SpringBoot集成Redisson步骤
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.6.5</version>
</dependency>
初始化客户端
@Bean
public RedissonClient redisson(){
// 单机模式
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.3.170:6379").setDatabase(0);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
Redisson实现分布式锁
```java
package com.wangcp.redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redisson;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
/**
* 模拟下单减库存的场景
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/duduct_stock")
public String deductStock(){
String lockKey = "product_001";
// 1.获取锁对象
RLock redissonLock = redisson.getLock(lockKey);
try{
// 2.加锁
redissonLock.lock(); // 等价于 setIfAbsent(lockKey,"wangcp",10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 从redis 中拿当前库存的值
int stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock"));
if(stock > 0){
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock",realStock + "");
System.out.println("扣减成功,剩余库存:" + realStock);
}else{
System.out.println("扣减失败,库存不足");
}
}finally {
// 3.释放锁
redissonLock.unlock();
}
return "end";
}
}
Redisson 分布式锁实现原理图
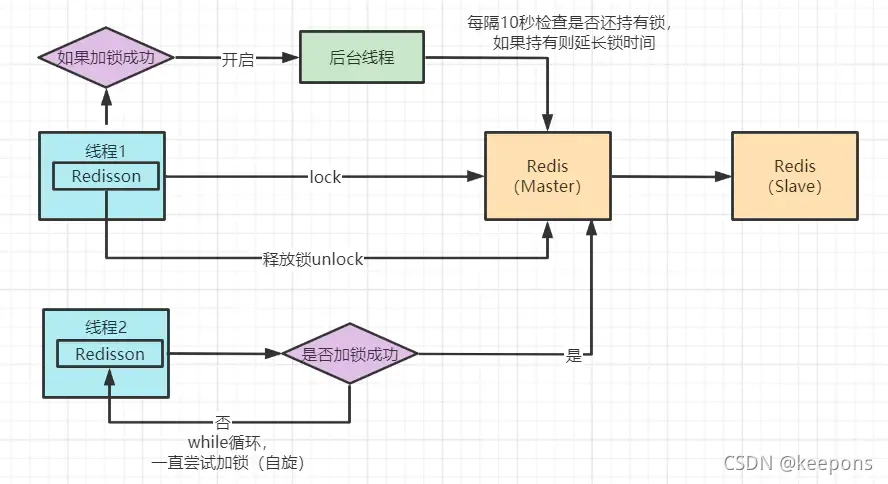
Redisson 底层源码分析
我们点击 lock() 方法,查看源码,最终看到以下代码
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
"redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
加锁最终执行的是下面这段 lua 脚本语言。
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then
redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return nil;
end;
脚本的主要逻辑为:
exists 判断 key 是否存在
当判断不存在则设置 key
然后给设置的key追加过期时间
这样来看其实和我们前面案例中的实现方法好像没什么区别,但实际上并不是。
这段lua脚本命令在Redis中执行时,会被当成一条命令来执行,能够保证原子性,故要不都成功,要不都失败。
我们在源码中看到Redssion的许多方法实现中很多都用到了lua脚本,这样能够极大的保证命令执行的原子性。
Redisson锁自动“续命”源码
private void scheduleExpirationRenewal(final long threadId) {
if (expirationRenewalMap.containsKey(getEntryName())) {
return;
}
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
RFuture<Boolean> future = commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
future.addListener(new FutureListener<Boolean>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Boolean> future) throws Exception {
expirationRenewalMap.remove(getEntryName());
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getName() + " expiration", future.cause());
return;
}
if (future.getNow()) {
// reschedule itself
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (expirationRenewalMap.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), task) != null) {
task.cancel();
}
}
这段代码是在加锁后开启一个守护线程进行监听。Redisson超时时间默认设置30s,线程每10s调用一次判断锁还是否存在,如果存在则延长锁的超时时间。