文章目录
Object类概述
- Object类是所有类的父类,也就是说 Java 的所有类都直接或间接的继承了 Object,Object位于继承树的最顶层
- 任何类,如果没有显示地用extends继承某个类,那么它都默认直接继承Object类
- Object类中所定义的方法,是所有对象都具备的方法
- Object类型可以存储任何对象:
- 作为参数,可接受任何对象
- 作为返回值,可返回任何对象
1. getClass()方法
概述
getClass() 方法用于获取对象的运行时对象的类。
语法
定义:public final Class getClass(){}
调用:对象名.getClass()
返回值
返回对象的类。
应用
通常用于判断两个引用中实际存储对象类型是否一致。
举例
Student类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.getclass;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
测试类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.getclass;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student("小明",20);
Student s2=new Student("小红",22);
//判断s1和s2是不是同一个类型
Class class1=s1.getClass();
Class class2=s2.getClass();
System.out.println(class1);
if (class1==class2){
System.out.println("s1和s2是同一类型");
}else {
System.out.println("s1和s2不是是同一类型");
}
}
}

getClass()与getClass().getName的区别
前者将返回:class+类名
后者将返回:类名
测试类2:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.getclass;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s=new Student("小明",20);
System.out.println(s.getClass());
System.out.println(s.getClass().getName());
}
}

2. hashCode() 方法
概述
hashCode() 方法用于获取对象的 hash 值。
语法
定义:public int hashCode(){}
调用:对象名.hashCode()
返回值
返回对象哈希值,是一个整数,表示在哈希表中的位置。
哈希值是根据字符串或数字或对象的地址,使用hash算法计算出来的int类型的数值。
一般情况下,相同对象返回相同的哈希值。
应用
判断两个对象是不是同一个对象。
举例
Student类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.hashcode;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
测试类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.hashcode;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student("小明",20);
Student s2=new Student("小红",22);
Student s3=new Student("小刚",23);
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(s2.hashCode());
s3=s1;
System.out.println(s3.hashCode());
s3= new Student("小兰",25);
System.out.println(s3.hashCode()); //注意:此处的哈希值改变是因为s3通过new关键字指向了新的对象,
//虽然之前s3和s1指向了同一地址,但由于给s3重新实例化,s3指向了一片新的内存空间
}
}

3. toString()方法
概述
toString() 方法用于返回对象的字符串表示形式。
语法
定义:public String toString(){}
调用:对象名.toString()
返回值
返回对象的字符串表示形式。
默认返回格式:对象的 class 名称 + @ + hashCode 的十六进制字符串
举例
Student类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.tostring;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
测试类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.tostring;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s=new Student("小明",20);
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
}

上述输出信息过于繁琐并且不宜阅读,大多数时候,我们需要重写toString()方法,使输出信息变得简洁、易阅读。我们将Student类的代码改成如下所示:
Student类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.tostring;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name+"今年"+age+"岁了";
}
}
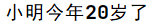
4. equals() 方法
概述
equals() 方法用于比较两个对象是否相等。
equals() 方法比较两个对象,是判断两个对象引用指向的是同一个对象,即比较两个对象的内存地址是否相等。
语法
定义:public boolean equals(Object obj){}
调用:对象名.equals()
参数
obj - 要比较的对象。
返回值
如果两个对象相等返回 true,否则返回 false。
举例
Student类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.equals;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
测试类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.equals;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student("小明",20);
Student s2=new Student("小红",22);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //输出必然为false,因为比较的是s1和s2的地址是否相同
}
}

重写equals() 方法实现比较两对象内容是否相等
在Java给的默认equals() 方法的功能为,判断两个对象的内存地址是否相等,而当我们想要实现比较两对象内容是否相等时,就需要重写equals() 方法。
步骤:
- 比较两个引用是否指向同一个对象
- 判断obj是否为null
- 判断两个引用指向的实际对象类型是否一致
- 强制类型转换(obj为父类类型,不能访问子类独有的属性,所以要进行强制类型转换,以便进行下一步)
- 依次比较各个属性值是否相等
注意: 省略第一步和第二步也可也完成同样的功能,但是效率低(因为每次都需要判断是否为同一类型)
代码:
Student类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.equals;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this==obj){ //比较两个引用是否指向同一个对象
return true;
}else if(obj==null){ //判断obj是否为null
return false;
}else{
if (obj instanceof Student){ //判断两个引用指向的实际对象类型是否一致
Student s=(Student) obj; //obj为父类类型,不能访问子类Student独有的属性,所以要进行强制类型转换
return this.name.equals(s.name) && this.age == s.age; //引用类型数据类型使用equals()方法判断内容是否相等
}
}
return false;
}
}
测试类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.equals;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1=new Student("小明",20);
Student s2=new Student("小红",22);
Student s3=new Student("小红",22);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s2.equals(s3));
}
}

5. finalize()方法
概述
finalize() 方法是实例被垃圾回收器回收时触发的操作。
当 GC (垃圾回收器) 确定不存在指向该对象的有效引用时,对象的垃圾回收器就会自动调用这个方法(程序员不需要手动调用),用以标记垃圾对象,进入回收队列。
相关名词
- 垃圾对象:没有有效引用指向当前对象时,该对象为垃圾对象
- 垃圾回收:由GC销毁垃圾对象,释放数据存储空间
- 自动回收机制:JVM的内存耗尽,一次性回收所有垃圾对象
- 手动回收机制:使用System.gc();通知JVM执行垃圾回收(注意此处只是通知JVM执行垃圾回收,具体是否执行垃圾回收,还是由JVM进行判断)
语法
定义:protected void finalize(){}
只需要重写,GC自动调用
举例
Student类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.finalize;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
System.out.println(this.name+"对象被回收了");
}
}
测试类:
package com.ibelifly.commonclass.object.finalize;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Student("小明",20);
new Student("小红",20);
System.gc();
System.out.println("回收垃圾");
}
}

参考文章:
https://www.runoob.com/java/java-object-class.html
参考视频:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vt4y197nY?p=10
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1mE411x7Wt?p=369