目录
1.读取控制台输入
Java的控制台输入由System.in完成。
为了获得一个绑定到控制台的字符流,你可以把 System.in 包装在一个 BufferedReader 对象中来创建一个字符流。
创建BufferedReader的基本语法
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
对象创建后,可以使用read()方法从控制台读取一个字符,或者用readLine()方法读取一个字符串。
从控制台读取多字符输入
从BufferedReader对象读取一个字符需要使用read()方法,语法如下:
int read() throws IOException?
每次调用read()方法,他就会从输入流读取一个字符并把该字符作为整数值返回。当流结束的时候返回-1.抛出IOException。
示例用read()方法从控制台不断读取字符直到用户输入q
/**
* @author asus
*/
public class BRRead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c = 0;
//使用System.in创建BufferedReader
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("输入字符,按下'q'键退出。");
//读取字符
do{
try {
c = (char) br.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(c);
} while (c != 'q');
}
}执行结果如下:

从控制台读取字符串
从标准输入读取一个字符串需要使用BufferedReader的readLine()方法
一般格式
String readLine() trhows IOException
示例程序读取和显示字符行直到输入了"end"
/**
* @author asus
*/
public class BRReadLines {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = null;
System.out.println("Enter lines of text.");
System.out.println("Enter 'end' to quit.");
do {
try {
str = br.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(str);
} while (!str.equals("end"));
}
}执行结果为:

?注:JDK5后的版本可使用Java Scanner类来获取控制台的输入
2.读写文件
一个流被定义为数据序列。输入流用于从源读取数据、输出流用于向目标写数据。
描述输入流和输出流的类层次图如下:
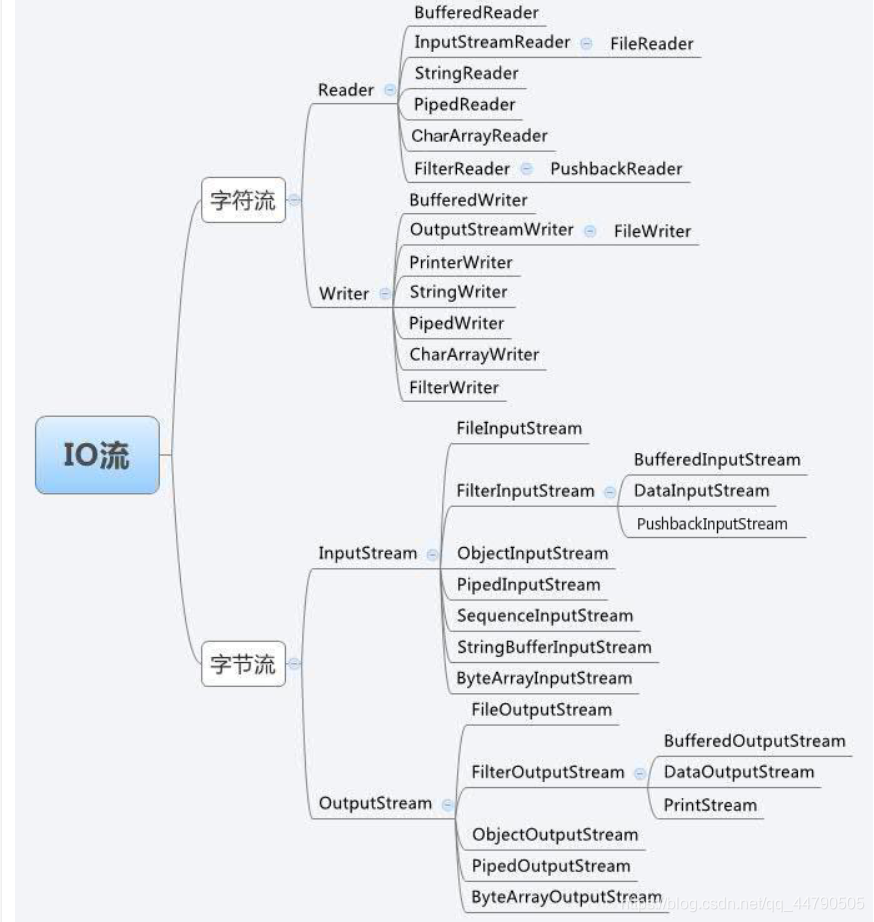
FileinputStream
该流用于从文件读取数据,它的对象可以用new关键字来创建。
有多种构造方法可以用来创建对象。
可以使用字符串类型的文件名来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件
InputStream f = new?FileInputStream("C:/java/hello");
也可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件。
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(f);
常见操作如下:

FileOutputStream
该类用来创建一个文件并向文件中写数据。
如果该流在打开文件进行输出前,目标文件不存在,那么该流会创建该文件。
同输入流,构造方法也差不多
OutputStream f = new FileOutputStream("C:/java/hello")
或者
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
OutputStream fOut = new FileOutputStream(f);
常用操作:

用法实例:
public class fileStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
byte bWrite[] = { 11, 66, 44, 36, 56};
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("E:" + File.separator + "xiaoyuan.txt");
for (int i = 0; i < bWrite.length; i++) {
//writes the bytes
os.write(bWrite[i]);
}
os.close();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("E:" + File.separator + "xiaoyuan.txt");
int size = is.available();
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
System.out.println((char) is.read() + " ");
}
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.print("Exception");
}
}
}?上面程序创建了一个xiaoyuan.txt文件,并把给定打的数字以二进制形式写进该文件,同时输出到控制台上。由于代码是二进制写入,会出现乱码。
解决乱码示例:
/**
* @author asus
*/
public class fileStreamTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File f = new File("D:" + File.separator + "xiaoyuan.txt");
//构建FileOutputStream对象,文件不存在时会自动创建
FileOutputStream fop = new FileOutputStream(f);
//构建OutputStreamWriter对象,参数可以指定编码,默认为操作系统默认编码
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fop, "UTF-8");
//写到缓冲区
writer.append("中文输入");
//换行
writer.append("\r\n");
//刷新缓冲区,写入到文件,如果下面已经没有写入的内容了,直接close也会写入
writer.append("English");
//关闭写入流,同时会把缓冲区内容写入文件
writer.close();
//关闭输出流,释放系统资源
fop.close();
//构建FileInputStream对象
FileInputStream fip = new FileInputStream(f);
// 构建InputStreamReader对象,编码与写入相同
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(fip, "UTF-8");
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while (reader.ready()) {
// 转成char加到StringBuffer对象中
sb.append((char) reader.read());
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
reader.close();
fip.close();
}catch (IOException e){
System.out.println("Exception");
}
}
}执行结果为:

?