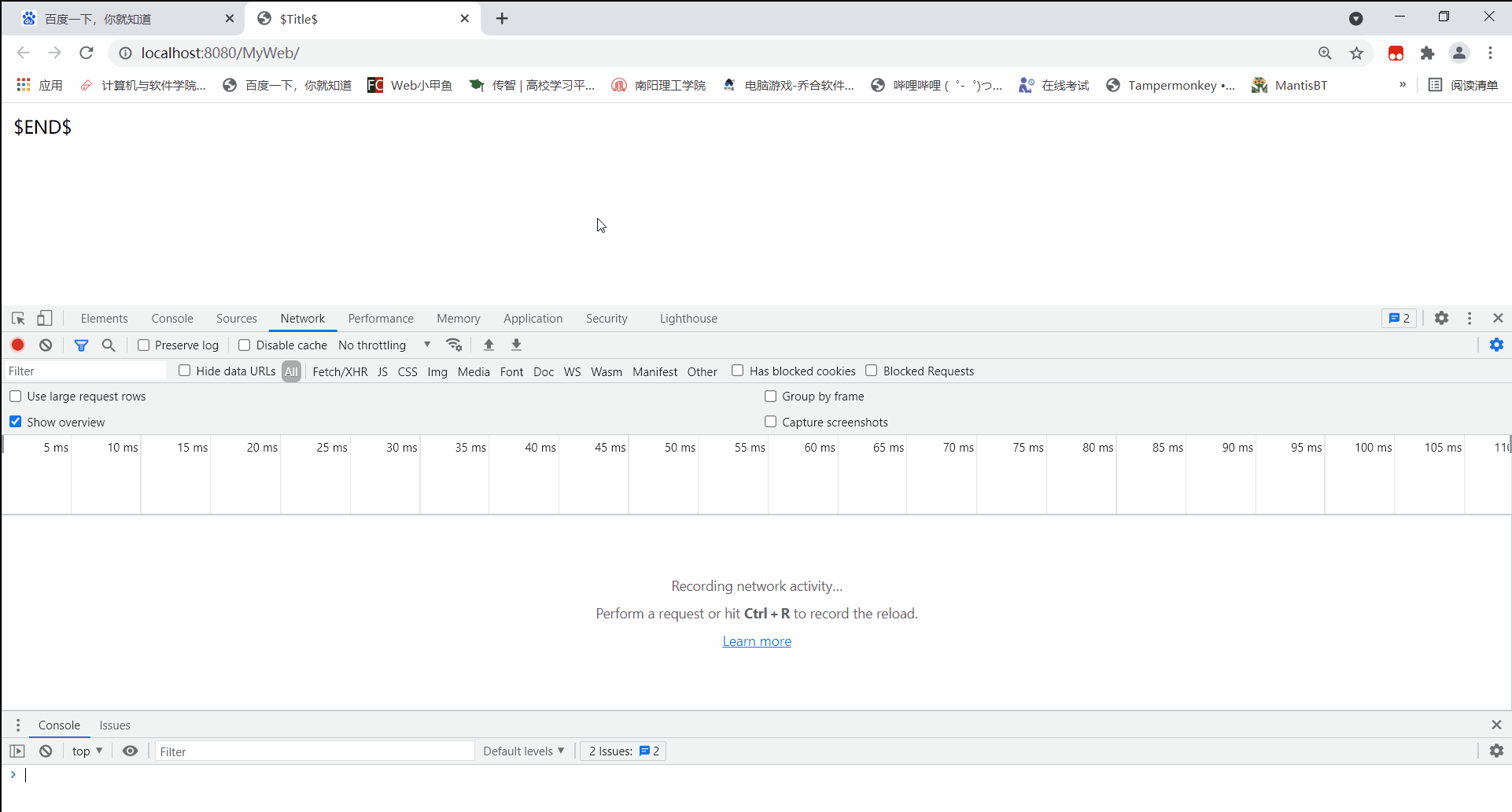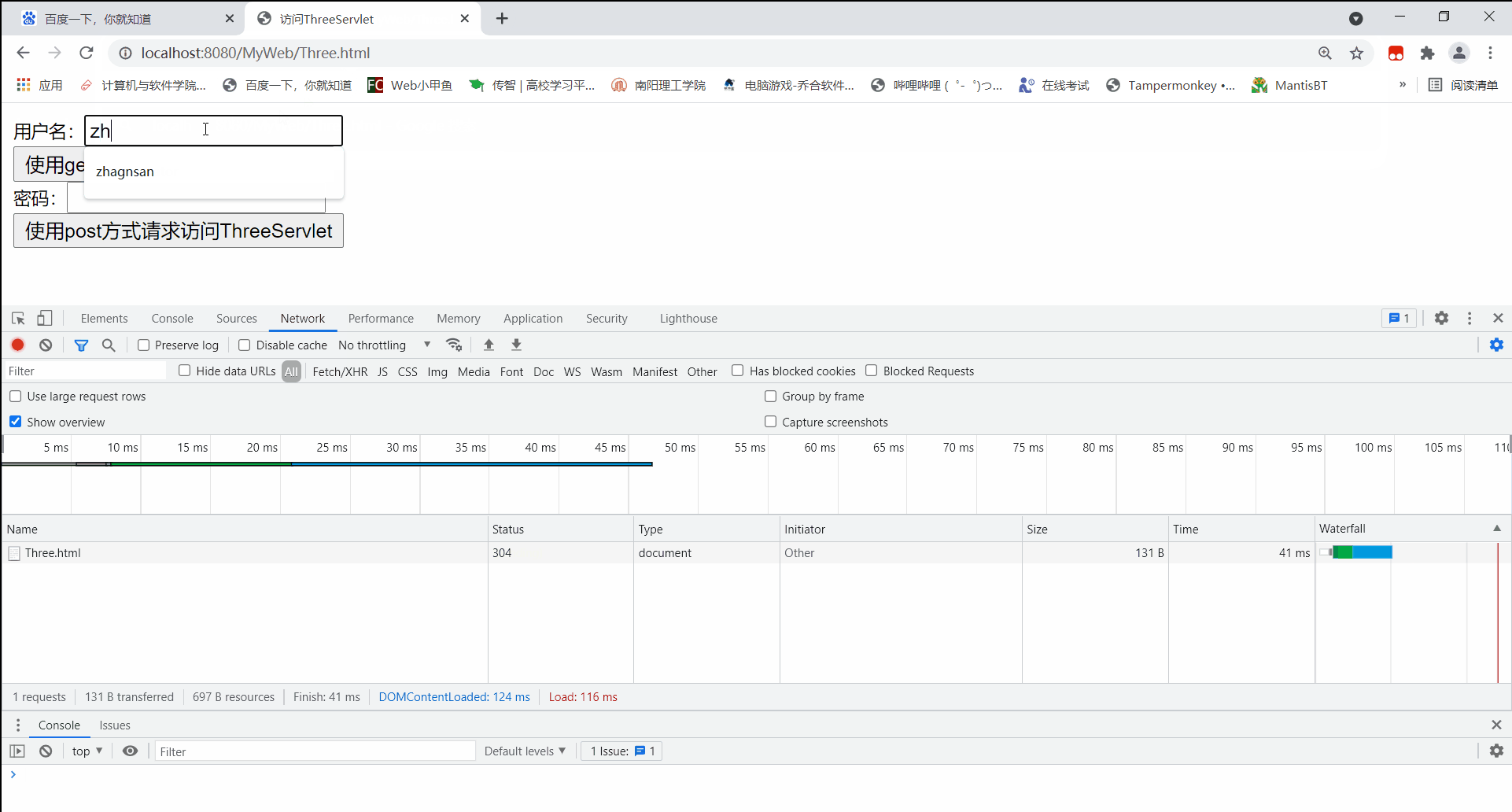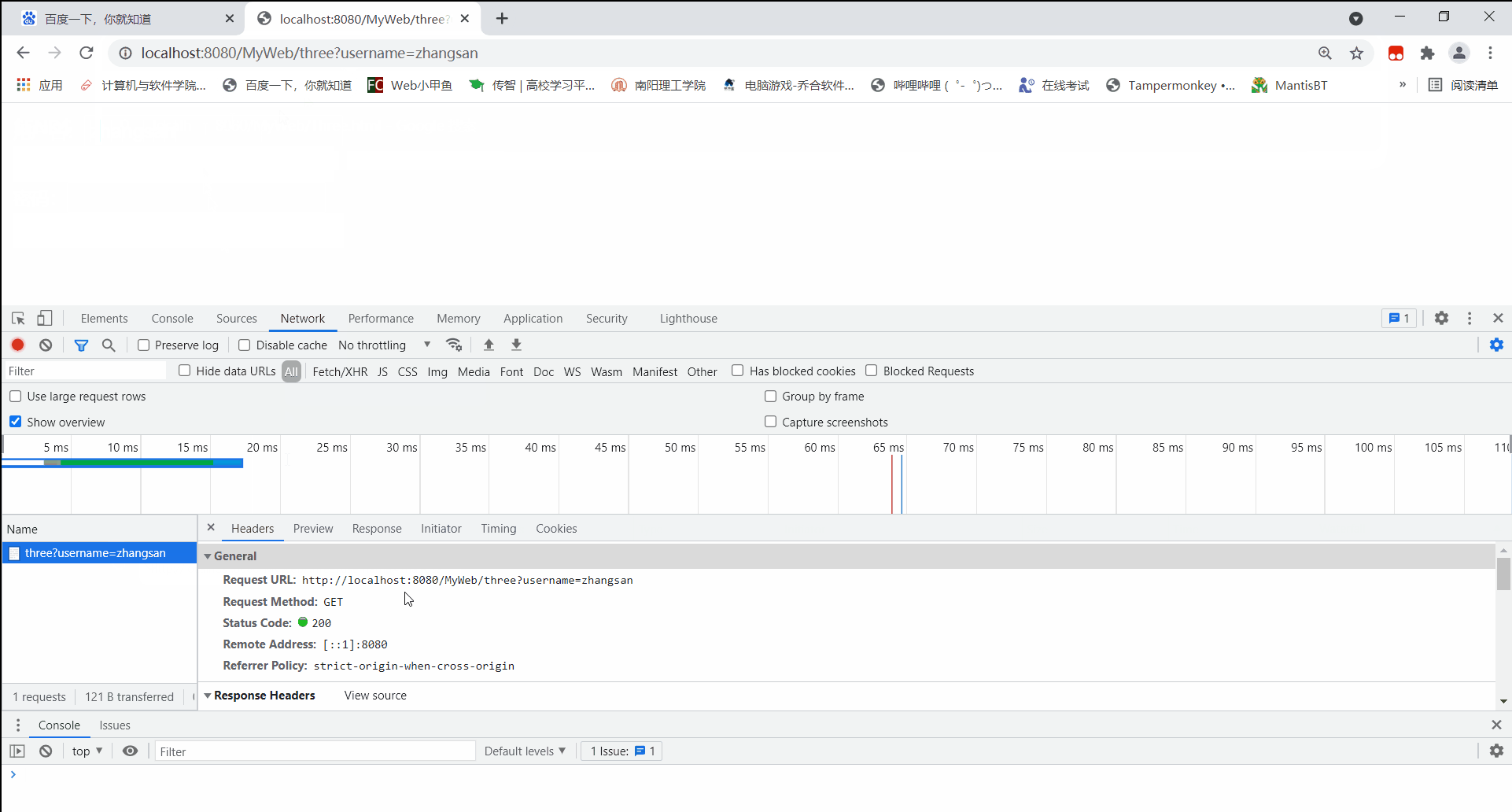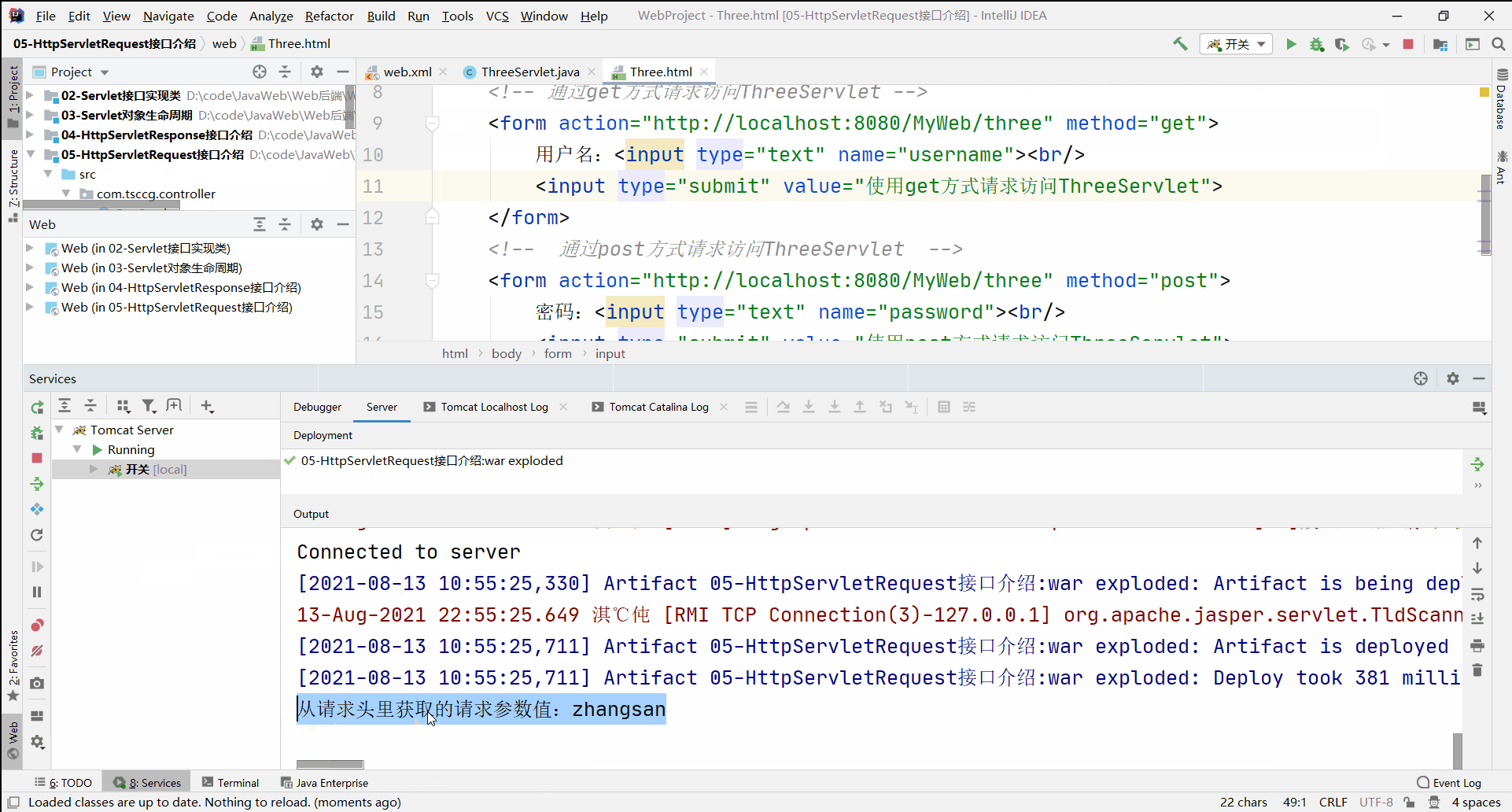
再通过post方式访问:
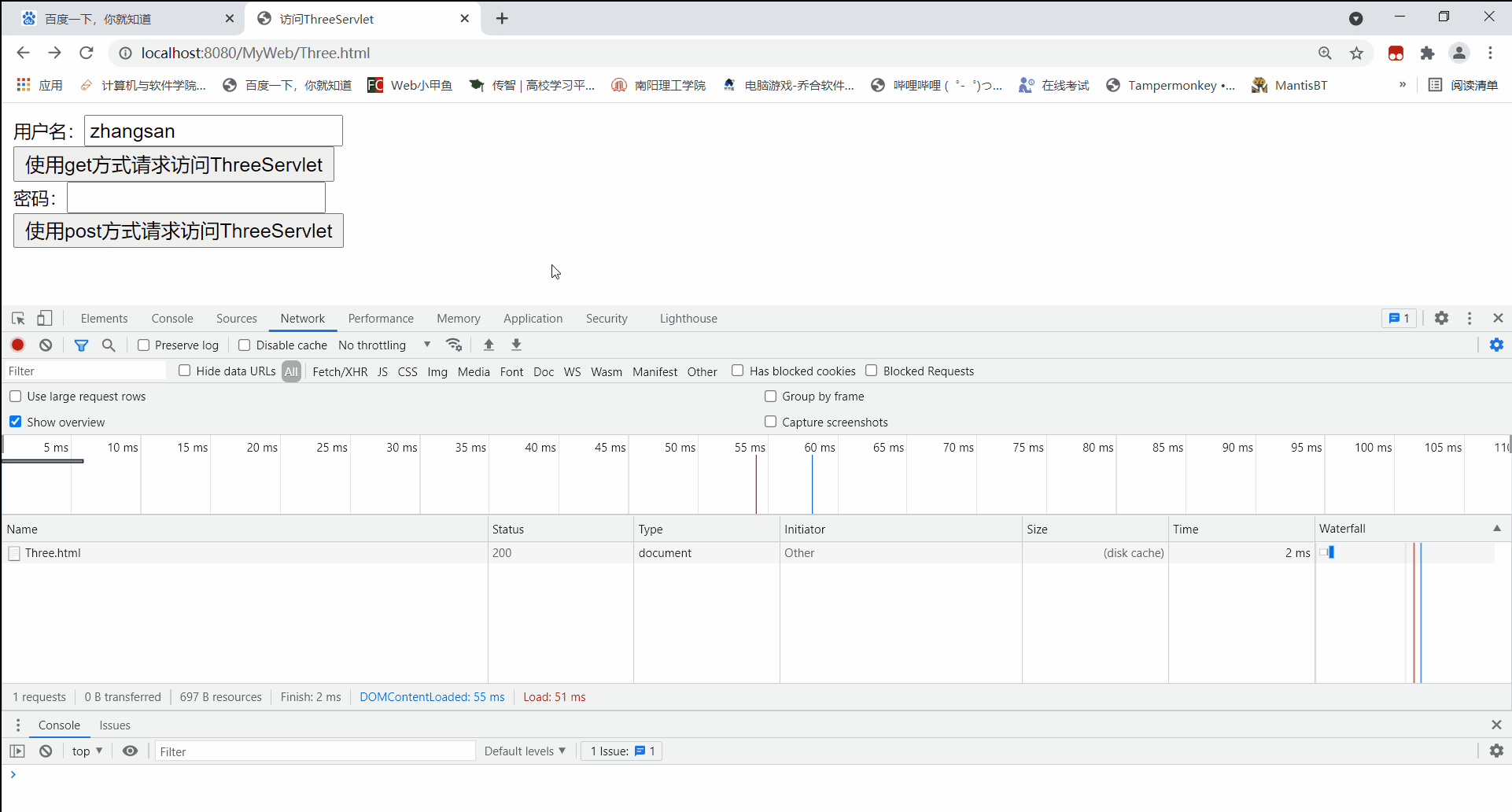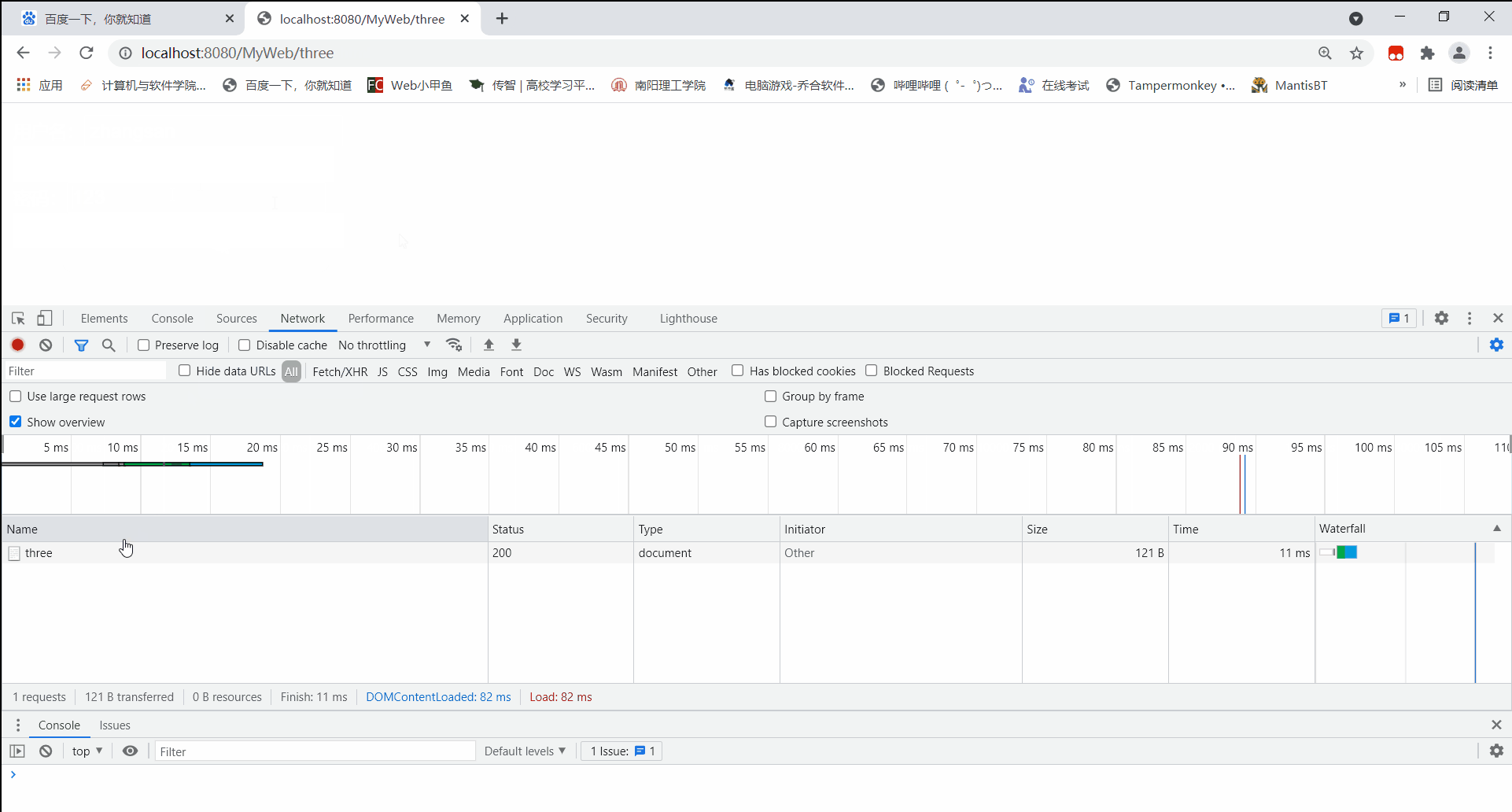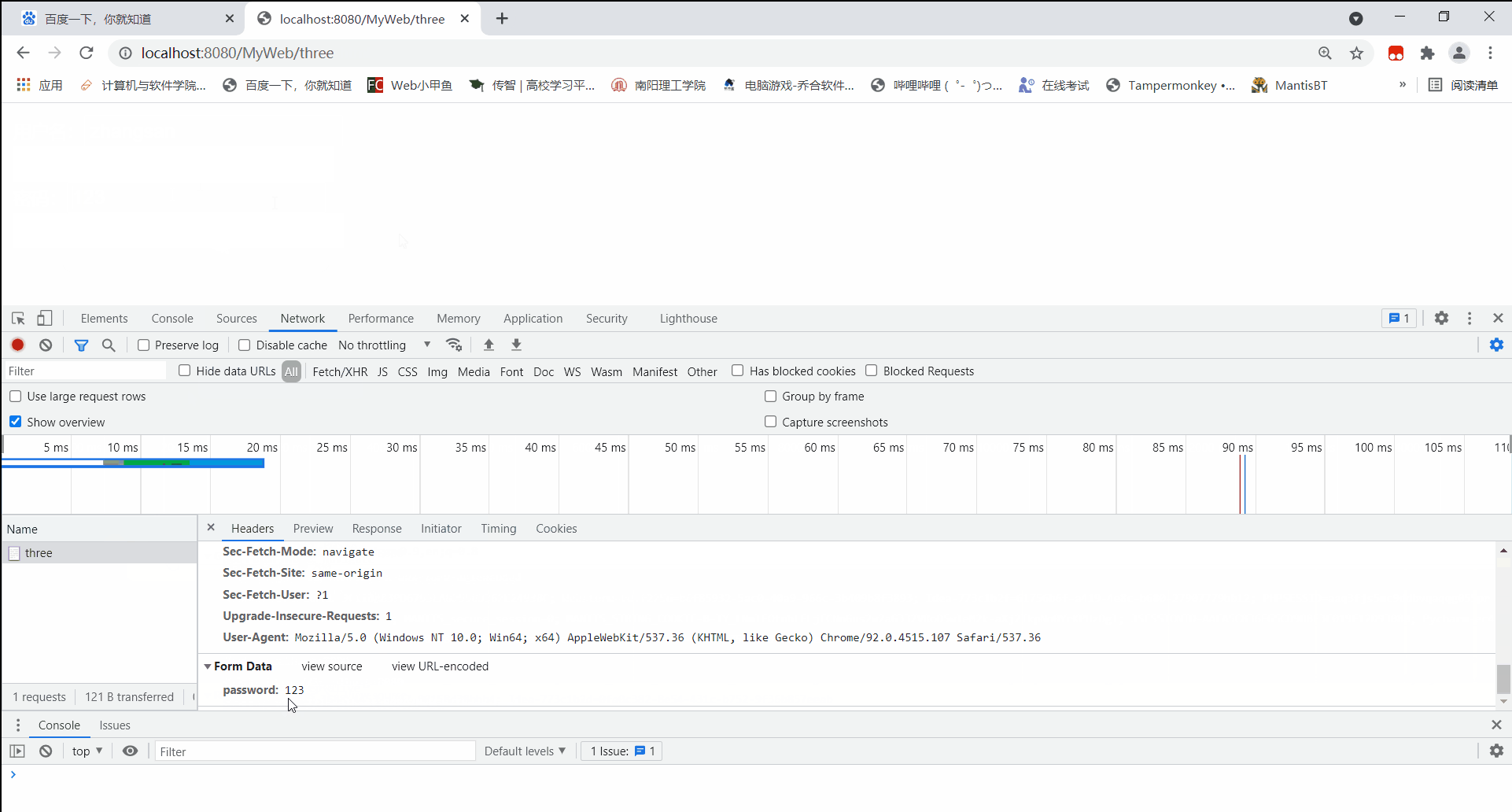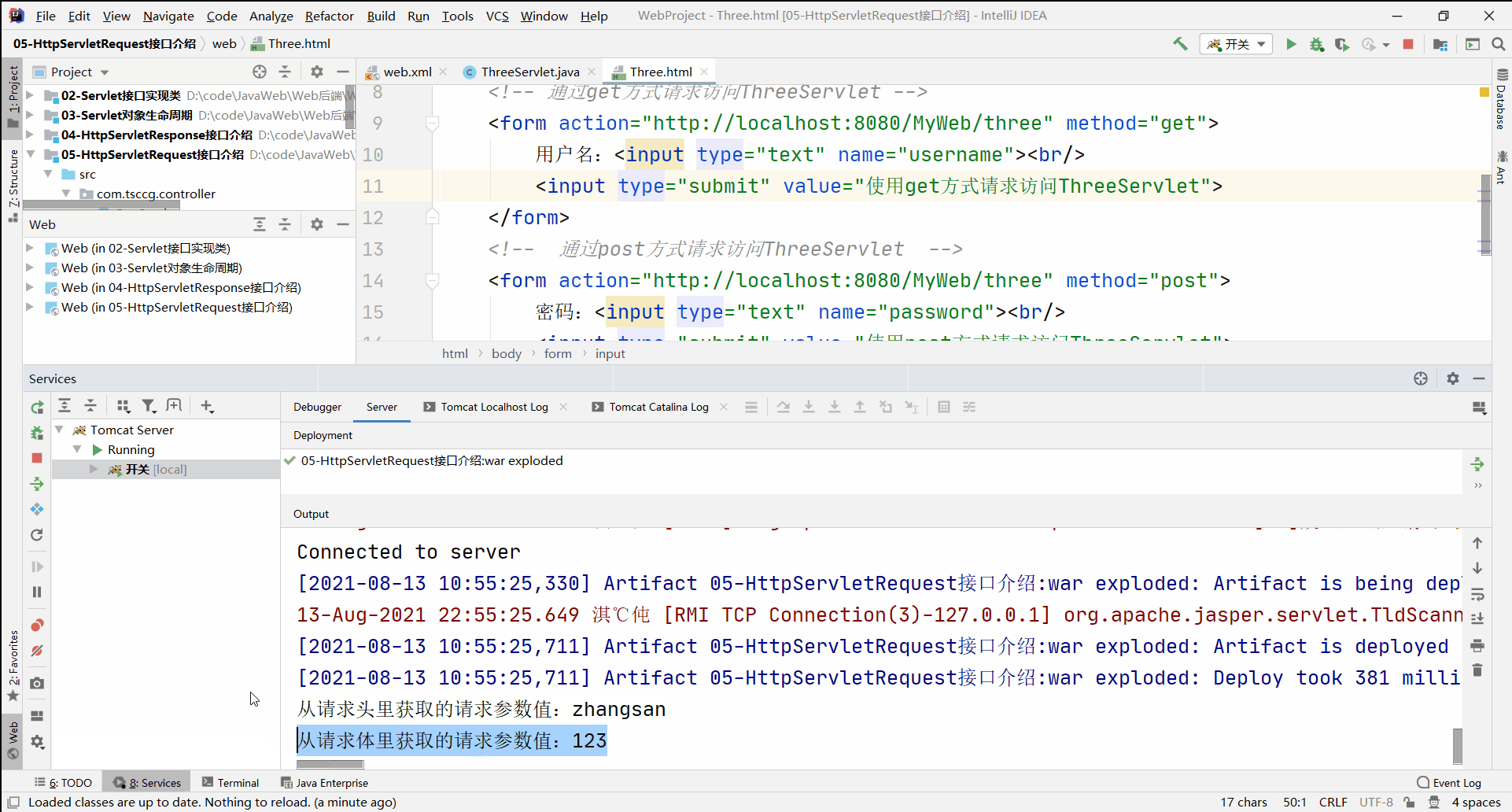
可见,通过post方式访问,所携带的请求参数信息并没有储存在请求头中,而是存储在请求体内。
3.2.3GET和POST的区别
当我们在Three.html中表单内:
在使用get方式访问ThreeServlet的文本框中写入中文时,后台能读取到正常请求参数信息
在使用post方式访问ThreeServlet的文本框中写入中文时,后台显示乱码。

问题:
当以GET方式发送中文参数内容时,得到正常结果【张三】
当以POST方式发送中文参数内容时,得到乱码【???】
原因:
-
当浏览器以GET方式发送请求时:
- 请求参数保存在【请求头】里。
- 在Http请求协议包到达Http服务器之后,第一时间就是进行解码。
- 请求头内的二进制内容是由【Tomcat】负责解码,Tomcat9.0默认使用【utf-8】字符集,可以解释一切国家文字。
-
当浏览器以POST方式发送请求时:
- 请求参数保存在【请求体】里。
- 在Http请求协议包到达Http服务器之后,第一时间就是进行解码。
- 请求体内的二进制内容是由【当前请求对象request】负责解码。request默认使用[ISO-8859-1]字符集,不支持中文。如果此时请求体内的参数内容是中文,将无法进行解码。
解决方法:
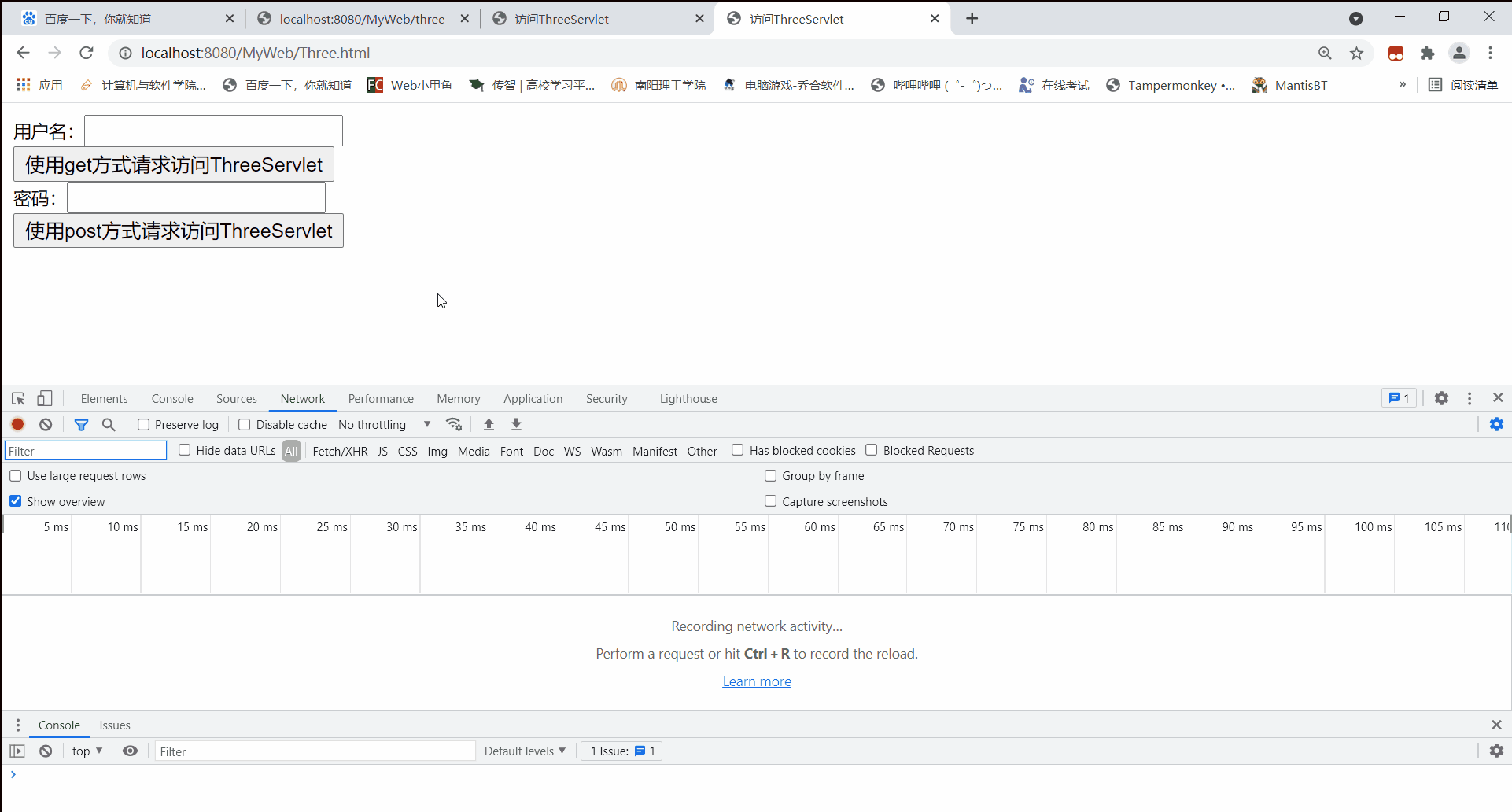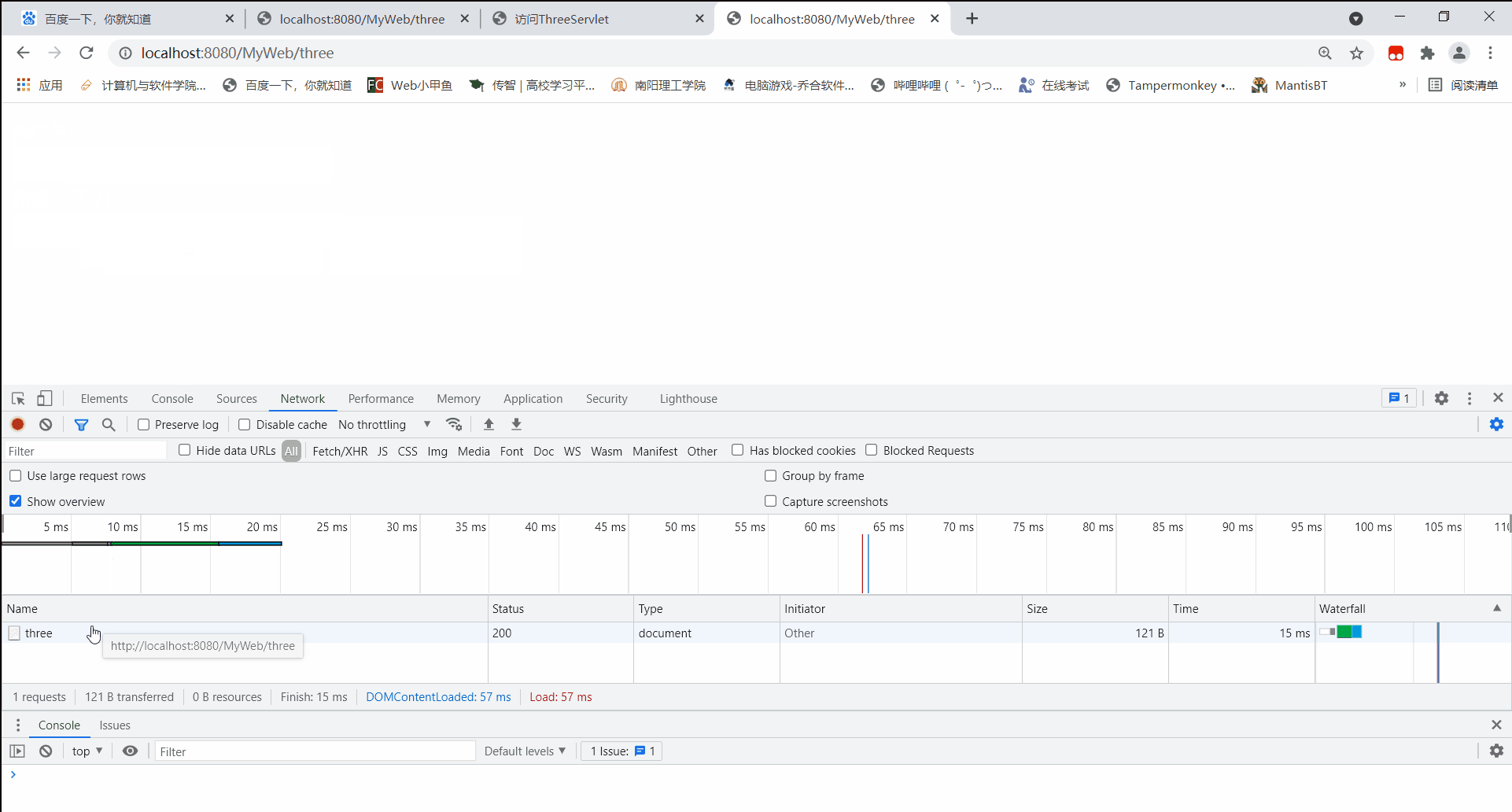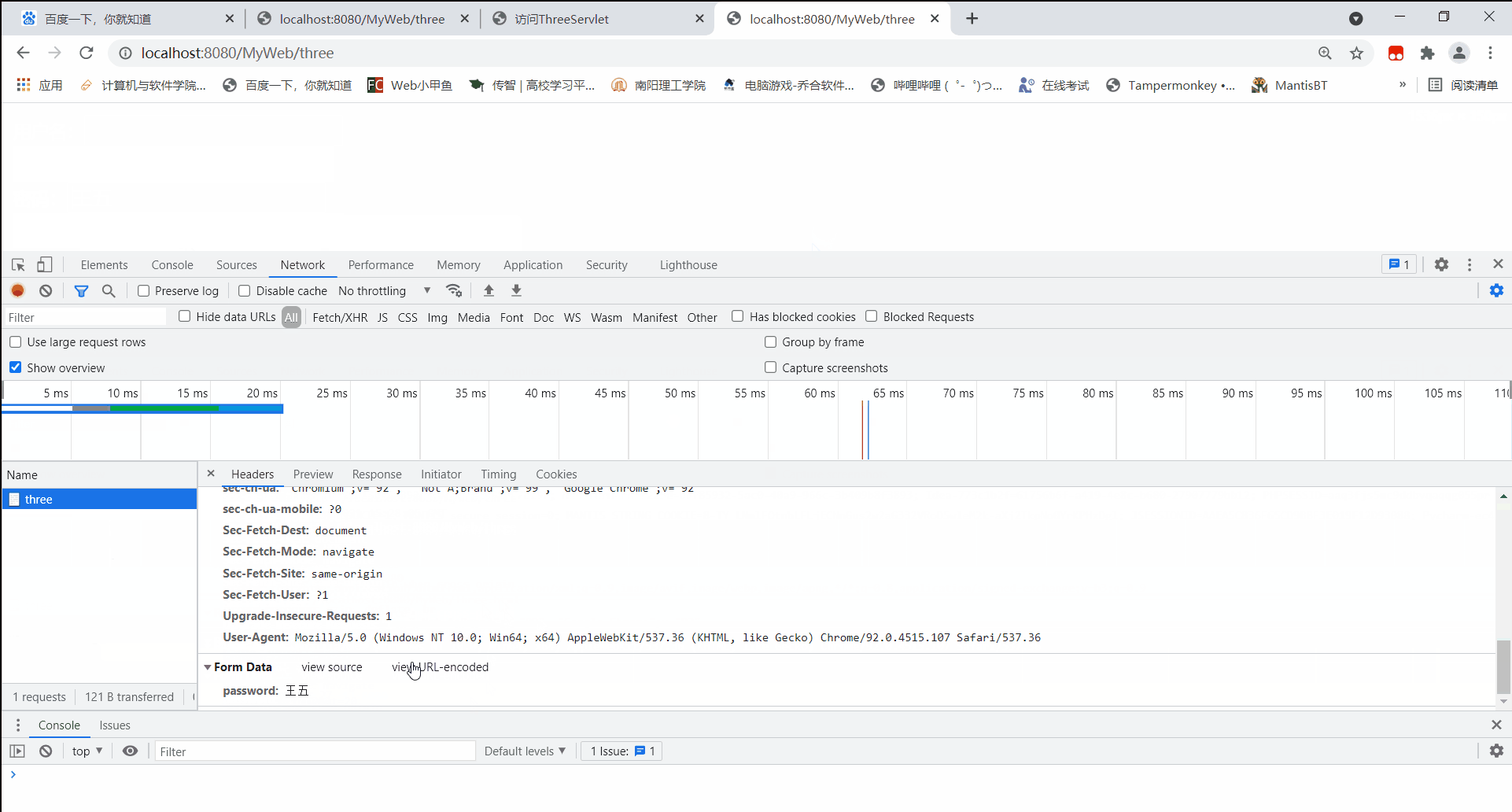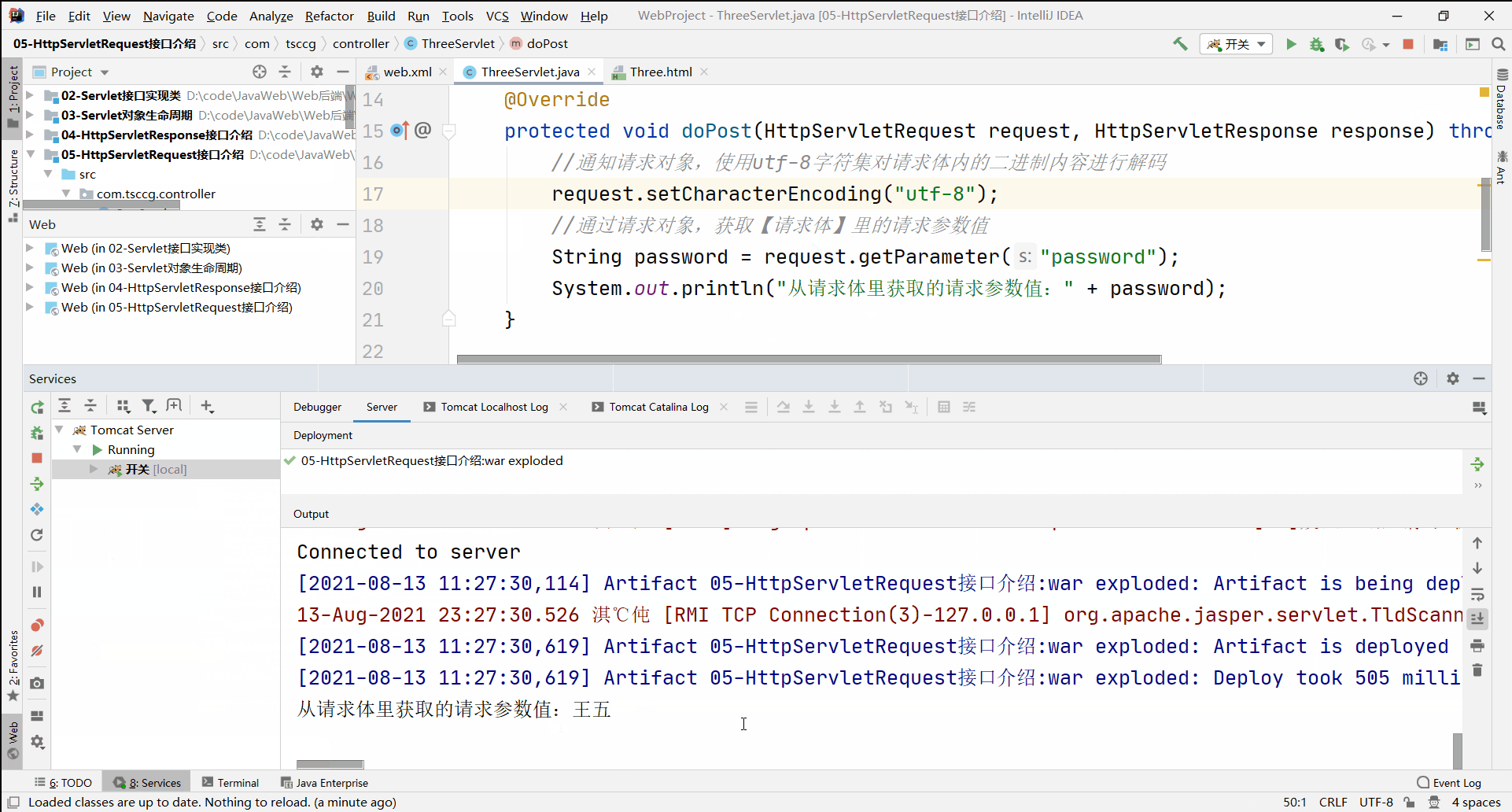
在POST请求方式下,在读取请求体内容之前,通知请求对象使用【utf-8】字符编码集对请求体内容进行一次重新解码。
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//通知请求对象,使用utf-8字符集对请求体内的二进制内容进行一次重新解码
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//通过请求对象,获取【请求体】里的请求参数值
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("从请求体里获取的请求参数值:" + password);
}