Spring框架是在项目中常用的一种。
Spring里面有两大核心,一个是IOC(控制反转),一个是AOP(面向切面编程)。
一:Spring由什么组成。
1.IOC是一种思想,IOC用两个词概括,一个是控制,一个是反转。
控制谁?控制什么?
在传统的JAVASE中,我们通过new对象进行对象的创建,是主动创建依赖对象。而Ioc是有自己的容器来控制创建这些对象,只要放在Ioc容器中,就不需要一个一个的去new创建对象了。
反转:
过去我们主动的new对象,这个属于正转,现在我们通过容器给依赖对象,对象被迫的接受,我们理解为反转。
有了这些关系,Ioc可以给程序解耦,耦合性降低,不至于牵一发动全身。
2.Aop也是一种思想,是一种面向切面编程的思想。
举一个例子,有很对人想要租房子住,有很多人想要把房子租出去,他们相互沟通比较麻烦,这个时候就会有一个房屋中介,房东把房子交给中介,需要房子的人来找中介,中介把两个的需求一匹配,给出最优方案。此处的中介就是属于aop的思想,对租户和房东遇见的共同问题统一解决,面向他们的切面编程。
AOP的底层是代理模式,动态代理的底层是反射机制!
二。
使用Spring框架之前,需要导入一些东西。
导入Spring依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.3.9</version>
</dependency>
在src的main目录下,创建一个resources目录,目录下,创建xml文件。xml文件中写入需要的依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
这样,Spirng就基本搭建结束。接下来,我们创建实体类,进行操作。
首先创建一个实体类,可以给实体类定义一个属性。
public class User {
private String name;
public User(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("name"+name);
}
}
通过xml注册。
通过Bean注册有很多种方法。
注册成功后,可以通过实体类中的方法,打印出来。
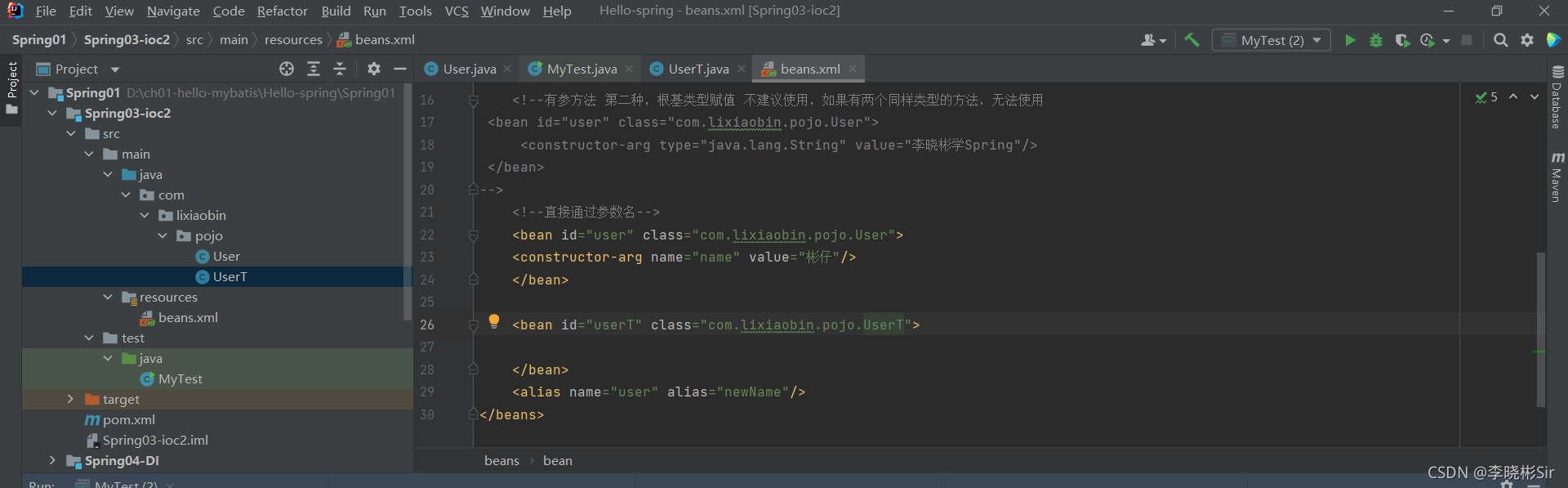
1. <!--无参构造方法 <bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User"> <property name="name" value="李晓彬"/> </bean> -->需要在实体类中创建无参构造。
此处的user是实体类的类型,规范用小写的。 class后面为这个实体类的路径。后面的方法都一样。
<!--有参方法 第一种,下标赋值 <bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="李晓彬学Java"/> </bean> -->若实实体类中有很多方法,可以通过下标进行赋值,实体类第一个属性的下标为0.
<!--有参方法 第二种,根基类型赋值 不建议使用,如果有两个同样类型的方法,无法使用 <bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User"> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="李晓彬学Spring"/> </bean> -->通过定义的属性类型赋值,如果两个属性一致,无法使用
<!--直接通过参数名--> <bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="彬仔"/> </bean>如果参数名一样,无法使用。
<alias name="user" alias="newName"/><alias 方法可以起别名。
实体类写好了,bean.xml注册完毕了,可以创建测试类测试了。
在src的test包下,创建测试类测试。
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
User user = (User) context.getBean("newName");
user.show();
}
}
此处的beans.xml是注册文件,通过
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("");获取beans.xml
context.getBean 获取文件中的对象。 此处的newName为user的别名。
注意:如果bean.xml文件中,注册了一个以上的类,先输入类中的无参方法。
?DI依赖注入
DI是基于Ioc的基础上实现的。Ioc是一种思想,DI是具体的操作。
给实体类一些属性,并且提供Set Get toString方法。
public class Student {
private String name;
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private String wife;
private Properties info;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String[] getBooks() {
return books;
}
public void setBooks(String[] books) {
this.books = books;
}
public List<String> getHobbys() {
return hobbys;
}
public void setHobbys(List<String> hobbys) {
this.hobbys = hobbys;
}
public Map<String, String> getCard() {
return card;
}
public void setCard(Map<String, String> card) {
this.card = card;
}
public Set<String> getGames() {
return games;
}
public void setGames(Set<String> games) {
this.games = games;
}
public String getWife() {
return wife;
}
public void setWife(String wife) {
this.wife = wife;
}
public Properties getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(Properties info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address.toString() +
", books=" + Arrays.toString(books) +
", hobbys=" + hobbys +
", card=" + card +
", games=" + games +
", wife='" + wife + '\'' +
", info=" + info +
'}';
}
}通过xml文件进行注入。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="哈尔滨"/>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.Student">
<!--第一种,普通值注入,直接使用value-->
<property name="name" value="李晓彬"/>
<!--第二种,Bean注入,使用ref注入 自己的理解(因为注入的是一个实体类)-->
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
<!--数组注入-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>三国演义</value>
<value>水浒传</value>
<value>西游记</value>
<value>红楼梦</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--List注入-->
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>学Java</value>
<value>学MyBatis</value>
<value>学Spring</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Map注入-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="身份证" value="123456"/>
<entry key="身份证" value="666666"/>
<entry key="身份证" value="19990522"/>
</map>
</property>
<!--Set注入-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>LoL</value>
<value>DNF</value>
<value>NBA2K</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--null注入-->
<property name="wife">
<null/>
</property>
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="学号">20181159</prop>
<prop key="性别">男</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
p命名空间注入和c命名空间注入。
使用时同样需要导入对应的约束。
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--P命名空间注入,可以直接注入属性的值。 property-->
<bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User" p:name="李晓彬" p:age="22"/>
<!--通过c命名注入,通过构造器constructs-args-->
<bean id="user2" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User" c:age="21" c:name="刘蕊"/>
</beans>注解
注解可以简化我们的开发。
使用注解的时候,我们需要在beans.xml文件中开启注解支持。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<!--开启注解支持-->
<!--扫描包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lixiaobin.pojo"/>
</beans>扫描需要使用注解的包
package com.lixiaobin.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component //等价于 <bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User"/>
public class User {
@Value("李晓彬")/*
相当于
<bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="李晓彬";
*/
public String name;
}
@Component 等价于不使用注解时候的 <bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User"/>。
帮助我们注册。
@Value 等价不使用注解时候的
<bean id="user" class="com.lixiaobin.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="李晓彬";
帮助我们赋值。
@Autowired注解??自动装配
不用在xml文件中配置Bean
Aop的底层是动态代理模式,动态代理模式的底层是反射机制!
浅谈动态代理:
场景:有房东要把房子出租,有人想要租房子,房东和租户互相找不到,通过中介完成交易!
首先创建一个接口,里面写租房子的方法
//租房的接口
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}
创建一个租户,实现接口
//房东
public class Host implements Rent {
public void rent(){
System.out.println("房东要出租房子");
}
}创建代理类,实现InvocationHandler接口。
public class Poxy implements InvocationHandler {
private Rent rent;
//被代理的接口
public void setRent(Rent rent) {
this.rent = rent;
}
//生成得到代理类
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), rent.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
}
//处理代理实例,并且返回结果
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//动态代理的本质就是反射机制的实现
Object invoke = method.invoke(rent, args);
return null;
}
}创建租户,实现类
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//真实角色
Host host=new Host();
//代理角色: 现在没有
Poxy pih = new Poxy();
//通过调用程序处理角色来处理我们要调用的接口对象
pih.setRent(host);
Rent proxy = (Rent) pih.getProxy();
proxy.rent();
}
}AOP:是一种思想,并不是某种操作就是aop。
第一种实现Aop的方式?使用原生态<Spring API>实现
创建一个接口,接口里面写上方法。
public interface UserService {
void add();
void delete();
void update();
void select();
}创建一个实体类,实现接口中的方法
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext Context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Context.xml");
//动态代理代理的是接口
UserService userService = (UserService) Context.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.add();
userService.delete();
userService.update();
userService.select();
}
}创建环绕(这个不是一定的,但是必须有类似的东西,如果没有,就不是面向三个类的切面编程了,就不能表达AOP的思想)
创建两个环绕,方法执行前环绕,方法执行后环绕
方法执行前环绕,要实现?MethodBeforeAdvice?接口并且实现接口的方法,这个是JAVA自带的接口!
前环绕
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
//method:要执行的目标对象方法
//objects:参数
//o:目标对象
public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(o.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"被执行了");
}
}方法中, method为要执行的目标对象方法,method.getName为要执行方法的名字。 objects为参数。 o代表目标对象,o.getClass().getName为目标对象的全路径类名。
后环绕
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
//o为返回值
public void afterReturning(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, Object o1) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行了"+method.getName()+"方法,返回值为"+o);
}
}在resources下创建xml。写上使用aop需要的约束
注册bean。注意:需要使用什么类,就注册什么Bean,不然容易报错,也是一种习惯。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.lixiaobin.log.AfterLog"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.lixiaobin.log.Log"/>
<!--使用原生态Spring API接口-->
<!--配置aop约束-->
<aop:config>
<!--切入点expression,表达式execution(* com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))
要执行哪个类,括号里面写哪个类的路径-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))" />
<!--执行环绕-->
<!--把log这个类切入到上面代码中(pointcut)-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>要在<aop:config>中写aop的语句
测试类
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext Context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Context.xml");
//动态代理代理的是接口
UserService userService = (UserService) Context.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.add();
userService.delete();
userService.update();
userService.select();
}
}这里要强调的是,动态代理代理的是接口,紫色! 但是,获取的是要输出的实体类,橙色!
运行结果:
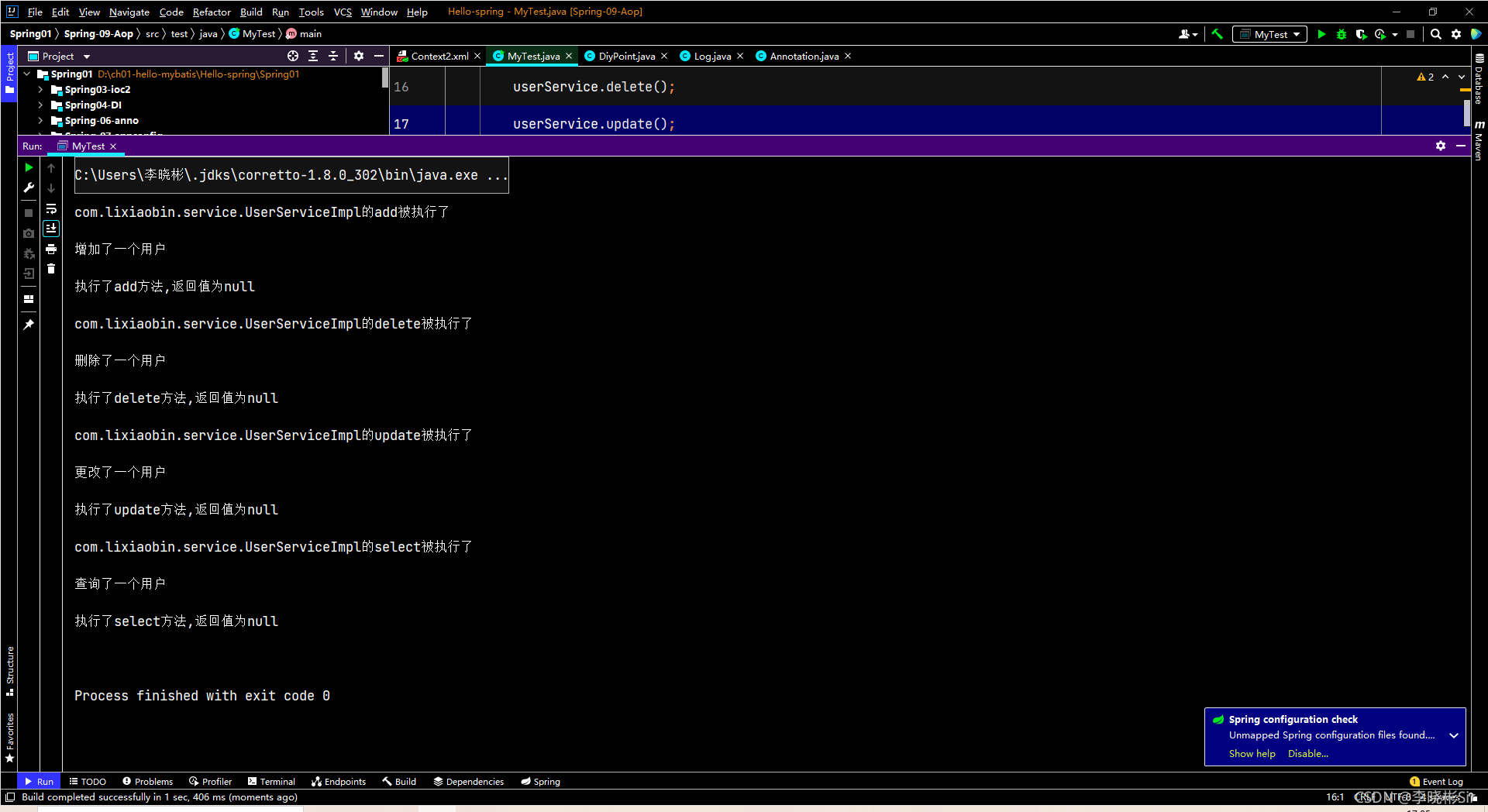
?
UserService userService = (UserService) Context.getBean("userServiceImpl");
第二种方式:
自己创建环绕类,不需要实现JAVA本身的MethodBeforeAdvice?接口
public class DiyPoint {
public void before(){
System.out.println("==========方法执行前");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("==========方法执行后");
}
}这次在xml文件中有所不同的是,把一个类当作切面。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.lixiaobin.log.AfterLog"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.lixiaobin.log.Log"/>
<!--方式二-->
<bean id="diy" class="com.lixiaobin.diy.DiyPoint"/>
<aop:config>
<!--aspect为切面,切入的是一个类-->
<aop:aspect ref="diy">
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--通知-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>运行结果:
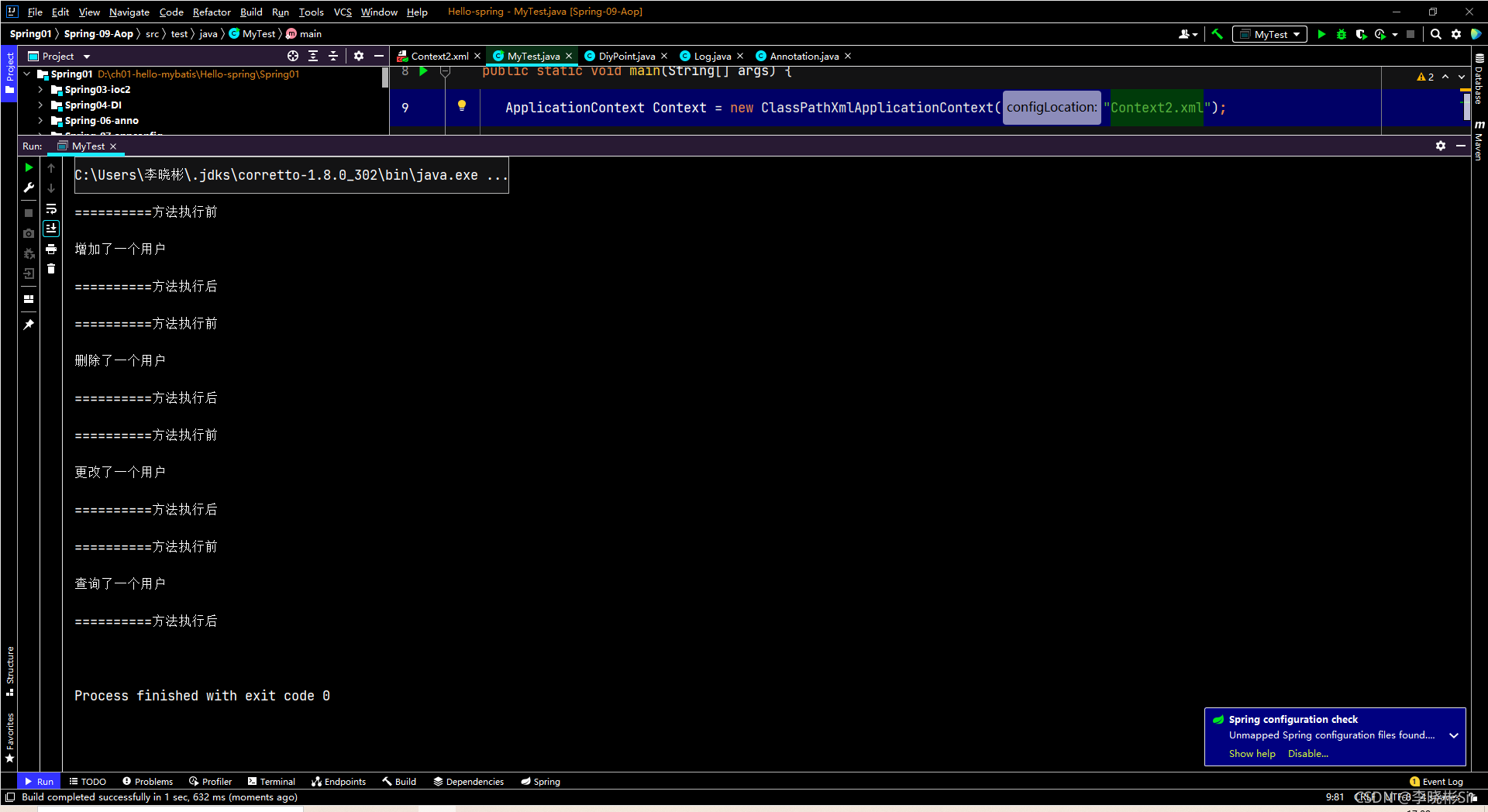
?
第三种方式,使用注解
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
//方式三 使用注解 实现aop
@Aspect //标注这个类是一个切面
public class Annotation {
@Before("execution(* com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("=============方法执行前");
}
@After("execution(* com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("=============方法执行后");
}
}这里要注意,Before和After都是 org.aspectj.lang.annotation包下的!
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="annotation" class="com.lixiaobin.diy.Annotation"/>
<!--开启注解支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>在xml中,只需要注册两个类的Bean,开启注解支持就可以了!
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.lixiaobin.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="annotation" class="com.lixiaobin.diy.Annotation"/>
<!--开启注解支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>运行结果:
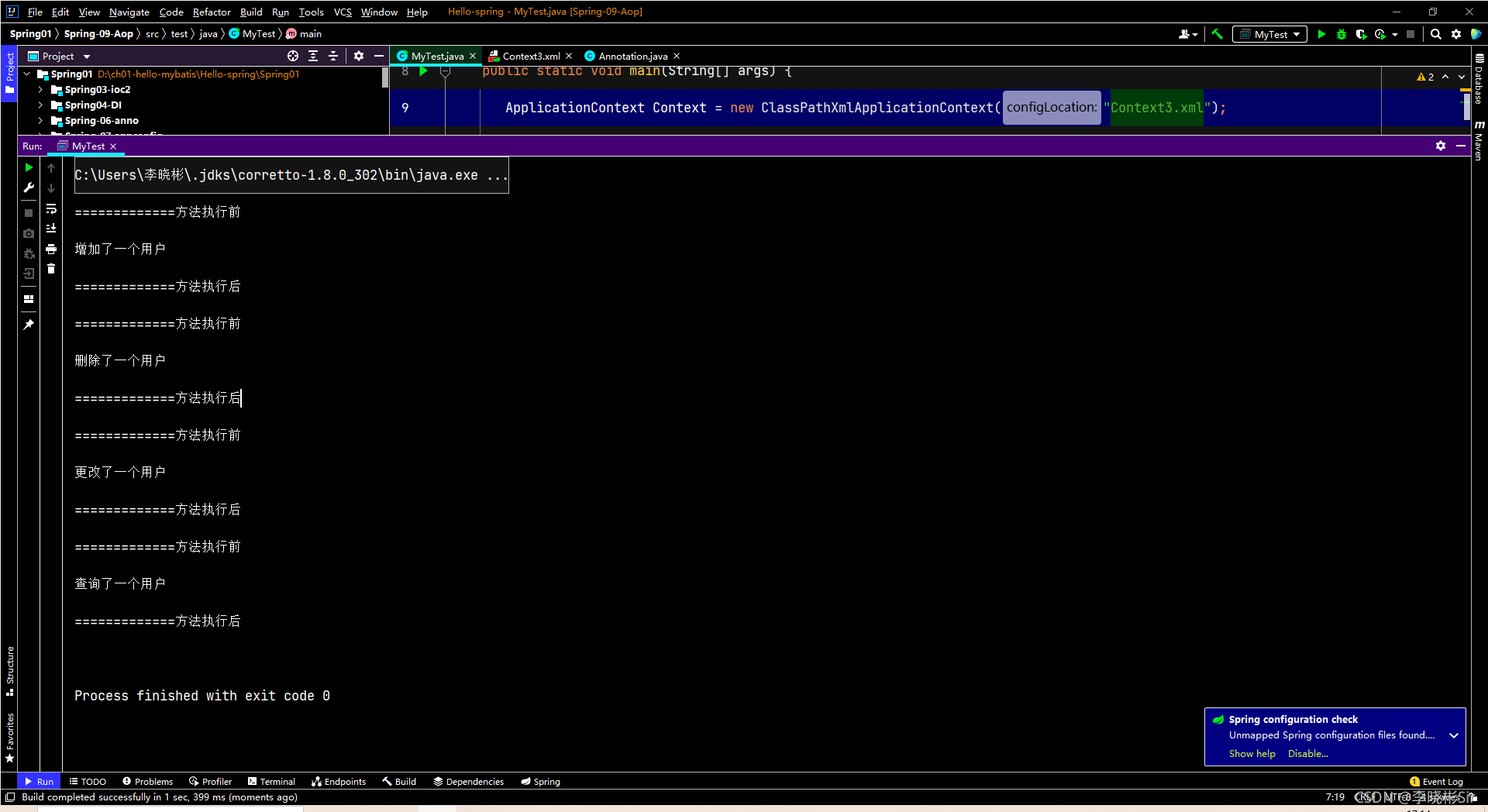
?
如有不对请大佬多多指证!
????????????????????????????????????????(此文仅供博主复习使用,若要系统学习请借鉴其他大神)