Java Stream如何写出高雅又装*的代码
如何让同事看不懂你写的代码 然后觉得你非常牛逼 这里用到了stream()与Lambda 需要有点基础,没基础你炫个🔨
优雅永不过时~ 看下面文章时记得穿燕尾服 拿高脚杯

List<String> strings = Lists.newArrayList("name=kk", "sex=1", "tel=1111", "email=xx@qq.com","name=ww","name=yy");
一. 冷静分析
如上代码,你现在要做一个分组的Map将上面list的值读取出来,然后分组统计类似于Map<String,List< String >> 将Key相同的Val全部存到一个list里面
二. 直接开装
不会真有人还直接遍历吧,那别人不就看的懂了~ 为了炫技直接装一波
定义封装对象
@Data
@Builder
static class ObiectMap{
private String key;
private String value;
}
2.1 初级炫
System.out.println("map1: ");
Map<String, List<String>> collect1 = strings.stream().map(e -> { //封装成对象
String[] split = e.split("\\=", 2);
return ObiectMap.builder().key(split[0]).value(split[1]).build();
}).collect(Collectors.toMap(ObiectMap::getKey,v->Lists.newArrayList(v.getValue()), (List<String> newList, List<String> oldList) -> { // Collectors.toMap(a,b,(n1,n2)) -> a代表Map的key (这里直接用方法引用拿到key) b代表value (n1,n2)代表key相同时value的处理办法,直接合并List
oldList.addAll(newList);
return oldList;
}));
collect1.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.printf(k+" { ");
String vList = v.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(",")); //加上逗号,最后一个不加
System.out.printf(vList);
System.out.printf(" }");
System.out.println();
});
System.out.println();
结果如下
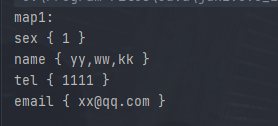
2.2 普通炫
System.out.println("map2: ");
Map<String, List<String>> collect2 = strings.stream().map(e -> {
String[] split = e.split("\\=", 2);
return ObiectMap.builder().key(split[0]).value(split[1]).build();
}).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(ObiectMap::getKey, Collectors.mapping(ObiectMap::getValue, Collectors.toList()))); //Collectors.groupingBy(a,b) a还是通过key来分组 ,b将value收集起来做list value
collect2.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.printf(k+" { ");
String vList = v.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(",")); //加上逗号,最后一个不加
System.out.printf(vList);
System.out.printf(" }");
System.out.println();
});
System.out.println();
结果如下
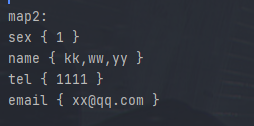
2.3 高级炫
用Guava来炫
import com.google.common.collect.*
System.out.println("map3: get name List with Multimap");
List<ObiectMap> collect3 = strings.stream().map(e -> {
String[] split = e.split("\\=", 2);
return ObiectMap.builder().key(split[0]).value(split[1]).build();
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
Multimap<String, String> multiMap = ArrayListMultimap.create(); //使用Guava的Multimap来存 value直接是collection,可以随意转换
collect3.forEach(c -> multiMap.put(c.getKey(), c.getValue()));
System.out.println(multiMap.get("name").stream().collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
System.out.println();
结果如下
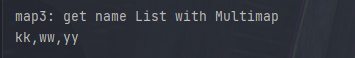
2.4 再炫一波 拿到当前key与对应的数量
System.out.println("map4: get name with count");
Map<String, Long> collect4 = strings.stream().map(e -> {
String[] split = e.split("\\=", 2);
return ObiectMap.builder().key(split[0]).value(split[1]).build();
}).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(ObiectMap::getKey, Collectors.counting())); // 拿到数量
collect4.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.printf(k+" { ");
System.out.printf("%d",v);
System.out.printf(" }");
System.out.println();
});
System.out.println();
结果如下
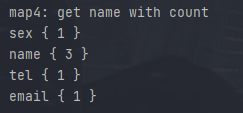
2.5 Map Reduce炫
这个不能处理重复value,只是将单一Map聚合到一个Map
List<String> strings = Lists.newArrayList("name=kk", "sex=1", "tel=1111", "email=xx@qq.com");
Map<String, String> reduce = strings.stream().map(e -> {
String[] split = e.split("\\=", 2); // 正则划分为单map
return Collections.singletonMap(split[0], split[1]);
}).reduce(new HashMap<String, String>(), (accMap, singleMap) -> { // reduce(a,(b,c))-> a 为初始值 b为累加值 c为当前值 操作返回当前值与累加值后的结果 将多个单KV的Map组合成一个Map
accMap.putAll(singleMap);
return accMap;
});
reduce.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println(k+" = "+v);
});
