思维导图:

jsp01
一、标签语言的特点
1.组成
? ? ? ? ①开始标签?
? ? ? ? ②标签体
? ? ? ? ③结束标签
2.分类
? ? ? ? ①空标签? ? ? ? br/hr
? ? ? ? ②UI标签? ? ? ? table/input
? ? ? ? ③控制标签? ? ? ? if/foreach
????????④数据标签? ? ? ? set/out
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://jsp.varyedu.cn" prefix="z"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<z:if test=""></z:if>
<!-- 标签的构成:开始标签、标签体、结束标签 -->
<a>标签语言的特点</a>
空标签
<!-- 没有内容 -->
<br>
<hr>
<!-- UI标签 -->
<table>
<tr></tr>
</table>
<input>
控制标签
<c:if test="true">输出</c:if>
<c:if test="false">不输出</c:if>
数据标签
<c:set var="name" value="zs"></c:set>
<c:out value="${name }"></c:out>
</body>
</html>二、自定义标签的步骤
1.tld文件
2.tag助手类????????==>继承BodyTagSupport? ? ? ? ==>doStartTag-->doAfterBodyTag-->doEndTag?
3.tarlib引入
标签库描述文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<taglib xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-jsptaglibrary_2_0.xsd"
version="2.0">
<description>zking 1.1 core library</description>
<display-name>zking core</display-name>
<tlib-version>1.1</tlib-version>
<short-name>zking</short-name>
<uri>http://jsp.varyedu.cn</uri>
<validator>
<description>
Provides core validation features for JSTL tags.
</description>
<validator-class>
org.apache.taglibs.standard.tlv.JstlCoreTLV
</validator-class>
</validator>
<tag>
<name>demo1</name>
<tag-class>com.tag.Demo1</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
</tag>
</taglib>标签库描述文件:
package com.tag;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
public class Demo1 extends BodyTagSupport{
//解析<z:demo1>执行
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
System.out.println("进来了");
// return super.doStartTag();
return EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE;
}
//解析demo1内容执行
@Override
public int doAfterBody() throws JspException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.doAfterBody();
}
//解析</z:demo1>执行
@Override
public int doEndTag() throws JspException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.doEndTag();
}
}
?jsp02
生命周期路线
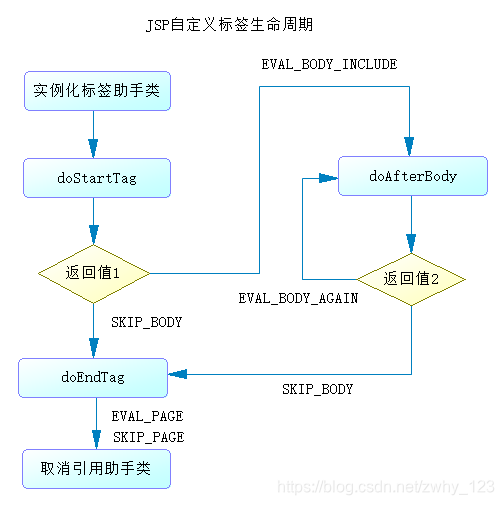
1.doStartTag方法内返回值SKIP_BODY????????==>????????跳转到doEndTag??
2.doStartTag方法内返回值EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE? ? ? ? ==>????????到doAfterBody方法返回值EVAL_PAGE? ? ? ? ==>????????再到doEndTag
3.doStartTag方法内返回值EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE? ? ? ? ==>????????到doAfterBody方法返回值EVAL_BODY_AGAIN? ? ? ? ==>????????再到doEndTag
?论证第一条路线:
package com.zhuwei.tag;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
public class Demo1 extends BodyTagSupport{
/**
* 1.论证这三条路线的执行顺序
* 第一条路线:Demo.java:呈现结果:打印出"Demo_doStartTag进去了"与"Demo_doEndTag进去了"
* 论证了第一条的正确性
*/
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
System.out.println("Demo_doStartTag进去了");
return super.doStartTag();
}
@Override
public int doAfterBody() throws JspException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.doAfterBody();
}
@Override
public int doEndTag() throws JspException {
System.out.println("Demo_doEndTag进去了");
return super.doEndTag();
}
}
?论证第二条路线:
package com.zhuwei.tag;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
public class Demo2 extends BodyTagSupport{
/**
* 1.论证这三条路线的执行顺序(Demo.java)
* 2.第二条路线:能打印小胡三条内容:"Demo2_doStartTag进来了","Demo2_doAfterBody进来了"
* 与"Demo2_doEndTag进来了",论证了第二条路线的正确性
*
*/
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
System.out.println("Demo2_doStartTag进来了");
// return super.doStartTag();
return EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE;
}
@Override
public int doAfterBody() throws JspException {
System.out.println("Demo2_doAfterBody进来了");
return EVAL_PAGE;
}
@Override
public int doEndTag() throws JspException {
System.out.println("Demo2_doEndTag进来了");
return super.doEndTag();
}
}
论证第三条路线:
package com.zhuwei.tag;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
public class Demo3 extends BodyTagSupport{
/**
* 1.论证这三条路线的执行顺序(Demo.java)
* 2.第三条路线:结果会执行出"Demo3_doStartTag进去了","Demo3_doAfterBody进去了"执行多遍,
* 最后执行"Demo3_doEndTag进去了",结论正确
*/
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
System.out.println("Demo3_doStartTag进来了");
// return super.doStartTag();
return EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE;
}
@Override
public int doAfterBody() throws JspException {
System.out.println("Demo3_doAfterBody进来了");
return EVAL_BODY_AGAIN;
}
@Override
public int doEndTag() throws JspException {
System.out.println("Demo3_doEndTag进来了");
return super.doEndTag();
}
}
<tag>
<name>demo1</name>
<tag-class>com.zhuwei.tag.Demo1</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
</tag>
<tag>
<name>demo2</name>
<tag-class>com.zhuwei.tag.Demo2</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
</tag>
<tag>
<name>demo3</name>
<tag-class>com.zhuwei.tag.Demo3</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
</tag>if标签(控制标签)
package com.zhuwei.tag;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
public class IfTag extends BodyTagSupport{
/**
* 案例:第一与第二条路线的实际应用
* 开发一个控制标签
*
* c:if test=true 是要输出标签体的 要输出就走第二条路线
* c:if test=false 是不输出标签体的 不输出就走第一条路线
* @author zjjt
*/
private boolean test;
public boolean isTest() {
return test;
}
public void setTest(boolean test) {
this.test = test;
}
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
// 需要一个变量来控制返回值,从而控制本标签走第一条路线还是第二条路线
return test?EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE:SKIP_BODY;
}
}
标签库描述文件:
<tag>
<name>if</name>
<tag-class>com.zhuwei.tag.IfTag</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
<attribute>
<!-- 自定义标签的成员变量名称 -->
<name>test</name>
<!-- 该成员变量是否必传 -->
<required>true</required>
<!-- 是否支持EL表达式 -->
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
</tag>?
测试:
![]()
?
set标签及out标签(数据标签)
1.第一条路线应用
2.JspWriter:在没有标签体的情况下向页面输出内容
①set:
package com.zhuwei.tag;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
/**
* 案例三四
* 开发数据标签
* 1.第一条路线
* 只不过set,out标签本身是没有标签体的,需要在页面导航输出内容
* 需要借助一个类JspWriter
* 2.在没有标签体的情况下,是通过JspWriter输出内容的
* @author zjjt
*
*/
public class SetTag extends BodyTagSupport{
// 存放标签的键
private String var;
// 存放标签对应的值
private Object value;
public String getVar() {
return var;
}
public void setVar(String var) {
this.var = var;
}
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Object value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
// 将value值保存到var对应的变量中
// jsp传递name给var,转递赵四给value
// 那么需要把赵四赋值给name
pageContext.setAttribute(var, value);
return super.doStartTag();
}
}
标签库描述文件:
<tag>
<name>set</name>
<tag-class>com.zhuwei.tag.SetTag</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
<attribute>
<name>var</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<name>value</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
</tag>测试:
![]() ?
?
?
②out:
package com.zhuwei.tag;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
public class OutTag extends BodyTagSupport{
private Object value;
public Object getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(Object value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
JspWriter out=pageContext.getOut();
try {
out.print(value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return super.doStartTag();
}
}
标签库描述文件:
<tag>
<name>out</name>
<tag-class>com.zhuwei.tag.OutTag</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
<attribute>
<name>value</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
</tag>测试:
![]()
?
foreach标签(控制标签)
1.第二条第三条路线的应用
2.理解迭代器指针的应用????????==>doStartTag保存迭代器及指针状态,在doAfterBody方法中反复使用
package com.zhuwei.tag;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
/**
* 熟悉第二第三路线的开发流程
* 1、最少接受两个参数
* 2、一定会有标签体的,那么对应需要重写doAfterBody方法
* 3.必定有判断条件决定doAfterBody的返回值是EVAL_PAGE还是EVAL_BODY_AGAIN
* 将取集合元素的过程,看成指针下移取值的过程,如果指针还能指向下一个,那么返回值为EVAL_BODY_AGAIN
* 如果指针没有指下一个元素,那么返回值为EVAL_PAGE
* 指针是迭代器里面的产物,所以需要将迭代器保存并提供到doAfterBody中使用
*
* @author zjjt
*
*/
public class ForeachTag extends BodyTagSupport {
private String var;
private List<Object> items = new ArrayList<Object>();
public String getVar() {
return var;
}
public void setVar(String var) {
this.var = var;
}
public List<Object> getItems() {
return items;
}
public void setItems(List<Object> items) {
this.items = items;
}
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
// 在此处保存迭代器,供doAfterBody中使用
Iterator<Object> it = items.iterator();
pageContext.setAttribute("it", it);
return EVAL_BODY_INCLUDE;
}
@Override
public int doAfterBody() throws JspException {
Iterator<Object> it = (Iterator<Object>) pageContext.getAttribute("it");
if (it.hasNext()) {
// 在页面上,需要通过var将集合中的对象拿到
pageContext.setAttribute(var, it.next());
// 保存指针下移后的状态
pageContext.setAttribute("it", it);
// 继续循环
return EVAL_BODY_AGAIN;
} else {
// 结束循环
return EVAL_PAGE;
}
}
}
标签库描述文件:
<tag>
<name>foreach</name>
<tag-class>com.zhuwei.tag.ForeachTag</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
<attribute>
<name>var</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<name>items</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
</tag>测试:

?select标签的开发
selectTag:
package com.zhuwei.tag;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspException;
import javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter;
import javax.servlet.jsp.tagext.BodyTagSupport;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
import com.sun.jdi.Value;
/**
* 最终案例
* 目的:将所学的自定义标签的知识点,用于实际项目开发
* 不管if/set/out/foreach 那都是c标签已经具备的功能,直接用别人就好
* 学习自定义标签理解其底层的目的,就是弥补现成C标签没有的功能
*
* 课堂的最终体现形式
* 以前
* 查询下拉框
* <select>
<option value="">---请选择---</option>
<option value="1">晓哥</option>
<option checked value="2">胡哥</option>
<option value="3">娜姐</option>
</select>
修改回显,在这里有大量的c:foreach、c:if判断
不足之处:代码过大,以及凡是涉及到下拉框以及复选框,相类似的代码过多
目前
<z:select></z:select>
目的:通过上述标签能够实现上述代码相同的功能
分析属性:
1.数据源属性items,用于遍历展示的 users->List<User>(id,name)->id=option>value;name=option>text
2.对象key属性textKey,用于对应option>value
3.对象value属性textVal,用于对应option>text
4.对象默认key属性headerTextKey,用于对应默认的option>value
5.对象默认key属性headerTextVal,用于对应默认的option>text
6.对象回显值属性selectedVal,用于判断是否数据回显选中
没有标签体,又需要往页面输出内容 JspWriter
* @author zjjt
*
*/
public class SelectTag extends BodyTagSupport{
private List<Object> items=new ArrayList<Object>();//用于遍历展示的
private String textKey;//用于对应option>value
private String textVal;//用于对应option>text
private String headerTextKey;//用于对应默认的option>value
private String headerTextVal;//用于对应默认的option>text
private String selectedVal;//用于判断是否数据回显选中
// 定义属性美化,扩展/操作标签
private String cssStyle;//美化
private String id;//绑定事件 操作标签
private String className;//美化
@Override
public int doStartTag() throws JspException {
JspWriter out=pageContext.getOut();
try {
out.print(ToHTML());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return super.doStartTag();
}
private String ToHTML() throws Exception {
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
sb.append("<select id='"+id+"' class='"+className+"' style='"+cssStyle+"'>");
if(headerTextVal!=null&&!"".equals(headerTextVal)) {
// 拼接默认显示标签
sb.append("<option value='>"+headerTextKey+"'>"+headerTextVal+"</option>");
}
// 循环显示数据源
if(items.size()>0) {
for (Object obj : items) {
// obj对应user
// 希望拿到当前user的id放入option——value,name放入option——text
// <option value="1">晓哥</option>
// 通过反射读取到id对应的属性对象
Field textKeyField = obj.getClass().getField(textKey);
textKeyField.setAccessible(true);
// 获取id对应的值
// textKeyField.get(obj);
// 此代码等价于上面三行代码
// PropertyUtils.getProperty(obj, textVal);
String value = textKeyField.get(obj).toString();
sb.append("<option value='"+value+"'>"+PropertyUtils.getProperty(obj, textVal)+"</option>");
// 修改页面下拉框回显选中
// 当下拉框的value值等于selectedVal,那么就要默认下拉框选中
if(value.equals(selectedVal)) {
sb.append("<option checked value='"+value+"'>"+PropertyUtils.getProperty(obj, textVal)+"</option>");
}else {
sb.append("<option value='"+value+"'>"+PropertyUtils.getProperty(obj, textVal)+"</option>");
}
}
}
sb.append("</select>");
return sb.toString();
}
public List<Object> getItems() {
return items;
}
public void setItems(List<Object> items) {
this.items = items;
}
public String getTextKey() {
return textKey;
}
public void setTextKey(String textKey) {
this.textKey = textKey;
}
public String getTextVal() {
return textVal;
}
public void setTextVal(String textVal) {
this.textVal = textVal;
}
public String getHeaderTextKey() {
return headerTextKey;
}
public void setHeaderTextKey(String headerTextKey) {
this.headerTextKey = headerTextKey;
}
public String getHeaderTextVal() {
return headerTextVal;
}
public void setHeaderTextVal(String headerTextVal) {
this.headerTextVal = headerTextVal;
}
public String getSelectedVal() {
return selectedVal;
}
public void setSelectedVal(String selectedVal) {
this.selectedVal = selectedVal;
}
public String getCssStyle() {
return cssStyle;
}
public void setCssStyle(String cssStyle) {
this.cssStyle = cssStyle;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
}
?标签库描述文件:
<tag>
<name>select</name>
<tag-class>com.zhuwei.tag.SelectTag</tag-class>
<body-content>JSP</body-content>
<attribute>
<name>items</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue>true</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<name>textKey</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<name>textVal</name>
<required>true</required>
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<name>headerTextKey</name>
<required>false</required>
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<name>headerTextVal</name>
<required>false</required>
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<name>selectedVal</name>
<required>false</required>
<rtexprvalue>false</rtexprvalue>
</attribute>
</tag>测试:
<!-- 模拟的是新增场景 -->
<z:select textVal="name" items="${users }" textKey="id"></z:select>
<!-- 模拟的修改场景 -->
<!-- 学生表的教员id外键是教员表中的主键id -->
<z:select selectVal="u002" textVal="name" items="${users }" textKey="id"></z:select>
<!-- 模拟查询的场景 查询所有 -->
<z:select headerTextKey="" headerTextVal="---请选择---" textVal="name" items="${users }" textKey=""></z:select>