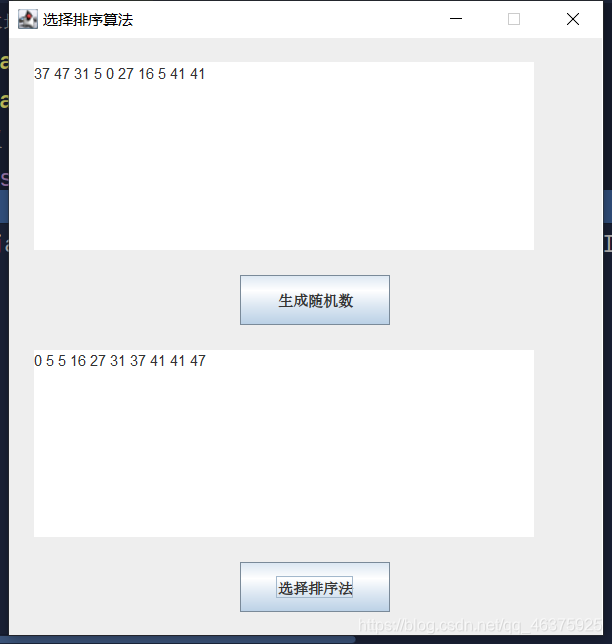
Java编程练习Day09 --》数组排序与查询
使用选择排序法
实例说明
选择排序是一种简单直观的排序算法。
本实例演示如何使用选择排序法对一维数组进行排序,运行本实例,首先单击生成随机数按钮,生成一个随即数组,并显示在上方的文本域控件中,然后单机选择排序法按钮,使用选择排序法对生成的一维数组进行排序,并将排序后的一维数组显示在下方的文本域控件中。
设计过程
选择排序:
选择排序的基本思想是,每一趟从待排序的数据元素中选出最小(或最大)的一个元素,顺序放在已排好序的数列后面,直到全部待排序的数据元素排完。
设计过程:
1.在项目中创建窗体类SelectSort类。在窗体中添加两个文本域控件和生成随机数,选择排序法两个按钮控件。
2.编写生成随机数按钮的事件处理方法,在该方法中创建Random随机数对象,初始化数组元素值时,通过该对象为每个数组元素生成随机数。
3.编写选择排序法按钮的事件处理方法,在该方法中使用排序算法对生成的随机数组进行排序,然后把排序后的数组元素显示到文本域控件中。
测试代码
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.Random;
public class SelectSort extends JFrame {
//创建文本域
JTextArea textArea1;
JTextArea textArea2;
//创建按钮
JButton sort;
JButton numRandom;
private int[] array = new int[10];
public SelectSort(){
textArea1 = new JTextArea(50,45);
textArea2 = new JTextArea(50,45);
sort = new JButton("选择排序法");
numRandom = new JButton("生成随机数");
//设置窗体标题
setTitle("选择排序算法");
//设置窗体的位置和大小
setBounds(250, 250, 490, 515);
//设置窗体的关闭方式
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
//设置窗体可见
setVisible(true);
//设置窗体不可缩放
setResizable(false);
//设置布局方式为空布局
setLayout(null);
//设置各组件在窗口中的位置和大小
textArea1.setBounds(20, 20, 400, 150);
numRandom.setBounds(185, 190, 120, 40);
textArea2.setBounds(20, 250, 400, 150);
sort.setBounds(185, 420, 120, 40);
//为按钮添加事件监听器
sort.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
textArea2.setText("");//清空文本域
int index;
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
index = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= array.length - i; j++) {
if(array[j] > array[index]){
index = j;
}
}
//交换在array.length - i 和 index (最大值) 位置上的两个数
int temp = array[array.length - i];
array[array.length - i] = array[index];
array[index] = temp;
}
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
textArea2.append(array[i]+" ");
}
}
});
numRandom.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Random random = new Random();//创建随即数组对象
textArea1.setText("");//清空文本域
//初始化数组元素
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
array[i] = random.nextInt(50);//生成50以内的随机数
textArea1.append(array[i]+" ");//把数组元素显示到文本域控件中
}
}
});
//将各组件添加到窗口中去
add(textArea1);
add(textArea2);
add(sort);
add(numRandom);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SelectSort();
}
}
运行结果
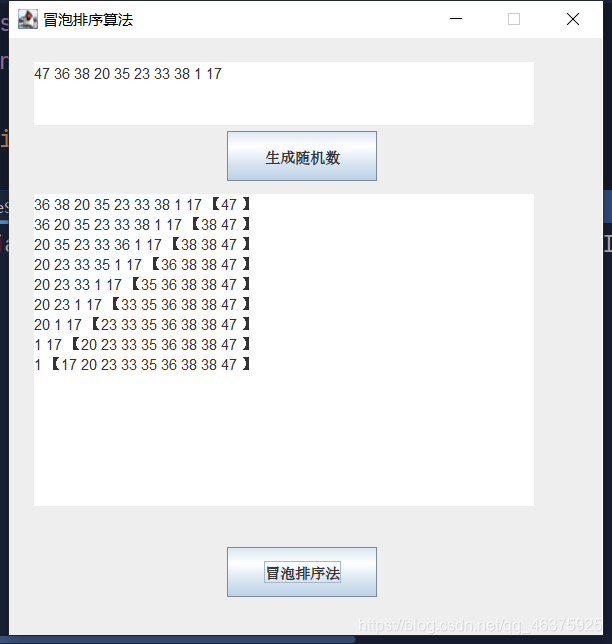
使用冒泡排序
实例说明
本实例演示如何使用冒泡排序法,对一维数组进行排序。运行本实例,首先单击生成随机数按钮,生成一个随机数组并显示在上方的文本域控件中;然后单击冒泡排序按钮,使用冒泡排序法对生成的一维数组进行排序,并将排序过程中一维数组的变化显示在下方的文本域控件中。
设计过程
冒泡排序:
冒泡排序的基本思想是对比相邻的元素值,如果满足条件就交换元素值,把较小的元素移动到数组前面,把大的元素移动到数组后面(也就是交换两个元素的位置),这样数组元素就像气泡一样从底部上升到顶部。
冒泡算法在双层循环中实现,其中外层控制排序轮数,要排序数组长度-1次,而内层循环主要是用于对比临近元素的大小,以确定是否交换位置,对比和交换次数随排序轮数而减少。
设计过程:
1.在项目中创建窗体类BubbleSort。在窗体中添加两个文本域控件和生成随机数,冒泡排序法两个按钮。
2.编写生成随机数按钮的事件处理方法,在该方法中使用排序算法对生成的随机数组进行排序,然后把排序后的数组元素显示到文本域控件中。
3.编写冒泡排序法按钮的事件处理方法,在该方法中使用排序算法对生成的随机数组进行排序,然后把排序后的数组元素显示到文本域控件中。
测试代码
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.Random;
public class BubbleSort extends JFrame {
//创建文本域
JTextArea textArea1;
JTextArea textArea2;
//创建按钮
JButton sort;
JButton numRandom;
private int[] array = new int[10];
public BubbleSort(){
textArea1 = new JTextArea(50,45);
textArea2 = new JTextArea(50,45);
sort = new JButton("冒泡排序法");
numRandom = new JButton("生成随机数");
//设置窗体标题
setTitle("冒泡排序算法");
//设置窗体的位置和大小
setBounds(250, 250, 490, 515);
//设置窗体的关闭方式
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
//设置窗体可见
setVisible(true);
//设置窗体不可缩放
setResizable(false);
//设置布局方式为空布局
setLayout(null);
//设置各组件在窗口中的位置和大小
textArea1.setBounds(20, 20, 400, 50);
numRandom.setBounds(175, 75, 120, 40);
textArea2.setBounds(20, 125, 400, 250);
sort.setBounds(175, 408, 120, 40);
//为按钮添加事件监听器
sort.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
textArea2.setText("");//清空文本域
int index;
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
//比较相邻的两个元素,较大的往后冒泡
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int temp = array[j];//把第一个元素值保存到临时变量中
array[j] = array[j + 1];//把第二个元素值保存到第一个元素单元中
array[j + 1] = temp;//把临时变量也就是第一个元素原值保存到第二个元素中
}
textArea2.append(array[j]+" ");//把排序后的数组元素显示到文本域中
}
textArea2.append("【");
for (int j = array.length - i; j < array.length; j++) {
textArea2.append(array[j]+" ");//把排序后的数组元素显示到文本域中
}
textArea2.append("】\n");
}
}
});
numRandom.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Random random = new Random();//创建随即数组对象
textArea1.setText("");//清空文本域
//初始化数组元素
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
array[i] = random.nextInt(50);//生成50以内的随机数
textArea1.append(array[i]+" ");//把数组元素显示到文本域控件中
}
}
});
//将各组件添加到窗口中去
add(textArea1);
add(textArea2);
add(sort);
add(numRandom);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new BubbleSort();
}
}
运行结果
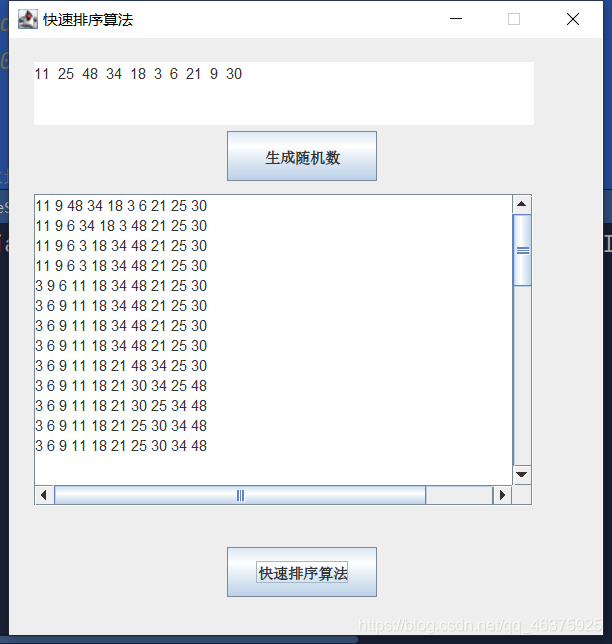
使用快速排序法
实例说明
快速排序是对起泡排序的一种改进,其排序速度相对较快。本实例演示如何使用快速排序法对一维数组进行排序,运行本实例首先单击生成随即数组按钮生成一个随即数组,并显示在上方的文本框中;然后单击快速排序法按钮,使用快速排序法对生成的一维数组进行排序,并将排序后的一维数组显示在下方的文本框中。
设计过程
快速排序的基本思想:
通过一趟排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据比另一部分的所有数据都要小,然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此使整个数据变成有序序列。
设计过程:
1.在项目中创建窗体类QuickSort。在窗体中添加一个文本框,一个文本域控件和生成随机数,快速排序法两个按钮。
2.编写快速排序法按钮的事件处理方法,在该方法中利用快速排序算法对生成的随即数组进行排序,并将排序过程输出到文本域控件中。
3.编写快速排序方法quickSort(),这个方法将被按钮的事件处理方法调用,该方法在实现快速排序的同时,把排序过程显示到文本域控件中。
4.由于快速排序方法中频繁的交换数组元素,而且在程序代码中出现的位置较多,所以应该把数组元素交换单独提炼为一个swap()方法,以实现代码重用并且可以在该方法中唱我排序过程并显示到文本域控件中。
测试代码
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.Random;
public class QuickSort extends JFrame {
//创建文本域
JTextArea textArea1;
JTextArea textArea2;
//创建按钮
JButton sort;
JButton numRandom;
//创建滚动面板
JScrollPane jsp;
private int[] array = new int[10];
public QuickSort(){
textArea1 = new JTextArea(50,45);
textArea2 = new JTextArea(50,45);
sort = new JButton("快速排序算法");
numRandom = new JButton("生成随机数");
jsp = new JScrollPane(textArea2);
//设置窗体标题
setTitle("快速排序算法");
//设置窗体的位置和大小
setBounds(250, 250, 490, 515);
//设置窗体的关闭方式
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
//设置窗体可见
setVisible(true);
//设置窗体不可缩放
setResizable(false);
//设置布局方式为空布局
setLayout(null);
//设置各组件在窗口中的位置和大小
textArea1.setBounds(20, 20, 400, 50);
numRandom.setBounds(175, 75, 120, 40);
jsp.setBounds(20, 125, 400, 250);
sort.setBounds(175, 408, 120, 40);
//为按钮添加事件监听器
sort.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
textArea2.setText("");//清空文本域
quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
}
});
numRandom.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Random random = new Random();//创建随即数组对象
textArea1.setText("");//清空文本域
//初始化数组元素
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
array[i] = random.nextInt(50);//生成50以内的随机数
textArea1.append(array[i]+" ");//把数组元素显示到文本域控件中
}
}
});
//将各组件添加到窗口中去
add(textArea1);
add(jsp);
add(sort);
add(numRandom);
}
private void quickSort(int sortArray[],int lowIndex,int highIndex){
int lo = lowIndex;//记录最小索引
int hi = highIndex;//记录最大索引
int mid;//记录分界点元素
if(highIndex > lowIndex){
mid = sortArray[(highIndex + lowIndex)/2];//确定中间分界点元素值
while(lo <= hi){
while((lo < highIndex) && (sortArray[lo] < mid))
++lo; //确定不大于分解元素值的最小索引
while((hi > lowIndex) && (sortArray[hi] > mid))
--hi; //确定不大于分解元素值的最小索引、
if(lo <= hi){//如果最小与最大索引没有重叠
swap(sortArray,lo,hi);//交换两个索引的元素
++lo;//递增最小索引
--hi;//递增最大索引
}
}
if(lowIndex < hi)
quickSort(sortArray, lowIndex, hi);//递归排序没有未分解元素
if(lo < highIndex)
quickSort(sortArray, lo, highIndex);//递归排序没有未分解元素
}
}
private void swap(int swapArray[],int i,int j){
int temp = swapArray[i];//交换数组元素
swapArray[i] = swapArray[j];
swapArray[j] = temp;
for (int k = 0; k < array.length; k++) {
textArea2.append(array[k]+" ");
}
textArea2.append("\n");//追加换行符
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new QuickSort();
}
}
运行结果