Gradle是一款构建系统工具,它的DSL基于Groovy实现,大部分功能都是通过插件的方法实现的,如果内置插件不能满足需求,可以自定义自己的插件。
Gradle入门
安装完成后,可以通过下面命令校验gradle版本
// Window os
gradlew -v
// Linux os
./gradle -v
现在来编写第一个Gradle脚本
// build.gradle
task hello {
doLast {
println "Hello World!"
}
}
// 执行build.gradle脚本中定义的hello任务
// -q 参数用于控制gradle输出的日志级别,以及哪些日志可以输出被看见
> gradlew -q hello
// 控制台输出信息
Hello World!
build.gradle是Gradle默认的构建脚本文件。定义一个任务(Task),任务的名字为hello,并给任务hello添加一个动作(Action),其实就是Groovy语言实现的闭包。doLast 是Task执行完毕后要回调执行的代码。
Gradle Wrapper
Wrapper,其实就是对Gradle的一层包装,以便开发中统一Gradle的构建版本,避免版本的不统一。
当使用Wrapper启动Gradle时,Wrapper会检查Gradle有没有被下载关联,没有就会从配置的地址下载并运行构建,不需要配置Gradle环境了。
生成Wrapper
我们可以执行Gradle内置的task自动生成Wrapper
> gradlew wrapper
// 将会生成下图的Wrapper配置,gradlew,gradlew.bat文件
// gradlew和gradlew.bat分别是Linux和Windows下的可执行脚本文件,与Gradle原生命令用法一样
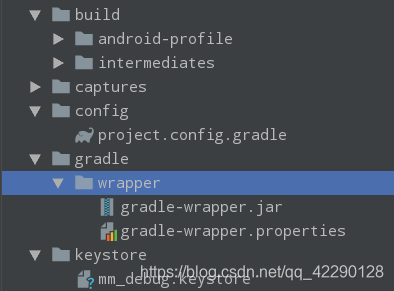
// 指定Gradle版本,不指定就默认当前安装的Gradle版本
> gradlew wrapper --gradle-version 4.1
该参数影响的是gradle-wrapper.properties配置中的distributionUrl的值,该值的规则:distributionUrl=https\://services.gradle.org/distributions/gradle-${gradle-version}-all.zip
自定义Wrapper Task
在build.gradle构建文件中自定义Wrapper Task
task wrapper(type: Wrapper) {
gradleVersion = '5.1'
}
> gradlew wrapper
执行完task后,就会生成5.1版本的Wrapper,就不需要手动指定Gradle版本。
Gradle日志
日志级别
Gradle日志级别增加了QUIET和LIFECYCLE两个级别。Gradle日志级别如下:
- ERROR 错误消息
- QUIET重要消息
- WARNING警告消息
- LIFECYCLE进度消息
INFO信息消息 - DEBUG调试消息
// -q 或者 --quite 输出QUIET级别及其之上的日志信息
> gradlew -q tasks
// -i 或者 --info 输出INFO级别及其之上的日志信息
> gradlew -i tasks
// 不加选项,输出LIFECYCLE级别及其更高级别
// -d 或者 --debug 输出DEBUG级别及其更高级别,这个会输出所有日志
输出Gradle错误堆栈信息
默认情况下,堆栈信息的输出是关闭的,可以通过命令行增加参数的形式打开它,在构建失败时,Gradle就会输出错误堆栈信息
// 推荐使用-s,因为-S输出的堆栈信息太多
> gradlew -s tasks
// -s 或者 --stacktrace 输出关键的堆栈信息
// -S 或者 --full-stacktrace 输出全部堆栈信息
脚本中添加日志输出
一般情况下,我们都是使用print系列的方法输出日志,它的级别为QUIET
println '输出的日志信息'
还可以使用内置的logger输出不同级别的日志信息:
logger.quiet('quiet日志')
logger.lifecycle("lifecycle日志")
其实内部实现就是调用Project的getLogger()方法获取Logger对象的实例。
Gradle命令行
查看帮助文档命令
一般查看帮助文档,只需在命令后加上**-h** 或者 –help,有的是**-?**
> gradlew -?
> gradlew -h
> gradlew --help
查看所有可执行的Tasks
执行下面命令后,会列出所有可执行的task
> gradlew tasks
强制刷新依赖
主要为了解决缓存引发的问题,通过下面命令重新下载依赖,不会走缓存
> gradlew --refresh-dependencies assemble
多任务调用方式
通过命令执行多个任务,只需要按顺序以空格隔开即可,比如下面命令,先是执行clean进行文件清理,再执行打包命令
> gradlew clean assembleArmDebug
Gradle生命周期探索
Gradle构建过程通常分为三步:
-
初始化阶段 Initialization
解析整个工程中所有Project,构建所有的Project对应的project对象。
Gradle支持单个和多个工程的编译。在初始化阶段,Gradle判断需要参与编译的工程,为每个工程创建一个Project对象。
在这个阶段,Gradle会创建Settings对象,并在其上执行
settings.gradle脚本,建立工程之间的层次关系。 -
配置阶段 Configuration
解析所有的projects对象中的task,构建好所有task的拓扑图
在这个阶段,Gradle会分别在每个Project对象上执行对应的
build.gradle脚本,对Project进行配置。 -
执行阶段 Execution
执行具体的task及其依赖task
在执行阶段,Gradle会判断配置阶段创建的哪些Task需要被执行,然后执行选中的每个Task。
在Gradle中可以监听各阶段:
在settings.gradle文件中
println "初始化阶段开始..."
在build.gradle文件中添加监听回调
this.afterEvaluate {
println "配置阶段完成之后的监听回调"
}
this.gradle.buildFinished {
println "gradle执行完毕后的监听回调"
}
Gradle构建脚本基础探索
settings文件
在Gradle中,settings文件主要用于初始化以及工程树的配置,默认名为settings.gradle,存放在项目根目录下。
根工程相当于Android Studio中的Project,一个根工程可以有多个子工程,也就是多个Module。
一个子工程只有在settings.gradle文件中配置了,Gradle才能识别,也就是在构建时在包含进入。
include ':app', ':basiclib'
build文件
每个Project都会有一个Build文件,该文件是该Project构建入口。可以配置版本,插件,依赖库等。
Root Project也有一个Build文件,在该文件中可以获取所有的Child Project,所以我们可以对Child Project统一配置,如插件,依赖Maven仓库等,这样就不用对每个Project去配置。如果配置所有的Child Project仓库为jcenter,可以如下配置:
subprojects {
repositories {
println "subprojects>> name: ${project.getName()}"
jcenter()
}
}
除了subprojects外,还提供了allprojects,这个是对所有的Project配置。
Projects 、Tasks
一个Project可以由多个Task组成。其实Task就是一个原子性操作,比如:打个jar包,复制一份文件,上次jar到Maven中心仓库等。
创建一个task
task customTask {
doFirst {
println "custom task>>> doFirst"
}
doLast {
println "custom task>>> doLast"
}
}
// 执行任务, -s 输出错误堆栈信息
> gradlew -s customTask
task 其实是Project对象的一个函数,customTask 为任务的名字。原型:Task task(String name, Closure configureClosure),Groovy语法中,最后一个参数是闭包时,可以放在括号的外面,而方法的括号可以省略。
还可以通过TaskContainer创建任务,Project对象已经定义好了一个TaskContainer
tasks.create("customTask") {
doFirst {
println "TaskContainer custom task>>> doFirst"
}
doLast {
println "TaskContainer custom task>>> doLast"
}
}
// 执行任务, -s 输出错误堆栈信息
> gradlew -s customTask
任务依赖
任务之间可以有依赖关系,也就是说一个任务执行完后,才能执行其他任务。可以通过dependsOn指定其依赖的任务。
task customTask1 {
doLast {
println "customTask1 running."
}
}
// customTask2的执行会依赖于customTask1
task customTask2(dependsOn: customTask1) {
doLast {
println "customTask2 running."
}
}
> gradlew customTask2
// 输出打印信息,customTask1 会优先 customTask2 执行
customTask1 running.
customTask2 running.
一个任务也可以同时依赖多个任务,dependsOn是Task类的一个方法,可以接受多个依赖的任务作为参数
task customTask1 {
doLast {
println "customTask1 running."
}
}
task customTask2 {
doLast {
println "customTask2 running."
}
}
task customTask3 {
// customTask3 的执行,依赖于customTask1 , customTask12
// 多个任务,用逗号隔开,在前面的任务会先执行,如:customTask1任务
dependsOn customTask1, customTask2
doLast {
println "customTask3 running."
}
}
// 执行customTask3任务
> gradlew customTask3
// 输出打印信息,
:customTask1
customTask1 running.
:customTask2
customTask2 running.
:customTask3
customTask3 running.
通过任务名操作任务
可以通过任务名(任务类型是Task),使用Task的API访问它的方法、属性、或者对任务重新配置。
task customTask1 {
println "customTask1 running."
}
customTask1.doFirst {
println "customTask1 doFirst running."
}
customTask1.doLast {
println "has customTask1 property ${project.hasProperty('customTask1')}"
println "customTask1 doLast running."
}
// 执行任务
> gradlew customTask1
// 输出打印信息
customTask1 running.
customTask1 doFirst running.
has customTask1 property true
customTask1 doLast running.
从上面脚本中可知,可以调用 doFirst 和 doLast 方法,在任务执行前后做一些操作。使用任务名操作任务的原理是:**Project在创建该任务的时候,同时把该任务对用的任务名注册为Project的一个属性,类型为Task。通过project.hasProperty(String propertyName)**可以检查是否有这个属性。
自定义属性
Project和Task都可以添加额外的自定义属性,通过应用所属对应的ext属性实现。如果自定义多个属性,使用代码块。可以跨Project,跨Task访问自定义属性。
// 自定义有个Project属性
ext.myName = 'kerwin'
// 自定义多个属性通过代码块
ext {
myAge = 12
myPhone = 13564954189
}
task customTask {
doLast {
println "myName: ${myName}"
println "myAge: ${myAge}"
println "myPhone: ${myPhone}"
}
}
// 执行任务
> gradlew customTask
// 输出结果
myName: kerwin
myAge: 12
myPhone: 13564954189
Project相关的API
获取Project
查看所有的Project,在Gradle中为我们提供了Task任务projects,执行下面命令后,会列出所有的Project
> gradlew projects
// 执行上面命令后,列出所有的project,包括Root project
------------------------------------------------------------
Root project
------------------------------------------------------------
Root project 'walletApp'
\--- Project ':app
我们可以通过Project提供的API访问所有的project。getAllprojects返回所有的project,包括当前project,返回类型:Set集合
def getMyAllProjects() {
println "-------------------------------------"
println "Root Project"
println "-------------------------------------"
// 获取所有project,包括本身
this.getAllprojects().eachWithIndex { Project project, int index ->
if (index == 0) {
println "Root Project: ${project.name}"
} else {
println "+---- Project: ${project.name}"
}
}
}
也提供了getSubprojects返回所有子project,返回类型:Set集合
def getMySubprojects() {
println "-------------------------------------"
println "Sub Project"
println "-------------------------------------"
// 获取所有子project
this.getSubprojects().eachWithIndex { Project project, int index ->
println "+---- Project: ${project.name}"
}
}
除了上面两种方式,还提供了获取 Parent project和 Root project ,对应的方法分别是getParent() 和 getRootProject()。他们主要区别是,**getParent()如果本身就是Root Project,则返回null;而getRootProject()**如果本身就是Root Project,返回Root project,不会返回null
/**
* 获取父Project, 如果本身就是Root Project,返回null
*/
def getMyParentProject() {
// The parent project, or null if this is the root project.
if (this.getParent()) {
println "the parent project name is : ${this.getParent().name}"
} else {
println "the parent project is null"
}
}
/**
* 获取Root Project,如果本身就是Root Project,返回自己,不会返回null
*/
def getMyRootProject() {
// The root project. Never returns null.
def name = this.getRootProject().name
println "the root project name is: ${name}"
}
统一配置Project
可以在Root project中通过Project提供的project方法对单个project进行独立配置,如应用插件、project分组、project版本、依赖等信息
project('app') { Project project ->
project.apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
project.group 'com.yqb.mm'
project.version '1.0.0'
project.dependencies {
}
}
每个Project都会有一个Build文件,可以通过Project提供的subprojects 或者 allprojects 可以对Child Project统一配置
this.subprojects {
println "The project name is ${project.name}"
}
// 输出日志信息
The project name is app
The project name is basiclib
属性相关的API
Project默认提供下面几种属性,从下图中可以看出,为什么gradle中build文件名是build.gradle了。
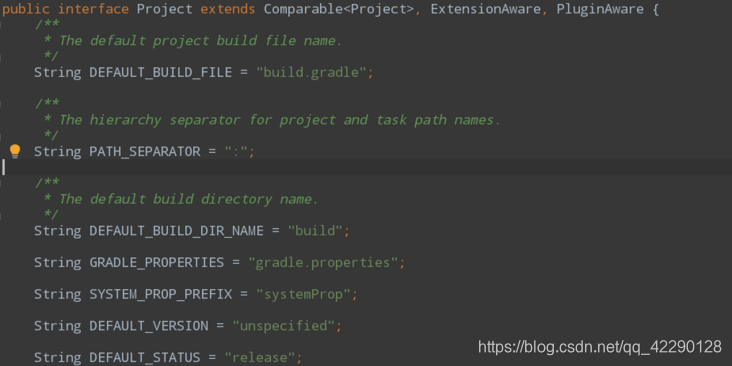
除了Project默认提供的,我们也可以通过ext关键字自定义属性。下面是我们自定义的应用包名、版本信息、依赖、签名文件等相关信息。
ext {
applicationId = "com.kerwin.test"
// android sdk version
// 使用如下:
// def versions = rootProject.ext.versions
// compileSdkVersion versions.compileSdkVersion
// buildToolsVersion versions.buildToolsVersion
versions = [
compileSdkVersion: 26,
minSdkVersion : 19,
targetSdkVersion : 26,
versionCode : 182,
versionName : '1.8.2',
]
// dependencies
// 使用如下:
// def dependencies = rootProject.ext.dependencies
// compile dependencies.support.appcompat
dependencies = [
support : [
appcompat : "com.android.support:appcompat-v7:26.1.0",
constraint: "com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.1.3",
design : "com.android.support:design:26.1.0"
],
gson : "com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.5"
]
signingConfigs = [
debug: [
storeFile : '../keystore/mm_debug.keystore',
storePassword: 'pa123456',
keyAlias : 'mm_key',
keyPassword : 'pa123456',
]
]
}
除了上面方式自定义属性外,还可以在gradle.properties文件中定义,但只能是简单的Key-Value形式.
在gradle.properties文件中自定义如下属性:
// gradle.properties
TINKER_ENABLE=true
例如可以在settings.gradle文件中根据在gradle.properties文件中定义的属性做一些操作
if (hasProperty('TINKER_ENABLE') ? Boolean.parseBoolean(TINKER_ENABLE) : false) {
println "TINKER_ENABLE 打开了."
} else {
println "TINKER_ENABLE 关闭了."
}
// 当TINKER_ENABLE=true,输出日志信息
TINKER_ENABLE 打开了.
文件相关API
路径获取相关API
在Project中提供了很多获取文件路径的方法,如:getProjectDir(),getRootDir(),getBuildDir()
// Root project的根目录路径
println "the root directory of this project, ${project.getRootDir().absolutePath}"
// 当前project的build文件路径
println "the build directory of this project, ${project.getBuildDir().absolutePath}"
// 当前project的目录路径,如果当前project是Root project,等同于getRootDir()
println "The directory containing the project build file, ${project.getProjectDir().absolutePath}"
// 输出的日志信息
the root directory of this project, D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp
the build directory of this project, D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp\build
The directory containing the project build file, D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp
文件操作相关API
文件的定位,根据文件路径获取文件内容
println getContent('settings.gradle')
def getContent(String path) {
try {
def file = file(path)
return file.text
} catch (Exception ex) {
println "getContent has error: ${ex.getMessage()}"
return ""
}
}
文件拷贝
Project为我们提供了简便的方法copy对文件进行拷贝。
def copyApk() {
this.copy {
// srcApkDir>>> D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp\app\build\bakApk
// destApkDir>>> D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp\build\apk
// from 用于指定拷贝的源文件或者文件夹
from file("${buildDir}/bakApk/")
// into 用于指定拷贝的目的地
into file("${getRootProject().getBuildDir().path}/apk")
}
}
除了使用from 和 into 指定源路径和目的地之外,还可以配置拷贝后使用rename文件重新命名、exclude移除不需拷贝的文件等。
def copyApk() {
this.copy {
// srcApkDir>>> D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp\app\build\bakApk
// destApkDir>>> D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp\build\apk
// 指定拷贝的源文件或者文件夹
from file("${buildDir}/bakApk/")
// 指定拷贝的目的地
into file("${getRootProject().getBuildDir().path}/apk")
// 移除不需要拷贝的文件, 例如:不拷贝以txt结尾的文件
//exclude "**/*.txt"
// 也可以使用闭包,移除不需要拷贝的文件
exclude { details ->
println "exclude>>> file: ${details.file}"
return details.file.name.endsWith('.txt')
}
// 重新命名拷贝的文件名
rename { String fileName ->
println "rename>> fileName: ${fileName}"
fileName.replace("app-arm-debug.apk", "test.apk")
}
}
}
文件树遍历
Project提供的fileTree方法,可以将指定文件目录下所有的文件封装成文件树对象操作
fileTree("build/outputs/apk") { ConfigurableFileTree fileTree ->
fileTree.visit { FileVisitDetails details ->
println "The file name is ${details.file}"
copy {
from details.file
into "${getRootProject().getBuildDir().path}/apk"
exclude { file ->
return file.file.isDirectory()
}
}
}
}
依赖相关API
Project提供了依赖相关的API,如 buildscript
buildscript {
repositories {
maven { url "http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/" }
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.0.1'
classpath 'com.alibaba:arouter-register:1.0.2'
classpath("com.tencent.tinker:tinker-patch-gradle-plugin:${TINKER_VERSION}") {
changing = TINKER_VERSION?.endsWith("-SNAPSHOT")
exclude group: 'com.android.tools.build', module: 'gradle'
}
}
}
执行外部命令API
可以使用Project提供的javaexec 或者 exec 执行一个外部命令。使用外部命令实现一个copy功能
tasks.create(name: 'copyAPK') {
doLast {
def srcFilePath = this.buildDir.path + "/outputs/apk"
def destFilePath = this.buildDir.path + "/outputs/backup"
def command = "mv -f ${srcFilePath} ${destFilePath}"
exec { ExecSpec execSpec ->
try {
executable 'bash'
args '-c', command
} catch (Exception ex) {
println "copyAPK>>> error: ${ex}"
}
}
}
}
任务创建方式,以及配置
可以使用Project提供的task方法或者通过TaskContainer提供的create方法。
任务名字方式创建任务
通过Project中的task(String name)方法创建任务
def customTask0 = task('customTask0')
// 调用任务的doLast 方法,该方法在任务执行阶段执行。
customTask0.doLast {
println "创建任务方法原型: Task task(String name)"
}
customTask0就是创建的任务名字,通过gradlew customTask0执行这个任务。
任务名字+一个对该任务配置的Map对象来创建任务
def customTask1 = task(group: 'help', 'customTask1')
customTask1.doLast {
println "创建任务方法原型: Task task(Map<String, ?> args, String name)"
println "任务分组: ${customTask1.group}, 任务名字:${customTask1.name}"
// 任务分组: build, 任务名字:customTask1
}
其中Map参数用来对创建的Task进行配置,上例中指定任务的分组为help,该任务就会分组到help组中。

任务名+闭包方式创建任务
// 方式一:创建任务并配置任务
task customTask2 {
// 配置任务的分组
group 'myTask'
// 配置任务的描述信息
description '任务名+闭包方式创建任务'
// 处理任务执行后需要做的事
doLast {
println "创建方法原型:Task task(String name, Closure configureClosure)"
println "任务分组:${customTask2.group}, 任务描述:${customTask2.description}"
}
}
// 方式二:创建任务并配置任务
task customTask2(group: 'myTask', description: '任务名+闭包方式创建任务') {
doLast {
println "创建方法原型:Task task(String name, Closure configureClosure)"
println "任务分组:${customTask2.group}, 任务描述:${customTask2.description}"
}
}
除了可以使用Map参数配置任务,还可以使用闭包的方式对任务进行配置。因为闭包中的委托对象就是Task,所有可以使用Task对象的任何方法、属性进行配置。
查看Task源码可知,可用的配置如下:
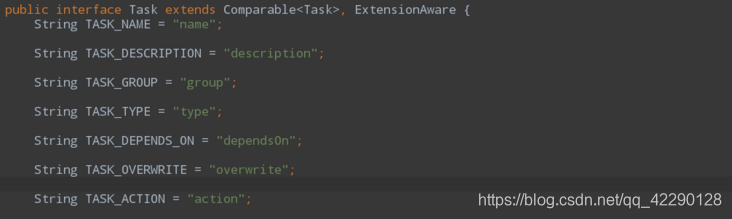
配置项的详细讲解:
// 用于配置任务的描述,默认值:null
String TASK_DESCRIPTION = "description";
// 用于配置任务的分组,默认值:null
String TASK_GROUP = "group";
// 基于一个存在的Task来创建,和我们类继承差不多,默认值:DefaultTask
String TASK_TYPE = "type";
// 用于配置任务的依赖,默认值:[]
String TASK_DEPENDS_ON = "dependsOn";
// 是否替换存在的Task,这个和type配合起来用,默认值:false
String TASK_OVERWRITE = "overwrite";
// 添加到任务中的一个Action或者一个闭包,默认值:null
String TASK_ACTION = "action";
通过TaskContainer创建任务
tasks.create('customTask3') {
group 'myTask'
description '通过TaskContainer创建任务'
doLast {
println "TaskContainer的create创建任务原型:Task create(String name, Closure configureClosure)"
println "任务分组: ${group}, 任务描述: ${description}"
}
}
tasks是Project对象的属性,类型是TaskContainer,可以直接调用它的create方法创建任务。
任务访问方式
通过任务名访问
我们创建的任务都会作为Project的一个属性,属性名就是任务名,所以可以直接通过任务名访问该任务。
def customTask0 = task('customTask0')
// 通过任务名访问
customTask0.doLast {
println "创建任务方法原型: Task task(String name)"
}
通过TaskContainer集合方式访问
其实TaskContainer就是我们创建任务的集合,在Project中可以通过tasks属性访问TaskContainer,可以通过访问集合的方式访问任务。
tasks['customTask3'].doFirst {
println "通过访问集合的方式访问任务."
}
通过任务名获取任务,其实调用的就是tasks.getAt(‘customTask3’),最后调用的是**findByName(String name)**实现。
通过TaskContainer的find或者get方式访问
get访问方式如果找不到任务,就会抛出UnknownTaskException异常。
find访问方式如果找不到任务,就会返回null
任务执行实战
统计执行阶段的时间,也就是所有Task的执行的所有时间。
def startBuildTime, endBuildTime
// afterEvaluate配置阶段完成调用
this.afterEvaluate { Project project ->
println "-----------配置阶段完成--------------"
// 所有Task配置完成后,找到第一个执行的Task
def preBuildTask = project.tasks.findByName('preBuild')
if (preBuildTask) {
preBuildTask.doFirst {
startBuildTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
println "task build start time: ${startBuildTime}"
}
}
def buildTask = project.tasks.findByName('build')
if (buildTask) {
buildTask.doLast {
endBuildTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
println "the build cost time: ${endBuildTime - startBuildTime}"
}
}
}
任务依赖
单个任务和多个任务依赖,可以通过dependsOn指定其依赖的任务。但是我们也可以通过匹配指定依赖的任务。
task myTask1 {
doLast {
println "myTask1>>doLast"
}
}
task myTask2 {
doLast {
println "myTask2>>doLast"
}
}
task customTask5 {
// 通过匹配,查看依赖任务
dependsOn this.project.tasks.findAll { Task task ->
println "task name>>> ${task.name}"
return task.name.startsWith('myTask')
}
doLast {
println "customTask5>>doLast"
}
}
任务依赖-项目实战
将发布版本文档的输出到每个版本单独文档中实战。
// releases.xml,发布版本文档格式
<releases>
<release>
<versionCode>100</versionCode>
<versionName>1.0.0</versionName>
<versionInfo>App的第1个版本,上线了一些最基础核心的功能.</versionInfo>
</release>
<release>
<versionCode>110</versionCode>
<versionName>1.1.0</versionName>
<versionInfo>App的第2个版本,上线了一些最基础核心的功能.</versionInfo>
</release>
</releases>
将解析文档后的内容写入到${buildDir}/generated/release/release-${versionCode}.txt文件中
tasks.create('handleReleaseInfoTask') {
println "buildDir>>> ${this.buildDir.path}"
def srcFile = file('releases.xml')
def destDir = new File(this.buildDir, 'generated/release/')
doLast {
println "开始解析releases.xml文件"
if (!destDir.isDirectory()) destDir.mkdirs()
def releases = new XmlParser().parse(srcFile)
releases.release.each { Node releaseNode ->
def versionCode = releaseNode.versionCode.text()
def versionName = releaseNode.versionName.text()
def versionInfo = releaseNode.versionInfo.text()
// 创建文件写入
def descFile = new File(destDir, "release-${versionCode}.txt")
descFile.withWriter { writer ->
writer.write("${versionCode}->${versionName}->${versionInfo}")
}
}
}
}
// 测试任务handleReleaseInfoTaskTest依赖handleReleaseInfoTask任务
task handleReleaseInfoTaskTest(dependsOn: handleReleaseInfoTask) {
def fileDir = fileTree("${this.buildDir.path}/generated/release/")
doLast {
fileDir.each {
println "the file name>>> ${it}"
}
println "解析完成."
}
}
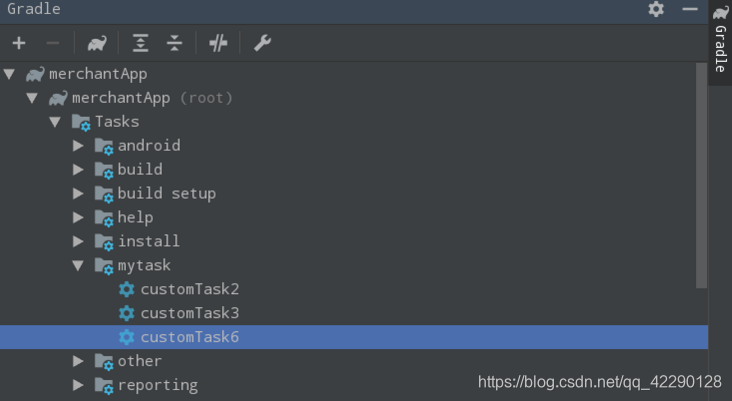
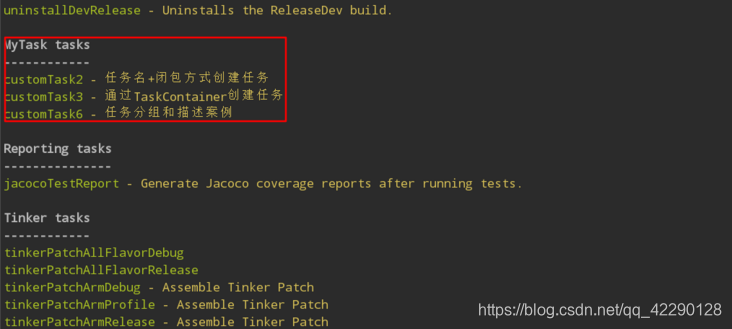
任务分组和描述
任务是可以分组和添加描述的,分组就是对任务分类。在通过执行gradlew tasks查看任务信息时,就可以看到不同组下的任务,并还可以看到任务描述信息。
// 配置任务的分组和描述信息
task customTask6(group: 'myTask', description: '任务分组和描述案例') {
doLast {
println "group: ${group}, description: ${description}"
}
}
添加分组后,可以在组里找到相应的任务,如下图所示:
<< 操作符(已过时,建议doLast)
<< 操作符是Gradle的Task中的doLast方法的短标记形式,也就是**<<**代替doLast方法。
task customTask7 << {
println "customTask7 doLast"
}
其实**<<操作符在Groovy中可以重载的,查看源码可知,在Task接口中对应leftShift方法重载了<<**操作符。
任务执行流程分析
当执行一个Task时,其实就是执行Task对象中的actions列表,其类型是一个List
task customTask8(type: CustomTask) {
doFirst {
println "Task执行之前执行:doFirst"
}
doLast {
println "Task执行之后执行:doLast"
}
}
class CustomTask extends DefaultTask {
@TaskAction
def doSelf() {
println "Task自己本身在执行:doSelf"
}
}
> gradlew customTask8
// 执行Task后输出的日志信息
Task执行之前执行:doFirst
Task自己本身在执行:doSelf
Task执行之后执行:doLast
上例中定义一个Task类型CustomTask , 被TaskAction注解标记的方法,代表Task本身执行要执行的方法。
其实doFirst ,doSelf,doLast 这个三个方法能够按照顺序执行,那么在actions列表中必须按照顺序排列的。
在Task创建时,Gradle就会解析被TaskAction标记的方法作为其Task执行的Action,通过actions.add(0, action)添加 到actions列表中。
doFirst方法通过actions.add(0, action)添加到actions列表中,doFirst就会出现在doSelf前面;而doLast通过actions.add(action)添加到actions列表中,doLast就会出现在doSelf后面。所以在执行Task的时,就达到顺序执行的目的。
任务排序
可以通过 mustRunAfter 和 shouldRunAfter 方法控制一个任务必须或者应该在某个任务后执行。
taskB.shouldRunAfter(taskA) 表示taskB应该在taskA执行后执行,可能任务顺序不会按照期望的执行。
taskB.mustRunAfter(taskA) 表示taskB必须在taskA执行后执行。
task customTask10 {
doLast {
println "TasK: customTask10"
}
}
task customTask9 {
mustRunAfter customTask10
doLast {
println "TasK: customTask9"
}
}
> gradlew customTask9 customTask10
// 执行后输出日志信息
TasK: customTask10
TasK: customTask9
任务的启动和禁用
Task有个enabled属性可以启动和禁用任务。默认为true,表示启动;当设置为false,输出会提示该任务被Skipping。
task customTask11 {
doLast {
println "TasK: customTask11"
}
}
customTask11.enabled = false
> gradlew -i customTask11
// 输出的日志信息
Skipping task ':customTask11' as task onlyIf is false.
任务的onlyIf断言
断言就是一个条件表达式。Task中有一个onlyIf方法,接受闭包作为参数,当该闭包返回true,该任务执行,否则跳过。
应用场景:可以控制程序哪些情况下打什么包,什么时候执行单元测试,什么情况下执行单元测试时候不执行网络测试。
案例实战:假设打渠道包时,如果直接build会编译出所有的包,太慢!可以通过onlyIf控制
tasks.create('buildHuaweiRelease') {
doLast {
println "build 华为渠道包."
}
onlyIf {
def execution = true
if (project.hasProperty('build_apps')) {
Object build_apps = project.property('build_apps')
println "buildHuaweiRelease>>> build_apps: ${build_apps}"
if ('all'.equals(build_apps) || 'shoufa'.equals(build_apps)) {
execution = true
} else {
execution = false
}
}
return execution
}
}
task buildMIUIRelease {
doLast {
println "build MIUI渠道包."
}
onlyIf {
def execution = true
if (project.hasProperty('build_apps')) {
Object build_apps = project.property('build_apps')
println "buildMIUIRelease>>> build_apps: ${build_apps}"
if ('all'.equals(build_apps) || 'shoufa'.equals(build_apps)) {
execution = true
} else {
execution = false
}
}
return execution
}
}
task buildQQRelease {
doLast {
println "build QQ渠道包."
}
onlyIf {
def execution = true
if (project.hasProperty('build_apps')) {
Object build_apps = project.property('build_apps')
println "buildMIUIRelease>>> build_apps: ${build_apps}"
if ('all'.equals(build_apps) || 'exclude_shoufa'.equals(build_apps)) {
execution = true
} else {
execution = false
}
}
return execution
}
}
task buildTask {
group BasePlugin.BUILD_GROUP
description '打渠道包'
dependsOn buildHuaweiRelease, buildMIUIRelease, buildQQRelease
}
上例中buildHuaweiRelease 和 buildMIUIRelease 是首发渠道包,buildQQRelease 不是首发渠道包,可以通过build_apps属性控制打哪些渠道包
// 打所有渠道包
gradlew buildTask
gradlew -Pbuild_apps=all buildTask
// 打首发渠道包
gradlew -Pbuild_apps=shoufa buildTask
// 打非首发渠道包
gradlew -Pbuild_apps=exclude_shoufa buildTask
命令行中**-P意思是:为Project指定K-V格式的属性键值对,格式为:-PK=V**
任务添加规则
当执行或者依赖的任务不存在时,添加任务规则后,可以对执行失败的任务做一些操作。
// 任务名作为闭包的参数
tasks.addRule('规则描述') {String taskName ->
task(taskName) {
doLast {
println "${taskName}任务不存在"
}
}
}
task ruleTaskTest {
dependsOn missTask
}
// 执行后属性日志信息
missTask任务不存在
任务输入输出
Task提供了inputs 和 outputs 输入输出属性。
Task输入输出案例实战:版本发布文档自动维护
步骤:请求本次发布的版本相关信息->将版本相关信息解析出来->将解析出来的数据生成xml格式数据->写入已有的文档数据中
请求版本信息这一步使用自定义属性方式代替,首先定义版本相关信息如下
ext {
versionCode = 105
versionName = '1.0.5'
versionInfo = 'App first version.'
destVersionOutputsFile = this.project.file('releases.xml')
if (!destVersionOutputsFile.exists()) {
destVersionOutputsFile.createNewFile()
}
}
// 用于封装版本信息
class Version {
def versionCode
def versionName
def versionInfo
}
创建一个写入任务writeVersionTask
tasks.create('writeVersionTask') {
group 'myTask'
description '版本信息自动写入任务.'
inputs.property('versionCode', versionCode)
inputs.property('versionName', versionName)
inputs.property('versionInfo', versionInfo)
outputs.file destVersionOutputsFile
doLast {
println "版本信息自动写入任务开始."
def versionData = inputs.getProperties()
def version = new Version(versionData)
def writerFile = outputs.files.singleFile
def sw = new StringWriter()
def markupBuilder = new MarkupBuilder(sw)
if (writerFile.text != null && writerFile.text.size() <= 0) {
// 第一次写入
markupBuilder.releases {
markupBuilder.release {
versionCode(version.versionCode)
versionName(version.versionName)
versionInfo(version.versionInfo)
}
}
writerFile.withWriter { Writer writer ->
writer.write(sw.toString())
}
} else {
// 已有其他版本信息
markupBuilder.release {
versionCode(version.versionCode)
versionName(version.versionName)
versionInfo(version.versionInfo)
}
def lines = writerFile.readLines()
def linesSize = lines.size()
writerFile.withWriter { Writer writer ->
lines.eachWithIndex { line, index ->
println "line: ${line}, index: ${index}"
if (index != linesSize - 1) {
writer.append(line).append('\n')
} else {
// 最后一行
writer.append(sw.toString()).append('\n').append('\n')
writer.append(line)
}
}
}
}
println "版本信息自动写入任务结束."
}
}
创建一个读取任务readVersionTask
tasks.create('readVersionTask') {
group 'myTask'
description '版本信息自动读取任务.'
mustRunAfter writeVersionTask
inputs.file destVersionOutputsFile
doLast {
def readFile = inputs.files.singleFile
println readFile.text
}
}
创建一个测试任务versionTaskTest
tasks.create('versionTaskTest') {
dependsOn writeVersionTask, readVersionTask
doLast {
println "版本信息自动维护结束"
}
}
挂载自定义的Task到构建过程中
上例中,每次发布版本,都要手动执行writeVersionTask任务,怎么挂载在build构建过程中呢?
// afterEvaluate:配置阶段完成调用,此时所有的Task解析完成
this.afterEvaluate {
// 找到build任务
def buildTask = project.tasks.findByName('build')
if (buildTask != null) {
buildTask.doLast {
// build任务执行完后调writeVersionTask任务
writeVersionTask.execute()
}
}
}
Gradle插件
Gradle内置了很多插件,其中Android Gradle插件就是基于内置的Java插件实现的。
应用一个插件
插件的应用都是通过Project的apply方法完成的,而插件又分为二进制插件和脚本插件。
应用插件方法
二进制插件就是实现了org.gradle.api.Plugin接口的插件,可以有plugin id,如java插件。二进制插件一般都是打包在一个jar独立发布
// 'java'就是Java插件的plugin id,是唯一的
// 它对应得到类型是org.gradle.api.plugins.JavaPlugin
apply plugin: 'java'
// 也可以通过该类型应用这个插件,包org.gradle.api.plugins是默认导入的,可以去掉
apply plugin: JavaPlugin
应用脚本插件其实就是把这个脚本加载进来,与二进制插件不同的是,脚本插件使用from关键字,后面跟一个脚本文件,可以是本地的,也可以是网络,如果是网络要使用HTTP URL。
更重要的是,脚本文件是模块化的基础。
// 在build.gradle文件中引用脚本文件
apply from: 'config/project.config.gradle'
// project.config.gradle脚本文件
ext {
// android sdk version
// 使用如下:
// def versions = rootProject.ext.versions
// compileSdkVersion versions.compileSdkVersion
// buildToolsVersion versions.buildToolsVersion
versions = [
compileSdkVersion: 26,
minSdkVersion : 19,
targetSdkVersion : 26,
versionCode : 182,
versionName : '1.8.2',
]
// dependencies
// 使用如下:
// def dependencies = rootProject.ext.dependencies
// compile dependencies.support.design
dependencies = [
support : [
appcompat : "com.android.support:appcompat-v7:26.1.0",
constraint: "com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:1.1.3",
design : "com.android.support:design:26.1.0"
],
gson : "com.google.code.gson:gson:2.8.5"
]
}
Project中的apply有3个重载方法可以应用插件
void apply(Closure closure);
void apply(Action<? super ObjectConfigurationAction> action);
void apply(Map<String, ?> options);
应用第三方发布的插件
第三方发布的二进制插件,需要在buildscript {}中配置classpath才能使用,跟Gradle提供的内置插件不一样。而Android Gradle插件就是第三方插件,需要配置,如果不配置,就会提示找不到这个插件。
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
// 配置插件
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.0.1'
}
}
配置好第三方插件后,就可以应用插件了
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
Grade社区提供了好多插件,可以在下面地址找到.
https://plugins.gradle.org/
自定义插件
我们可以根据自己的实际业务自定义一些插件,来辅助项目构建。
自定义插件需要实现Plugin接口,这个接口只有apply一个方法,该方法配置阶段调用,我们可以在该方法中创建任务,创建方法等。
仅自己项目使用自定义插件
如果自定义的插件只在自己的项目使用,可以简单的定义在build脚本文件里
// build.gradle文件中
// 应用自定义的插件
apply plugin: CustomPlugin
//
class CustomPlugin implements Plugin<Project> {
@Override
void apply(Project project) {
println "我是自定义插件."
project.task('customPluginTask') {
println "我是自定义任务.."
doLast {
println "这是一个通过自定义插件方式创建任务."
}
}
}
}
或者新建buildSrc,目录结构如下:

只需要在build.gradle脚本中应用就OK了
// 注意包名需要加上
apply plugin: com.example.gradle.plugins.MyCustomPlugin
自定义插件供其他项目使用
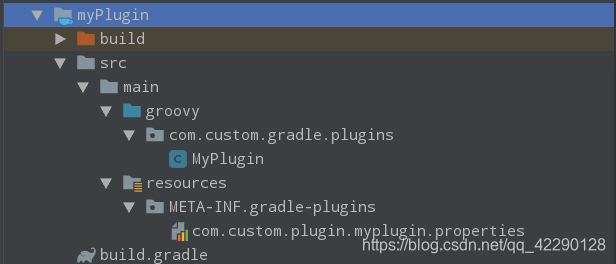
但是如果想开发一个独立的插件供其他的项目使用,怎么做呢?这需要单独创建一个Groovy工程开发自定义插件:
首先按照下如图建立groovy目录后,自定义一个MyPlugin插件类,包名可以任意,如:com.custom.gradle.plugins
然后实现插件类,自定义插件MyPlugin,实现Plugin接口
package com.custom.gradle.plugins
import org.gradle.api.Plugin
import org.gradle.api.Project
// 自定义插件,需要实现Plugin接口
class MyPlugin implements Plugin<Project> {
@Override
void apply(Project project) {
project.task('myCustomPluginTask') {
doLast {
println "这个在myPlugin中自定义插件的方式创建任务."
}
}
}
}
而每个插件都有一个唯一的plugin id,需要我们自定义。
Gradle是通过META-INF里的properties文件来查找对应插件实现类的。
我这里定义的plugin id是com.custom.plugin.myplugin,然后在src/main/resources/META-INF/gradle-plugins/目录中新建一个名字为plugin id的properties文件,如com.custom.plugin.myplugin.properties,文件内容如下:
// key为implementation-class,value就是自定义的插件实现类
implementation-class=com.custom.gradle.plugins.MyPlugin
在build.gradle文件中配置自定义插件所需的依赖:
// 应用groovy插件
apply plugin: 'groovy'
dependencies {
implementation gradleApi()
implementation localGroovy()
compileOnly 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.4.2'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
sourceSets {
main {
groovy {
srcDir 'src/main/groovy'
}
resources {
srcDir 'src/main/resources'
}
}
}
打包到本地的Maven仓库
打包到本地的Maven仓库(仅仅为了测试自定义插件),最终打包上传到远程Maven仓库
// 应用maven插件
apply plugin: 'maven'
//配置分组group和版本version
group = 'com.custom.plugin'
version = '1.0.1'
uploadArchives {
repositories {
mavenDeployer {
//提交到远程服务器:
// repository(url: "http://www.xxx.com/repos") {
// authentication(userName: "admin", password: "admin")
// }
//本地的Maven地址设置为D:/repos
repository(url: uri('D:/repos'))
}
}
}
执行gradlew uploadArchives命令后,就是上传到本地的repos仓库
其他项目使用自定义插件
在Root Project中的build.gradle文件中配置
buildscript {
repositories {
maven { // 配置自定义插件本地Maven仓库地址
url uri('D:/repos')
}
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.4.2'
// 配置自定义的插件 group:com.custom.plugin, name:myPlugin,version:1.0.1
// 简写格式: group:name:version
classpath 'com.custom.plugin:myPlugin:1.0.1'
// 标准的写法,上面简写格式,使用 冒号 分隔group,name,version
// classpath group: 'com.custom.plugin', name: 'myPlugin', version: '1.0.2'
}
}
在Sub Project中build.gradle文件中应用plugin id
// com.custom.plugin.myplugin是plugin id
// plugin id为resources/META-INF/gradle-plugins/com.custom.plugin.myplugin.properties文件名
apply plugin: 'com.custom.plugin.myplugin'
Android Gradle插件
Android插件就是Gradle的一个第三方插件,基于Gradle构建的。
Android Gradle插件根据Android工程属性分3类:
- App应用工程,可生成一个APK应用,插件id: com.android.application
- Library库工程,可生成AAR包,包含资源信息,插件id: com.android.library
- Test测试工程,插件id: com.android.test
应用Android Gradle插件
Android Gradle是托管在jcenter上,在根工程的build.gradle中要先配置依赖classpath
// 根工程build.gradle
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.0.1'
}
}
配置好后,在子工程的build.gradle就可以应用插件了,其实**android {}**是Android插件提供的一个扩展类型。
// 子工程build.gradle
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
android {
compileSdkVersion 23
}
Android Gradle工程
Android Gradle插件继承Java插件,需要在settings.gradle中配置子工程。
Android Gradle工程的配置,都是在android {},这是唯一的一个入口。可以对Android Gradle工程自定义配置,它的具体实现是com.android.build.gradle.AppExtension,是Project的一个扩展。
compileSdkVersion
配置Android SDK的版本,该配置的原型是:
public void compileSdkVersion(int apiLevel) {
compileSdkVersion("android-" + apiLevel);
}
除了上面方法外,还提供了set方法,可以当做android的一个属性使用
android.compileSdkVersion = 23
buildToolsVersion
buildToolsVersion “23.0.1” 表示Android构建工具版本。可以直接通过 buildToolsVersion 方法赋值,也可以通过android.buildToolsVersion 这个属性赋值。
defaultConfig
defaultConfig是默认的配置,它是一个ProductFlavor。ProductFlavor允许根据不同的情况生成多个不同的APK包,比如多渠道打包。如果不针对自定义的ProductFlavor单独配置,会为这个ProductFlavor使用默认的defaultConfig配置。
android{
defaultConfig {
// 是一个属性,指定包名,没有指定从AndroidManifest.xml文件中读取
applicationId "com.kerwin"
// 是一个方法,配置最低支持的Android系统版本
minSdkVersion 19
// 是一个方法,配置基于哪个Android版本开发,没有配置从AndroidManifest.xml文件中读取
targetSdkVersion 26
// 是一个属性,配置App应用的内部版本号,一般控制App升级,建议配置
versionCode 100
// 是一个属性,配置App应用的版本名称,可查看App是哪一个版本,外部使用
versionName "1.0.0"
//是一个属性,默认是:applicationId + ".test"
testApplicationId "com.kerwin.test"
// 配置单元测试时使用的Runner,默认:android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner
testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
}
buildTypes
buildTypes是一个NamedDomainObjectContainer类型,是一个域对象。可以在buildTypes {} 中增加多个需要构建的类型,如:release,debug
release就是Gradle自动创建的一个对应的BuildType
buildTypes {
release {
// 是否为该构建类型启用混淆,true:启用
minifyEnabled true
// 当启动混淆时,所使用的proguard的配置文件,proguardFiles 接受可变参数
// getDefaultProguardFile方法 获取Android SDK目录下默认的配置文件
// 路径:android-sdk\tools\proguard\proguard-android.txt
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard/proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
signingConfigs配置签名信息
配置签名信息,对生成的APK签名。
android{
// 是一个方法,其类型NamedDomainObjectContainer,debug 和 release 定义的是一个SigningConfig
// 一个SigningConfig就是一个签名配置
signingConfigs {
def signingConfig = rootProject.ext.signingConfigs
def debugSigningConfig = signingConfig.debug
// debug配置,一般debug模式是已经配置好的。debug证书位于:${HOME}\.android\debug.keystore
debug {
// 签名文件
storeFile file(debugSigningConfig.storeFile)
// 签名证书文件密码
storePassword debugSigningConfig.storePassword
// 签名证书中密钥别名
keyAlias debugSigningConfig.keyAlias
// 签名证书中密钥的密码
keyPassword debugSigningConfig.keyPassword
}
// release 配置
release {
storeFile file(jenkinsProperties['KEY_STORE'])
storePassword jenkinsProperties['KEY_STOREPWD']
keyAlias jenkinsProperties['KEY_ALIAS']
keyPassword jenkinsProperties['KEY_ALIASPWD']
}
}
}
可以在defaultConfig中默认的签名配置,也可以在构建类型分别配置签名信息。
android {
buildTypes {
release {
// signingConfigs是Android对象实例的一个属性,对应是getSigningConfigs(),release是创建的签名配置名称
signingConfig signingConfigs.release
}
debug {
signingConfig signingConfigs.debug
}
}
}
buildTypes构建类型
buildTypes也是Android的一个方法,接受参数是域对象NamedDomainObjectContainer,每添加一个都是BuildType类型,如debug
android {
buildTypes {
debug {
// 是一个属性,配置基于applicationId 的后缀。配置后,debug版本包名为applicationId.debug
applicationIdSuffix ".debug"
// 是一个属性,配置是否生成一个可供调试的apk
debuggable true
// 是一个属性,配置是否生成一个可供调试JNI代码的apk
jniDebuggable true
// 是一个属性,是否开启混淆
minifyEnabled true
// 是一个属性,是否启用自动拆分多个dex的功能
multiDexEnabled true
// 是一个属性,配置签名配置
signingConfig signingConfigs.release
// 是一个方法,配置多个混淆文件
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'),
'proguard/proguard-rules.pro'
// 是一个属性,配置是否自动清理未使用的资源,默认false
shrinkResources true
// 是一个属性,zipalign是Android提供的一个整理优化apk文件工具。
// 可以提高应用运行效率,更快读写apk中资源,降低内存使用
zipAlignEnabled true
}
}
Android Gradle 高级自定义
批量修改生成的apk文件名
Android Gradle中有很多相同的任务,这些任务的名字都是通过Build Types 和 Product Flavors 动态创建和生成的。
如果修改生成的apk文件名,就要修改Android Gradle打包的输出。Android对象提供了3个属性:applicationVariants 仅仅用于Android应用Gradle插件,libraryVariants 仅仅适用于Android库Gradle插件,testVariants 以上两种Gradle插件都适用。
这3个属性返回的都是DomainObjectSet对象集合,里面元素分别是ApplicationVariant,LibraryVariant,TestVariant ,这3个元素都是变体(就是Android构建产物)。如:ApplicationVariant表示Baidu渠道的release包,是基于Build Types 和 Product Flavors 生成的产物。
android {
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled true
signingConfig signingConfigs.release
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt')
}
debug {
minifyEnabled false
}
}
productFlavors {
//发布使用
arm {
}
//开发使用
dev {
}
}
// variant就是生成的产物,共有armRelease,armDebug,devRelease,devDebug四个产物
applicationVariants.all { variant ->
variant.outputs.all { output ->
println "applicationVariants>>>>> outputFile: ${output.outputFile}, name: ${output.outputFile.name}"
println "applicationVariants>>>>> flavorName: ${variant.flavorName}, baseName: ${variant.baseName}, name: ${variant.name}"
if (output.outputFile != null && output.outputFile.name.endsWith('.apk')
&& 'debug'.equals(variant.buildType.name)) {
def apkFile = new File(output.outputFile.getParent(),
"${project.name}-${variant.baseName}-${new Date().format('yyyyMMdd')}.apk")
outputFileName = apkFile.name
println "output apk file: >>>>>${output.outputFile}"
}
}
}
}
其中一个输出
applicationVariants>>>>> outputFile: D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp\app\build\outputs\apk\dev\debug\app-dev-debug.apk, name: app-dev-debug.apk
applicationVariants>>>>> flavorName: dev, baseName: dev-debug, name: devDebug
output apk file: >>>>>D:\work\yqb.com\newCode\merchantApp\app\build\outputs\apk\dev\debug\app-dev-debug-20190903.apk
动态修改版本信息
版本一般由3个部分构成:major.minor.patch,版本号.副版本号.补丁号
原始配置方式,比较直观。最大问题就是修改不方便
android {
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.kerwin"
minSdkVersion 19
targetSdkVersion 26
versionCode 100
versionName "1.0.0"
}
}
可以分模块方式配置,将版本号的配置单独抽取出来,放在单独的文件里,供其他build引用。Android是可以通过apply from方式引用
// 新建config.gradle文件
ext {
versionCode = 100
versionName = '1.0.0'
}
**ext { }**块为当前project创建扩展属性。其他build.gradle中引用后就可以使用
apply from: 'config.gradle'
我们也可以从属性文件中动态获取,例如创建一个config.properties属性文件
// config.properties
versionCode=100
versionName='1.0.0'
然后在build.gradle文件中动态获取
Properties properties = new Properties()
if (project.hasProperty("config.properties")
&& file(project.property("config.properties")).exists()) {
properties .load(new FileInputStream(file(project.property("config.properties"))))
}
if (properties != null && properties .size() > 0) {
String versionCode= properties ['versionCode']
String versionName= properties ['versionName']
}
动态配置AndroidManifest文件
在构建的过程中,动态修改AndroidManifest文件中内容。在使用友盟第三方分析统计时,要求在AndroidManifest文件中指定渠道名
<meta-data
android:name="UMENG_CHANNEL"
// ${UMENG_CHANNEL}占位符,UMENG_CHANNEL是变量名
android:value="${UMENG_CHANNEL}"/>
其中Channel ID要替换成不同渠道名,如google,baidu,miui。在构建时,根据生成的不同渠道包来指定不同的渠道名,Android Gradle提供manifestPlaceholders、Manifest占位符替换AndroidManifest文件中的内容
android {
productFlavors {
google {
// 是一个属性,Map类型。key就是在AndroidManifest文件中占位符变量
manifestPlaceholders.put("UMENG_CHANNEL", "google")
}
}
// 也可以迭代productFlavors批量修改
productFlavors.all { flavor ->
println "productFlavors>>> name: ${flavor.name}"
manifestPlaceholders.put("UMENG_CHANNEL", flavor.name)
}
}
自定义BuildConfig
下面是Android Gradle自动生成的
/**
* Automatically generated file. DO NOT MODIFY
*/
package ${packageName};
public final class BuildConfig {
public static final boolean DEBUG = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
public static final String APPLICATION_ID = "${packageName}";
public static final String BUILD_TYPE = "debug";
public static final String FLAVOR = "arm";
public static final int VERSION_CODE = 215;
public static final String VERSION_NAME = "2.1.5";
}
还可以自定义一些常量,动态配置。Android Gradle提供了**buildConfigField(@NonNull String type, @NonNull String name, @NonNull String value)**可以自定义常量到BuildConfig中。
android {
buildTypes {
debug {
buildConfigField "String", "testBuildConfig", "\"测试\""
}
release {
buildConfigField "String", "testBuildConfig", "\"测试\""
}
}
}
动态添加自定义的资源
除了可以res/values文件夹中使用xml的方式定义资源外,还可以在Android Gradle中定义。
通过**resValue(@NonNull String type,
@NonNull String name,
@NonNull String value)**方法,在 BuildType 和 ProjectFlavor 中都存在,可以针对不同的渠道,或者不同的构建类型自定义特有资源。
android {
buildTypes {
debug {
// 第一个参数可以是 string、id、bool、dimen、integer、color
resValue "string", "baidu_map_api_key", "\"1234567\""
}
release {
resValue "string", "baidu_map_api_key", "\"76544321\""
}
}
}
在下图目录中可以找到生成的自定义资源

Java编译选项
可以通过compileOptions对java源文件编码、源文件使用的JDK版本配置
android {
compileOptions {
encoding Charsets.UTF_8.name()
// Java源代码编译级别,格式可以是 "1.8" 、1.8 、JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8 、VERSION_1_8
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
// 配置生成的Java字节码的版本
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
DEX选项配置
android {
dexOptions {
// 配置最大堆内存
javaMaxHeapSize "4g"
// 函数超过65535个时,有时需要开启jumbo模式才可以构建成功。默认是false
jumboMode = true
// 配置是否预执行dex Libraries库工程,开启后可以提高增量构建速度,默认是开启的
// 当使用dx的--multi-dex选项生成多个dex,会导致和库工程冲突,应该关闭
preDexLibraries true
// Integer类型,配置运行dx命令时使用的线程数
threadCount 4
}
}
开启MultiDex,突破65535方法限制
APK中包含 Dalvik Executable (DEX) 文件形式的可执行字节码文件,这些DEX文件包含应用运行已编译代码。 65,535等于 64 X 1024 - 1
因为Dalvik虚拟机在执行DEX文件时,使用short类型索引DEX文件中方法,单个DEX文件中方法可以被定义最多是65535个,当超过就会报错。
trouble writing output:
Too many field references: 131000; max is 65536.
You may try using --multi-dex option.
较低版本的编译系统会报告一个不同的错误,但指示的是同一问题:
Conversion to Dalvik format failed:
Unable to execute dex: method ID not in [0, 0xffff]: 65536
可采用生成多个DEX文件来解决这个问题。
在Android 5.0之后,Android使用ART运行时方式,支持从APK文件加载多个DEX文件,ART在APK安装时执行预编译,扫描classes*N*.dex文件,将多个DEX文件合并成一个**.oat**文件执行;在 minSdkVersion 为 21 或者更高,不需要多dex文件支持库。
在Android 5.0之前,Android使用Dalvik运行,而Dalvik虚拟机限制每个APK只能使用一个classes.dex字节码文件,要使用必须使用Multidex库。
配置多dex
minSdkVersion为 21 或者 以上,只需将 multiDexEnabled 设置为 true 就可以。
当配置multidex后,当超过65535时生成多个dex文件,文件名为classes.dex,classes2.dex,classesN.dex
android {
defaultConfig {
// 启用multidex
multiDexEnabled true
}
}
如果minSdkVersion为 21 以下(不包括21)
- multiDexEnabled 设置为 true,同时还需添加多dex依赖库
dependencies {
// 配置multidex依赖
implementation 'com.android.support:multidex:1.0.1'
}
- 控制Application入口
// 1. 如果没有自定义Application,只需在AndroidManifest文件中直接配置MultiDexApplication
<application
android:name="android.support.multidex.MultiDexApplication" />
// 2. 如果有自定义的Application,并且是直接继承Application的。可以将修改为MultiDexApplication
public class MMApplication extends MultiDexApplication{ }
// 3. 如果自定义的Application已经继承的第三方提供的Application,就不能继承了。可以在重新attachBaseContext方法实现
@Override
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
super.attachBaseContext(base);
MultiDex.install(this);
}
在 MultiDex.install(this)完成之前,不要通过反射或者其他任何代码,否则导致ClassNotFoundException
Android 编译工具会根据需要构建主 DEX 文件 (classes.dex) 和辅助 DEX 文件(classes2.dex 和 classes3.dex 等)。然后,编译系统会将所有 DEX 文件打包到您的 APK 中。
后续会讲解下MultiDex实现原理
多dex局限性
- 如果辅助DEX文件较大,可能导致应用无响应ANR
- 多DEX文件配置会增加编译处理时间,因为编译系统需要做出决策,哪些类包含在主DEX中,哪些类包含在辅助DEX中。
可以使用dex预处理缩短增量编译时间。dex 预处理依赖于Android 5.0或以上版本中提供的 ART 格式。Android Studio2.3或以上版本会自动使用此功能。如果命令行运行Gradle编译。需要设置minSdkVersion 21或以上启用dex预处理。
一个开发类型dev 和一个发布类型prod,它们具有不同的 minSdkVersion 值,来创建两个应用版本
android {
defaultConfig {
...
multiDexEnabled true
// The default minimum API level you want to support.
minSdkVersion 15
}
productFlavors {
// Includes settings you want to keep only while developing your app.
dev {
// Enables pre-dexing for command line builds. When using
// Android Studio 2.3 or higher, the IDE enables pre-dexing
// when deploying your app to a device running Android 5.0
// (API level 21) or higher—regardless of what you set for
// minSdkVersion.
minSdkVersion 21
}
prod {
// If you've configured the defaultConfig block for the production version of
// your app, you can leave this block empty and Gradle uses configurations in
// the defaultConfig block instead. You still need to include this flavor.
// Otherwise, all variants use the "dev" flavor configurations.
}
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled true
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'),
'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
dependencies {
compile 'com.android.support:multidex:1.0.3'
}
声明主DEX中必需的类
在构建多DEX时, 编译工具会执行复杂的决策来确定主DEX文件中需要的类,以便能够成功启动。如果主DEX文件中没有提供启动时需要的任何类,就会奔溃出现java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError错误。
对于代码依赖复杂或者自检机制,就可能不会将这些类识别为主DEX文件中必需类。需要使用multiDexKeepFile 或者multiDexKeepProguard 声明主DEX文件中必需的类,在构建时如果匹配到就添加到主DEX文件中。
- multiDexKeepFile
创建一个名为multidex-config.txt文件,在文件中添加需要放在主DEX的类,每行包含一个类,格式如下:
com/example/MyClass.class
com/example/MyOtherClass.class
Gradle会读取相对于build.gradle文件路径,multidex-config.txt 与 build.gradle 文件在同一目录中。
android {
buildTypes {
release {
multiDexKeepFile file('multidex-config.txt')
}
}
}
- multiDexKeepProguard
multiDexKeepProguard中文件添加内容格式与支持 Proguard 语法相同,包含**-keep**选项
-keep class com.example.MyClass
-keep class com.example.MyClassToo
或者指定包中所有的类
-keep class com.example.** { *; } // All classes in the com.example package
android {
buildTypes {
release {
multiDexKeepFile file('multidex-config.pro')
}
}
}
代码和资源压缩
为了减小APK的大小,应该启动压缩来移除发布构建中未使用的代码和资源。
代码压缩通过 ProGuard 提供,ProGuard 会检测和移除应用中未使用的类、字段、方法和属性,包括自带代码库中的未使用项。ProGuard 还可优化字节码,移除未使用的代码指令,以及用短名称混淆其余的类、字段和方法。
资源压缩通过 Gradle 的 Android 插件提供,该插件会移除应用中未使用的资源,包括代码库中未使用的资源。
代码压缩
要通过 ProGuard 启用代码压缩,在 build.gradle 文件内相应的构建类型中添加 minifyEnabled true
代码压缩会影响构建速度,避免在调试中使用。
android {
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled true
// 用于定义 ProGuard 规则,getDefaultProguardFile 从 ${Android SDK}\tools\proguard\文件夹获取默认的ProGuard 配置
// proguard-rules.pro文件用于添加自定义ProGuard 配置,默认文件位于模块根目录
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'),
'proguard/proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
每次构建时,ProGuard 都会输出下列文件:
- dump.txt 说明 APK 中所有类文件的内部结构
- mapping.txt 提供原始与混淆过的类、方法和字段名称之间的转换
- seeds.txt 列出未进行混淆的类和成员
- usage.txt 列出从 APK 移除的代码
这些文件保存在 ${module-name}/build/outputs/mapping/release/ 中
自定义要保留的代码
默认 ProGuard 配置文件 (proguard-android.txt) 足以满足需要,ProGuard 会移除所有(并且只会移除)未使用的代码。但是,ProGuard 很难以对多情况进行正确分析,可能会移除应用需要的代码。举例来说,它可能错误移除代码的情况包括:
- 当应用引用的类只来自 AndroidManifest.xml 文件时
- 当应用调用的方法来自 Java 原生接口 (JNI) 时
- 当应用在运行时(例如使用反射或自检)操作代码时
可以强制 ProGuard 保留指定代码,在 ProGuard 配置文件中添加一行 -keep 代码。或者在想保留的代码添加 @keep 注解,在类上添加 @keep 可原样保留整个类,在方法或者字段上添加可完整保留方法/字段以及类名称。
-keep public class * extends android.app.Activity
解码混淆过的代码追踪
在 ProGuard 压缩代码后,代码追踪变得困难,因为方法名称都混淆处理了。但是ProGuard 每次运行时都会创建一个 mapping.txt 文件,其中显示了与混淆过的名称对应的原始类名称、方法名称和字段名称。ProGuard 将该文件保存在应用的 /build/outputs/mapping/release/ 目录中。
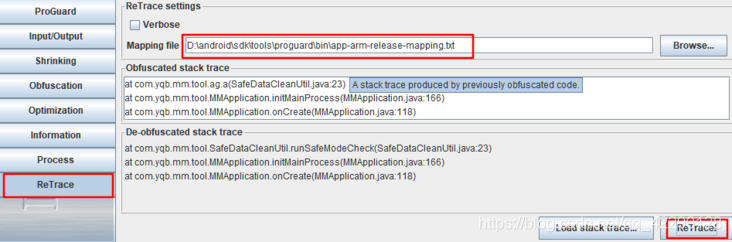
可以使用Android SDK 提供的工具解码混淆过的代码,retrace脚本(Window上为retrace.bat,Mac/Linux上为retrace.sh),位于**/tools/proguard/**目录中
retrace.bat|retrace.sh [-verbose] mapping.txt [<stacktrace_file>]
例如:
retrace.bat -verbose mapping.txt obfuscated_trace.txt
也可以直接使用 proguardgui.bat 图形化工具,位于**/tools/proguard/bin/**目录中
资源压缩
资源压缩只与代码压缩协同工作。代码压缩器移除所有未使用的代码后,资源压缩器便可确定应用仍然使用的资源。
启用资源压缩,在 build.gradle 文件中将 shrinkResources 属性设置为 true,默认是false
android {
buildTypes {
release {
shrinkResources true
minifyEnabled true
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'),
'proguard/proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
资源压缩器目前不会移除 values/ 文件夹中定义的资源(例如字符串、尺寸、样式和颜色)。这是因为 Android 资源打包工具 (AAPT) 不允许 Gradle 插件为资源指定预定义版本
在开始 shrinkResources 后,打包构建时,Android Gradle自动处理未使用的资源,生成的apk就不会包含。可以在构建输出日志中查看,gradlew assembleArmRelease --info | grep "unused resource"
Removed unused resources: Binary resource data reduced from 2977KB to 2879KB: Removed 3%
但是可能会误删有用的资源,如使用反射去引用资源文件,Android Gradle区分不出来,认为这些资源没有被使用。我们可以使用keep配置哪些资源不被清理。
自定义要保留的资源
如果有想要保留或舍弃的特定资源,在项目中创建一个包含 resources 标记的 XML 文件,并在 tools:keep 属性中指定每个要保留的资源,在 tools:discard 属性中指定每个要舍弃的资源。这两个属性都接受逗号分隔的资源名称列表。还可以使用星号字符作为通配符。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:keep="@layout/l_used*_c,@layout/l_used_a,@layout/l_used_b*"
tools:discard="@layout/unused2" />
将该文件保存在项目资源中,例如,保存在 res/raw/keep.xml。构建不会将该文件打包到 APK 之中。
启用严格引用检查
正常情况下,资源压缩器可准确判定系统是否使用了资源。但是,如果在代码调用 Resources.getIdentifier(),这就表示代码会根据动态生成的字符串查询资源名称。当执行这一调用时,默认情况下资源压缩器会采取防御性行为,将所有具有匹配名称格式的资源标记为可能已使用,无法移除。
// 会使所有带 img_ 前缀的资源标记为已使用
String name = String.format("img_%1d", angle + 1);
res = getResources().getIdentifier(name, "drawable", getPackageName());
默认情况下启用的是安全压缩模式,tools:shrinkMode=“safe”。如果将 keep.xml 文件中 shrinkMode 设置为 strict,也就是启用严格压缩模式,并且代码也引用了包含动态生成字符串的资源,则必须利用 tools:keep 属性手动保留这些资源。如果不保留,也会被清理掉。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:shrinkMode="strict" />
移除未使用的备用资源
shrinkResources只会移除代码未被引用的资源,不会移除不同设备的备用资源。比如引用的第三方库,特别是Support Library,为了国际化支持几十种语言,但是有的App不用支持这么多的语言,只需中文和英文就可以了;比如图片只支持xhdpi格式就可以。
可以使用 Android Gradle 插件的 resConfigs 属性来移除您的应用不需要的备用资源文件。
android {
defaultConfig {
// 只会保留默认的default 和 en 资源 ,其他的不会打包到APK中
resConfigs "en"
}
}
resConfigs的参数是资源限定符,包括屏幕方向(port,land),屏幕尺寸(small,normal,large,xlarge),屏幕像素密度(hdpi,xhdpi),API Level(V3,V4)等
Android Gradle 多项目构建
Android 项目一般分为库项目、应用项目、测试项目,对应的插件是com.android.library、com.android.application、com.android.test
应用项目一般只有一个,最终打包成一个APK,库项目可以有多个,可以被应用项目引用。
多项目设置
在Gradle中可以创建多个项目,并且可以通过文件夹管理,最终在settings.gradle里配置就可以。
// 项目结构
MyProject
+ app
+ libraries
+ lib1
+ lib2
settings.gradle
上面项目结构中,一个根项目MyProject,并有一个settings.gradle配置文件,Sub Project有一个应用项目 App,两个库项目 lib1 和 lib2 放在libraries文件夹下。
在settings.gradle文件中配置
// void include(String[] projectPaths);
include ':app', ':libraries:lib1', ':libraries:lib1:lib2'
如果项目路径很多,可以下面方式指定配置
include ':example1'
project(":example1").projectDir = new File(rootDir, 'chapter/example1')
库项目引用和配置
库项目引用通过dependencies实现。Android Lib打包生成的是aar包,Java Lib打包生成的是jar包,aar包可以有res资源。
dependencies {
implementation project(':libraries:lib1')
}
引用Android库项目,其实就是引用库项目发布的aar包。 默认Android库项目发布都是release版本,可以配置修改默认发布
android {
// 配置 发布debug版本的aar包
defaultPublishConfig "debug"
// 如果配置多个flavor,可以配置flavor + buildtype
// defaultPublishConfig "flavorDebug"
}
发布多个版本aar,默认情况下,是不能同时发布多个arr包,但是可以开启
android {
// 告诉Android Gradle插件,可同时发布不同的aar包
publishNonDefault true
}
其它项目就可以引用不同的aar
dependencies {
flavor1Implementation project(path: ':lib1', configuration: 'flavor1Release')
flavor2Implementation project(path: ':lib1', configuration: 'flavor2Release')
}
发布aar包到Maven中心库
- 在build.gradle文件中应用Maven插件
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
// 应用Maven仓库
apply plugin: 'maven'
- 配置Maven构建三要素,分别是group:artifact:version
// build.gradle
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
// 应用Maven仓库
apply plugin: 'maven
group = 'com.custom.plugin'
version = '1.0.2'
为了更好的联调测试,提供快照版本SNAPSHOT,如:配置成1.0.0-SNAPSHOT。发布到snapshot中心库时,每次发布版本号不会变化,只会在版本号后按顺序号+1,如:1.0.0-1,1.0.0-2,1.0.0-3等。引用时版本号写成1.0.0-SNAPSHOT即可,Maven会自动下载最新版本快照。
- 发布配置,如:发布哪个Maven仓库,使用的用户名和密码,发布什么格式的存档,artifact是什么等
boolean needUploadToLocal = false;//是否将Library发布到本地
boolean isArchivesRelease = false;//是否将Library发布到Release仓库;false 为发布到SnapShot仓库
//gradlew :sub-project:newsindiasdk:clean :sub-project:newsindiasdk:uploadArchives
//com.cmcm.onews.sdk:onews_sdk:5.3.1.12-SNAPSHOT@aar
apply plugin: 'maven'
//注意了,以后maven帐户请在local.properties里配置,eg:
//maven.u= your user
//maven.p= your pwd
Properties props = new Properties()
props.load(new FileInputStream(project.rootProject.file("local.properties")))
String u = props.get('maven.u');
String p = props.get('maven.p');
uploadArchives {
repositories {
mavenDeployer {
if (needUploadToLocal) {
pom.version = "Debug"
repository(url: "D:/NewsArch")
} else {
pom.version = "6.3.1.3"
if (isArchivesRelease) {
repository(url: "http://10.60.80.74:8081/nexus/content/repositories/cleanmasterrelease") {
authentication(userName: u, password: p)
}
} else {
pom.version += "-SNAPSHOT" // -SNAPSHOT
repository(url: "http://10.60.80.74:8081/nexus/content/repositories/cleanmastersnapshot") {
authentication(userName: u, password: p)
}
}
}
pom.artifactId = "onews_sdk"
pom.groupId = "com.cmcm.onews.sdk"
}
}
}
- 使用它们需要配置仓库,因为是私有仓库,使用时告诉Gradle
// Root Project中build.gradle
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.0.1'
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
jcenter()
// 发布版本
maven {
url "http://10.60.80.74:8081/nexus/content/repositories/cleanmasterrelease"
}
// 快照版本
maven {
url "http://10.60.80.74:8081/nexus/content/repositories/cleanmastersnapshot"
}
}
}
// Sub Project中添加依赖
dependencies {
implementation "com.cmcm.onews.sdk:onews_sdk:6.2.4.7-SNAPSHOT@aar"
}
Android Gradle 多渠道构建
多渠道构建基本原理
在Android Gradle中,有一个Build Variant概念,翻译就是构建变体,构建的产物(APK)。
Build Variant = Project Flavor + Build Type
Build Type 构建类型,如:Release,Debug;Project Flavor 构建渠道,如:Baidu,Google。
Build Variant 构建变体,如:baiduRelease,baiduDebug,googleRelease,googleDebug
Android Gradle提供productFlavors 方法添加不同的渠道,参数接受域对象类型,ProductFlavor作为闭包参数
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {}
google {}
}
}
配置发布渠道后,Android Gradle就会产生很多Task,基本上都是基于 Project Flavor + Build Type方式生成的,如:assembleBaidu,assembleRelease,assembleBaiduRelease。assemble开头的负责生成构建产物APK。
每个Project Flavor,也就是每个渠道,可以定义自己的SourceSet,Dependencies依赖。
Flurry多渠道 和 友盟多渠道 构建
- Flurry多渠道配置
Flurry的统计是已Application划分渠道的,每个Application都有一个key。在Flurry上创建Application时自动生成,可以为每个渠道配置不同的Flurry Key,使用BuildConfig配置。
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {
buildConfigField 'String', 'FLURRY_KEY', "\"QHHJNNGGHJK\""
}
google {
buildConfigField 'String', 'FLURRY_KEY', "\"kkkiihhhgggv\""
}
}
}
...
Flurry.init(this, BuildConfig.FLURRY_KEY);
- 友盟多渠道配置
友盟存在渠道概念,但它不是在代码中指定的,而是在AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置的,通过配置meta-data标签来设置。
<meta-data
android:name="UMENG_CHANNEL"
android:value="Channel ID" />
Channel ID就是渠道值,如:Baidu,Google。可通过manifestPlaceholders来动态改变渠道值。
多渠道构建定制
通过配置Android Gradle 插件的 ProductFlavor可灵活控制每个渠道包.
- applicationId
它是ProductFlavor属性,设置该渠道的包名,想为渠道设置特别的包名,可以使用applicationId这个属性设置
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {
applicationId "com.gradle.test.baidu"
}
}
}
- consumerProguardFiles
即是一个属性,也有一个同名的方法,只对Android库项目有用。consumerProguardFiles方法是一直添加,不会清空之前的混淆文件,而consumerProguardFiles属性方式每次都是新的混淆文件列表,以前的配置会先被清空。
// 属性
public void setConsumerProguardFiles(@NonNull Iterable<?> proguardFileIterable) {
getConsumerProguardFiles().clear();
consumerProguardFiles(Iterables.toArray(proguardFileIterable, Object.class));
}
// 方法
public void consumerProguardFiles(@NonNull Object... proguardFiles) {
for (Object proguardFile : proguardFiles) {
consumerProguardFile(proguardFile);
}
}
当发布库项目生成AAR时,使用consumerProguardFiles配置的混淆文件也会被打包到AAR里一起发布,当应用项目引用这个AAR时,并启动混淆时,会自动使用AAR包里的混淆文件对AAR包里代码进行混淆,就不用对AAR包进行混淆配置,因为AAR自带了。
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {
consumerProguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
}
- manifestPlaceholders
- multiDexEnabled
启动多个dex配置,用来突破65535方法问题。
- proguardFiles
配置混淆文件
- signingConfig
配置签名
- testApplicationId
是一个属性,用来适配测试包的包名,值一般为App的包名+.test
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {
testApplicationId "com.gradle.test"
}
}
}
- testFunctionalTest 和 testHandleProfiling
testFunctionalTest 表示是否为功能测试,testHandleProfiling表示是否启动分析功能。
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {
testFunctionalTest true
testHandleProfiling true
}
}
}
- testInstrumentationRunner
配置运行测试使用的 Instrumentation Runner 的全路径的类名,且必须是android.app.Instrumentation 的子类。
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {
testInstrumentationRunner "android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner"
}
}
}
- testInstrumentationRunnerArguments
与testInstrumentationRunner一起使用,配置 Instrumentation Runner 使用的参数,最终使用的都是adb shell am instrument 这个命令。testInstrumentationRunnerArguments 参数被转换传递给 am instrument这个命令使用,如:-e key value
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {
testInstrumentationRunnerArguments.put("converage", 'true')
}
}
}
- versionName 和 versionCode
配置渠道的版本号和版本名称
android {
productFlavors {
baidu {
versionName "2.1.5"
versionCode 215
}
}
}
- dimension
为了基于不同标准构建App,可以通过dimension 多维度的方式解决。
dimension是ProductFlavor的属性,接受一个字符串,该字符串就是维度名称,作为ProductFlavor的维度。维度名称不是随意指定的,在使用前需要声明,可以通过flavorDimensions 方法声明。
android {
// 声明维度后,才能在productFlavors中使用
// flavorDimensions 可同时指定多个维度,但是维度有顺序优先级的,第一个优先级最大
flavorDimensions 'api', 'version'
productFlavors {
demo {
dimension 'version'
...
}
full {
dimension 'version'
...
}
minApi24 {.
dimension 'api'
minSdkVersion '24'
versionNameSuffix "-minApi24"
...
}
minApi21 {
dimension "api"
minSdkVersion '21'
versionNameSuffix "-minApi21"
...
}
}
}
上例中,最后生成的variant(构建变体)会被几个 ProductFlavor对象配置:
- Android中的defaultConfig配置,也是一个ProductFlavor
- api维度的ProductFlavor,被dimension 配置标记为api的ProductFlavor
- version维度的ProductFlavor, 被dimension 配置标记为version的ProductFlavor
维度优先级很重要,高优先级的flavor会替换掉低优先级的资源、代码、配置等,上例中优先级:api>version>defaultConfig
通过dimension 指定维度后,Android Gradle会帮助生成相应 Task、SourceSet、Dependencies等。现在构建变体的产物=Api+Version+BuildType, 如:MinApi21DemoRelease、MinApi21FullRelease、MinApi21DemoDebug、MinApi21FullDebug等
提供多渠道构建的效率
生成多个渠道包主要是为了跟踪每个渠道的情况,如:新增、活跃、留存。除了根据渠道号区分每个渠道外,大部分情况下没有什么不同,唯一区别是属于哪个渠道。
因为Android Gradle对每个渠道包都要执行构建过程,导致速度变慢。美团研究一个办法,在APK的MEAT-INF目录下添加空文件不用重新签名原理。
- 利用Android Gradle打一个基本包(母包)
- 基于母包复制一个,文件名要区分产品,打包时间,版本,渠道
- 对复制的APK进行修改,在META-INF目录下新增空文件,文件名必须要区分渠道,如:mtchannel_google
- 利用python脚本执行 2, 3 步骤操作
使用时,在APK启动(Application onCreate)读取APK中META-INF目录下的前缀为mtchannel_文件,如果找到,把文件名取出来,然后就可以得到渠道标识(google)了,美团实现的代码:
public static String getChannel(Context context) {
ApplicationInfo appinfo = context.getApplicationInfo();
String sourceDir = appinfo.sourceDir;
String ret = "";
ZipFile zipfile = null;
try {
zipfile = new ZipFile(sourceDir);
Enumeration<?> entries = zipfile.entries();
while (entries.hasMoreElements()) {
ZipEntry entry = ((ZipEntry) entries.nextElement());
String entryName = entry.getName();
if (entryName.startsWith("mtchannel")) {
ret = entryName;
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (zipfile != null) {
try {
zipfile.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
String[] split = ret.split("_");
if (split != null && split.length >= 2) {
return ret.substring(split[0].length() + 1);
} else {
return "";
}
}
利用python脚本批处理,向APK中META-INF目录写入渠道文件,文件名前缀为mtchannel_
import zipfile
zipped = zipfile.ZipFile(your_apk, 'a', zipfile.ZIP_DEFLATED)
empty_channel_file = "META-INF/mtchannel_{channel}".format(channel=your_channel)
zipped.write(your_empty_file, empty_channel_file)
然后就是配置渠道列表,下载AndroidMultiChannelBuildTool工程后,在PythonTool/Info/channel.txt文件中添加渠道,渠道以换行隔开。
将想要批量打包的apk文件拷贝到PythonTool目录下(与MultiChannelBuildTool.py同级),运行py脚本即可打包完成。(生成的渠道apk包在output_** 目录下)
参考资料:
https://www.cnblogs.com/ct201…
https://github.com/GavinCT/An…
https://github.com/Meituan-Di…
Android Gradle 测试
Android为测试程序提供了很好支持,既可以使用传统的JUnit测试,又可以使用Android提供的Instrument测试。
基本概念
使用Android Studio新建一个项目时,会帮助我们默认生成 main 和 androidTest SourceSet。运行测试时,androidTest SourceSet会被构建成一个可以安装到设备上测试的APK,这个测试APK中有写好的测试用例,会被执行来测试APP。
在androidTest SourceSet中可以依赖各种测试库,如:单元测试的,集成测试的,espresso UI测试的,uiautomator自动化测试的。
一般测试APK会统一配置,而不是针对每个渠道都配置,在defaultConfig对测试APK配置后,会自动生成所需的包名、AndroidManifest.xml文件等信息。
android {
compileSdkVersion 29
buildToolsVersion "29.0.2"
defaultConfig {
testApplicationId "com.example.myapplication.test"
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
testFunctionalTest true
testHandleProfiling true
}
}
根据配置自动生成AndroidManifest.xml文件,android:targetPackage是Android自动生成的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.myapplication.test" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="21"
android:targetSdkVersion="29" />
<instrumentation
android:name="androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
android:functionalTest="true"
android:handleProfiling="true"
android:label="Tests for com.example.myapplication"
android:targetPackage="com.example.myapplication" />
<application android:debuggable="true" >
<uses-library android:name="android.test.runner" />
</application>
</manifest>
也可以在androidTest中配置依赖,正式APK不会编译到APK中,只有Android测试的时候才会被编译到测试APK中。
dependencies {
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test:runner:1.2.0'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.2.0'
}
默认情况下测试APK主要在debug模式下,debug模式下不会混淆代码,有利于发现问题,且对测试代码覆盖率也有帮助。Android Gradle提供了testBuildType,可以修改BuildType
android {
// 修改测试的是release类型的apk,默认类型是debug
testBuildType 'release'
}
怎么运行写好的测试代码呢?
使用 gradlew connectedCheck 任务来运行测试。这个任务是一个引导性的任务,首先使用assembleAndroidTest 和 assembleDebug 任务构建测试应用 和 被测试应用,然后通过**install*任务安装这两个应用,再运行写好的测试代码,运行完后,卸载这两个应用。
最后测试结果会保存在build/reports/androidTests/connected目录下,可以通过浏览器查看index.html测试结果。

本地单元测试
这种测试和原生的java测试一样,不依赖android框架或只有非常少的依赖,直接运行在本地开发机器上,不需要运行在Android设备上。但有时也需要Android框架本身一些代码依赖,如:Context,可以使用模拟框架来模拟这种依赖关系,如:Mockito 和 JMock
AndroidTest测试有自己的SourceSet目录 src/androidTest/java; 对于本地单元测试也有自己的目录src/test/java,测试用例用来测试main这个SourceSet代码。
Android本地单元测试,也使用JUnit这个流行的测试框架测试
dependencies {
// JUnit3的测试用例需要集成junit.framework.TestCase,且测试方法要以test为前缀
// JUnit4只需要使用 @Test 注解标记就可以,推荐使用JUnit4
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
编写好测试用例后, 运行 gradlew test 任务可以运行所有的单元测试用例,然后在build/reports/tests目录下生成测试报告。
如果想运行debug模式下的使用gradlew testDebugUnitTest任务。
在执行test任务时,如果想依赖Android框架,只能使用模拟对象框架,如:Mockito ,版本要是1.9.5以上,与Android单元测试兼容。
dependencies {
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12'
testImplementation 'org.mockito:mockito-all:1.10.19'
}
编写需要测试的代码,需要使用Context
public class Utils {
private Context mContext;
public Utils(Context context) {
this.mContext = context;
}
public String getAppName(){
return mContext.getString(R.string.app_name);
}
}
如果要测试上面的代码,因为需要一个Context,就要使用Mockito来模拟Context
import android.content.Context;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.Mock;
import org.mockito.runners.MockitoJUnitRunner;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.*;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.*;
/**
* kerwin <xujinbing839@pingan.com.cn> 2019-09-11
*/
@RunWith(MockitoJUnitRunner.class)
public class UtilsTest {
private static final String APP_NAME = "MyApplication";
@Mock
Context mMockContext;
@Test
public void readAppNameFromContext() {
when(mMockContext.getString(R.string.app_name)).thenReturn(APP_NAME);
Utils utils = new Utils(mMockContext);
String appName = utils.getAppName();
assertThat(appName, is(APP_NAME));
}
}
首先要告诉JUnit4,要使用MockitoJUnitRunner这个单元测试的运行者来执行,不然 @Mock 注解就不认识了。使用@Mock 注解模拟一个Context对象,mMockContext就是被Mockito模拟出来的。
when逻辑需要和Utils里的getAppName方法逻辑一样,然后使用thenReturn告诉模拟期望返回的值
使用 gradlew test 执行任务,查看报告结果。
Instrument测试
Instrument测试是基于Android设备或模拟器的测试,是一种高模拟和仿真测试。它可以使用Android SDK框架的所有类和特性,如:Context。还提供了Instrumenttation类,可以很方便的获得测试APK的Context、Activity。且可以使用Instrument测试做单元测试、UI自动化测试、集成测试。
Instrument测试要生成一个测试的APK,所以要对测试APK配置。testInstrumentationRunner 这个runner可以编写基于JUnit4测试用例,且可搭配使用JUnit4新特性。
android {
defaultConfig {
// 指定生成测试APK的包名,默认:被测试APK包名+test
testApplicationId "com.example.myapplication.test"
// 配置使用Runner
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
}
// 添加依赖
dependencies {
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test:runner:1.2.0'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test:rules:1.2.0'
// Optional
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.2.0'
// Optional
androidTestImplementation 'org.hamcrest:hamcrest-library:2.1'
// Optional
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.uiautomator:uiautomator-v18:2.2.0-alpha1'
}
rules库,为测试定义一些规则,实现自JUnit的rule,可以对JUnit扩展。如:ActivityTestRule指定要测试的Activity。编写好测试用例后,运行gradlew connectedAndroidTest 执行所有Instrument测试,在build/reports/androidTests目录下查看报告.
import android.util.Log;
import androidx.test.filters.LargeTest;
import androidx.test.rule.ActivityTestRule;
import androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnit4;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Rule;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
// LargeTest标记,说明有更高的权限,如多线程、访问数据库、时间限制也更长
@LargeTest
public class ExampleInstrumentedTest {
// 指定规则,测试MainActivity
@Rule
public ActivityTestRule<MainActivity> mActivityRule = new ActivityTestRule<>(MainActivity.class);
@Before
public void init() {
Log.d("kerwin_test", "init :::" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// init :::Instr: androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner
}
@Test
public void valid() throws Throwable {
mActivityRule.runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mActivityRule.getActivity().findViewById(R.id.text1).performClick();
}
});
}
}
测试选项配置
Android Gradle插件提供testOptions { } ,可对测试进行配置,如:生成测试报告的目录。
TestOptions提供配置项:
- resultsDir 是一个属性,配置生成测试结果目录
- reportDir 是一个属性,配置生成测试报告目录
- unitTests 即是属性,也是一个闭包,控制单元测试的执行
android {
testOptions {
resultsDir "${project.buildDir}/myResults"
reportDir "${project.buildDir}/myReports"
}
}
单个项目,测试报告可以生成在指定的目录下,有多个项目怎么办呢?
比如引用了多个库项目,每个库项目也有自己的测试,生成自己的报告,这样比较分散,不容易查看,如果统一起来查看就方便了。Android 提供了另一个插件 android-reporting ,应用后新增一个名为 mergeAndroidReports 任务,执行完测试后调用即可。
// 在Root Project中的build.gradle 文件最后应用后,添加的任务也在Root项目中。
apply plugin: 'android-reporting'
然后执行 gradlew deviceCheck mergeAndroidReports --continue 任务。mergeAndroidReports合并报告,–continue在测试失败的时候,也继续执行其他测试用例,一直执行完成为止。合并后的报告在Root项目的build目录中。
unitTests配置,对应的类型是UnitTestOptions,它是所有测试任务的一个集合。UnitTestOptions 对象有一个Test类型的域对象集合DomainObjectSet。对应源码:
public static class UnitTestOptions {
private DomainObjectSet<Test> testTasks = new DefaultDomainObjectSet<Test>(Test.class);
public void all(final Closure<Test> configClosure) {
testTasks.all(
new Action<Test>() {
@Override
public void execute(Test testTask) {
ConfigureUtil.configure(configClosure, testTask);
}
});
}
}
all方法可以遍所有的Test,它是Task类型。可以对他们做一些配置,或者根据任务做一些判断等。
android {
testOptions {
unitTests.all {
println "testName: >>>>>>${it.name}"
}
}
}
代码覆盖率
有了测试用例,就要有相应的测试代码覆盖率统计,这样才能知道代码是否被测试用例完全覆盖,还有哪些没有覆盖到,如何进行补全测试用例。Android Gradle内置了代码覆盖lv的报告生成,默认是关闭的。
android {
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
debug {
testCoverageEnabled true
}
}
}
testCoverageEnabled用于控制代码覆盖率统计是否开启,它是BuildType的一个属性,true代表开启,默认是false。
运行 gradlew createDebugCoverageReport 任务后,就会自动执行测试用例,并生成测试代码覆盖率报告,报告路径build/reports/coverage

Lint支持
Android提供了针对代码、资源优化工具Lint。可帮助检查哪些资源没有被使用,哪些使用了新的API,哪些资源没有国际化等,并生成一份报告,告诉哪些需要优化。
运行 gradle lint 任务即可生成报告,默认生成报告在build/reports/lint-results.html
Lint是一个命令行工具,在Android Tools目录下。在Android Gradle插件提供了 **lintOptions {}**这个闭包配置Lint。
android {
lintOptions {
// 遇到错误终止构建
abortOnError true
// 警告也会被当前错误处理
warningsAsErrors true
// 需要检查是否使用了新的API
check 'NewApi'
}
}
1. abortOnError
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,配置Lint发现错误时是否退出Gradle构建。默认true
2. absolutePaths
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,配置错误的输出里是否应该显示绝对路径,默认true,显示相对路径
3. check
是一个属性,也是一个方法,配置哪些项目需要Lint检查,这个项目就是Issue Id(s)。
NewApi这个就是一个issue id,lint有很多可用的issue id,通过lint --list可以查看可用的id。冒号前面是id,后面是对这个issue id的说明。可以使用lint --show命令查看详细说明.
Valid issue categories:
Correctness
Correctness:Messages
Correctness:Chrome OS
Security
Performance
Usability:Typography
Usability:Icons
Usability
Accessibility
Internationalization
Internationalization:Bidirectional Text
Valid issue id's:
"ContentDescription": Image without contentDescription
"AddJavascriptInterface": addJavascriptInterface Called
"ShortAlarm": Short or Frequent Alarm
"AllCaps": Combining textAllCaps and markup
"AllowAllHostnameVerifier": Insecure HostnameVerifier
"AlwaysShowAction": Usage of showAsAction=always
"InvalidUsesTagAttribute": Invalid name attribute for uses element.
"MissingIntentFilterForMediaSearch": Missing intent-filter with action
android.media.action.MEDIA_PLAY_FROM_SEARCH
"MissingMediaBrowserServiceIntentFilter": Missing intent-filter with action
android.media.browse.MediaBrowserService.
"MissingOnPlayFromSearch": Missing onPlayFromSearch.
"ImpliedTouchscreenHardware": Hardware feature touchscreen not explicitly
marked as optional
"MissingTvBanner": TV Missing Banner
"MissingLeanbackLauncher": Missing Leanback Launcher Intent Filter.
"MissingLeanbackSupport": Missing Leanback Support.
"PermissionImpliesUnsupportedHardware": Permission Implies Unsupported
Hardware
"UnsupportedTvHardware": Unsupported TV Hardware Feature
"SupportAnnotationUsage": Incorrect support annotation usage
"ShiftFlags": Dangerous Flag Constant Declaration
"LocalSuppress": @SuppressLint on invalid element
"SwitchIntDef": Missing @IntDef in Switch
"UniqueConstants": Overlapping Enumeration Constants
"InlinedApi": Using inlined constants on older versions
"Override": Method conflicts with new inherited method
"ObsoleteSdkInt": Obsolete SDK_INT Version Check
"NewApi": Calling new methods on older versions
"UnusedAttribute": Attribute unused on older versions
"AppCompatMethod": Using Wrong AppCompat Method
"AppCompatCustomView": Appcompat Custom Widgets
"AppCompatResource": Menu namespace
"GoogleAppIndexingApiWarning": Missing support for Firebase App Indexing Api
"GoogleAppIndexingWarning": Missing support for Firebase App Indexing
"AppLinksAutoVerifyError": App Links Auto Verification Failure
"AppLinksAutoVerifyWarning": Potential App Links Auto Verification Failure
"AppLinkUrlError": URL not supported by app for Firebase App Indexing
"TestAppLink": Unmatched URLs
"InconsistentArrays": Inconsistencies in array element counts
"Assert": Assertions
"BadHostnameVerifier": Insecure HostnameVerifier
"BatteryLife": Battery Life Issues
"BackButton": Back button
"ButtonCase": Cancel/OK dialog button capitalization
"ButtonOrder": Button order
"ButtonStyle": Button should be borderless
"ByteOrderMark": Byte order mark inside files
"MissingSuperCall": Missing Super Call
"AdapterViewChildren": AdapterViews cannot have children in XML
"ScrollViewCount": ScrollViews can have only one child
"PermissionImpliesUnsupportedChromeOsHardware": Permission Implies Unsupported
Chrome OS Hardware
"UnsupportedChromeOsHardware": Unsupported Chrome OS Hardware Feature
"GetInstance": Cipher.getInstance with ECB
"CommitTransaction": Missing commit() calls
"Recycle": Missing recycle() calls
"CommitPrefEdits": Missing commit() on SharedPreference editor
"ApplySharedPref": Use apply() on SharedPreferences
"ClickableViewAccessibility": Accessibility in Custom Views
"EasterEgg": Code contains easter egg
"StopShip": Code contains STOPSHIP marker
"MissingConstraints": Missing Constraints in ConstraintLayout
"VulnerableCordovaVersion": Vulnerable Cordova Version
"CustomViewStyleable": Mismatched Styleable/Custom View Name
"CutPasteId": Likely cut & paste mistakes
"SimpleDateFormat": Implied locale in date format
"SetTextI18n": TextView Internationalization
"Deprecated": Using deprecated resources
"MissingPrefix": Missing Android XML namespace
"MangledCRLF": Mangled file line endings
"DuplicateIncludedIds": Duplicate ids across layouts combined with include
tags
"DuplicateIds": Duplicate ids within a single layout
"DuplicateDefinition": Duplicate definitions of resources
"ReferenceType": Incorrect reference types
"StringEscaping": Invalid string escapes
"UnpackedNativeCode": Missing android:extractNativeLibs=false
"UnsafeDynamicallyLoadedCode": load used to dynamically load code
"UnsafeNativeCodeLocation": Native code outside library directory
"EllipsizeMaxLines": Combining Ellipsize and Maxlines
"ExifInterface": Using android.media.ExifInterface
"ExtraText": Extraneous text in resource files
"FieldGetter": Using getter instead of field
"InvalidAnalyticsName": Invalid Analytics Name
"MissingFirebaseInstanceTokenRefresh": Missing Firebase Instance ID Token
Refresh
"FontValidationError": Validation of font files
"FontValidationWarning": Validation of font files
"FullBackupContent": Valid Full Backup Content File
"ValidFragment": Fragment not instantiatable
"GetContentDescriptionOverride": Overriding getContentDescription() on a View
"PackageManagerGetSignatures": Potential Multiple Certificate Exploit
"AccidentalOctal": Accidental Octal
"UseOfBundledGooglePlayServices": Use of bundled version of Google Play
services
"GradleCompatible": Incompatible Gradle Versions
"GradleDependency": Obsolete Gradle Dependency
"GradleDeprecated": Deprecated Gradle Construct
"DevModeObsolete": Dev Mode Obsolete
"DuplicatePlatformClasses": Duplicate Platform Classes
"GradleGetter": Gradle Implicit Getter Call
"GradlePluginVersion": Incompatible Android Gradle Plugin
"HighAppVersionCode": VersionCode too high
"GradleIdeError": Gradle IDE Support Issues
"GradlePath": Gradle Path Issues
"GradleDynamicVersion": Gradle Dynamic Version
"NotInterpolated": Incorrect Interpolation
"StringShouldBeInt": String should be int
"NewerVersionAvailable": Newer Library Versions Available
"MinSdkTooLow": API Version Too Low
"GridLayout": GridLayout validation
"HandlerLeak": Handler reference leaks
"HardcodedDebugMode": Hardcoded value of android:debuggable in the manifest
"HardcodedText": Hardcoded text
"HardwareIds": Hardware Id Usage
"IconDuplicatesConfig": Identical bitmaps across various configurations
"IconDuplicates": Duplicated icons under different names
"GifUsage": Using .gif format for bitmaps is discouraged
"IconColors": Icon colors do not follow the recommended visual style
"IconDensities": Icon densities validation
"IconDipSize": Icon density-independent size validation
"IconExpectedSize": Icon has incorrect size
"IconExtension": Icon format does not match the file extension
"IconLauncherShape": The launcher icon shape should use a distinct silhouette
"IconLocation": Image defined in density-independent drawable folder
"IconMissingDensityFolder": Missing density folder
"IconMixedNinePatch": Clashing PNG and 9-PNG files
"IconNoDpi": Icon appears in both -nodpi and dpi folders
"IconXmlAndPng": Icon is specified both as .xml file and as a bitmap
"ConvertToWebp": Convert to WebP
"WebpUnsupported": WebP Unsupported
"IncludeLayoutParam": Ignored layout params on include
"DisableBaselineAlignment": Missing baselineAligned attribute
"InefficientWeight": Inefficient layout weight
"NestedWeights": Nested layout weights
"Orientation": Missing explicit orientation
"Suspicious0dp": Suspicious 0dp dimension
"InstantApps": Instant App Issues
"DuplicateDivider": Unnecessary Divider Copy
"TrustAllX509TrustManager": Insecure TLS/SSL trust manager
"InvalidImeActionId": Invalid imeActionId declaration
"InvalidPackage": Package not included in Android
"DrawAllocation": Memory allocations within drawing code
"UseSparseArrays": HashMap can be replaced with SparseArray
"UseValueOf": Should use valueOf instead of new
"JavascriptInterface": Missing @JavascriptInterface on methods
"JobSchedulerService": JobScheduler problems
"KeyboardInaccessibleWidget": Keyboard inaccessible widget
"LabelFor": Missing labelFor attribute
"InconsistentLayout": Inconsistent Layouts
"InflateParams": Layout Inflation without a Parent
"StaticFieldLeak": Static Field Leaks
"DefaultLocale": Implied default locale in case conversion
"LocaleFolder": Wrong locale name
"GetLocales": Locale crash
"InvalidResourceFolder": Invalid Resource Folder
"WrongRegion": Suspicious Language/Region Combination
"UseAlpha2": Using 3-letter Codes
"LogConditional": Unconditional Logging Calls
"LongLogTag": Too Long Log Tags
"LogTagMismatch": Mismatched Log Tags
"AllowBackup": AllowBackup/FullBackupContent Problems
"MissingApplicationIcon": Missing application icon
"DeviceAdmin": Malformed Device Admin
"DuplicateActivity": Activity registered more than once
"DuplicateUsesFeature": Feature declared more than once
"GradleOverrides": Value overridden by Gradle build script
"IllegalResourceRef": Name and version must be integer or string, not
resource
"MipmapIcons": Use Mipmap Launcher Icons
"MockLocation": Using mock location provider in production
"MultipleUsesSdk": Multiple <uses-sdk> elements in the manifest
"ManifestOrder": Incorrect order of elements in manifest
"MissingVersion": Missing application name/version
"OldTargetApi": Target SDK attribute is not targeting latest version
"UniquePermission": Permission names are not unique
"UsesMinSdkAttributes": Minimum SDK and target SDK attributes not defined
"WearableBindListener": Usage of Android Wear BIND_LISTENER is deprecated
"WrongManifestParent": Wrong manifest parent
"InvalidPermission": Invalid Permission Attribute
"ManifestResource": Manifest Resource References
"ManifestTypo": Typos in manifest tags
"FloatMath": Using FloatMath instead of Math
"MergeMarker": Code contains merge marker
"MergeRootFrame": FrameLayout can be replaced with <merge> tag
"IncompatibleMediaBrowserServiceCompatVersion": Obsolete version of
MediaBrowserServiceCompat
"InnerclassSeparator": Inner classes should use $ rather than .
"Instantiatable": Registered class is not instantiatable
"MissingRegistered": Missing registered class
"MissingId": Fragments should specify an id or tag
"LibraryCustomView": Custom views in libraries should use res-auto-namespace
"ResAuto": Hardcoded Package in Namespace
"NamespaceTypo": Misspelled namespace declaration
"UnusedNamespace": Unused namespace
"NegativeMargin": Negative Margins
"NestedScrolling": Nested scrolling widgets
"NetworkSecurityConfig": Valid Network Security Config File
"MissingBackupPin": Missing Backup Pin
"PinSetExpiry": Validate <pin-set> expiration attribute
"NfcTechWhitespace": Whitespace in NFC tech lists
"UnlocalizedSms": SMS phone number missing country code
"ObjectAnimatorBinding": Incorrect ObjectAnimator Property
"AnimatorKeep": Missing @Keep for Animated Properties
"ObsoleteLayoutParam": Obsolete layout params
"OnClick": onClick method does not exist
"Overdraw": Overdraw: Painting regions more than once
"DalvikOverride": Method considered overridden by Dalvik
"OverrideAbstract": Not overriding abstract methods on older platforms
"ParcelCreator": Missing Parcelable CREATOR field
"UnusedQuantity": Unused quantity translations
"MissingQuantity": Missing quantity translation
"ImpliedQuantity": Implied Quantities
"ExportedPreferenceActivity": PreferenceActivity should not be exported
"PrivateApi": Using Private APIs
"PackagedPrivateKey": Packaged private key
"PrivateResource": Using private resources
"ProguardSplit": Proguard.cfg file contains generic Android rules
"Proguard": Using obsolete ProGuard configuration
"PropertyEscape": Incorrect property escapes
"UsingHttp": Using HTTP instead of HTTPS
"SpUsage": Using dp instead of sp for text sizes
"InOrMmUsage": Using mm or in dimensions
"PxUsage": Using 'px' dimension
"SmallSp": Text size is too small
"ParcelClassLoader": Default Parcel Class Loader
"PendingBindings": Missing Pending Bindings
"RecyclerView": RecyclerView Problems
"Registered": Class is not registered in the manifest
"RelativeOverlap": Overlapping items in RelativeLayout
"RequiredSize": Missing layout_width or layout_height attributes
"AaptCrash": Potential AAPT crash
"ResourceCycle": Cycle in resource definitions
"ResourceName": Resource with Wrong Prefix
"ValidRestrictions": Invalid Restrictions Descriptor
"RtlCompat": Right-to-left text compatibility issues
"RtlEnabled": Using RTL attributes without enabling RTL support
"RtlSymmetry": Padding and margin symmetry
"RtlHardcoded": Using left/right instead of start/end attributes
"ScrollViewSize": ScrollView size validation
"SdCardPath": Hardcoded reference to /sdcard
"SecureRandom": Using a fixed seed with SecureRandom
"TrulyRandom": Weak RNG
"ExportedContentProvider": Content provider does not require permission
"ExportedReceiver": Receiver does not require permission
"ExportedService": Exported service does not require permission
"SetWorldReadable": File.setReadable() used to make file world-readable
"SetWorldWritable": File.setWritable() used to make file world-writable
"GrantAllUris": Content provider shares everything
"WorldReadableFiles": openFileOutput() or similar call passing
MODE_WORLD_READABLE
"WorldWriteableFiles": openFileOutput() or similar call passing
MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE
"ServiceCast": Wrong system service casts
"WifiManagerLeak": WifiManager Leak
"WifiManagerPotentialLeak": WifiManager Potential Leak
"SetJavaScriptEnabled": Using setJavaScriptEnabled
"SignatureOrSystemPermissions": signatureOrSystem permissions declared
"SQLiteString": Using STRING instead of TEXT
"SSLCertificateSocketFactoryCreateSocket": Insecure call to
SSLCertificateSocketFactory.createSocket()
"SSLCertificateSocketFactoryGetInsecure": Call to
SSLCertificateSocketFactory.getInsecure()
"StateListReachable": Unreachable state in a <selector>
"AuthLeak": Code might contain an auth leak
"StringFormatCount": Formatting argument types incomplete or inconsistent
"StringFormatMatches": String.format string doesn't match the XML format
string
"StringFormatInvalid": Invalid format string
"PluralsCandidate": Potential Plurals
"UseCheckPermission": Using the result of check permission calls
"CheckResult": Ignoring results
"ResourceAsColor": Should pass resolved color instead of resource id
"MissingPermission": Missing Permissions
"Range": Outside Range
"ResourceType": Wrong Resource Type
"RestrictedApi": Restricted API
"WrongThread": Wrong Thread
"WrongConstant": Incorrect constant
"VisibleForTests": Visible Only For Tests
"ProtectedPermissions": Using system app permission
"TextFields": Missing inputType or hint
"TextViewEdits": TextView should probably be an EditText instead
"SelectableText": Dynamic text should probably be selectable
"MenuTitle": Missing menu title
"ShowToast": Toast created but not shown
"TooDeepLayout": Layout hierarchy is too deep
"TooManyViews": Layout has too many views
"ExtraTranslation": Extra translation
"MissingTranslation": Incomplete translation
"Typos": Spelling error
"TypographyDashes": Hyphen can be replaced with dash
"TypographyEllipsis": Ellipsis string can be replaced with ellipsis character
"TypographyFractions": Fraction string can be replaced with fraction
character
"TypographyOther": Other typographical problems
"TypographyQuotes": Straight quotes can be replaced with curvy quotes
"UnsafeProtectedBroadcastReceiver": Unsafe Protected BroadcastReceiver
"UnprotectedSMSBroadcastReceiver": Unprotected SMS BroadcastReceiver
"UnusedResources": Unused resources
"UnusedIds": Unused id
"UseCompoundDrawables": Node can be replaced by a TextView with compound
drawables
"UselessLeaf": Useless leaf layout
"UselessParent": Useless parent layout
"EnforceUTF8": Encoding used in resource files is not UTF-8
"VectorRaster": Vector Image Generation
"VectorDrawableCompat": Using VectorDrawableCompat
"VectorPath": Long vector paths
"InvalidVectorPath": Invalid vector paths
"ViewConstructor": Missing View constructors for XML inflation
"ViewHolder": View Holder Candidates
"ViewTag": Tagged object leaks
"WrongViewCast": Mismatched view type
"FindViewByIdCast": Add Explicit Cast
"Wakelock": Incorrect WakeLock usage
"WakelockTimeout": Using wakeLock without timeout
"InvalidWearFeatureAttribute": Invalid attribute for Wear uses-feature
"WearStandaloneAppFlag": Invalid or missing Wear standalone app flag
"WebViewLayout": WebViews in wrap_content parents
"WrongCall": Using wrong draw/layout method
"WrongCase": Wrong case for view tag
"InvalidId": Invalid ID declaration
"NotSibling": RelativeLayout Invalid Constraints
"UnknownId": Reference to an unknown id
"UnknownIdInLayout": Reference to an id that is not in the current layout
"SuspiciousImport": 'import android.R' statement
"WrongFolder": Resource file in the wrong res folder
"WrongThreadInterprocedural": Wrong Thread (Interprocedural)
4. checkAllWarnings
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,true表示需要检查所有警告的issue,包括默认被关闭的issue;false不检查
5. checkReleaseBuilds
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,配置在release构建的过程中,Lint 是否检查致命的错误问题,默认true,一旦发现有fatal级别的问题,release构建就会终止。
6. disable
用来关闭给定issue ids的Lint检查,参数接受是issue id。
7. enable
与disable相反
8. explainIssues
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,配置Lint检查出的错误报告是否应该包含解释说明,默认开启
9. htmlOutput
是一个属性,接受一个File类型参数,配置HTML报告输出的文件路径
android {
lintOptions {
htmlOutput new File("${buildDir}/lintReports/lint-results.html")
}
}
10. htmlReport
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于配置是否生成HTML报告,默认true
11. ignoreWarnings
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于配置Lint是否忽略警告级别的检查,只检查错误级别的。默认false,不忽略警告级别的检查
12. lintConfig
是一个属性,接受一个File类型参数,用于指定Lint的配置文件,这是一个XML格式的文件,可以指定一些默认的设置。
13. noLines
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,如果true,error输出将不会包含源代码的行号,默认是false
14. quiet
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,表示是否开启安静模式,true代表安静模式,Lint分析的进度或者其他信息将不会显示。默认false
15. severityOverrides
是一个只读属性,返回一个Map类型的结果,用来获取issue的优先级。Map的key是issue id, value是优先级,优先级是**“fatal”、“error”、“warning”、“informational”、“ignore”**
16. showAll
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于标记是否应该显示所有的输出,不会对过长的消息截断等
17. textOutput
是一个只读属性,也有对应同名方法,接受一个File类型参数,用于指定生成的text格式的报告路径。如果指定stdout这个值,会被指向标准的输出,一般是终端控制台
18. textReport
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于配置是否生成text报告,默认false,不生成报告
19. warningsAsErrors
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于配置是否把所有的警告也当做错误处理,默认false。
20. xmlOutput
是一个属性,接受一个File类型参数,用于生成XML报告的路径
21. xmlReport
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于控制是否生成XML格式的报告,默认true
22. error、fatal、ignore、warning、informational
这5个方法用来配置issue的优先级,接受的都是issue id作为参数。
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#FATAL */
int SEVERITY_FATAL = 1;
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#ERROR */
int SEVERITY_ERROR = 2;
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#WARNING */
int SEVERITY_WARNING = 3;
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#INFORMATIONAL */
int SEVERITY_INFORMATIONAL = 4;
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#IGNORE */
int SEVERITY_IGNORE = 5;
/**
* A severity for lint. This severity means that the severity should be whatever the default
* is for this issue (this is used when the DSL just says "enable", and Gradle doesn't know
* what the default severity is.)
*/
int SEVERITY_DEFAULT_ENABLED = 6;
Invalid vector paths
“ViewConstructor”: Missing View constructors for XML inflation
“ViewHolder”: View Holder Candidates
“ViewTag”: Tagged object leaks
“WrongViewCast”: Mismatched view type
“FindViewByIdCast”: Add Explicit Cast
“Wakelock”: Incorrect WakeLock usage
“WakelockTimeout”: Using wakeLock without timeout
“InvalidWearFeatureAttribute”: Invalid attribute for Wear uses-feature
“WearStandaloneAppFlag”: Invalid or missing Wear standalone app flag
“WebViewLayout”: WebViews in wrap_content parents
“WrongCall”: Using wrong draw/layout method
“WrongCase”: Wrong case for view tag
“InvalidId”: Invalid ID declaration
“NotSibling”: RelativeLayout Invalid Constraints
“UnknownId”: Reference to an unknown id
“UnknownIdInLayout”: Reference to an id that is not in the current layout
“SuspiciousImport”: ‘import android.R’ statement
“WrongFolder”: Resource file in the wrong res folder
“WrongThreadInterprocedural”: Wrong Thread (Interprocedural)
#### 4. checkAllWarnings
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,true表示需要检查所有警告的issue,包括默认被关闭的issue;false不检查
#### 5. checkReleaseBuilds
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,配置在release构建的过程中,Lint 是否检查致命的错误问题,默认true,一旦发现有**fatal**级别的问题,release构建就会终止。
#### 6. disable
用来关闭给定issue ids的Lint检查,参数接受是issue id。
#### 7. enable
与disable相反
#### 8. explainIssues
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,配置Lint检查出的错误报告是否应该包含解释说明,默认开启
#### 9. htmlOutput
是一个属性,接受一个File类型参数,配置HTML报告输出的文件路径
```groovy
android {
lintOptions {
htmlOutput new File("${buildDir}/lintReports/lint-results.html")
}
}
10. htmlReport
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于配置是否生成HTML报告,默认true
11. ignoreWarnings
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于配置Lint是否忽略警告级别的检查,只检查错误级别的。默认false,不忽略警告级别的检查
12. lintConfig
是一个属性,接受一个File类型参数,用于指定Lint的配置文件,这是一个XML格式的文件,可以指定一些默认的设置。
13. noLines
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,如果true,error输出将不会包含源代码的行号,默认是false
14. quiet
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,表示是否开启安静模式,true代表安静模式,Lint分析的进度或者其他信息将不会显示。默认false
15. severityOverrides
是一个只读属性,返回一个Map类型的结果,用来获取issue的优先级。Map的key是issue id, value是优先级,优先级是**“fatal”、“error”、“warning”、“informational”、“ignore”**
16. showAll
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于标记是否应该显示所有的输出,不会对过长的消息截断等
17. textOutput
是一个只读属性,也有对应同名方法,接受一个File类型参数,用于指定生成的text格式的报告路径。如果指定stdout这个值,会被指向标准的输出,一般是终端控制台
18. textReport
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于配置是否生成text报告,默认false,不生成报告
19. warningsAsErrors
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于配置是否把所有的警告也当做错误处理,默认false。
20. xmlOutput
是一个属性,接受一个File类型参数,用于生成XML报告的路径
21. xmlReport
是一个属性,接受boolean类型值,用于控制是否生成XML格式的报告,默认true
22. error、fatal、ignore、warning、informational
这5个方法用来配置issue的优先级,接受的都是issue id作为参数。
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#FATAL */
int SEVERITY_FATAL = 1;
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#ERROR */
int SEVERITY_ERROR = 2;
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#WARNING */
int SEVERITY_WARNING = 3;
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#INFORMATIONAL */
int SEVERITY_INFORMATIONAL = 4;
/** A severity for Lint. Corresponds to com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Severity#IGNORE */
int SEVERITY_IGNORE = 5;
/**
* A severity for lint. This severity means that the severity should be whatever the default
* is for this issue (this is used when the DSL just says "enable", and Gradle doesn't know
* what the default severity is.)
*/
int SEVERITY_DEFAULT_ENABLED = 6;