一、商品规格数据结构
商品中都有属性,不同商品,属性往往不同,这一部分数据很重要,我们一起来看看:
1、规格属性内容
(1) 我们看下京东中商品的规格属性︰
—款华为手机的属性:
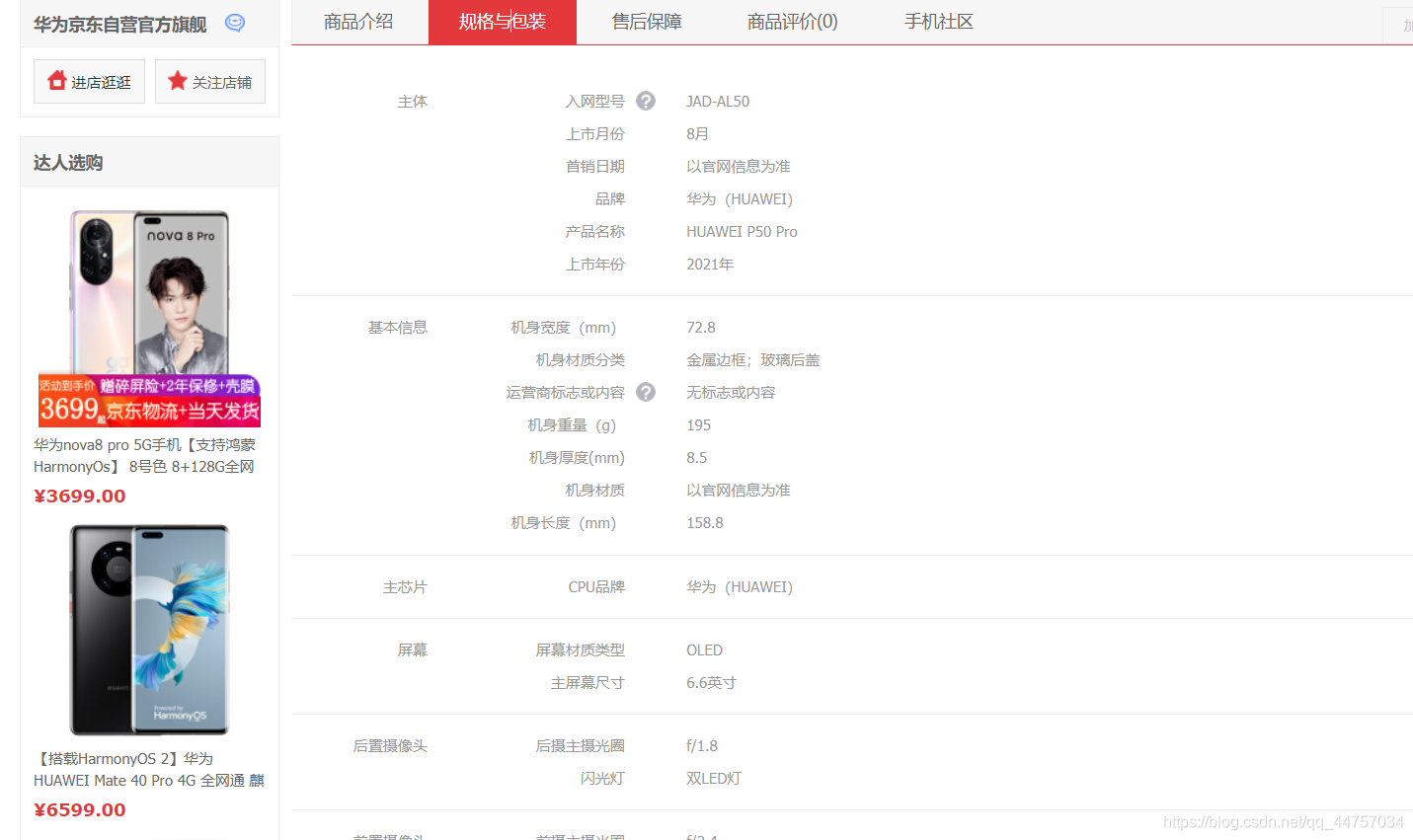
(2)横表和竖表
值我们暂且不管,新增商品时,再来填写规格参数值即可,我们先思考规格参数模板(key)该如何设计。
来看下规格参数的结构:
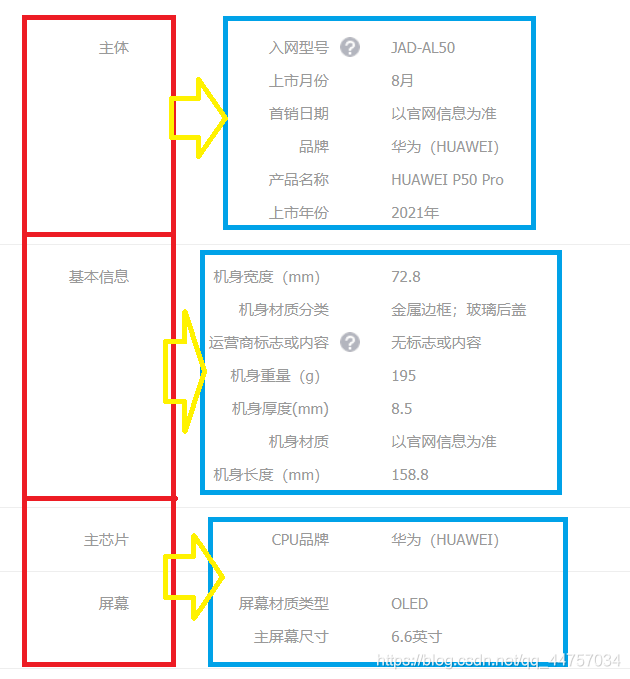
- 规格数据首先要分组,组内再有不同的规格参数
- 不同分类,其分组名称不同
- 不同分类,组内属性也不同
这样就意味着:有多少分类,就有多少分组,至少有数千数据,组内属性也是一样,数量更多。
如果按照传统设计,我们会以规格参数作为数据库字段名,如品牌、型号等都是字段,那么表的字段就会无限多。
这样的表称为横表。
一条信息,描述所有数据。
例如∶

我们不这么做,我们一条信息,只描述一条规格属性,也就是把规格参数作为字段的值,而非字段本身。这样的设计称为竖表设计。例如∶

- 规格组:
tb_spec_group- 一个商品分类下有多个规格组
- 规格参数:
tb_spec_param- 一个规格组下,有多个规格参数
如图:

(3)表结构
1)规格组
规格参数分组表:tb_spec_group
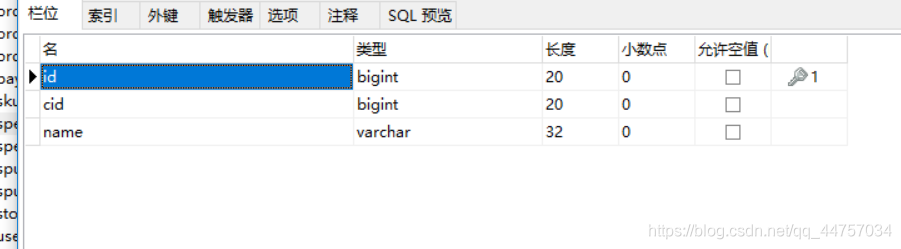
规格组有3个字段:
- id:主键
- cid:商品分类id,一个分类下有多个模板
- name:该规格组的名称。
CREATE TABLE `tb_spec_group` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`cid` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品分类id,一个分类下有多个规格组',
`name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '规格组的名称',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,
KEY `key_category` (`cid`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=28 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='规格参数的分组表,每个商品分类下有多个规格参数组';
2)规格参数
规格参数表:tb_spec_param
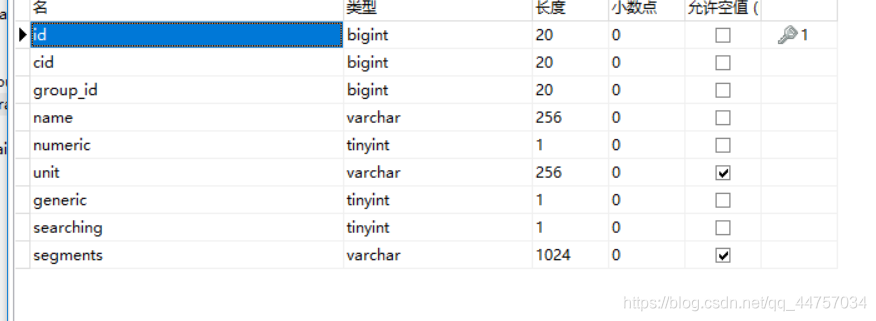
CREATE TABLE `tb_spec_param` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`cid` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品分类id',
`group_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(256) NOT NULL COMMENT '参数名',
`numeric` tinyint(1) NOT NULL COMMENT '是否是数字类型参数,true或false',
`unit` varchar(256) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '数字类型参数的单位,非数字类型可以为空',
`generic` tinyint(1) NOT NULL COMMENT '是否是sku通用属性,true或false',
`searching` tinyint(1) NOT NULL COMMENT '是否用于搜索过滤,true或false',
`segments` varchar(1024) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '数值类型参数,如果需要搜索,则添加分段间隔值,如CPU频率间隔:0.5-1.0',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,
KEY `key_group` (`group_id`) USING BTREE,
KEY `key_category` (`cid`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=33 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='规格参数组下的参数名';
二、商品规格组管理
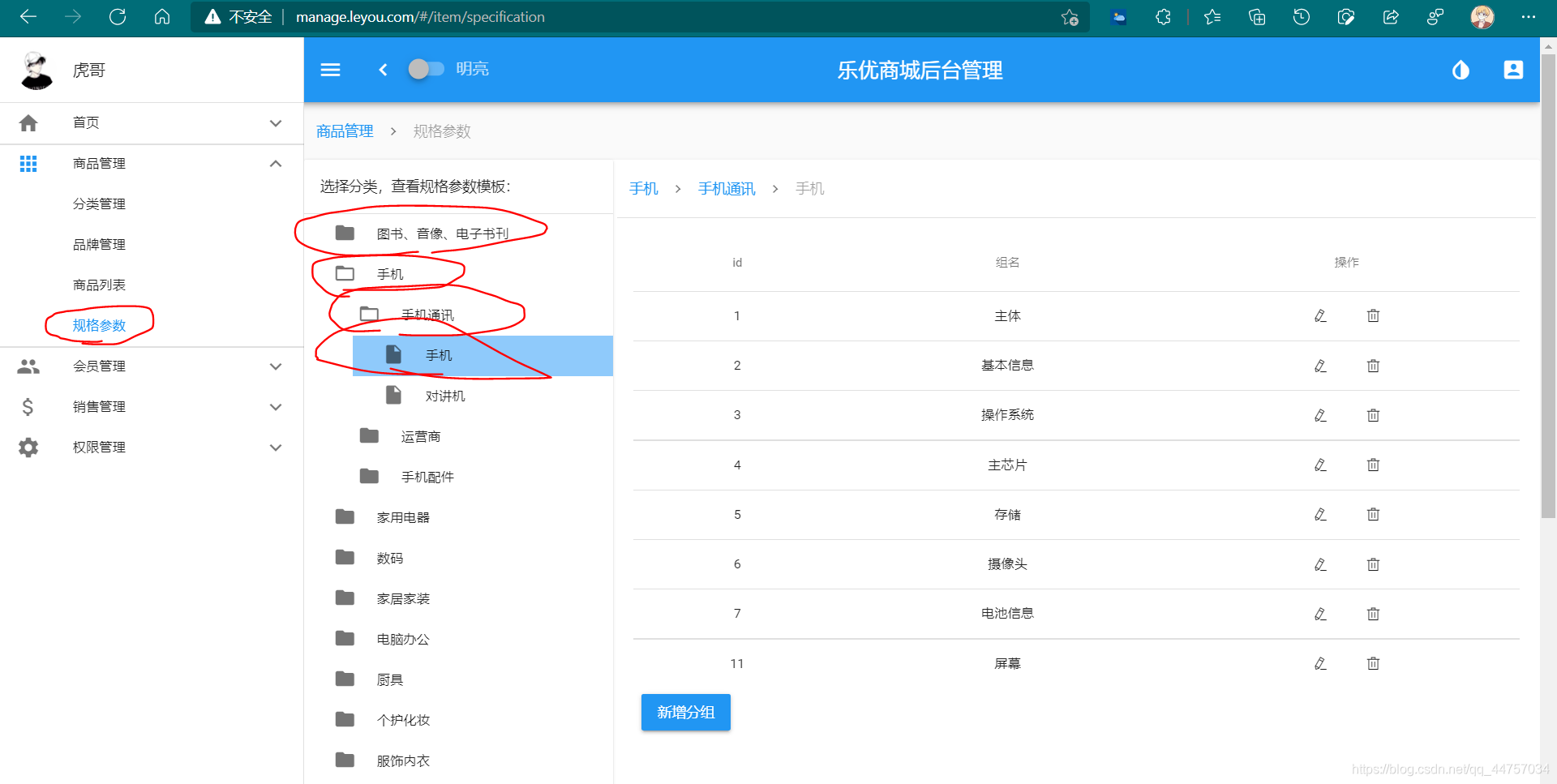
1、页面布局
(1)整体布局


2、后台代码实现规格组的查询
(1)创建对应的实体类

package com.leyou.item.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.annotation.KeySql;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Table(name = "tb_spec_group")
@Data
public class SpecGroup {
@Id
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)
private Long id;
private Long cid;
private String name;
}
(2)实体类对应的Mapper
package com.leyou.item.mapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.SpecGroup;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper;
public interface SpecGroupMapper extends Mapper<SpecGroup> {
}
(3)实体类对应的Service
package com.leyou.item.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SpecificationService {
}
(4)实体类对应的Controller(根据分类id查询规格组)
package com.leyou.item.web;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.SpecGroup;
import com.leyou.item.service.SpecificationService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("spec")
public class SpecificationController {
@Autowired
private SpecificationService specificationService;
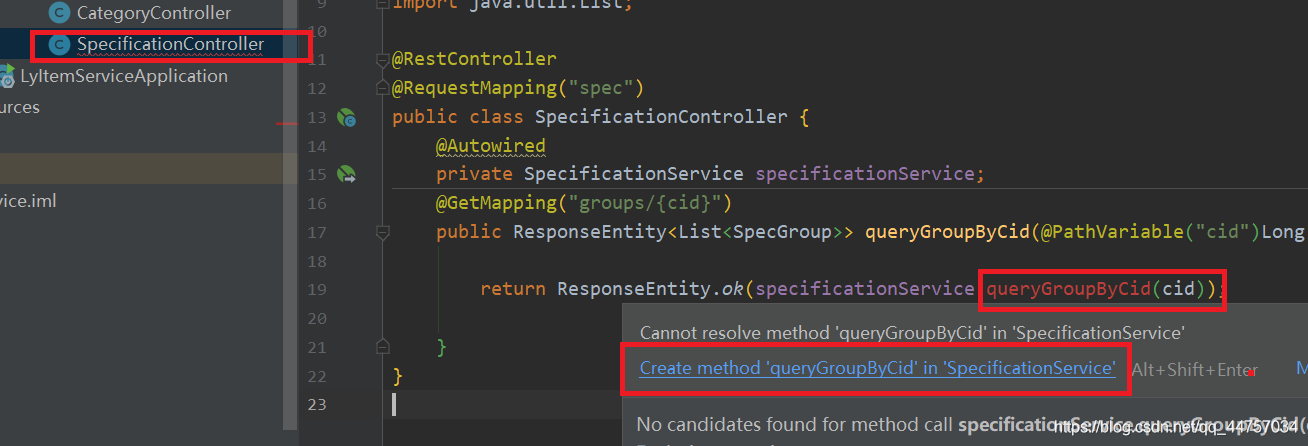
@GetMapping("groups/{cid}")
public ResponseEntity<List<SpecGroup>> queryGroupByCid(@PathVariable("cid")Long cid){
return ResponseEntity.ok(specificationService.queryGroupByCid(cid));
}
}
(5)完善Service层
1)创建对应抛出异常的枚举
SPEC_GROUP_NOT_FOND(404,"商品规格组不存在"),
2)继续完善Service

package com.leyou.item.service;
import com.leyou.common.enums.ExceptionEnum;
import com.leyou.common.exception.LyException;
import com.leyou.item.mapper.SpecGroupMapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.SpecGroup;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class SpecificationService {
@Autowired
private SpecGroupMapper specGroupMapper;
public List<SpecGroup> queryGroupByCid(Long cid) {
//设置查询条件
SpecGroup specGroup = new SpecGroup();
specGroup.setCid(cid);
List<SpecGroup> list = specGroupMapper.select(specGroup);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)){
// 没有查询到
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.SPEC_GROUP_NOT_FOND);
}
return list;
}
}
(6)运行测试
3、后台代码实现规格组的添加
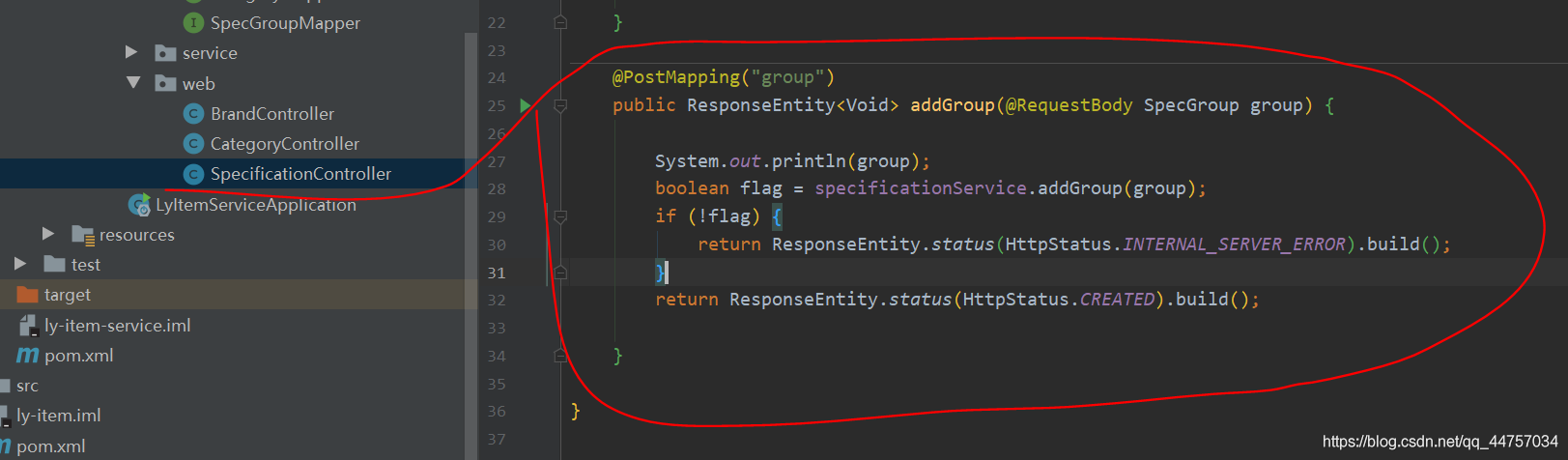
@PostMapping("group")
public ResponseEntity<Void> addGroup(@RequestBody SpecGroup group) {
System.out.println(group);
boolean flag = specificationService.addGroup(group);
if (!flag) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).build();
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).build();
}

public boolean addGroup(SpecGroup specGroup) {
int count = specGroupMapper.insert(specGroup);
if(count > 0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
运行测试
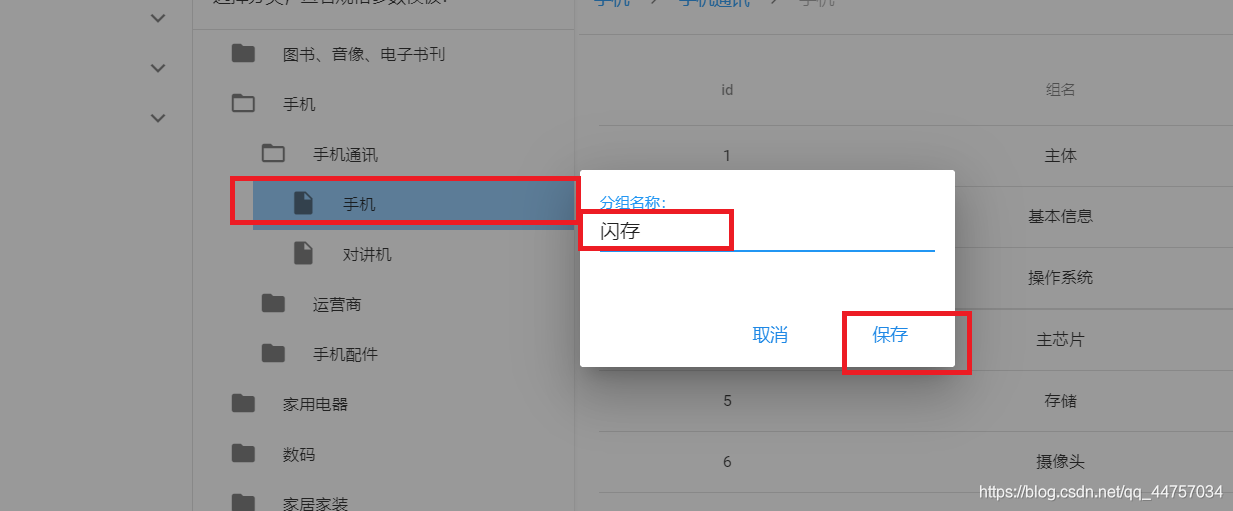
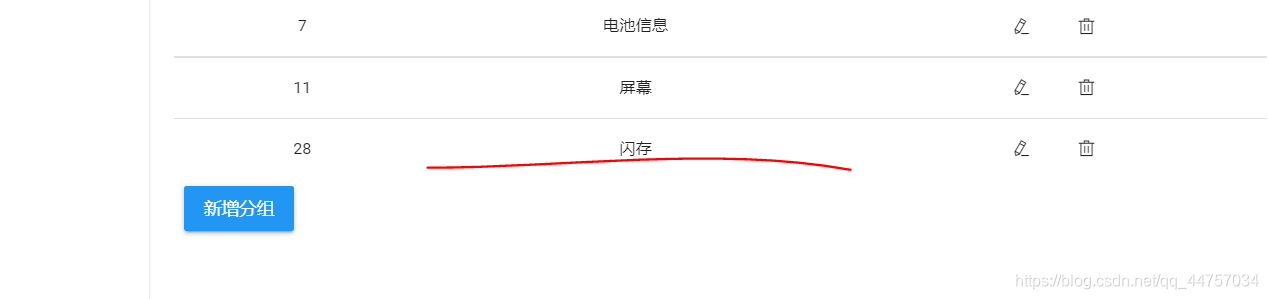
4、完善实现规格组的修改
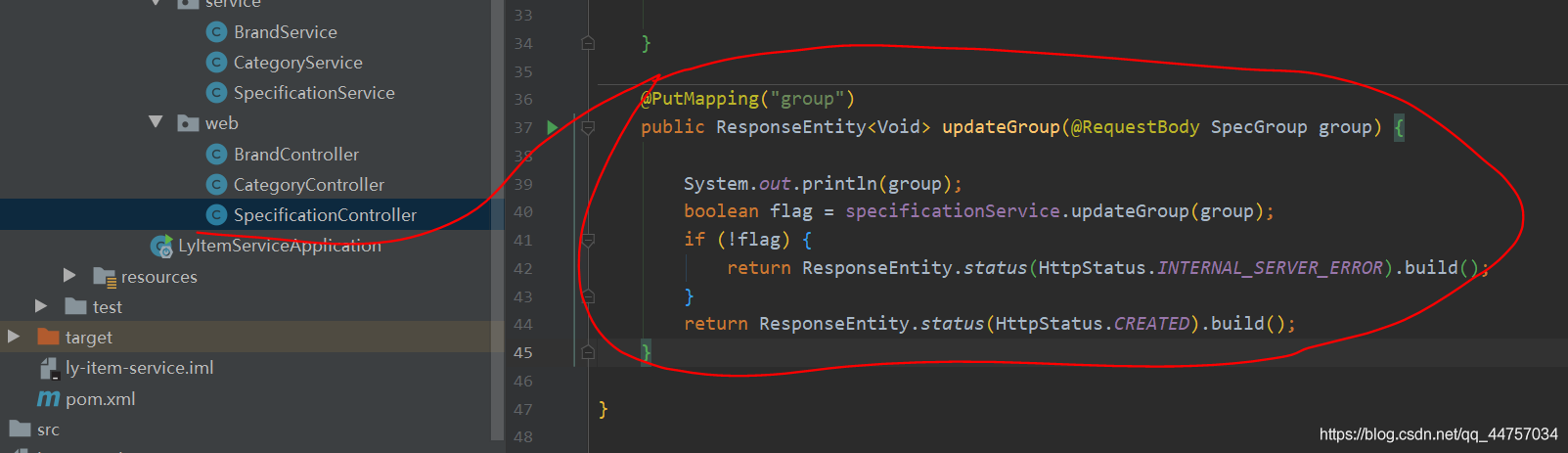
@PutMapping("group")
public ResponseEntity<Void> updateGroup(@RequestBody SpecGroup group) {
System.out.println(group);
boolean flag = specificationService.updateGroup(group);
if (!flag) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).build();
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).build();
}
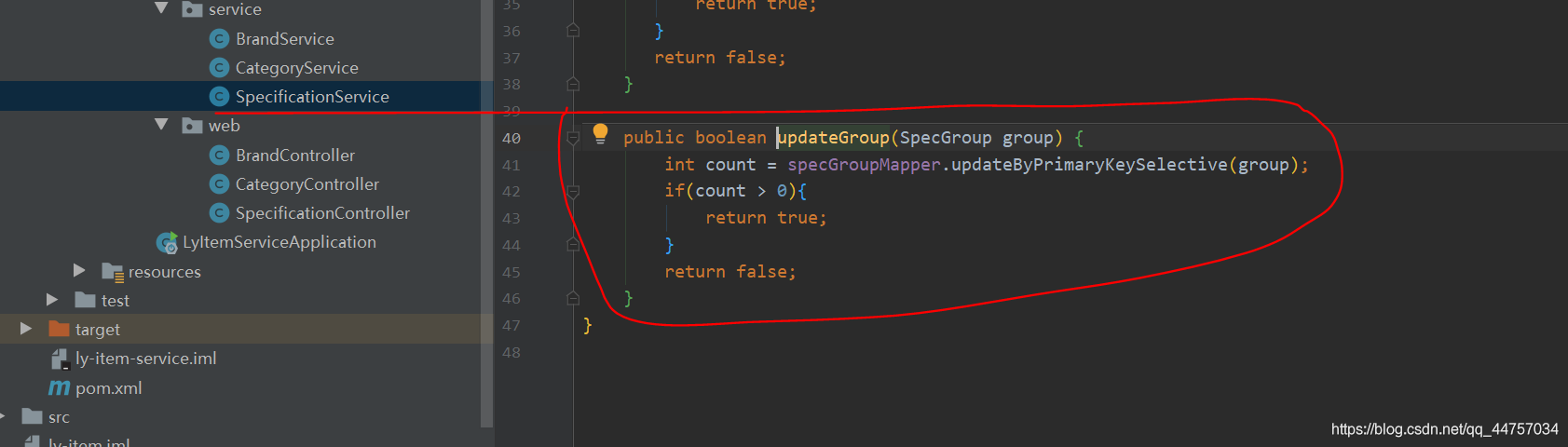
public boolean updateGroup(SpecGroup group) {
int count = specGroupMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(group);
if(count > 0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
运行测试
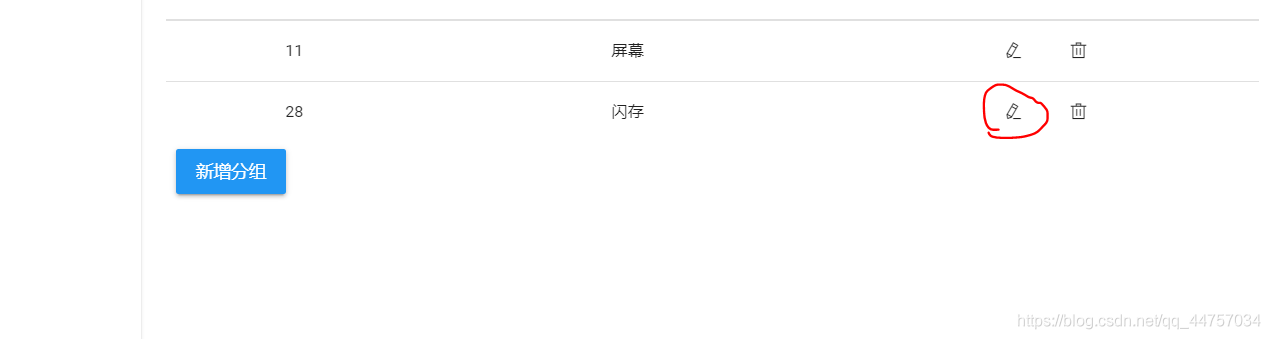
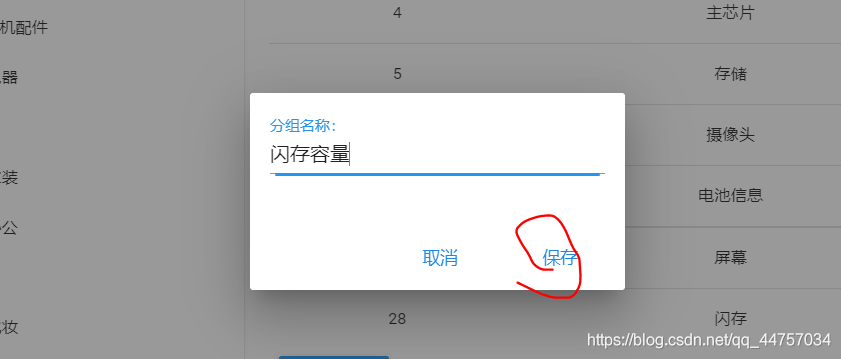
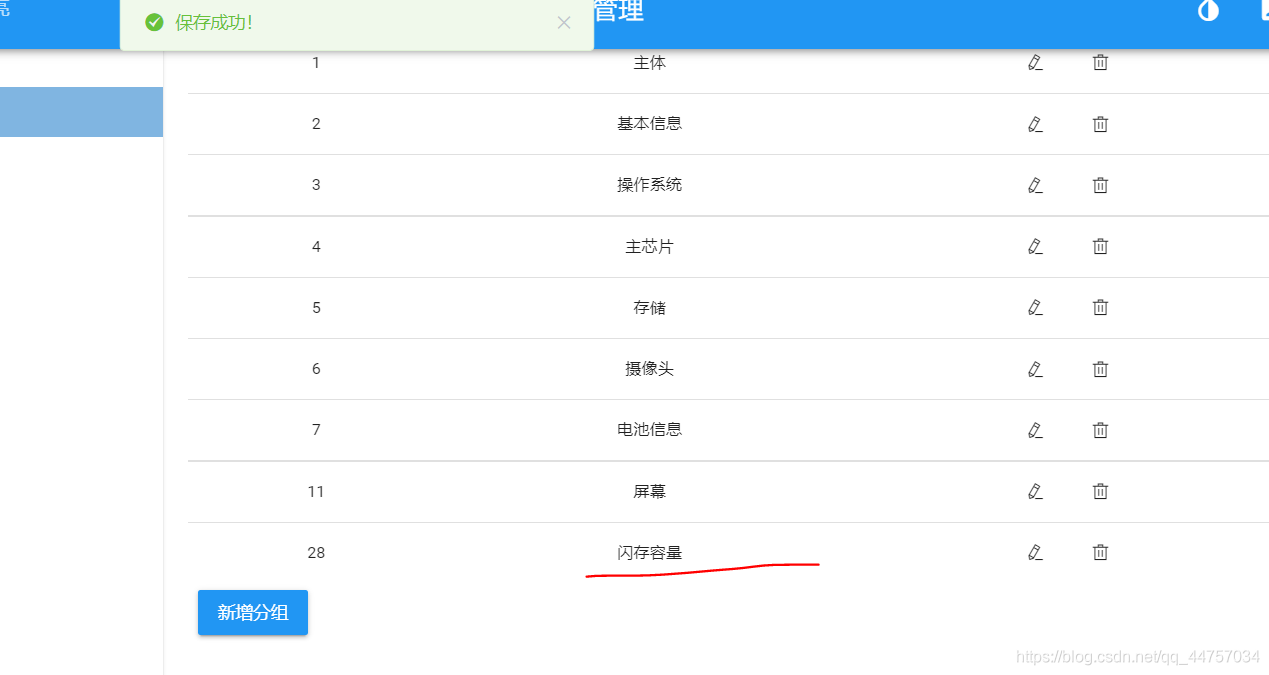
5、完善实现规格组的删除
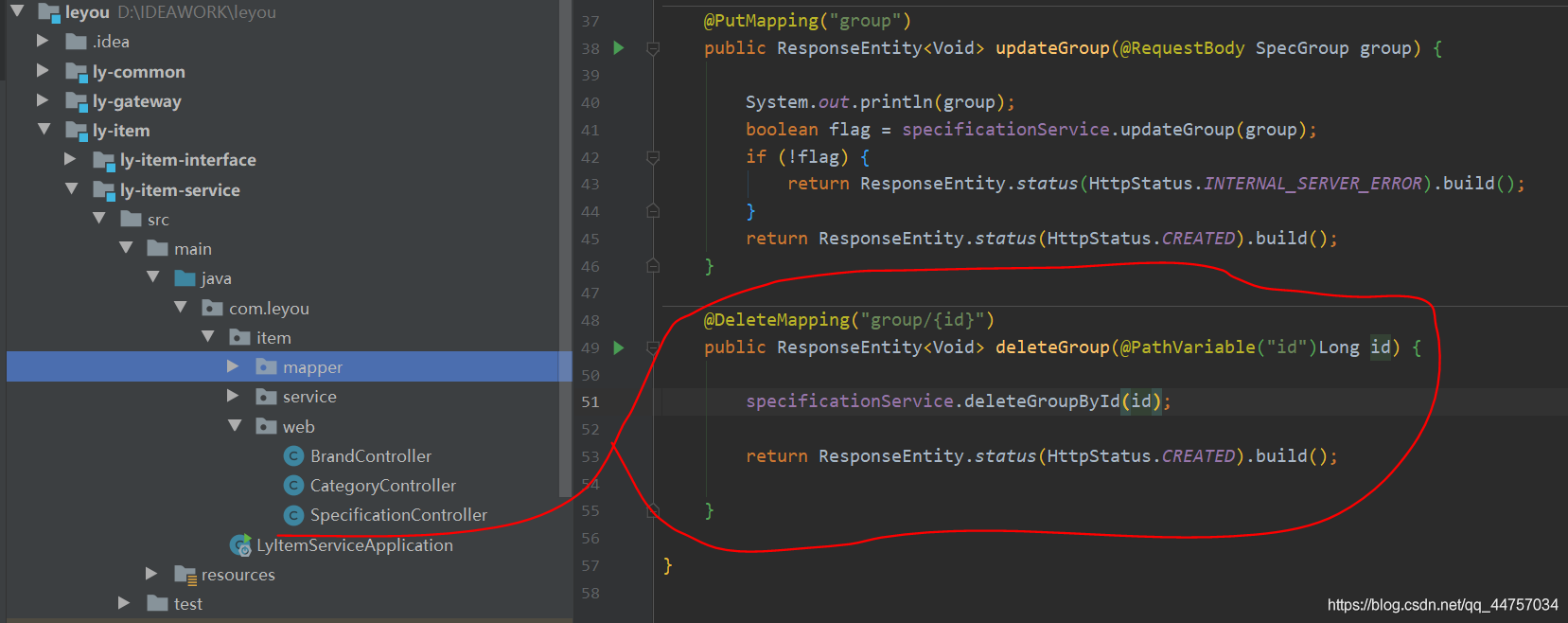
@DeleteMapping("group/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteGroup(@PathVariable("id")Long id) {
specificationService.deleteGroupById(id);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).build();
}

public void deleteGroupById(Long id) {
SpecGroup specGroup = new SpecGroup();
specGroup.setId(id);
int count = specGroupMapper.delete(specGroup);
if(count <= 0){
// 没有查询到
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.INVALID_FILE_TYPE);
}
}
运行测试
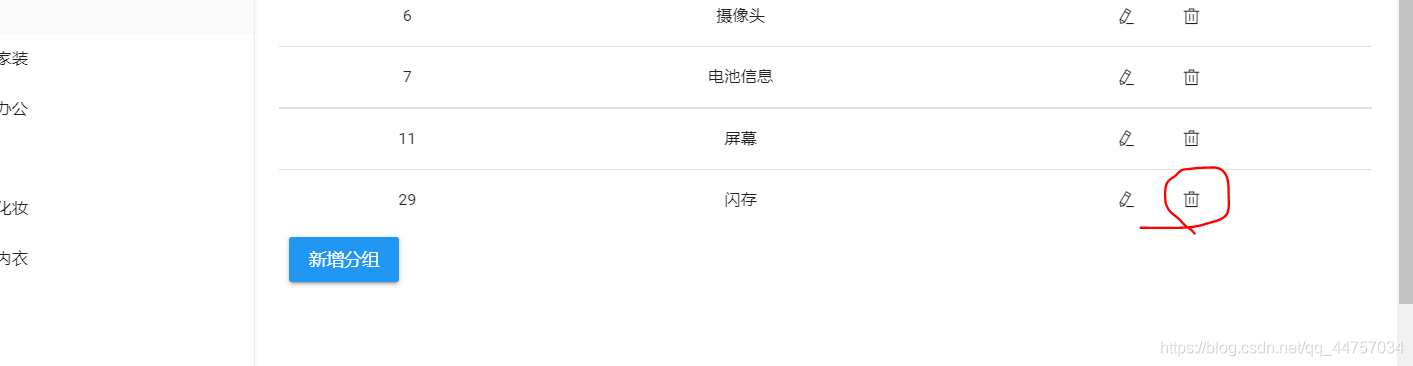
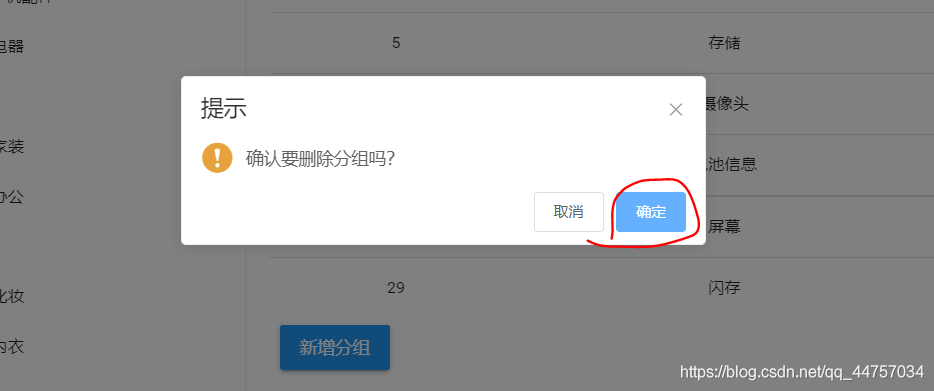
删除成功
三、商品规格参数管理
1、页面分析
点击上面的规格组我们会发现

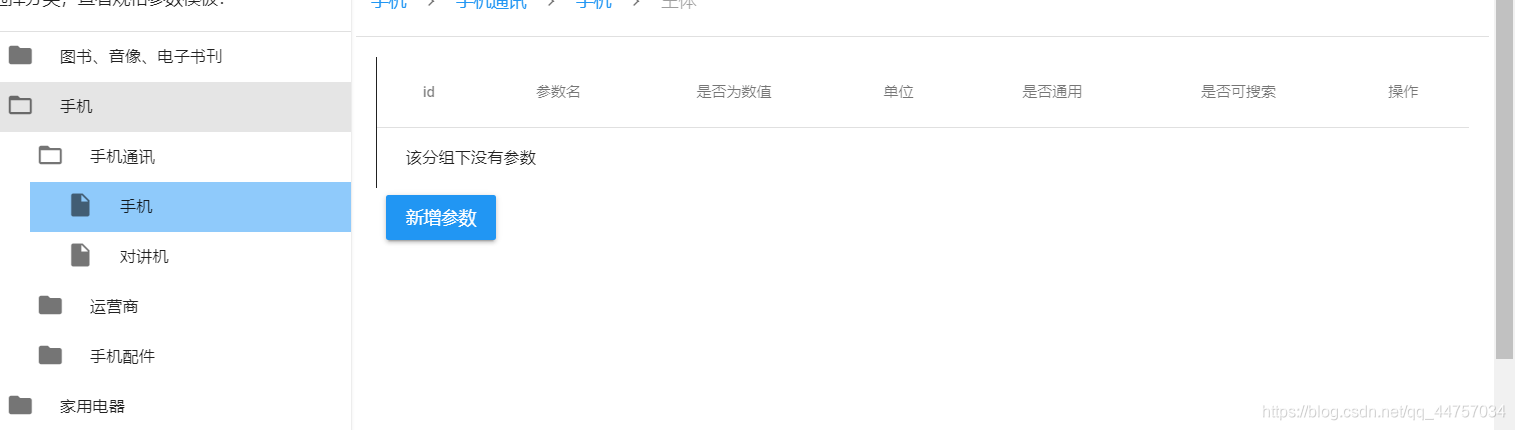
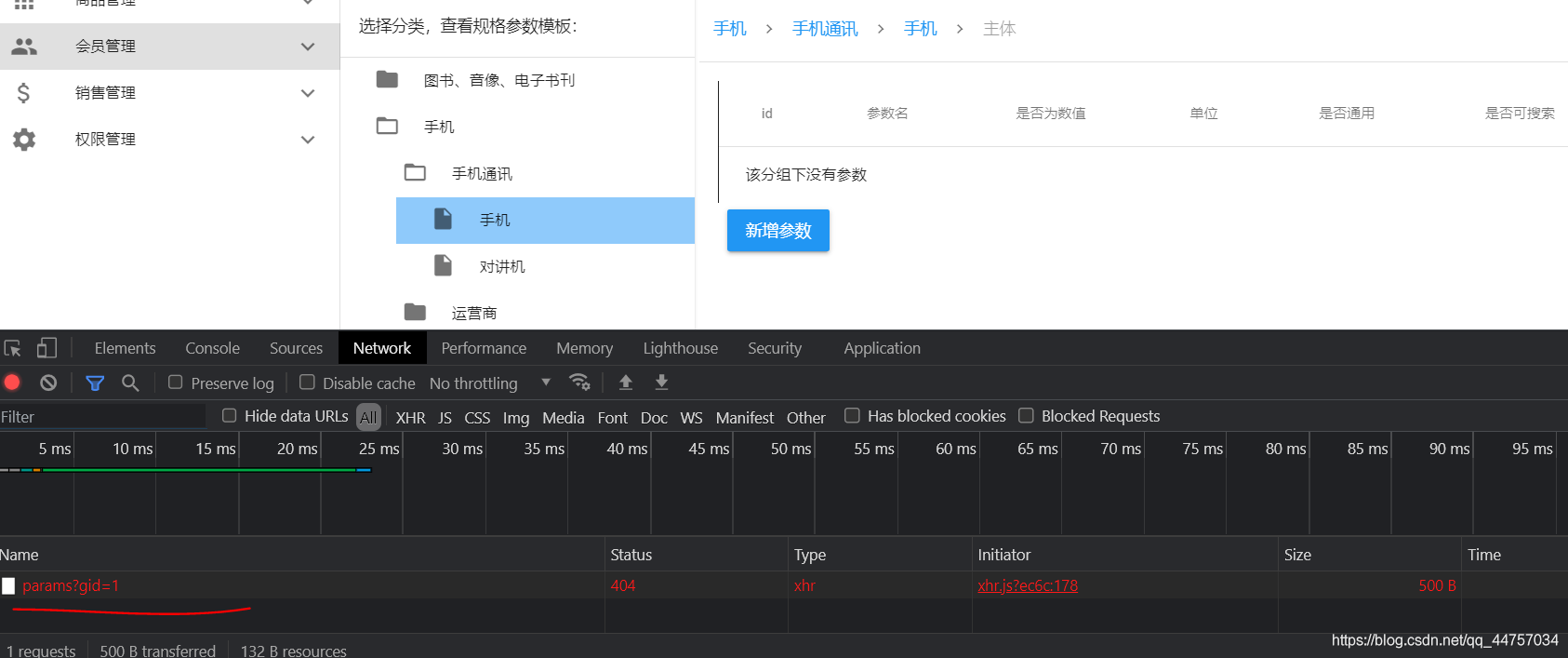
我们可以看到当前请求参数是规格组id,返回值为当前组下面的所有规格参数
2、实现规格参数的查询(后台实现)
1)实体类

package com.leyou.item.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.annotation.KeySql;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Table(name = "tb_spec_param")
@Data
public class SpecParam {
@Id
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)
private Long id;
private Long cid;
private Long groupId;
private String name;
@Column(name = "`numeric`")
private Boolean numeric;
private String unit;
private Boolean generic;
private Boolean searching;
private String segments;
}
2)实体类对应的通用Mapper

package com.leyou.item.mapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.SpecParam;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper;
public interface SpecParamMapper extends Mapper<SpecParam> {
}
3)实体类对应的Service,在SpecificationService当中注入SpecParamMapper 即可

@Autowired
private SpecParamMapper specParamMapper;
4)在SpecificationController当中

/*
根据组id查询参数
*/
@GetMapping("params")
public ResponseEntity<List<SpecParam>> queryParamByGid(@RequestParam("gid") Long gid){
return ResponseEntity.ok(specificationService.queryParamByGid(gid));
}
5)完善SpecificationService
创建抛出异常的枚举

SPEC_PARAM_NOT_FOND(404,"商品规格参数不存在"),
完善SpecificationService


public List<SpecParam> queryParamByGid(Long gid) {
SpecParam specParam = new SpecParam();
specParam.setGroupId(gid);
List<SpecParam> list = specParamMapper.select(specParam);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)){
// 没有查询到
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.SPEC_PARAM_NOT_FOND);
}
return list;
}
6)重新运行并测试



3、SPU和SKU数据结构
(1)什么是SPU和SKU
SPU: Standard Product Unit(标准产品单位),一组具有共同属性的商品集
SKU: Stock Keeping Unit(库存量单位),SPU商品集因具体特性不同而细分的每个商品
以图为例来看:

- 本页的华为就是一个商品集(SPU)
- 因为颜色、内存等不同,而细分出不同的手机,如亮黑色128G版。(SKU)可以看出;
- SPU是一个抽象的商品集概念,为了方便后台的管理。
- SKU才是具体要销售的商品,每一个SKU的价格、库存可能会不一样,用户购买的是SKU而不是SPU
(2)数据库设计分析
1)思考分析
弄清楚了SPU和SKU的概念区分,接下来我们一起思考一下该如何设计数据库表。
首先来看SPU,大家一起思考下SPU应该有哪些字段来描述?
- SPU共享数据
id:主键
title:标题
description:描述
specification:规格
packaging_list:包装
after _service:售后服务
comment:评价
category_id:商品分类
brand_id:品牌
似乎并不复杂
- 再看下SKU(每个商品的特殊属性)
大家觉得应该有什么字段?
id:主健
spu_id:关联的
spuprice:价格
images:图片
stock:库存颜色?
内存?
硬盘?
上述做法是错误的:SKU的特有属性也是变化的。
不同分类特有属性也不一定相同。
2)SKU的特有属性
SPU中会有一些特殊属性,用来区分不同的SKU,我们称为sKU特有属性。如华为META10的颜色、内存属性.不同种类的商品,一个手机,一个衣服,其SKU属性不相同。
同一种类的商品,比如都是衣服,SKU属性基本是一样的,都是颜色、尺码等。
这样说起来,似乎SKU的特有属性也是与分类相关的?事实上,仔细观察你会发现,
SKU的特有属性是商品规格参数的一部分∶
也就是说,我们没必要单独对SKu的特有属性进行设计,它可以看做是规格参数中的一部分。这样规格参数中性可以标记成两部分:
- 所有sku共享的规格属性〈称为通用属性),我们记录在SPU表中。
- 每个sku不同的规格属性(称为特有属性),我们记录在SKU表中。
回一下之前我们设计的tb _spec_param表,是不是有一个字段,名为generic,标记通用和特有属性。就是为使用。
(3)SPU表
1)表结构
SPU表:
CREATE TABLE `tb_spu` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'spu id',
`title` varchar(128) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '标题',
`sub_title` varchar(256) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '子标题',
`cid1` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '1级类目id',
`cid2` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '2级类目id',
`cid3` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '3级类目id',
`brand_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品所属品牌id',
`saleable` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '是否上架,0下架,1上架',
`valid` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '是否有效,0已删除,1有效',
`create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '添加时间',
`last_update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '最后修改时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=195 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='spu表,该表描述的是一个抽象性的商品,比如 iphone8';
与我们前面分析的基本类似,但是似乎少了一些字段,比如商品描述。
我们做了表的垂直拆分,将SPu的详情放到了另一张表: tb_spu_detail
CREATE TABLE `tb_spu_detail` (
`spu_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`description` text COMMENT '商品描述信息',
`generic_spec` varchar(2048) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '通用规格参数数据',
`special_spec` varchar(1024) NOT NULL COMMENT '特有规格参数及可选值信息,json格式',
`packing_list` varchar(1024) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '包装清单',
`after_service` varchar(1024) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '售后服务',
PRIMARY KEY (`spu_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC;

下面的参数字段是JSON格式的字符串,与规格参数表当中的数据是一致的


(4)SKU表
1)表结构
CREATE TABLE `tb_sku` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'sku id',
`spu_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT 'spu id',
`title` varchar(256) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品标题',
`images` varchar(1024) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '商品的图片,多个图片以‘,’分割',
`price` bigint(15) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '销售价格,单位为分',
`indexes` varchar(32) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '特有规格属性在spu属性模板中的对应下标组合',
`own_spec` varchar(1024) DEFAULT '' COMMENT 'sku的特有规格参数键值对,json格式,反序列化时请使用linkedHashMap,保证有序',
`enable` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '是否有效,0无效,1有效',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '添加时间',
`last_update_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '最后修改时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE,
KEY `key_spu_id` (`spu_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=27359021729 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='sku表,该表表示具体的商品实体,如黑色的 64g的iphone 8';
还有一张表代表库存
CREATE TABLE `tb_stock` (
`sku_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '库存对应的商品sku id',
`seckill_stock` int(9) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '可秒杀库存',
`seckill_total` int(9) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '秒杀总数量',
`stock` int(9) NOT NULL COMMENT '库存数量',
PRIMARY KEY (`sku_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='库存表,代表库存,秒杀库存等信息';
问题:为什么要将库存独立—张表?
因为库存字段写频率较高,而SKu的其它字段以读为主,因此我们将两张表分离,读写不会干扰。
特别需要注意的是sku表中的 indexes 字段和 own_spec字段。
sku中应该保存特有规格参数的值,就在这两个字段中。

4、功能实现
(1)页面分析
请求方式为GET
请求参数:
上架saleable是true
下降saleable是false
全部是没有saleable
key搜索的关键字
初始也page
以及显示的行数rows



发起的请求

(2)后台代码实现
1)实体类
a)SPU


package com.leyou.item.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.annotation.KeySql;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import java.util.Date;
@Table(name = "tb_spu")
@Data
public class Spu {
@Id
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)
private Long id;
private Long brandId;
private Long cid1; //1级类目
private Long cid2; //2级类目
private Long cid3; //2级类目
private String title;//标题
private String subTitle;//子标题
private Boolean saleable;//是否上架
private Boolean valid;//是否有效。逻辑删除用
private Date createTime;//创建时间
private Date lastUpdateTime;//最后修改时间
}
b)SPU详情SpuDetail

package com.leyou.item.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Table(name = "tb_spu_detail")
public class SpuDetail {
@Id
private Long spuId;//对应SPU的id
private String description ; //商品描述
private String specialSpec ; //商品特殊规格的名称及可选值模板
private String genericSpec; //商品的全局规格属性
private String packingList; //包装清单
private String afterService ; //售后服务
}
2)实体类对应的mapper
a)SpuMapper


package com.leyou.item.mapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.Spu;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper;
public interface SpuMapper extends Mapper<Spu> {
}
b)SpuDetailMapper


package com.leyou.item.mapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.SpuDetail;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper;
public interface SpuDetailMapper extends Mapper<SpuDetail> {
}
3)实体类对应的service


package com.leyou.item.service;
import com.leyou.item.mapper.SpuDetailMapper;
import com.leyou.item.mapper.SpuMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class GoodsService {
@Autowired
private SpuMapper spuMapper;
@Autowired
private SpuDetailMapper spuDetailMapper;
}
4)实体类对应的Controller


package com.leyou.item.web;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.Spu;
import com.leyou.item.service.GoodsService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("spu")
public class GoodsController {
@Autowired
private GoodsService goodsService;
}
5)完善实体类对应返回的字段
a、添加依赖

<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
b、完善Spu实体类

package com.leyou.item.pojo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore;
import lombok.Data;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.annotation.KeySql;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Transient;
import java.util.Date;
@Table(name = "tb_spu")
@Data
public class Spu {
@Id
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)
private Long id;
private Long brandId;
private Long cid1; //1级类目
private Long cid2; //2级类目
private Long cid3; //2级类目
private String title;//标题
private String subTitle;//子标题
private Boolean saleable;//是否上架
@JsonIgnore //设置返回页面数据的时候,忽略当前字段
private Boolean valid;//是否有效。逻辑删除用
private Date createTime;//创建时间
@JsonIgnore //设置返回页面数据的时候,忽略当前字段
private Date lastUpdateTime;//最后修改时间
@Transient //Transient声明当前字段不是数据对应的字段
private String cname;
@Transient //Transient声明当前字段不是数据对应的字段
private String bname;
}
c、完善GoodsController

package com.leyou.item.web;
import com.leyou.common.vo.PageResult;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.Spu;
import com.leyou.item.service.GoodsService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping
public class GoodsController {
@Autowired
private GoodsService goodsService;
/*
分页查询SPU
*/
@GetMapping("/spu/page")
public ResponseEntity<PageResult<Spu>> querySpuByPage(
@RequestParam(value = "page",defaultValue = "1") Integer page,
@RequestParam(value = "rows",defaultValue = "5") Integer rows,
@RequestParam(value = "saleable",required = false) Boolean saleable,
@RequestParam(value = "key",required = false) String key
){
return ResponseEntity.ok(goodsService.querySpuByPage(page,rows,saleable,key));
}
}
d、完善GoodsService
- 设置对应商品查询不存在的枚举

GOODS_NOT_FOND(404,"商品不存在"),
- 完善GoodsService

package com.leyou.item.service;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import com.leyou.common.enums.ExceptionEnum;
import com.leyou.common.exception.LyException;
import com.leyou.common.vo.PageResult;
import com.leyou.item.mapper.SpuDetailMapper;
import com.leyou.item.mapper.SpuMapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.Spu;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.entity.Example;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class GoodsService {
@Autowired
private SpuMapper spuMapper;
@Autowired
private SpuDetailMapper spuDetailMapper;
public PageResult<Spu> querySpuByPage(Integer page, Integer rows, Boolean saleable, String key) {
//分页
PageHelper.startPage(page,rows);
//过滤
Example example = new Example(Spu.class);
Example.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
//搜索条件过滤
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(key)){
criteria.andLike("title","%"+key+"%");//第一个参数的数据对应的字段,第二个为页面传入的参数的值
}
//上下架过滤
if(saleable != null){
criteria.andEqualTo("saleable",saleable);
}
//设置默认排序方式为商品的更新时间
example.setOrderByClause("last_update_time DESC");
//查询
List<Spu> spus = spuMapper.selectByExample(example);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(spus)){
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.GOODS_NOT_FOND);
}
//解析父类和品牌的名称
loadCategoryAndBrandName(spus);
//解析分页的结果
PageInfo<Spu> info = new PageInfo<>(spus);
return new PageResult<>(info.getTotal(),spus);//将分页信息和结果集合放入PageResult当前返回到页面
}
private void loadCategoryAndBrandName(List<Spu> spus) {
for (Spu spu : spus) {
//处理父类名称
//处理品牌名称
}
}
}
- 完善CategoryService商品分类

public List<Category> queryByIds(List<Long> ids){
}
- 需要扩展CategoryMapper,可以继承多个接口

package com.leyou.item.mapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.Category;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.additional.idlist.IdListMapper;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
public interface CategoryMapper extends Mapper<Category>, IdListMapper<Category,Long> {//Long第二个参数是主键类型
/**
* 根据品牌id查询商品分类id 然后通过商品分类id查询对应所有的商品分类
*/
@Select("SELECT * FROM tb_category WHERE id IN (SELECT category_id FROM tb_category_brand WHERE brand_id = #{bid})")
List<Category> queryByBrandId(Long id);
}
- 继续完善CategoryService当中queryByIds方法
public List<Category> queryByIds(List<Long> ids){
List<Category> list = categoryMapper.selectByIdList(ids);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(list)){
//查询失败抛出自定义的通用异常
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.CATEGORY_NOT_FOND);
}
return list;
}
- 继续完善GoodsService当中的loadCategoryAndBrandName方法
注入CategoryService

处理父类名称
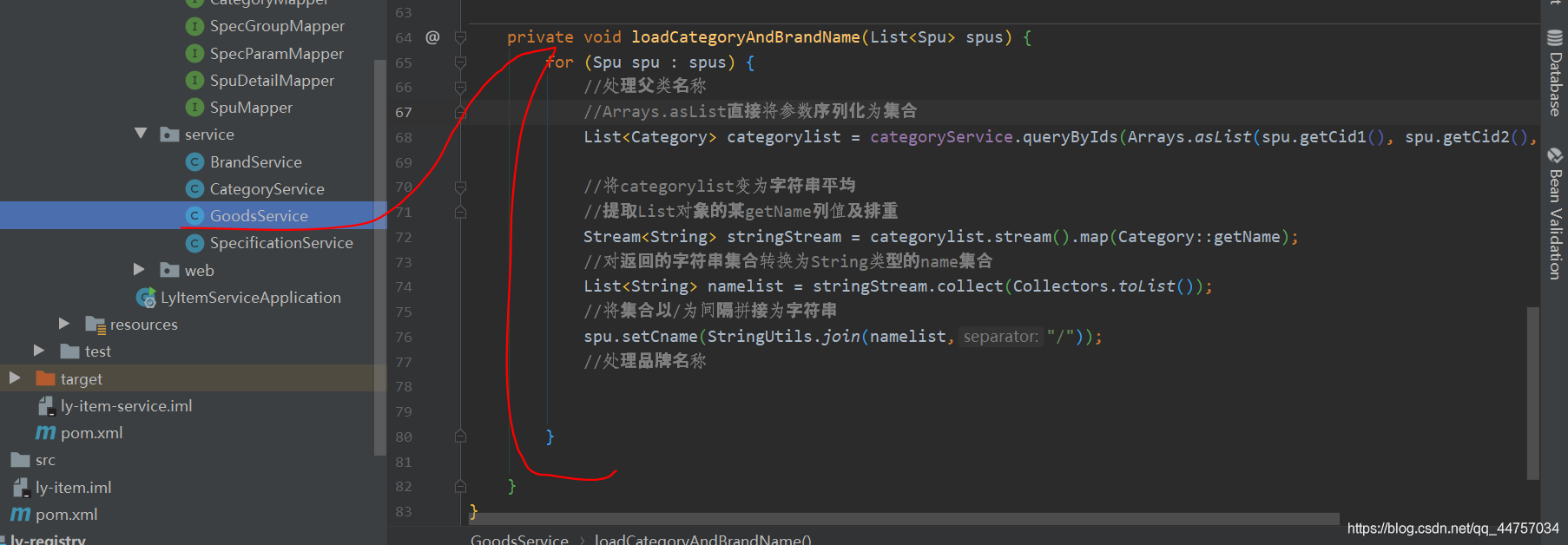
private void loadCategoryAndBrandName(List<Spu> spus) {
for (Spu spu : spus) {
//处理父类名称
//Arrays.asList直接将参数序列化为集合
List<Category> categorylist = categoryService.queryByIds(Arrays.asList(spu.getCid1(), spu.getCid2(), spu.getCid3()));
//将categorylist变为字符串平均
//提取List对象的某getName列值及排重
Stream<String> stringStream = categorylist.stream().map(Category::getName);
//对返回的字符串集合转换为String类型的name集合
List<String> namelist = stringStream.collect(Collectors.toList());
//将集合以/为间隔拼接为字符串
spu.setCname(StringUtils.join(namelist,"/"));
//处理品牌名称
}
}
- 在BrandService当中新增通过id查询
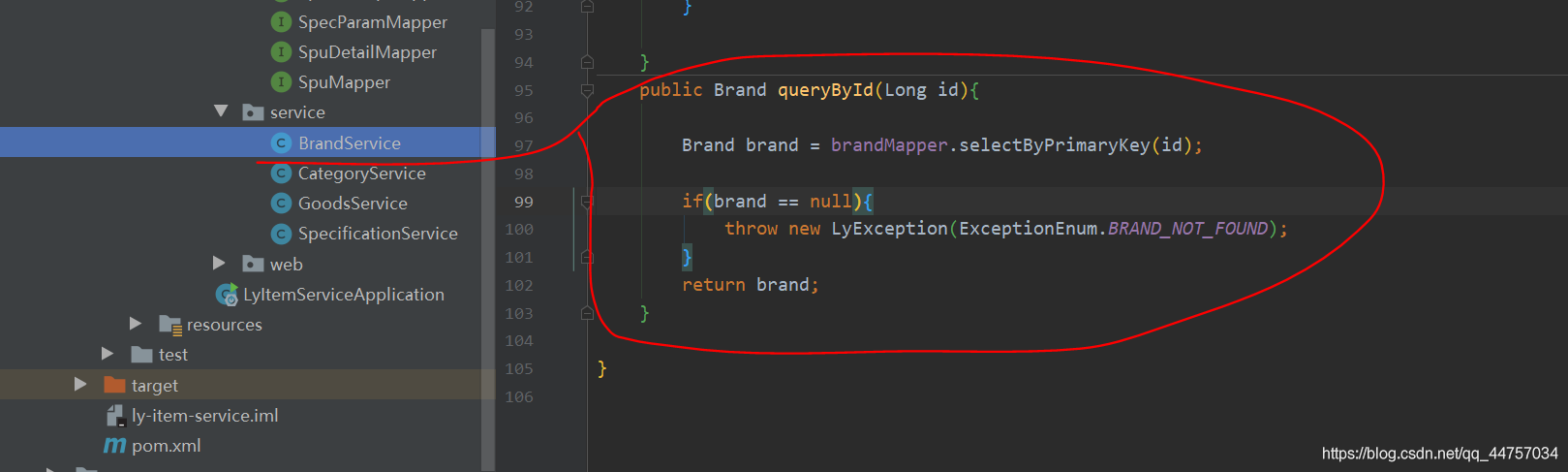
public Brand queryById(Long id){
Brand brand = brandMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
if(brand == null){
throw new LyException(ExceptionEnum.BRAND_NOT_FOUND);
}
return brand;
}
- 继续完善GoodsService当中的loadCategoryAndBrandName方法当中的:处理品牌名称
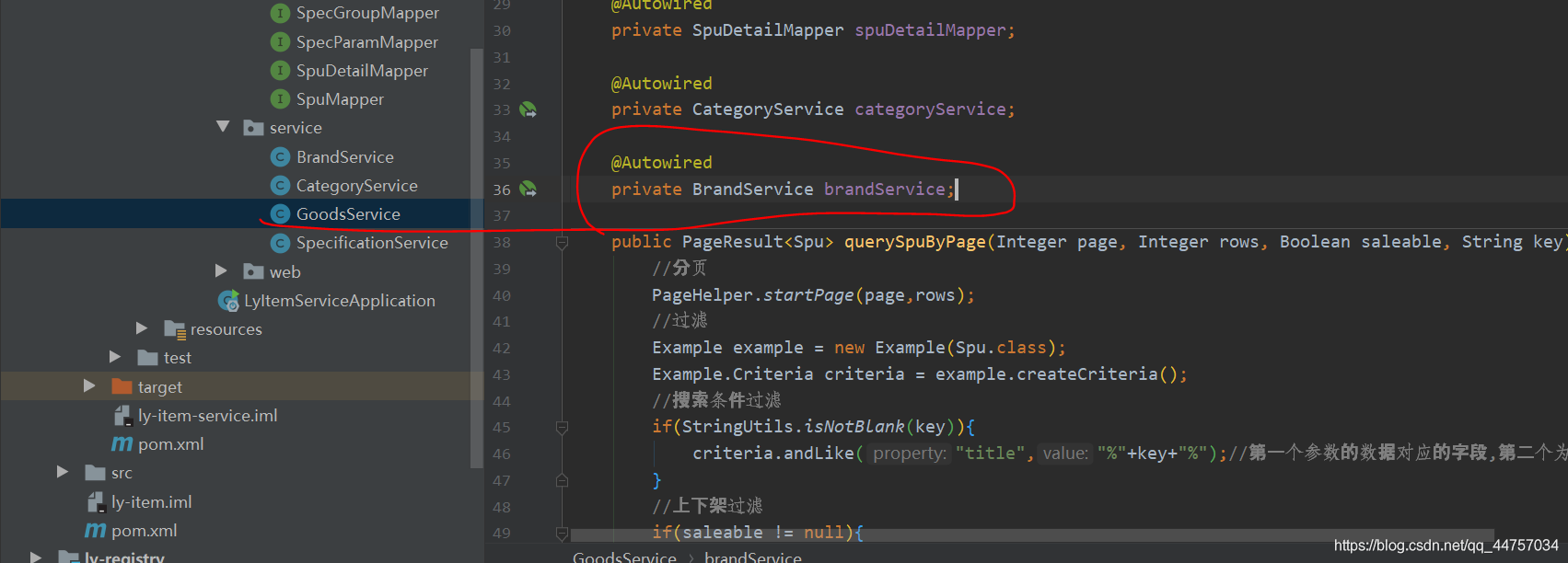
@Autowired
private BrandService brandService;
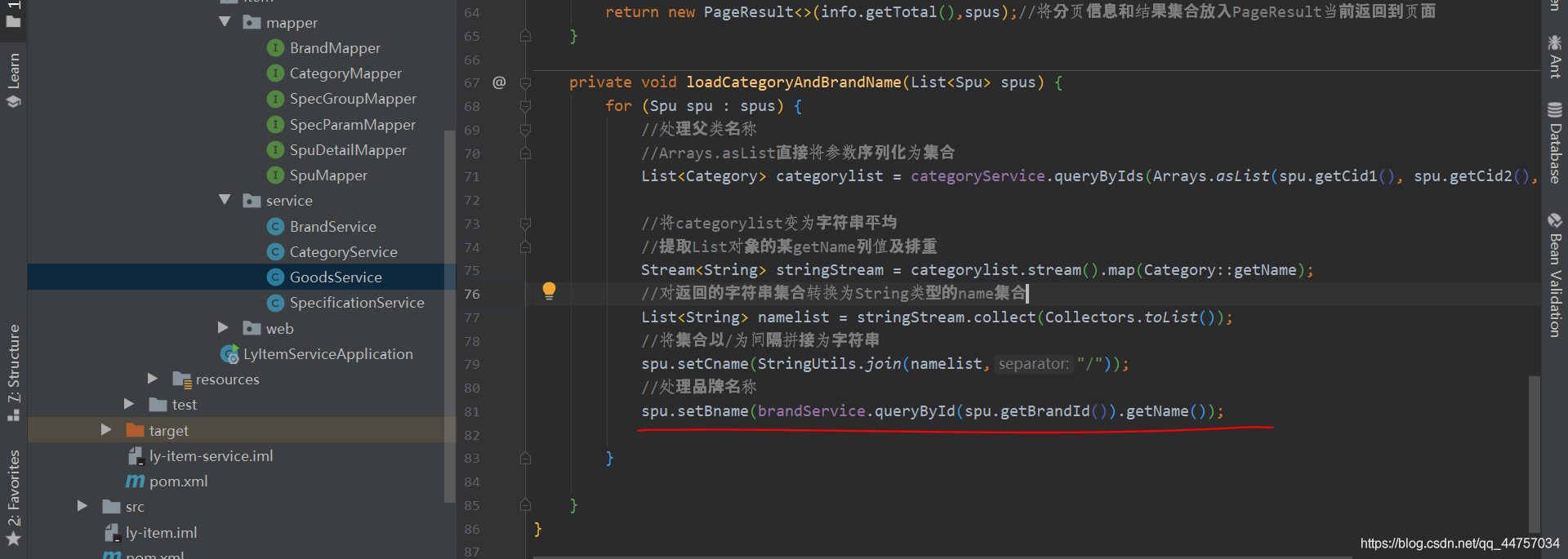
//处理品牌名称
spu.setBname(brandService.queryById(spu.getBrandId()).getName());
6)运行测试