目录
前言
? ? ? ? 本次我将分享的是java中常用的容器集合,大体分为了两类(Collection单列集合和Map双列集合),什么是双列,单列集合呢?看完这篇博客,或许你将有些许收获。Collection集合下主要讲解List集合和Set集合,而双列集合,我主要讲解HashMap集合。
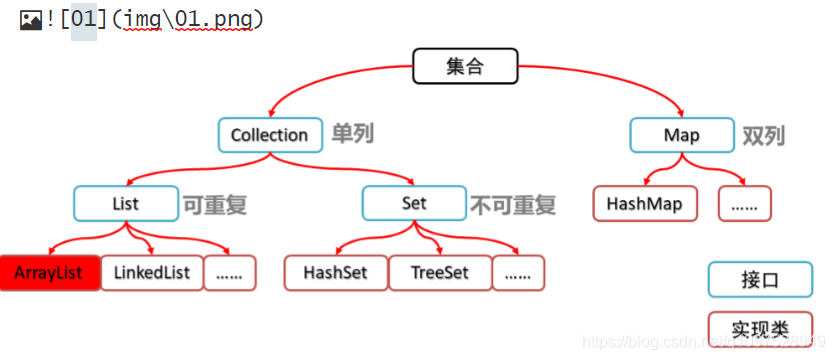
一.Collection集合
? ? ? ??
Collection集合概述
-
是单例集合的顶层接口,它表示一组对象,这些对象也称为Collection的元素
-
JDK 不提供此接口的任何直接实现,它提供更具体的子接口(如Set和List)实现
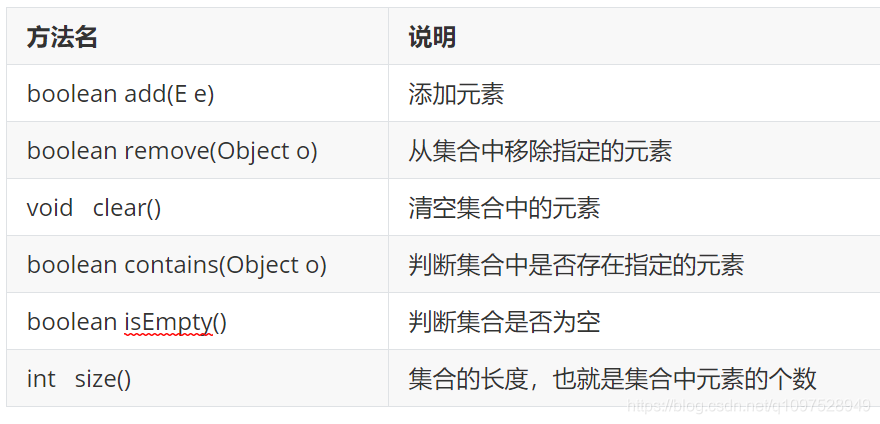
常用方法:
?1.1List集合
List集合概述:
-
有序集合(也称为序列),用户可以精确控制列表中每个元素的插入位置。用户可以通过整数索引访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素
-
与Set集合不同,列表通常允许重复的元素
List集合特点:
-
有索引
-
可以存储重复元素
-
元素存取有序
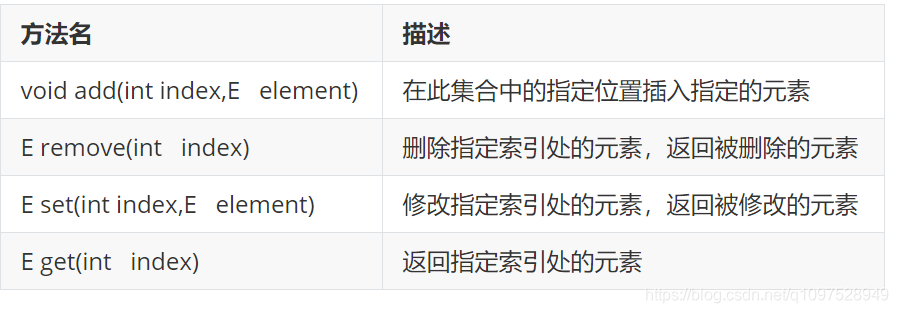
List集合特有的方法:
?遍历方式:
//学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------
//测试类
public class ListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建List集合对象
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 30);
Student s2 = new Student("张曼玉", 35);
Student s3 = new Student("王祖贤", 33);
//把学生添加到集合
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
//迭代器:集合特有的遍历方式
Iterator<Student> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Student s = it.next();
System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());
}
System.out.println("--------");
//普通for:带有索引的遍历方式
for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
Student s = list.get(i);
System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());
}
System.out.println("--------");
//增强for:最方便的遍历方式
for(Student s : list) {
System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());
}
}
}? ? ? ? 接下来讲的是List集合的实现类:
1.1.1ArrayList集合
? ? ?ArrayList集合的底层是数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢,它的一些常用方法可以参考List集合的
常用方法。
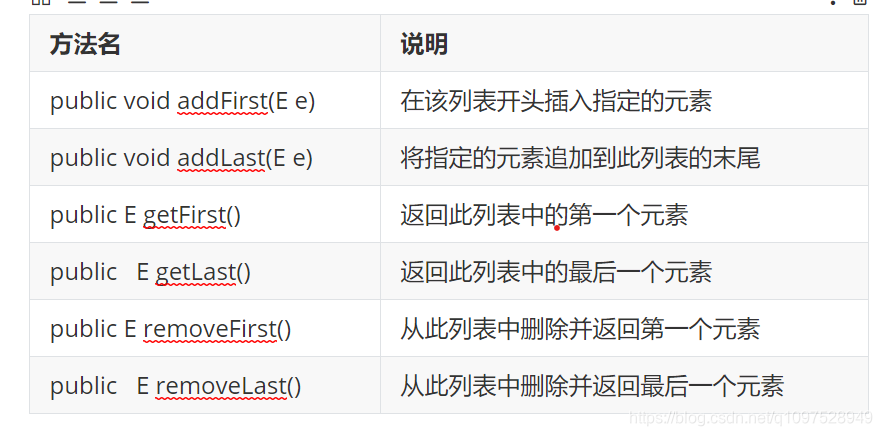
1.1.2LinkedList集合
? ? ?LinkedList集合底层是链表结构实现,查询慢、增删快,它有一些特有的常用方法
1.2Set集合
???????
Set集合的特点
-
元素存取无序
-
没有索引、只能通过迭代器或增强for循环遍历
-
不能存储重复元素
在我讲解HashSet之前我们必须先了解哈希值的概念,方便我们理解接下来的一些集合
-
哈希值简介
是JDK根据对象的地址或者字符串或者数字算出来的int类型的数值
-
如何获取哈希值
Object类中的public int hashCode():返回对象的哈希码值
-
哈希值的特点
-
同一个对象多次调用hashCode()方法返回的哈希值是相同的
-
默认情况下,不同对象的哈希值是不同的。而重写hashCode()方法,可以实现让不同对象的哈希值相同
-
1.2.1HashSet集合
????????
HashSet集合的特点
-
底层数据结构是哈希表
-
对集合的迭代顺序不作任何保证,也就是说不保证存储和取出的元素顺序一致
-
没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
-
由于是Set集合,所以是不包含重复元素的集合
HashSet的基本使用:
public class HashSetDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
//添加元素
hs.add("hello");
hs.add("world");
hs.add("java");
hs.add("world");
//遍历
for(String s : hs) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
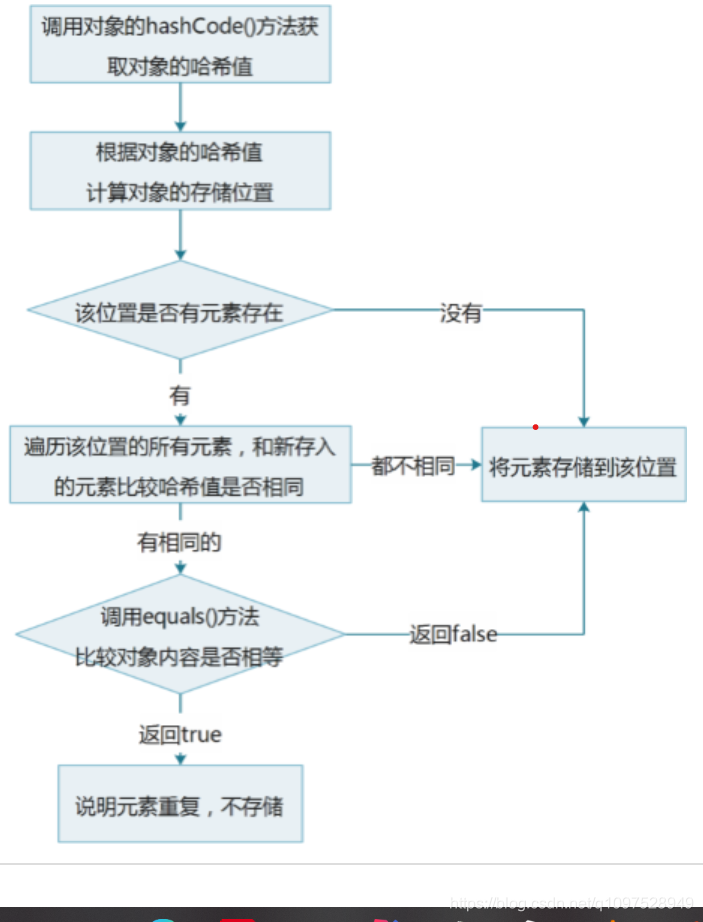
HashSet集合保证元素唯一性源码分析:
1.根据对象的哈希值计算存储位置
如果当前位置没有元素则直接存入
如果当前位置有元素存在,则进入第二步
2.当前元素的元素和已经存在的元素比较哈希值
如果哈希值不同,则将当前元素进行存储
如果哈希值相同,则进入第三步
3.通过equals()方法比较两个元素的内容
如果内容不相同,则将当前元素进行存储
如果内容相同,则不存储当前元素
图解:
拓展:LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet集合特点
-
哈希表和链表实现的Set接口,具有可预测的迭代次序
-
由链表保证元素有序,也就是说元素的存储和取出顺序是一致的
-
由哈希表保证元素唯一,也就是说没有重复的元素
1.2.2TreeSet集合
????????
TreeSet集合概述
-
元素有序,可以按照一定的规则进行排序,具体排序方式取决于构造方法
-
TreeSet():根据其元素的自然排序进行排序
-
TreeSet(Comparator comparator) :根据指定的比较器进行排序
-
-
没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
-
由于是Set集合,所以不包含重复元素的集合
要理解好TreeSet必须先了解自然排序Comparable:
-
案例需求
-
存储学生对象并遍历,创建TreeSet集合使用无参构造方法
-
要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
-
-
实现步骤
-
用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,无参构造方法使用的是自然排序对元素进行排序的
-
自然排序,就是让元素所属的类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo(T o)方法
-
重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
-
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student s) {
// return 0;
// return 1;
// return -1;
//按照年龄从小到大排序
int num = this.age - s.age;
// int num = s.age - this.age;
//年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
int num2 = num==0?this.name.compareTo(s.name):num;
return num2;
}
}
//------------------------------------------------
public class TreeSetDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("xishi", 29);
Student s2 = new Student("wangzhaojun", 28);
Student s3 = new Student("diaochan", 30);
Student s4 = new Student("yangyuhuan", 33);
Student s5 = new Student("linqingxia",33);
Student s6 = new Student("linqingxia",33);
//把学生添加到集合
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6);
//遍历集合
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
}
比较器排序Comparator的使用:
-
案例需求
-
存储学生对象并遍历,创建TreeSet集合使用带参构造方法
-
要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名的字母顺序排序
-
-
实现步骤
-
用TreeSet集合存储自定义对象,带参构造方法使用的是比较器排序对元素进行排序的
-
比较器排序,就是让集合构造方法接收Comparator的实现类对象,重写compare(T o1,T o2)方法
-
重写方法时,一定要注意排序规则必须按照要求的主要条件和次要条件来写
-
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
//===================================================================
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
//this.age - s.age
//s1,s2
int num = s1.getAge() - s2.getAge();
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num;
return num2;
}
});
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("xishi", 29);
Student s2 = new Student("wangzhaojun", 28);
Student s3 = new Student("diaochan", 30);
Student s4 = new Student("yangyuhuan", 33);
Student s5 = new Student("linqingxia",33);
Student s6 = new Student("linqingxia",33);
//把学生添加到集合
ts.add(s1);
ts.add(s2);
ts.add(s3);
ts.add(s4);
ts.add(s5);
ts.add(s6);
//遍历集合
for (Student s : ts) {
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
}?二.Map集合
? ? ? ? 2.1Map集合的概述与特点
-
Map集合概述
interface Map<K,V> ?K:键的类型;V:值的类型 -
Map集合的特点
-
键值对映射关系
-
一个键对应一个值
-
键不能重复,值可以重复
-
元素存取无序
-
Map集合的基本使用:
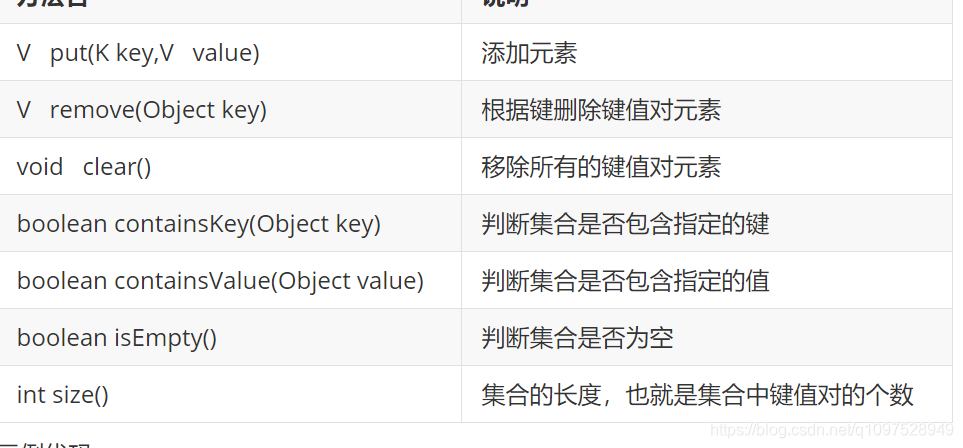
Map集合的一些常用方法:
public class MapDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
//V put(K key,V value):添加元素
map.put("张无忌","赵敏");
map.put("郭靖","黄蓉");
map.put("杨过","小龙女");
//V remove(Object key):根据键删除键值对元素
// System.out.println(map.remove("郭靖"));
// System.out.println(map.remove("郭襄"));
//void clear():移除所有的键值对元素
// map.clear();
//boolean containsKey(Object key):判断集合是否包含指定的键
// System.out.println(map.containsKey("郭靖"));
// System.out.println(map.containsKey("郭襄"));
//boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
// System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
//int size():集合的长度,也就是集合中键值对的个数
System.out.println(map.size());
//输出集合对象
System.out.println(map);
}
}2.2Map集合的获取功能
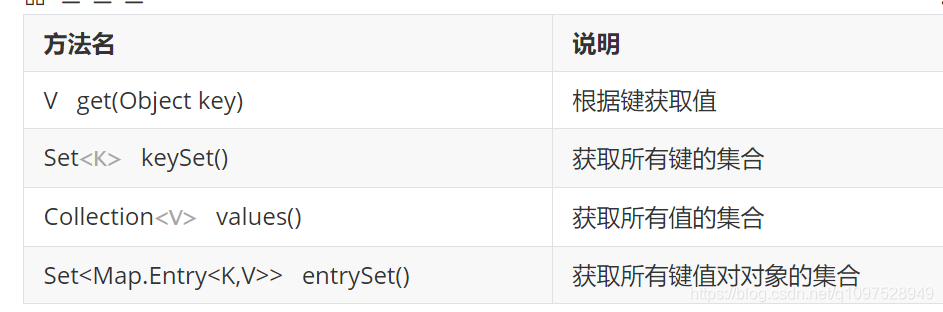
? ?方法介绍:
public class MapDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//添加元素
map.put("张无忌", "赵敏");
map.put("郭靖", "黄蓉");
map.put("杨过", "小龙女");
//V get(Object key):根据键获取值
// System.out.println(map.get("张无忌"));
// System.out.println(map.get("张三丰"));
//Set<K> keySet():获取所有键的集合
// Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
// for(String key : keySet) {
// System.out.println(key);
// }
//Collection<V> values():获取所有值的集合
Collection<String> values = map.values();
for(String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}2.3Map集合的遍历方式(方式一)
-
遍历思路
-
我们刚才存储的元素都是成对出现的,所以我们把Map看成是一个夫妻对的集合
-
把所有的丈夫给集中起来
-
遍历丈夫的集合,获取到每一个丈夫
-
根据丈夫去找对应的妻子
-
-
-
步骤分析
-
获取所有键的集合。用keySet()方法实现
-
遍历键的集合,获取到每一个键。用增强for实现
-
根据键去找值。用get(Object key)方法实现
-
public class MapDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); //添加元素 map.put("张无忌", "赵敏"); map.put("郭靖", "黄蓉"); map.put("杨过", "小龙女"); //获取所有键的集合。用keySet()方法实现 Set<String> keySet = map.keySet(); //遍历键的集合,获取到每一个键。用增强for实现 for (String key : keySet) { //根据键去找值。用get(Object key)方法实现 String value = map.get(key); System.out.println(key + "," + value); } } }2.4Map集合的遍历方式(方式二)
-
-
遍历思路
-
我们刚才存储的元素都是成对出现的,所以我们把Map看成是一个夫妻对的集合
-
获取所有结婚证的集合
-
遍历结婚证的集合,得到每一个结婚证
-
根据结婚证获取丈夫和妻子
-
-
-
步骤分析
-
获取所有键值对对象的集合
-
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():获取所有键值对对象的集合
-
-
遍历键值对对象的集合,得到每一个键值对对象
-
用增强for实现,得到每一个Map.Entry
-
-
根据键值对对象获取键和值
-
用getKey()得到键
-
用getValue()得到值
-
-
-
代码实现
public class MapDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//添加元素
map.put("张无忌", "赵敏");
map.put("郭靖", "黄蓉");
map.put("杨过", "小龙女");
//获取所有键值对对象的集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
//遍历键值对对象的集合,得到每一个键值对对象
for (Map.Entry<String, String> me : entrySet) {
//根据键值对对象获取键和值
String key = me.getKey();
String value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "," + value);
}
}
}2.5HashMap集合
? ? ? ? HashMap是Map的实现类,HashMap可实现快速存储和检索,但缺点是包含的元素是无序的,适用于在Map中插入、删除和定位元素。常用方法参考Map集合。