前言
????????异常,一个开发人员再熟悉不过的名词,除数不能为 0 的异常,IO 异常,数组下标越界异常,操作数据库的 sql 异常,以及让所有程序员都头疼的 NPE
? ? ? ? 本文就来谈谈,SpringBoot 和异常的那些事儿
正文
java 异常分类
? ? ? ? java 中主要存在两种类型的异常
- 检查性异常:是用户错误或问题引起的异常,这是程序员无法预见的。例如要打开一个不存在文件时,一个异常就发生了,这些异常在编译时不能被简单地忽略。
- 运行时异常:?运行时异常是可能被程序员避免的异常。与检查性异常相反,运行时异常可以在编译时被忽略。
如何理解两种异常呢,我们通过下面的例子来理解
首先定义一个异常类 CustomException?,继承 RuntimeException
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException {
public CustomException() {
super();
}
public CustomException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public CustomException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public CustomException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}该异常就属于运行时异常,检查性异常就是非 RuntimeException 及其子类,拿 IOException 为例
public static void runtimeExTest() throws CustomException {
throw new CustomException("test");
}
public static void checkExTest() throws IOException {
throw new IOException("test");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
runtimeExTest();
checkExTest();
}
public static void errorTest() throws Error {
throw new Error("test");
}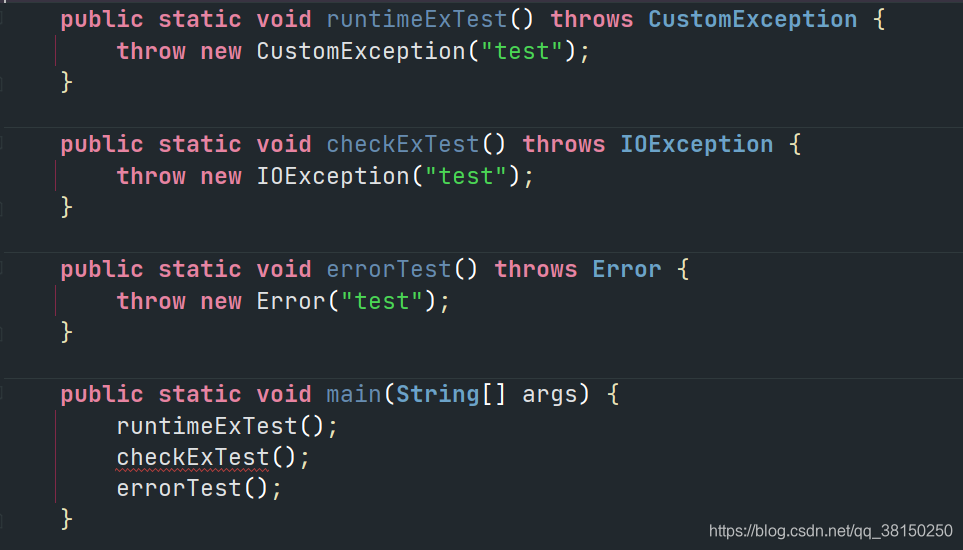
?可以看到,checkExTest() 在编译时会报错,提示?Unhandled exception: java.io.IOException
其实还有一类异常,Error,个人感觉使用场景不多,因此一笔带过吧,Error 和 RuntimeException 类似。
SpringBoot 全局异常处理
????????SpringBoot 提供了默认的异常处理方式,是会转到对应的错误页面(ErrorPage)去的,但是现如今的前后端分离的开发方式,更多的是使用?RestControllerAdvice (ControllerAdvice)这种方式,小编也是最先接触并了解这种方式的,因此在此先行介绍这种方式。
1?@ControllerAdvice
? ? ? ? 见名知意,这是一个 Advice,是对 controller 的增强,直接上用法
@ControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 捕捉 CustomException ,返回 response 的 status 设置为 HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST
*
* @param e CustomException
*/
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public String handleCustomException(CustomException e) {
return e.getMessage();
}
}
????????与之 共同使用的有 @ExceptionHandler 和 @ResponseStatus 两个注解
????????@ExceptionHandler 用以声明处理的异常类型
? ? ? ? @ResponseStatus 用以声明返回的 http code
- 实际上述两个注解也可以使用在 RequestMapping 上,这边只是做了全局处理
- ResponseStatus 个人建议不要修改,http code 多用来判断请求是否成功,业务逻辑可以在请求返回体中添加 code 来实现
?2?BasicErrorController
? ? ? ? 本来觉得 @ControllerAdvice 已经很强大了,以后有什么异常直接往里面抛并处理即可。
? ? ? ? 最近接了个项目,项目中用到了 SpringSecurity + jwt 的方式来进行登录鉴权。调试接口时,发现请求一直 403 ,但是没有任何返回值。DEBUG 后发现,在 jwt 鉴权的过滤器(Filter)中, jwt 解析时抛出了异常,但是居然没有被?GlobalExceptionHandler? 捕捉到。正当我百思不得七姐时,一位热心的网友点醒了我。
????????ControllerAdvice 是用来处理Controller 抛出的异常的
? ? ? ? 如此简单明了答案竟让我不知道用什么词语来反驳,只能为自己的愚蠢感到羞愧。
?
? ? ? ? ?那么,如何解决呢。
? ? ? ? 从返回的信息中看到这么一句话,大致意思就是没有 /error 路径的映射。
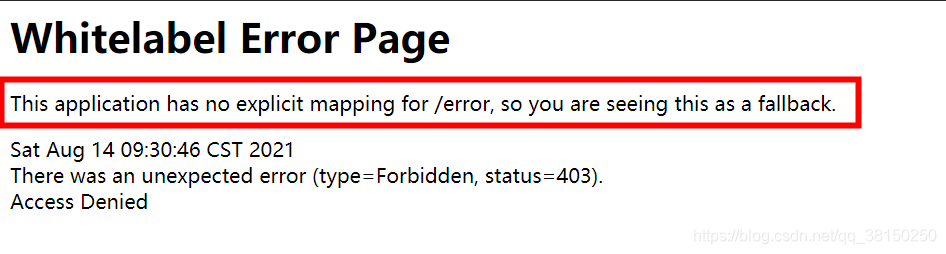
? ? ? ? ?所以一切要从 SpringBoot 的默认异常处理机制说起
????????Spring Boot 提供了一套默认的异常处理机制,一旦程序中出现了异常,Spring Boot 会自动识别客户端的类型(浏览器客户端或机器客户端),并根据客户端的不同,以不同的形式展示异常信息。
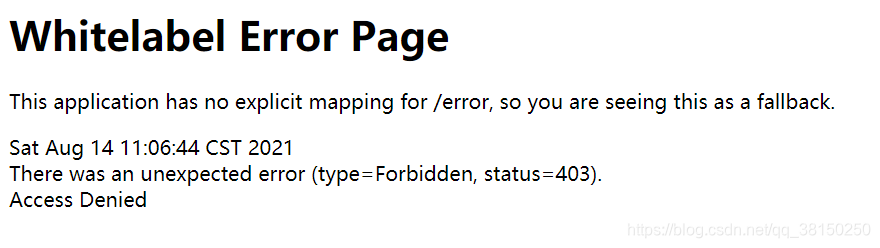
? ? ? ? 对于浏览器客户端,Spring Boot 会响应一个“ whitelabel”错误视图,以 HTML 格式呈现错误信息,如上面的图所示
? ? ? ?而 对于机器客户端而言,Spring Boot 将生成 JSON 响应,来展示异常消息。
{
"timestamp": "2021-08-14T02:32:20.075+00:00",
"status": 403,
"error": "Forbidden",
"message": "Access Denied",
"path": "/level1/1"
}????????Spring Boot 通过配置类 ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 对异常处理提供了自动配置,该配置类向容器中注入了以下 4 个组件。
- ErrorPageCustomizer:该组件会在在系统发生异常后,默认将请求转发到“/error”上。
- BasicErrorController:处理默认的“/error”请求。
- DefaultErrorViewResolver:默认的错误视图解析器,将异常信息解析到相应的错误视图上。
- DefaultErrorAttributes:用于页面上共享异常信息。
? ? ? ? SpringBoot 的自动配置流程,可以移步一些网上的教程(比如尚硅谷的 SpringBoot 教程,源码级的讲解,非常适合对 SpringBoot 使用过一段时间,但是没有深入了解其原理的同学),小编这边只介绍如何转发,及如何处理。
? ? ? ? 1)转发过程可以关注一个 StandardHostValue 的类
// 寻找 ErrorPage
ErrorPage errorPage = context.findErrorPage(statusCode);
if (errorPage == null) {
// Look for a default error page
errorPage = context.findErrorPage(0);
}
if (errorPage != null && response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
response.setAppCommitted(false);
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_STATUS_CODE,
Integer.valueOf(statusCode));
String message = response.getMessage();
if (message == null) {
message = "";
}
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_MESSAGE, message);
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR,
errorPage.getLocation());
request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR,
DispatcherType.ERROR);
Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();
if (wrapper != null) {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_SERVLET_NAME,
wrapper.getName());
}
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_REQUEST_URI,
request.getRequestURI());
// 该方法会转发到 ErrorPage
if (custom(request, response, errorPage)) {
response.setErrorReported();
try {
response.finishResponse();
} catch (ClientAbortException e) {
// Ignore
} catch (IOException e) {
container.getLogger().warn("Exception Processing " + errorPage, e);
}
}
}? ? ? ? ? 默认的 ErrorPage

?????????然后是 custom(Request request, Response response,?ErrorPage errorPage)方法
if (response.isCommitted()) {
// Response is committed - including the error page is the
// best we can do
rd.include(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
} else {
// Reset the response (keeping the real error code and message)
response.resetBuffer(true);
response.setContentLength(-1);
// forward 服务端转发
rd.forward(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
// If we forward, the response is suspended again
response.setSuspended(false);
}? ? ? ? 2) 请求处理过程关注?BasicErrorController
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
// 2.3.0 版本后不再通过此处获取,而是通过 server.error.path 配置文件获取
@Override
public String getErrorPath() {
return null;
}
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(status);
}
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
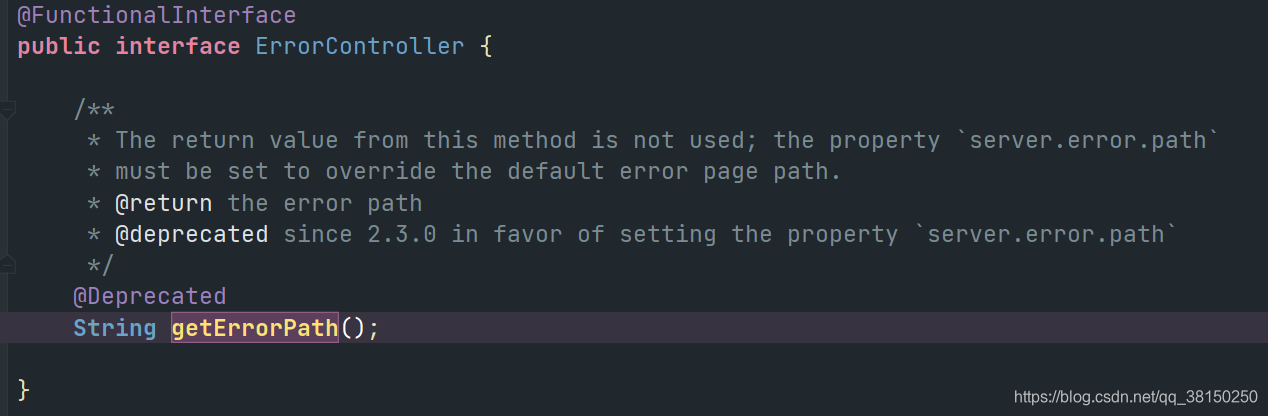
}- public String getErrorPath()
? ? ? ? 获取错误 page ,默认为 /error
? ? ? ??2.3.0 版本后不再通过此处获取,而是通过 server.error.path 配置文件获取
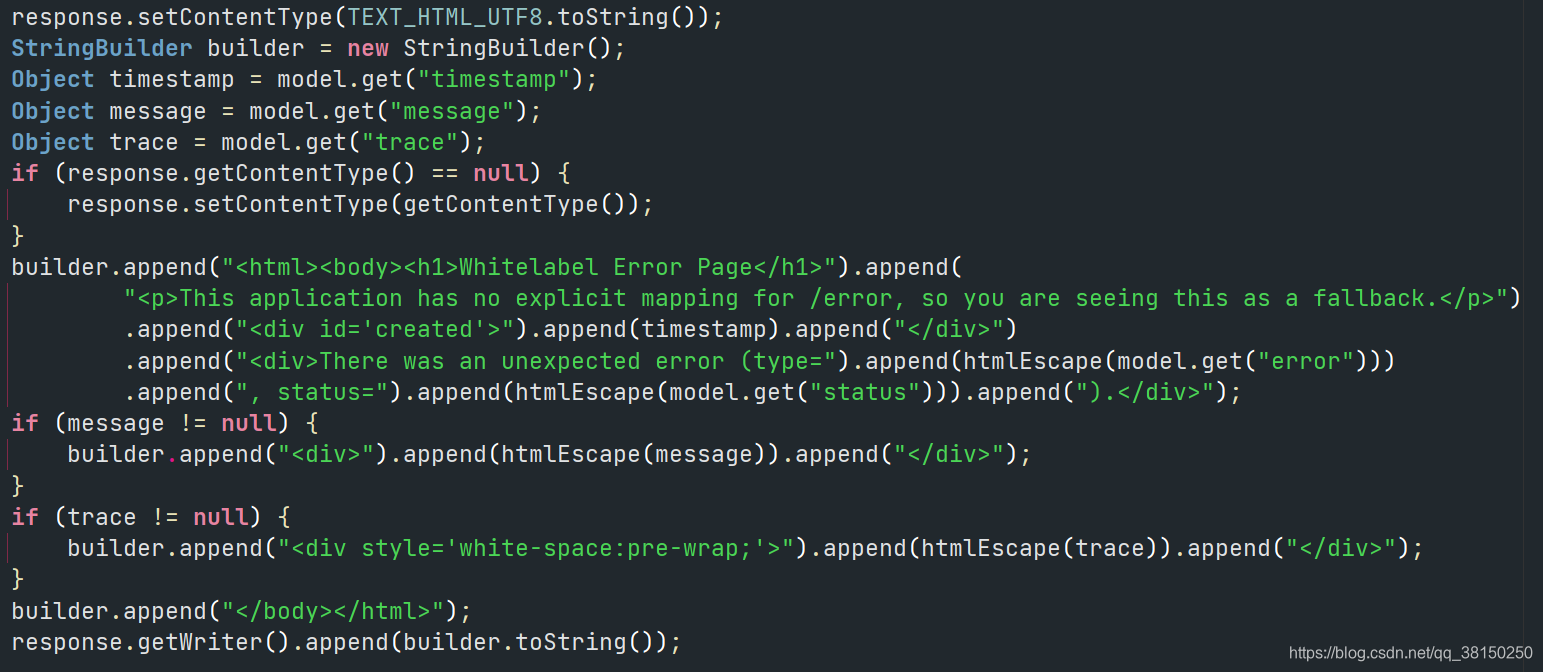
- public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)?
????????浏览器客户端返回的页面
? ? ? ? 一开始以为默认页面会是某个静态的 html ,但是找了半天没找到。后来在?ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 配置类中找到了这段代码
- public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request)
????????机器客户端返回的 json 数据
? ? ? ? ?知道了原理,那就可以继续了,自己重新实现?BasicErrorController,代码如下
public class CustomErrorController extends BasicErrorController {
public CustomErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ErrorProperties errorProperties) {
super(errorAttributes, errorProperties);
}
public CustomErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ErrorProperties errorProperties, List<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
super(errorAttributes, errorProperties, errorViewResolvers);
}
@Override
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = getErrorAttributes(request);
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<>(errorAttributes, status);
}
@Override
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
private Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(HttpServletRequest request) {
// 获取异常参数
ErrorAttributeOptions options = ErrorAttributeOptions.of(
// 异常 message
ErrorAttributeOptions.Include.MESSAGE,
// 异常类型
ErrorAttributeOptions.Include.EXCEPTION,
// 异常堆栈,比较长
// ErrorAttributeOptions.Include.STACK_TRACE,
// 绑定的错误 error
ErrorAttributeOptions.Include.BINDING_ERRORS
);
return getErrorAttributes(request, options);
}
}? ? ? ? 记得注册为 Bean
@Bean
public CustomErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ServerProperties serverProperties,
ObjectProvider<List<ErrorViewResolver>> errorViewResolversProvider) {
return new CustomErrorController(errorAttributes, serverProperties.getError(),
errorViewResolversProvider.getIfAvailable());
}????????结果演示:
????????浏览器客户端:
? ? ? ? 机器客户端(postman或者 swagger):

最后,附上 git 地址 security-demo