1.Spring注解
Spring除了默认的使用xml配置文件的方式实现配置之外,也支持使用注解方式实现配置,这种方式效率更高,配置信息清晰,修改更方便,推荐使用。
所谓注解就是给程序看的提示信息,很多时候都用来作为轻量级配置的方式。
2.Spring引入context名称空间
在MyEclipse中导入spring-context-3.2.xsd约束文件,要求Spring来管理。在applicationContext.xml文件中,引入该schema文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
">
</beans>
3.Spring注解方式实现IOC
a.开启包扫描
在spring的配置文件中,开启包扫描,指定spring自动扫描哪些个包下的类。只有在指定的扫描包下的类上的IOC注解才会生效。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
">
<!-- 开启包扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.beans"></context:component-scan>
<!--
<bean id="person" class="cn.tedu.beans.Person"></bean>
<bean id="cat" class="cn.tedu.beans.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="dog" class="cn.tedu.beans.Dog"></bean>
-->
</beans>
b.使用注解注册bean
在配置的包中的类上使用@Component注解,则这个类会自动被注册为bean,使用当前类的class为的class,通常情况下使用类名首字母小写为id。
案例:
package cn.tedu.beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Person{
}
c.bean的id
通常情况下注解注册bean使用类名首字母小写为bean的id,但是如果类名的第二个字母为大写则首字母保留原样。
cn.tedu.beans.Person --> <bean id="person" class="cn.tedu.beans.Person"/>
cn.tedu.beans.PErson --> <bean id="PErson" class="cn.tedu.beans.Person"/>
cn.tedu.beans.NBA --> <bean id="NBA" class="cn.tedu.beans.NBA"/>
也可以通过在@Component中配置value属性,明确的指定bean的id
案例:可以使bean类实现BeanNameAware接口,并实现其中的setBeanName方法,spring容器会在初始化bean时,调用此方法告知当前bean的id。通过这个方式可以获取bean的id信息。
package cn.tedu.beans;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("per")
public class Person implements BeanNameAware{
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("==="+this.getClass().getName()+"==="+name);
} }
4.Spring注解方式实现DI
a.在配置文件中开启注解实现DI
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd
">
<!-- 开启IOC包扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.domain"/>
<!-- 开启注解配置DI -->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
</beans>
b.注解方式注入spring内置支持的类型数据 - 非集合类型
spring中可以通过@Value注解来实现spring内置支持的类型的属性的注入。
package cn.tedu.domain;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Student {
@Value("zs")
private String name;
@Value("19")
private int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
} }
这种方式可以实现spring内置支持类型的注入,但是这种方式将注入的值写死在了代码中,后续如果希望改变注入的值,必须来修改源代码,此时可以将这些值配置到一个properties配置文件中,再在spring中进行引入。
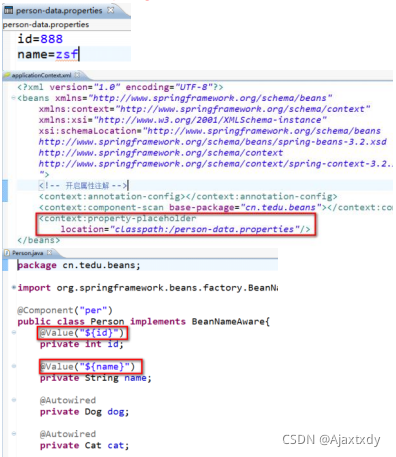
c.注解方式注入spring内置支持的类型数据 - 集合类型
将spring-util-3.2.xsd交给MyEclipse管理在当前spring容器的配置文件中导入util名称空间再通过适当的util标签注册数据。
案例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd
">
<!-- 开启IOC包扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.domain"/>
<!-- 开启注解配置DI -->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<!-- 引入Properties文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:/stu.properties"/>
<!-- 配置集合数据 -->
<util:list id="l1">
<value>aaa</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</util:list>
<util:set id="s1">
<value>111</value>
<value>222</value>
<value>333</value>
</util:set>
<util:map id="m1">
<entry key="k1" value="v1"></entry>
<entry key="k2" value="v2"></entry>
<entry key="k3" value="v3"></entry>
</util:map>
<util:properties id="p1">
<prop key="p1">v1</prop>
<prop key="p2">v2</prop>
<prop key="p3">v3</prop>
</util:properties>
</beans>
再在类的属性中通过@Value注入赋值
package cn.tedu.domain;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Student {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
@Value("${age}")
private int age;
@Value("#{@l1}")
private List<String> list;
@Value("#{@s1}")
private Set<String>
private Set<String> set;
@Value("#{@m1}")
private Map<String,String> map;
@Value("#{@p1}")
private Properties prop;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", list=" + list
+ ", set=" + set + ", map=" + map + ", prop=" + prop + "]";
}
}
d.使用注解注入自定义bean类型数据:
在bean中的属性上通过@Autowired实现自定义bean类型的属性注入代码:
package cn.tedu.domain;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Student {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
private Cat cat;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [dog="+ dog + ", cat=" + cat + "]";
}
}
当Spring容器解析到@Component注解时,创建当前类的bean在spring容器中进行管理,在创建bean的过程中发现了@Autowired注解,会根据当前bean属性名称,寻找在spring中是否存在id等于该名称的bean,如果存在自动注入。如果不存在,再检查是否存在和当前bean属性类型相同的bean,如果存在就注入进来,如果都不存在则抛出异常。
也可以使用@Qualifier(value=“dog1”)注解,明确的指定,要注入哪个id的bean
**也可以使用@Resource(name=“id”)指定注入给定id的bean,但是这种方式不建议大家使用
5.其他注解
a.@Scope(value=“prototype”)
配置修饰的类的bean是单例还是多例,如果不配置默认为单例
案例:
package cn.tedu.domain;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class Teacher {
}
b.@Lazy
配置修饰的类的bean采用懒加载机制
案例:
package cn.tedu.domain;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Lazy
public class Teacher {
public Teacher() {
System.out.println("teacher construct..");
} }
c.@PostConstruct
在bean对应的类中 修饰某个方法 将该方法声明为初始化方法,对象创建之后立即执行。
d.@PreDestroy
在bean对应的类中 修饰某个方法 将该方法声明为销毁的方法,对象销毁之前调用的方法。
案例:
package cn.tedu.beans;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Dog {
public Dog() {
System.out.println("Dog...被创建出来了...");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Dog的初始化方法。。。");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destory(){
System.out.println("Dog的销毁方法。。。");
} }
e.@Controller @Service @Repository @Component
这四个注解的功能是完全相同的,都是用来修饰类,将类声明为Spring管理的bean的。
其中@Component一般认为是通用的注解
而@Controller用在软件分层中的控制层,一般用在web层 而@Service用在软件分层中的业务访问层,一般用在service层 而@Repository用在软件分层中的数据访问层,一般用在dao层。