一、NIO 简介
java.nio 全称 java non-blocking IO,是指 JDK 提供的新 API。从 JDK1.4 开始,Java 提供了一系列改进的输入/输出的新特性,被统称为 NIO(即 New IO)。新增了许多用于处理输入输出的类,这些类都被放在 java.nio 包及子包下,并且对原 java.io 包中的很多类进行改写,新增了满足 NIO 的功能。

NIO 以块的方式处理数据,块 IO 的效率比流 IO 的效率高很多。
NIO 是非阻塞的,同时实现了 IO 多路复用。NIO 中用户线程不会被读写操作阻塞住,它可以继续干事情,所以 NIO 是可以做到用一个线程来处理多个操作的,使用它可以提供非阻塞的高伸缩性网络。

1、NIO 三大核心
NIO 主要有三大核心:Channel(通道)、Buffer(缓冲区)、Selector(选择器)。
NIO 是基于 Channel 和缓冲区进行操作的,
数据是从通道读取到缓冲区,或者是缓冲区写入到通道中。Selector(选择区)用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接请求、数据到达等),使用单个线程就可以监听到多个客户端通道。
(1)缓冲区 Buffer
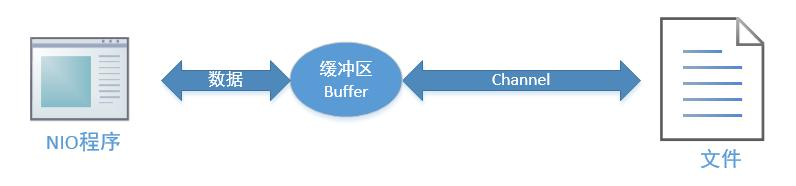
缓冲区就是用来存放具体要被操作和传输的数据。
缓冲区实际上是一个容器对象,更直接的说,其实就是一个数组,在 NIO 库中,所有数据都是用缓冲区处理的。在读取数据时,它是直接读到缓冲区中的; 在写入数据时,它也是写入到缓冲区中的;任何时候访问 NIO 中的数据,都是将它放到缓冲区中。Channel 提供从文件、网络读取数据的渠道,但是读取或写入的数据都必须经由 Buffer,如下图所示:
在 NIO 中,所有的缓冲区类型都继承于抽象类 Buffer,最常用的就是 ByteBuffer,对于 Java 中的基本类型,基本都有一个具体 Buffer 类型与之相对应,它们之间的继承关系如下图所示:
Buffer 的基本原理:缓冲区对象本质上是一个数组,但它其实是一个
特殊的数组,缓冲区对象内置了一些机制,能够跟踪和记录缓冲区的状态变化情况,如果使用 get()方法从缓冲区获取数据或者使用 put()方法把数据写入缓冲区,都会引起缓冲区状态的变化。 在缓冲区中,最重要的属性有下面三个,它们一起合作完成对缓冲区内部状态的变化跟踪:1)position:指定下一个将要被写入或者读取的元素索引,它的值由 get()/put()方法自动更新,在新创建一个 Buffer 对象时,position 被初始化为 0。
2)limit:指定还有多少数据需要取出(在从缓冲区写入通道时),或者还有多少空间可以放入数据(在从通道读入缓冲区时)。
3)capacity:指定了可以存储在缓冲区中的最大数据容量,实际上,它指定了底层数组的大小,或者至少是指定了准许我们使用的底层数组的容量。
以上三个属性值之间有一些相对大小的关系:0 <= position <= limit <= capacity。如果我们创建一个新的容量大小为20 的 ByteBuffer 对象,在初始化的时候,position 设置为 0,limit 和 capacity 被设置为 10,在以后使用 ByteBuffer对象过程中,capacity 的值不会再发生变化,而其它两个个将会随着使用而变化。
(2)通道 Channel
通道 Channel 就是数据传输用的通道,作用是打开到IO设备的连接、文件或套接字。
通道是一个对象,通过它可以读取和写入数据,当然了所有数据都通过 Buffer 对象来处理。不会将字节直接写入通道中,相反是将数据写入包含一个或者多个字节的缓冲区。同样不会直接从通道中读取字节,而是将数据从通道读入缓冲区,再从缓冲区获取这个字节。
在 NIO 中,提供了多种通道对象,而所有的通道对象都实现了 Channel 接口。
FileChannel、DatagramChannel 用于 UDP 的数据读写;
ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel 用于 TCP 的数据读写;
(3)Selector 选择器
能够检测多个注册的通道上是否有事件发生,如果有事件发生,便获取事件然后针对每个事件进行相应的处理。这样就可以
只用一个单线程去管理多个通道,也就是管理多个连接。这样使得只有在连接真正有读写事件发生时,才会调用函数来进行读写,就大大地减少了系统开销,并且不必为每个连接都创建一个线程,不用去维护多个线程,并且避免了多线程之间的上下文切换导致的开销。

NIO 中实现非阻塞 I/O 的核心对象就是 Selector,Selector 就是注册各种 I/O 事件的地方,而且当那些事件发生时,就是这个对象告诉我们所发生的事件,如下图所示:
从图中可以看出,当有读或写等任何注册的事件发生时,可以从 Selector 中获得相应的 SelectionKey,同时从 SelectionKey 中可以找到发生的事件和该事件所发生的具体的 SelectableChannel,以获得客户端发送过来的数据。
2、NIO 和 IO 的区别

面向目标不同
NIO 和传统 IO(一下简称IO)之间第一个最大的区别是,IO 是面向流的,NIO 是面向缓冲区的。
Java IO 面向流意味着每次从流中读一个或多个字节,直至读取所有字节,它们没有被缓存在任何地方。此外,它不能前后移动流中的数据。如果需要前后移动从流中读取的数据,需要先将它缓存到一个缓冲区。NIO 的缓冲导向方法略有不同。数据读取到一个它稍后处理的缓冲区,需要时可在缓冲区中前后移动。这就增加了处理过程中的灵活性。但是,NIO 还需要检查是否该缓冲区中包含所有您需要处理的数据。而且,需确保当更多的数据读入缓冲区时,不要覆盖缓冲区里尚未处理的数据。
阻塞/非阻塞
IO 的各种流是阻塞的。这意味着,当一个线程调用 read() 或 write() 时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取,或数据完全写入。该线程在此期间不能再干任何事情了。
NIO 是非阻塞模式,使一个线程从某通道发送请求读取数据,但是它仅能得到目前可用的数据,如果目前没有数据可用时,就什么都不会获取。而不是保持线程阻塞,所以直至数据变的可以读取之前,该线程可以继续做其他的事情。线程通常将非阻塞 IO 的空闲时间用于在其它通道上执行 IO 操作,所以一个单独的线程现在可以管理多个输入和输出通道。
二、NIO 的 API
1、Selector
Selector 可以同时监控多个 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况,是非阻塞 IO 的核心。
public abstract class Selector implements Closeable {
protected Selector() { }
// 创建 Selector 实例
public static Selector open() throws IOException {
return SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
}
public abstract boolean isOpen();
public abstract SelectorProvider provider();
// key set 代表了所有注册在这个 Selector 上的 channel ,这个集合可以通过 keys() 方法拿到。
public abstract Set<SelectionKey> keys();
// Selected-key set 代表了所有通过 select() 方法监测到可以进行 IO 操作的 channel ,这个集合可以通过 selectedKeys() 拿到。
public abstract Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys();
public abstract int selectNow() throws IOException;
// 可以设置超时的 select() 操作。
public abstract int select(long timeout) throws IOException;
// 监控所有注册的 channel ,当其中有注册的 IO 操作可以进行时,该函数返回,并将对应的 SelectionKey 加入 selected-key set 。
public abstract int select() throws IOException;
// 使一个还未返回的 select() 操作立刻返回。
public abstract Selector wakeup();
public abstract void close() throws IOException;
}
2、Buffer

Buffer 定义了一个可以线性存放 primitive type 数据的容器接口。 Buffer 主要包含了与类型( byte, char… )无关的功能。值得注意的是 Buffer 及其子类都不是线程安全的。
public abstract class Buffer {
static final int SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS =
Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED;
// Invariants: mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
private int mark = -1; // 一个临时存放的位置下标。调用 mark() 会将 mark 设为当前的 position 的值,以后调用 reset() 会将 position 属性设置为 mark 的值。 mark 的值总是小于等于 position 的值,如果将 position 的值设的比 mark 小,当前的 mark 值会被抛弃掉。
private int position = 0; // 读 / 写操作的当前下标。当使用 buffer 的相对位置进行读 / 写操作时,读 / 写会从这个下标进行,并在操作完成后, buffer 会更新下标的值。
private int limit; // 在 Buffer 上进行的读写操作都不能越过这个下标。当写数据到 buffer 中时, limit 一般和 capacity 相等,当读数据时, limit 代表 buffer 中有效数据的长度。
private int capacity; // 这个 Buffer 最多能放多少数据。 capacity 一般在 buffer 被创建的时候指定
long address;
Buffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap) { // package-private
if (cap < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative capacity: " + cap);
this.capacity = cap;
limit(lim);
position(pos);
if (mark >= 0) {
if (mark > pos)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("mark > position: ("
+ mark + " > " + pos + ")");
this.mark = mark;
}
}
public final int capacity() {
return capacity;
}
public final int position() {
return position;
}
public final Buffer position(int newPosition) {
if ((newPosition > limit) || (newPosition < 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
position = newPosition;
if (mark > position) mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final int limit() {
return limit;
}
public final Buffer limit(int newLimit) {
if ((newLimit > capacity) || (newLimit < 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
limit = newLimit;
if (position > limit) position = limit;
if (mark > limit) mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final Buffer mark() {
mark = position;
return this;
}
//
public final Buffer reset() {
int m = mark;
if (m < 0)
throw new InvalidMarkException();
position = m;
return this;
}
// 把 position 设为 0 ,把 limit 设为 capacity ,一般在把数据写入 Buffer 前调用。
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
// 把 limit 设为当前 position ,把 position 设为 0 ,一般在从 Buffer 读出数据前调用。
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
// 把 position 设为 0 , limit 不变,一般在把数据重写入 Buffer 前调用。
public final Buffer rewind() {
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final int remaining() {
return limit - position;
}
public final boolean hasRemaining() {
return position < limit;
}
// 用来判断一个 Buffer 是否只读
public abstract boolean isReadOnly();
public abstract boolean hasArray();
public abstract Object array();
public abstract int arrayOffset();
public abstract boolean isDirect();
final int nextGetIndex() { // package-private
if (position >= limit)
throw new BufferUnderflowException();
return position++;
}
final int nextGetIndex(int nb) { // package-private
if (limit - position < nb)
throw new BufferUnderflowException();
int p = position;
position += nb;
return p;
}
final int nextPutIndex() { // package-private
if (position >= limit)
throw new BufferOverflowException();
return position++;
}
final int nextPutIndex(int nb) { // package-private
if (limit - position < nb)
throw new BufferOverflowException();
int p = position;
position += nb;
return p;
}
final int checkIndex(int i) { // package-private
if ((i < 0) || (i >= limit))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return i;
}
final int checkIndex(int i, int nb) { // package-private
if ((i < 0) || (nb > limit - i))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
return i;
}
final int markValue() { // package-private
return mark;
}
final void truncate() { // package-private
mark = -1;
position = 0;
limit = 0;
capacity = 0;
}
final void discardMark() { // package-private
mark = -1;
}
static void checkBounds(int off, int len, int size) { // package-private
if ((off | len | (off + len) | (size - (off + len))) < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
Buffer子类(以下以ByteBuffer为例子)通用方法:
1)ByteBuffer(int N) :构造方法,设定缓冲区大小为N个byte大小的空间 ;
2)byte[] get():读取buffer中的所有数据;
3)void put(byte[]):数据写入buffer【功能和从channel中读取数据到buffer中一样】;
4)void filp():切换模式(写模式->读模式);
5)void rewind():重读buffer中的数据(position重置为0);
6)void clear():清空。重置所有指针,不删除数据!!(position=0,limit=capacity,重新供写入);
7)void compact():半清空,保留仍未读取的数据。(position=最后一个未读单元之后的位置,limit=cap,重新供写入);
8)mark():标记时刻A的当前pos【与reset()一起用】 reset():回到时刻A时标记的pos位置;
9)close():关闭并释放channel对象。;
3、Package java.nio.channels
Channel 是一个可以进行 IO 操作的通道(比如,通过 FileChannel ,我们可以对文件进行读写操作)。 java.nio.channels 包含了文件系统和网络通讯相关的 channel 类。这个包通过 Selector 和SelectableChannel 这两个类,还定义了一个进行非阻塞( non-blocking ) IO 操作的 API ,这对需要高性能 IO 的应用非常重要。
(1) java.nio.channels 中 interface 的关系:
1)Channel
Channel 表现了一个可以进行 IO 操作的通道,该 interface 定义了以下方法:
boolean isOpen() // 该 Channel 是否是打开的。 void close() // 关闭这个 Channel ,相关的资源会被释放。2)ReadableByteChannel
定义了一个可从中读取 byte 数据的 channel interface 。
int read(ByteBuffer dst) // 从 channel 中读取 byte 数据并写到 ByteBuffer 中。返回读取的 byte 数。3)WritableByteChannel
定义了一个可向其写 byte 数据的 channel interface 。
int write(ByteBuffer src) // 从 ByteBuffer 中读取 byte 数据并写到 channel 中。返回写出的 byte 数。4)ByteChannel
ByteChannel 并没有定义新的方法,它的作用只是把 ReadableByteChannel 和 WritableByteChannel 合并在一起。
5)ScatteringByteChannel
继承了 ReadableByteChannel 并提供了同时往几个 ByteBuffer 中写数据的能力。
6)GatheringByteChannel
继承了 WritableByteChannel 并提供了同时从几个 ByteBuffer 中读数据的能力。
7)InterruptibleChannel
用来表现一个可以被异步关闭的 Channel 。
(2)java.nio.channels 中类的关系:
1)非阻塞 IO 的支持可以算是 NIO API 中最重要的功能,非阻塞 IO 允许应用程序同时监控多个 channel 以提高性能,这一功能是通过 Selector , SelectableChannel 和 SelectionKey 这 3 个类来实现的。
2)SelectableChannel 抽象类是所有支持非阻塞 IO 操作的 channel (如 DatagramChannel 、 SocketChannel )的父类。 SelectableChannel 可以注册到一个或多个 Selector 上以进行非阻塞 IO 操作。
3) SelectableChannel 可以是 blocking 和 non-blocking 模式(所有 channel 创建的时候都是 blocking 模式),只有 non-blocking 的 SelectableChannel 才可以参与非阻塞 IO 操作。
4)Selector 这个类通过 select() 函数,给应用程序提供了一个可以同时监控多个IO channel 的方法。
5)Channel 的相关实现类:FileChannel、SocketChannel与ServerSocketChannel、DatagramChannel,分别对应:“文件操作通道”、“TCP通信操作通道”、“UDP通信操作通道”。这几个实现类中,除了 FileChannel 不能进入非阻塞状态,其他实现类都可以进入非阻塞状态。
(3)SelectableChannel 接口
public abstract class SelectableChannel extends AbstractInterruptibleChannel implements Channel
{
protected SelectableChannel() { }
public abstract SelectorProvider provider();
// 返回一个 bit mask ,表示这个 channel 上支持的 IO 操作。当前在 SelectionKey 中,用静态常量定义了 4 种 IO 操作的 bit 值: OP_ACCEPT , OP_CONNECT , OP_READ 和 OP_WRITE 。
public abstract int validOps();
// 该 channel 是否已注册在一个或多个 Selector 上
public abstract boolean isRegistered();
// 返回该 channe 在 Selector 上的注册关系所对应的 SelectionKey 。若无注册关系,返回 null 。
public abstract SelectionKey keyFor(Selector sel);
// 多出来的 att 参数会作为 attachment 被存放在返回的 SelectionKey 中,这在需要存放一些 session state 的时候非常有用。
public abstract SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att) throws ClosedChannelException;
// 将当前 channel 注册到一个 Selector 上并返回对应的 SelectionKey 。在这以后,通过调用 Selector 的 select() 函数就可以监控这个 channel 。 ops 这个参数是一个 bit mask ,代表了需要监控的 IO 操作。
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops) throws ClosedChannelException
{
return register(sel, ops, null);
}
// 设置 blocking 模式
public abstract SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block) throws IOException;
// 返回是否为 blocking 模式
public abstract boolean isBlocking();
public abstract Object blockingLock();
}
(4)Channel 通用方法:
int read(Buffer):将数据从 channel 读取到 buffer 中【读channel,写buffer】;
int read(Buffer[]):将数据从 channel 读取到 buffer 数组中;
int write(Buffer):将数据从 buffer 写入到 channel 中【读buffer,写channel】;
int write(Buffer[]):将数据从 buffer 数组写入到 channel 中;
三、NIO 示例
1、TCP 通信 —— SocketChannel
使用 NIO 开发一个入门案例,实现服务器端和客户端之间的数据通信(非阻塞)。
(1)客户端
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//得到一个网络通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//设置非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//连接网络
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress("localhost",8081);
//判断是否连接
if(!socketChannel.connect(address)){
while(!socketChannel.finishConnect()){
System.out.println("没有服务端进行连接");
}
}
//要发送的内容
String str = "hello NIO 服务端!";
// 将要转发的字符串内容转换成 Byte 类型
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
//写入通道
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
System.in.read();
}
}
(2)服务端
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//得到通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//得到selector对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//设置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//设置端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8081));
//注册到selector对象上
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(true){
//监控客户端
if(selector.select(200)==0){
System.out.println("没有服务端连接");
continue;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//获取所有的监听对象
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
//连接客户端
if(selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
//得到通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1023));
}
//读取数据
if(selectionKey.isReadable()){
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) selectionKey.attachment();
socketChannel.read(buffer);
System.out.printf("客户端发来的数据:%s%n", new String(buffer.array()));
}
//删除防止重复发送
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
2、文件 IO —— FileChannel
(1)读文件
public static byte[] readBytes(String fileName) {
try {
///获取对应文件的FileChannel对象
RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = accessFile.getChannel();
/// 创建一个缓冲区(大小为48byte)
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
// 从文件向缓冲区写入数据
int bytesRead = fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
// 若读取到该通道数据的末尾,则返回-1
while (bytesRead != -1) {
System.out.println("Read " + bytesRead);
// 由向缓冲区写入数据转换成从缓冲区读取数据需要调用该方法
byteBuffer.flip();
///每次读取完之后,输出缓存中的内容
while (byteBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println((char) byteBuffer.get());
builder.append((char) byteBuffer.get());
}
// 然后清空缓存区
byteBuffer.clear();
// 重新再读数据到缓存区中
bytesRead = fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
}
accessFile.close();
return builder.toString().getBytes();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
(2)写文件
public static void writeBytes(String fileName, byte[] data) {
try {
RandomAccessFile accessFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "rw");
FileChannel channel = accessFile.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
buffer.put(data);
channel.write(buffer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
(3)通道间内容传输
/**
* channel 间的传输
*
* @param sFileName 源文件
* @param dFileName 目标文件
*/
public static void channelToChannel(String sFileName, String dFileName) {
try {
RandomAccessFile sAccess = new RandomAccessFile(sFileName, "rw");
RandomAccessFile dAccess = new RandomAccessFile(dFileName, "rw");
FileChannel sChannel = sAccess.getChannel();
FileChannel dChannel = dAccess.getChannel();
long pos = 0;
long sCount = sChannel.size();
long dCount = dChannel.size();
// dChannel.transferFrom(sChannel,pos,sCount);//dChannel 必须是FileChannel
sChannel.transferTo(pos, dCount, dChannel);///sChannel 是FileChannel
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3、UDP通信 —— DatagramChannel
/**
* 关于:DatagramChannel
* UDP 无连接网络协议
* 发送和接收的是数据包
*/
public static void datagramChannel() {
DatagramChannel datagramChannel = null;
try {
///打开
datagramChannel = DatagramChannel.open();
///连接并开始监听UDP 9999端口
datagramChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
// 接收数据包(receive()方法会将接收到的数据包内容复制到指定的Buffer. 如果Buffer容不下收到的数据,多出的数据将被丢弃。 )
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
buf.clear();
datagramChannel.receive(buf);
// 发送数据 send()
String sendMsg = "要发送的数据";
ByteBuffer sendBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
sendBuf.clear();
sendBuf.put(sendMsg.getBytes());
sendBuf.flip();
datagramChannel.send(sendBuf,new InetSocketAddress("xxxxx",80));
// TODO: 连接到特定的地址(锁住DatagramChannel ,让其只能从特定地址收发数据 因为UDP无连接,本身没有真正的连接产出)
datagramChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("jenkov.com", 80));
///连接后,也可以使用Channal 的read()和write()方法,就像在用传统的通道一样。只是在数据传送方面没有任何保证
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (datagramChannel != null)
try {
datagramChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4、NIO 管道(Pipe)
NIO Pipe,是两个线程之间的单向连接通道(读下图可知)

整体原理:ThreadA 中获取的数据通过 SinkChannel 传入(写入)管道,当 ThreadB 要读取 ThreadA 的数据,则通过管道的 SourceChannel 传出(读取)数据。
Pipe 类内部有两个成员属性,分别是:
Pipe.SinkChannel:数据入口通道
Pipe.SourceChannel:数据出口通道
/**
* 关于NIO管道(Pipe)
* 定义:2个线程之间的单向数据连接
*/
public static void aboutPipe(){
Pipe pipe=null;
try {
/// 打开管道
pipe = Pipe.open();
///TODO: 一、 向管道写入数据
/// 访问Pipe.sinkChannel,向Pipe写入数据
/// 首先,获取Pipe.sinkChannel
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();
/// 然后,调用write(),开始写入数据
String newData = "New String to write to file..." + System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
buf.clear();
buf.put(newData.getBytes());
buf.flip();
while(buf.hasRemaining()){
sinkChannel.write(buf);
}
// TODO: 二、读取管道中的数据
// 首先,获取Pipe.sourceChannel
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();
/// 读取数据到buffer
ByteBuffer buf2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
int bytesRead = sourceChannel.read(buf2);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}