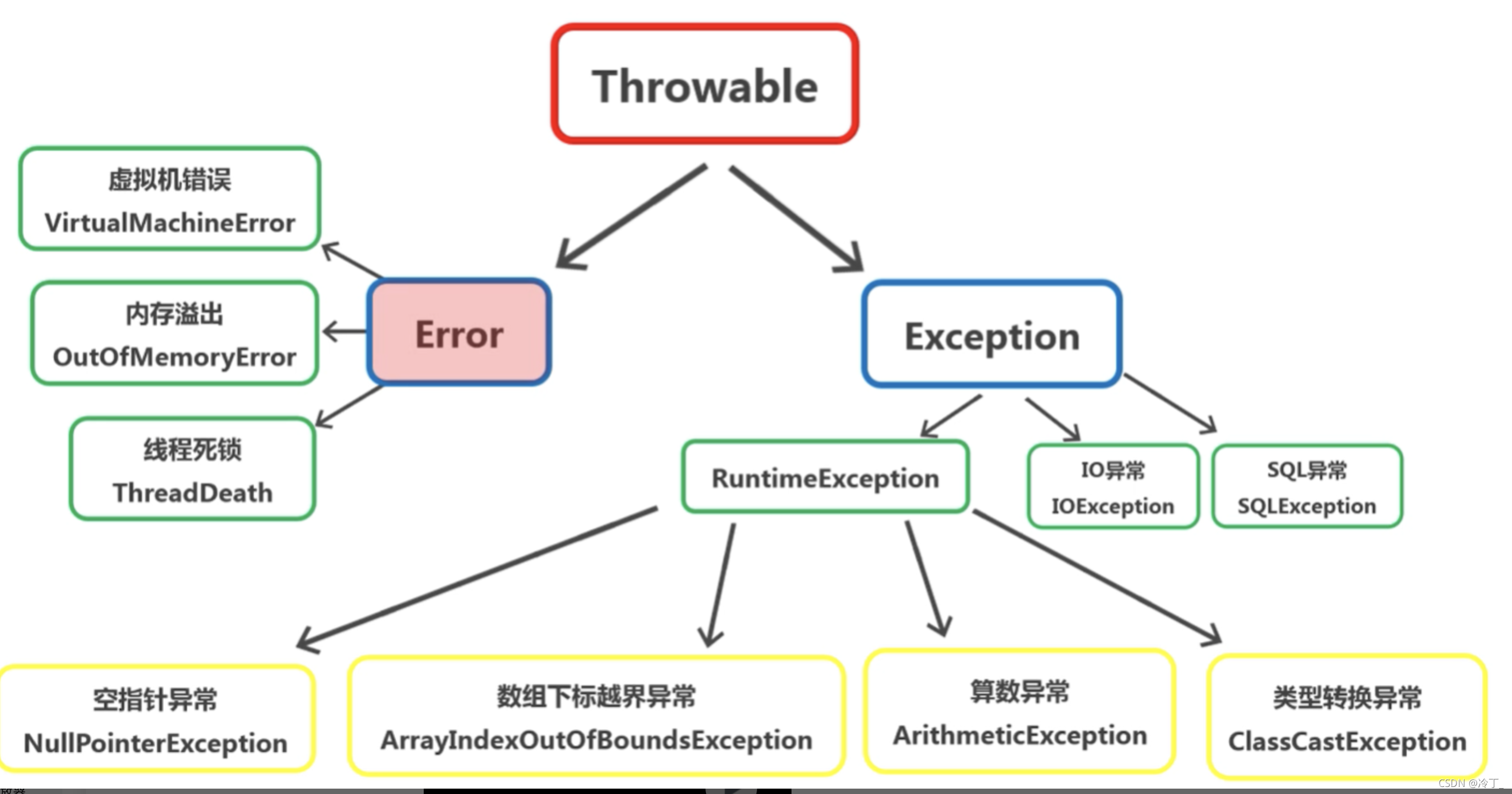
Error
Java中的错误是不能被处理的,由JVM(Java虚拟机)抛出
Exception
异常是可以被处理的
常见的错误和异常如下图
对于异常,必须要进行捕捉或声明抛出
-
捕获异常
try-执行可能产生异常的代码
catch-捕获异常
finally-无论是否发送异常代码总能执行
try… catch… 相当于自己处理了异常 -
声明异常
throws -声明可能要抛出的异常
throws会将异常直接抛给上层处理 -
throw
throw-生成一个异常类对象
throw相当于手动抛出异常
try…catch
测试1
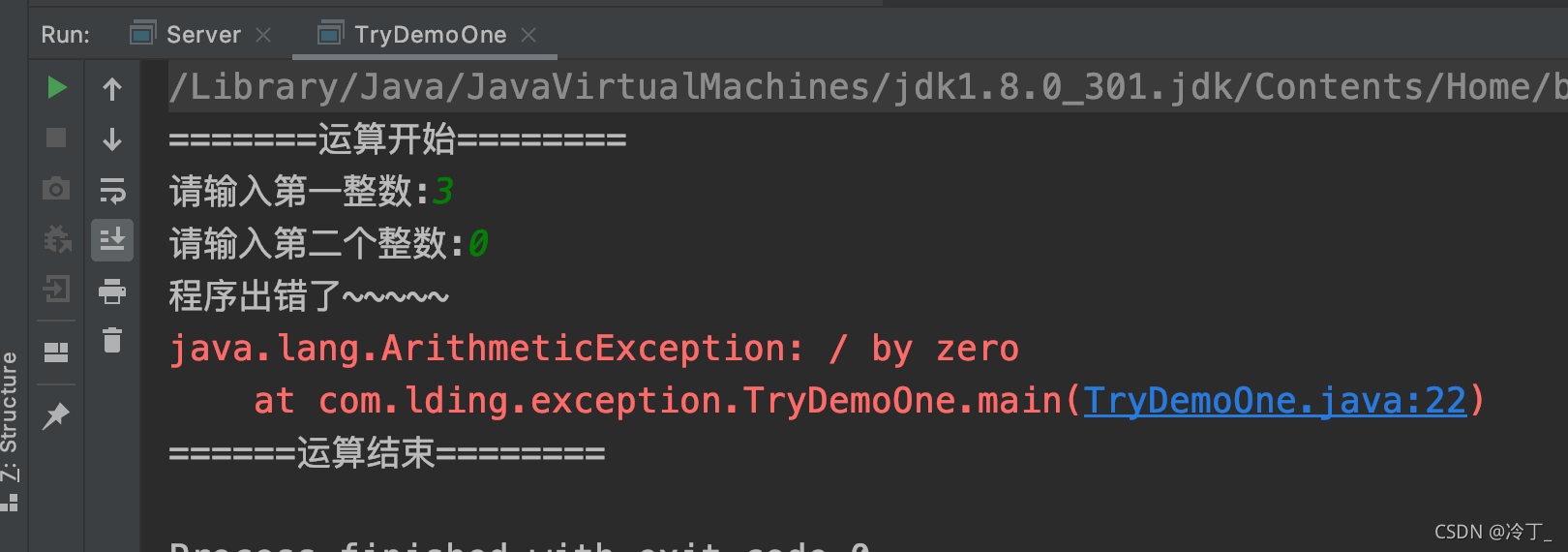
package com.lding.exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @program: Chat
* @description:
* @author: 王丁
* @date: 2021-09-28 10:49
**/
public class TryDemoOne {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//要求:定义两个整数,接受用户键盘输入,输出两数之商
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("=======运算开始========");
try { //包裹可能出错的代码
System.out.print("请输入第一整数:");
int one = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("请输入第二个整数:");
int two = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("one和two的商是:" + (one / two));
}catch (Exception e){//捕获异常
e.printStackTrace();//打印出错的位置
System.out.println("程序出错了~~~~~");//出错后执行的语句
}
finally {//无论是否出错都一定会执行的语句
System.out.println("======运算结束========");
}
}
}
运行结果
注意:当使用多重try…catch时要注意范围,大范围的(即父类)要后置
自定义异常类
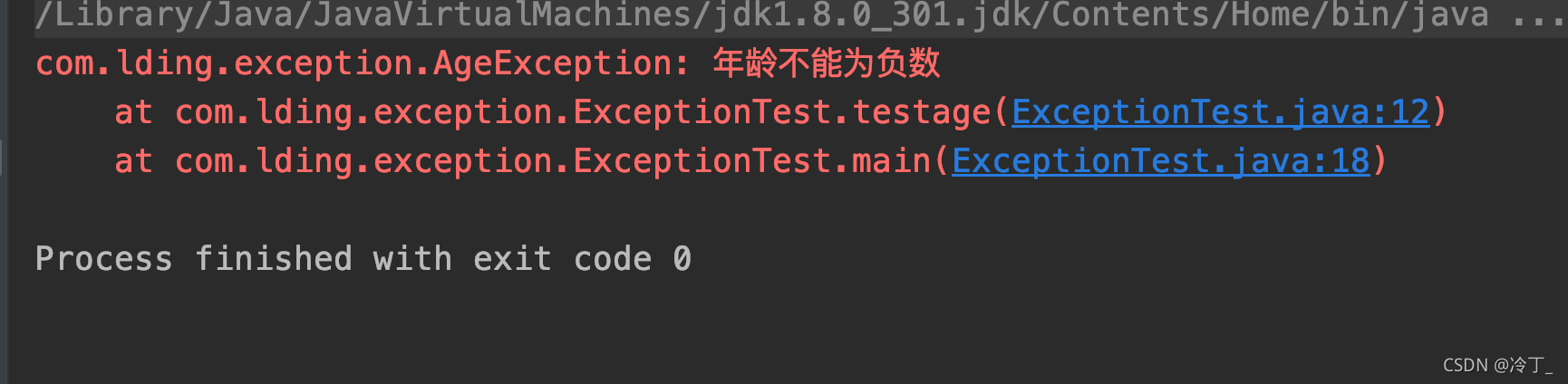
AgeException类 写一个类继承Exception
在里面写其构造方法,在构造方法中调用父类方法,传入字符串
package com.lding.exception;
/**
* @program: Chat
* @description:
* @author: 王丁
* @date: 2021-09-28 11:22
**/
public class AgeException extends Exception {
public AgeException(){
super("年龄不能为负数");
}
}
AgeTest测试类
package com.lding.exception;
/**
* @program: Chat
* @description:
* @author: 王丁
* @date: 2021-09-28 11:23
**/
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void testage(int age) throws AgeException {
if(age<0){
throw new AgeException();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age=-1;
try {
testage(age);
} catch (AgeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试结果