文章目录
前言
RabbitMQ 简介:RabbitMQ 基于 AMQP 标准,采用 Erlang 语言开发的消息中间件。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容
一、RabbitMQ 基础架构

- Producer:作为消息的生成者。
- Consumer:作为消息的消费者。
- Connection:消息的发布方或者消息的消费方 和broker 之间的 TCP 连接。
- Channel:Channel 是在 connection内部建立的逻辑连接,如果应用程序支持多线程,通常每个thread创建单独的 channel 进行通讯,AMQP method包含了channel id 帮助客户端和message broker 识别 channel,所以 channel之间是完全隔离的,减少了操作系统建立 TCP connection 的开销。
- Broker:接收和分发消息的应用,RabbitMQ服务就是Message Broker。
- Virtual host:虚拟机,出于多租户和安全因素设计的,把 AMQP的基本组件划分到一个虚拟的分组中,可以类比mysql数据库会创建很多库,库和库之间是独立的。当多个不同的用户使用同一个RabbitMQserver 提供的服务时,可以划分出多个vhost,每个用户在自己的 vhost 创建 exchange/queue 等。
- Queue:队列,消息队列,接收消息、缓存消息,消息最终被送到这里等待 consumer 取走。
- Binding:绑定,exchange 和 queue 之间的虚拟连接,binding 中可以包含 routing key。Binding 信息被保存到 exchange 中的查询表中,用于 message 的分发依据
- Exchange:交换机,message 到达 broker 的第一站,根据分发规则,匹配查询表中的 routing key,分发消息到queue 中去。
交换机常用的类型有:
Fanout:广播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列
Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key 的队列
Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式) 的队列
二、工作模式
一、6 种工作模式理论
RabbitMQ 提供了 6 种工作模式,简单模式、work queues、Publish/Subscribe
发布与订阅模式、Routing 路由模式、Topics 主题模式、RPC 远程调用模式(远程调用,不太算消息队列)
简单模式:一个生产者生产消息发送到队列里面,一个消费者从队列里面拿消息,进行消费消息。一个生产者、一个消费者,不需要设置交换机(使用默认的交换机)
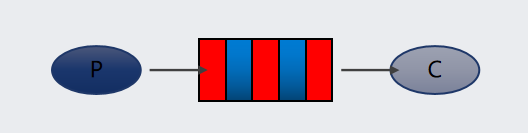
说明:类似一个邮箱,可以缓存消息;生产者向其中投递消息,消费者从其中取出消息。
Work queues 工作队列模式:一个生产者生产消息发送到队列里面,一个或者多个消费者从队列里面拿消息,进行消费消息。一个生产者、多个消费者(竞争关系),不需要设置交换机(使用默认的交换机)
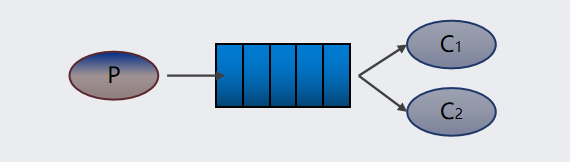
说明:对于任务过重或任务较多情况使用工作队列可以提高任务处理的速度。应用场景:过年过节12306抢票,发短信给用户,可以接入多个短信服务进行发送,提供任务的处理速度。
Pub/Sub 订阅模式 :一个生产者生产消息发送到交换机里面,由交换机处理消息,队列与交换机的任意绑定,将消息指派给某个队列,一个或者多个消费者从队列里面拿消息,进行消费消息。需要设置类型为 fanout 的交换机,并且交换机和队列进行绑定,当发送消息到交换机后,交换机会将消息发送到绑定的队列。
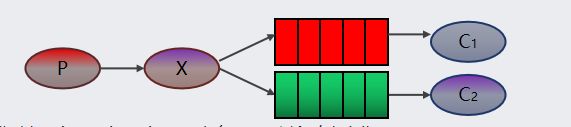
说明:Exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息,不具备存储消息的能力,因此如果没有任何队列与 Exchange 绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那么消息会丢失!
Routing 路由模式:一个生产者生产消息发送到交换机里面,并且指定一个路由key,队列与交换机的绑定是通过路由key进行绑定的,消费者在消费的时候需要根据路由key从交换机里面拿消息,进行消费消息。需要设置类型为 direct 的交换机,交换机和队列进行绑定,并且指定 routing key,当发送消息到交换机后,交换机会根据 routing key 将消息发送到对应的队列。
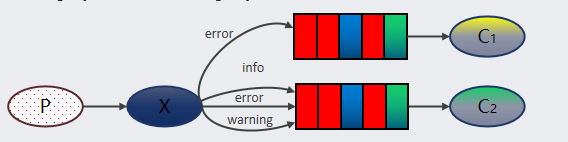
说明:Routing 模式要求队列在绑定交换机时要指定 routing key,消息会转发到符合 routing key 的队列。
Topics 通配符模式:一个生产者生产消息发送到交换机里面,并且使用通配符的形式(类似mysql里面的模糊查询,比如想获取一批带有item前缀的数据),队列与交换机的绑定是通过通配符进行绑定的,消费者在消费的时候需要根据根据通配符从交换机里面拿消息,进行消费消息。需要设置类型为 topic 的交换机,交换机和队列进行绑定,并且指定通配符方式的 routing key,当发送消息到交换机后,交换机会根据 routing key 将消息发送到对应的队列
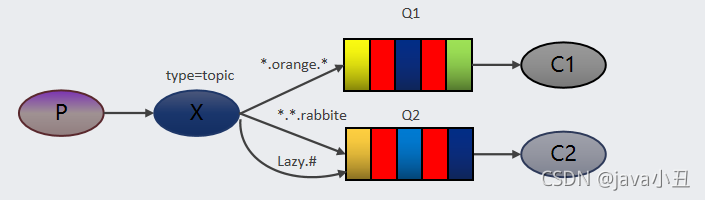 说明:通配符规则:# 匹配一个或多个词,* 匹配不多不少恰好1个词。例如:Lazy.# 能够匹配 Lazy.insert.content或者 Lazy.insert,Lazy.* 只能匹配Lazy.insert。
说明:通配符规则:# 匹配一个或多个词,* 匹配不多不少恰好1个词。例如:Lazy.# 能够匹配 Lazy.insert.content或者 Lazy.insert,Lazy.* 只能匹配Lazy.insert。
二、6 种工作模式的代码
一、6 种工作模式的Demo演示

创建一个Maven工程,引入pom依赖:
<dependencies>
<!--rabbitmq客户端-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--json转换工具包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建一个连接Rabbitmq的工具类:
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class RabbitUtils {
private static ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
static {
connectionFactory.setHost("你的rabbitmq的ip地址");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);//RabbitMQ的默认端口号,根据实际情况修改
connectionFactory.setUsername("你的rabbitmq的用户名称");
connectionFactory.setPassword("你的rabbitmq的用户密码");
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("你的rabbitmq的虚拟机");
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = connectionFactory.newConnection();
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
简单模式:
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
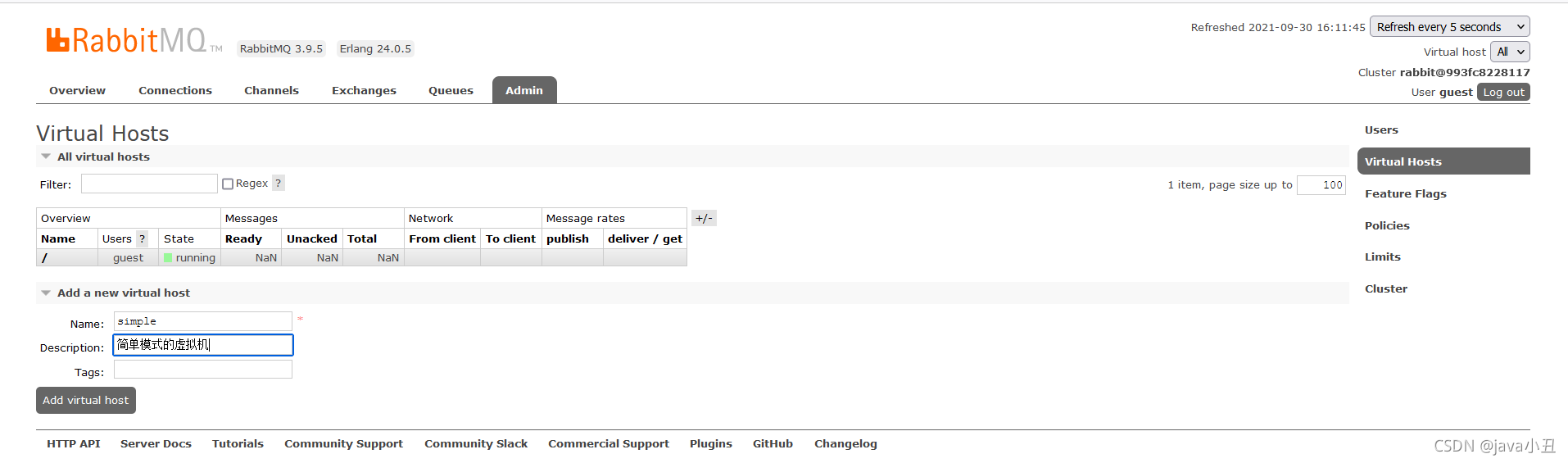
修改工具类的虚拟机:

生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取TCP长连接
Connection conn = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//创建通信“通道”,相当于TCP中的虚拟连接
Channel channel = conn.createChannel();
//创建队列,声明并创建一个队列,如果队列已存在,则使用这个队列
//channel.queueDeclare的五个参数
//第一个参数:队列名称ID
//第二个参数:是否持久化,false对应不持久化数据,MQ停掉数据就会丢失
//第三个参数:是否队列私有化,false则代表所有消费者都可以访问,true代表只有第一次拥有它的消费者才能一直使用,其他消费者不让访问
//第四个:是否自动删除,false代表连接停掉后不自动删除掉这个队列
//其他额外的参数, null
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TEST,false, false, false, null);
String message = "要发送的message";
//channel.basicPublish的四个参数
//exchange 交换机,暂时用不到,在后面进行发布订阅时才会用到
//队列名称
//额外的设置属性
//最后一个参数是要传递的消息字节数组
channel.basicPublish("", RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TEST, null,message.getBytes());
channel.close();
conn.close();
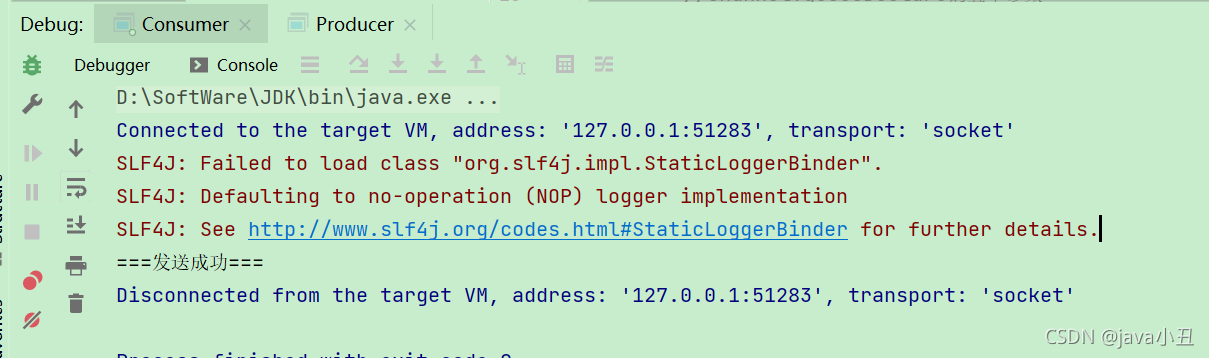
System.out.println("===发送成功===");
}
}
消费者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//获取TCP长连接
Connection conn = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//创建通信“通道”,相当于TCP中的虚拟连接
Channel channel = conn.createChannel();
//创建队列,声明并创建一个队列,如果队列已存在,则使用这个队列
//第一个参数:队列名称ID
//第二个参数:是否持久化,false对应不持久化数据,MQ停掉数据就会丢失
//第三个参数:是否队列私有化,false则代表所有消费者都可以访问,true代表只有第一次拥有它的消费者才能一直使用,其他消费者不让访问
//第四个:是否自动删除,false代表连接停掉后不自动删除掉这个队列
//其他额外的参数, null
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TEST,false, false, false, null);
//从MQ服务器中获取数据
//创建一个消息消费者
//第一个参数:队列名
//第二个参数代表是否自动确认收到消息,false代表手动编程来确认消息,这是MQ的推荐做法
//第三个参数要传入DefaultConsumer的实现类
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TEST, false, new Reciver(channel));
}
}
class Reciver extends DefaultConsumer {
private Channel channel;
//重写构造函数,Channel通道对象需要从外层传入,在handleDelivery中要用到
public Reciver(Channel channel) {
super(channel);
this.channel = channel;
}
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println("消费者接收到的消息:"+message);
System.out.println("消息的TagId:"+envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//false只确认签收当前的消息,设置为true的时候则代表签收该消费者所有未签收的消息
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
我先启动消费者后启动生产者,这样只要生产者一生产消息,消费者就可以立马消费。

Work queues 工作队列模式:
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
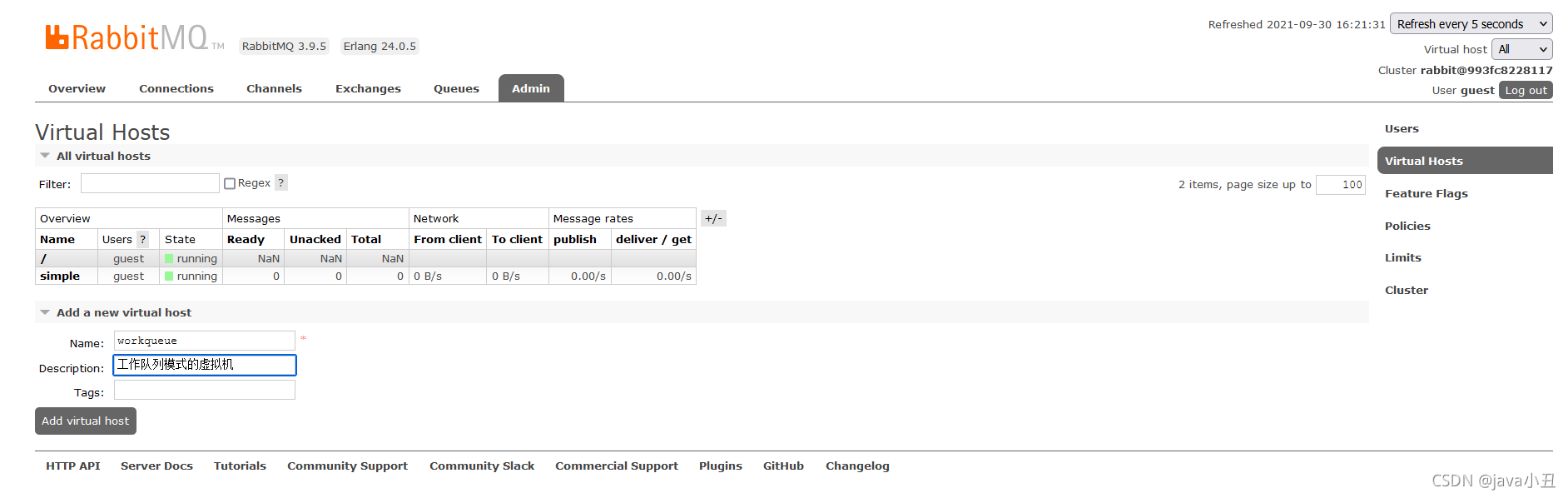 修改工具类的虚拟机
修改工具类的虚拟机

为了模拟某些业务,这里使用自定义实体类发送消息,所以我新建了一个自定义实体类
/**
* 自定义的实体类:发送内容
*/
public class SenderContent {
private String name;
private String content;
public SenderContent(String name, String content) {
this.name = name;
this.content = content;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
/**
* 生成者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT, false, false, false, null);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 100 ; i++) {
SenderContent senderContent = new SenderContent("姓名:" + i, "内容:" + i);
String jsonSMS = new Gson().toJson(senderContent);
channel.basicPublish("" , RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT , null , jsonSMS.getBytes());
}
System.out.println("发送数据成功");
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者一:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者1
*/
public class ConsumerOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT, false, false, false, null);
//如果不写basicQos(1),则自动MQ会将所有请求平均发送给所有消费者
//basicQos,MQ不再对消费者一次发送多个请求,而是消费者处理完一个消息后(确认后),在从队列中获取一个新的
channel.basicQos(1);//处理完一个取一个
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String jsonSMS = new String(body);
System.out.println("ConsumerOne-发送成功:" + jsonSMS);
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//确认签收
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者二:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者2
*/
public class ConsumerTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT, false, false, false, null);
//如果不写basicQos(1),则自动MQ会将所有请求平均发送给所有消费者
//basicQos,MQ不再对消费者一次发送多个请求,而是消费者处理完一个消息后(确认后),在从队列中获取一个新的
channel.basicQos(1);//处理完一个取一个
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String jsonSMS = new String(body);
System.out.println("ConsumerTwo-发送成功:" + jsonSMS);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//确认签收
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者三:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者3
*/
public class ConsumerThree {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT, false, false, false, null);
//如果不写basicQos(1),则自动MQ会将所有请求平均发送给所有消费者
//basicQos,MQ不再对消费者一次发送多个请求,而是消费者处理完一个消息后(确认后),在从队列中获取一个新的
channel.basicQos(1);//处理完一个取一个
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String jsonSMS = new String(body);
System.out.println("ConsumerThree-发送成功:" + jsonSMS);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//确认签收
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
这里对每个消费者设置不同的休眠时间演示每个消费者处理业务的时间不同,查看消息消费的情况
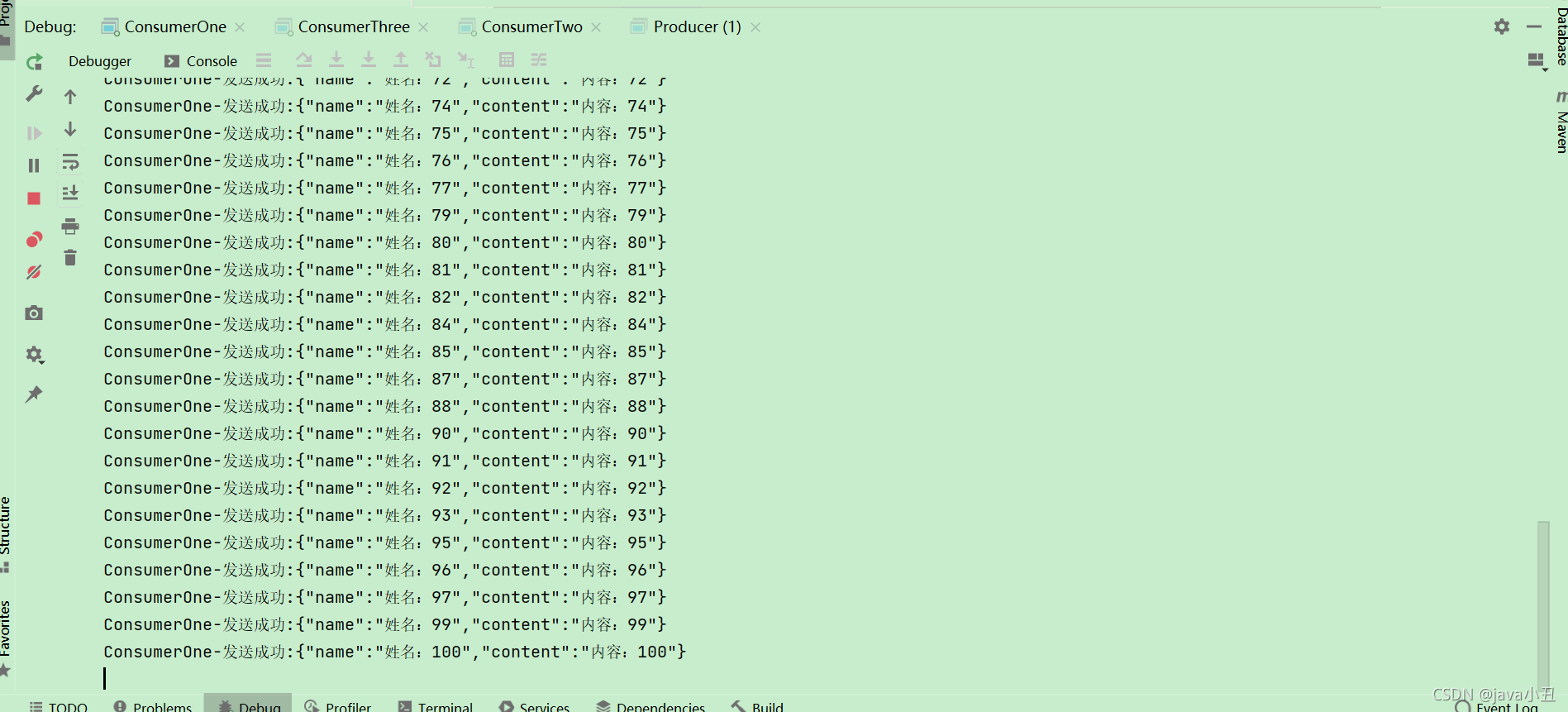
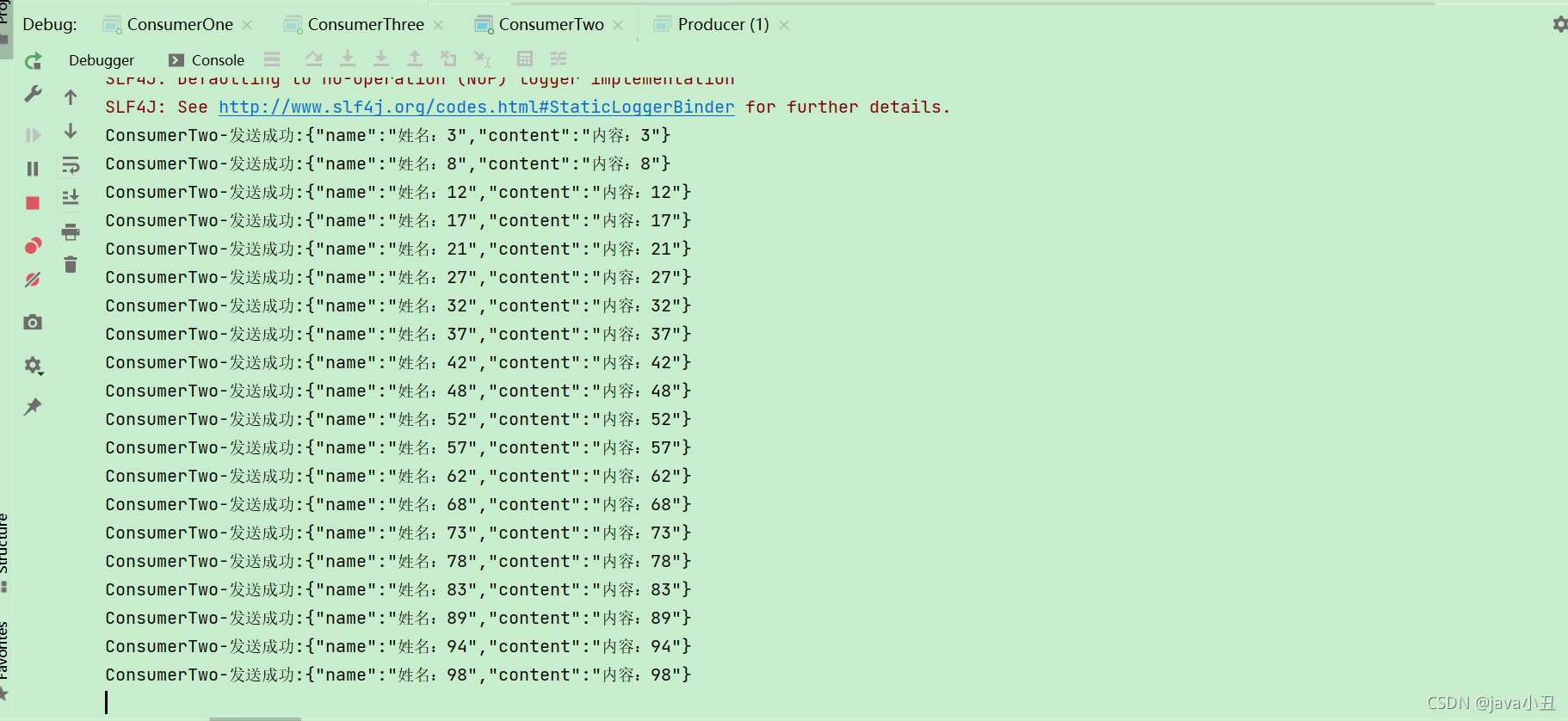
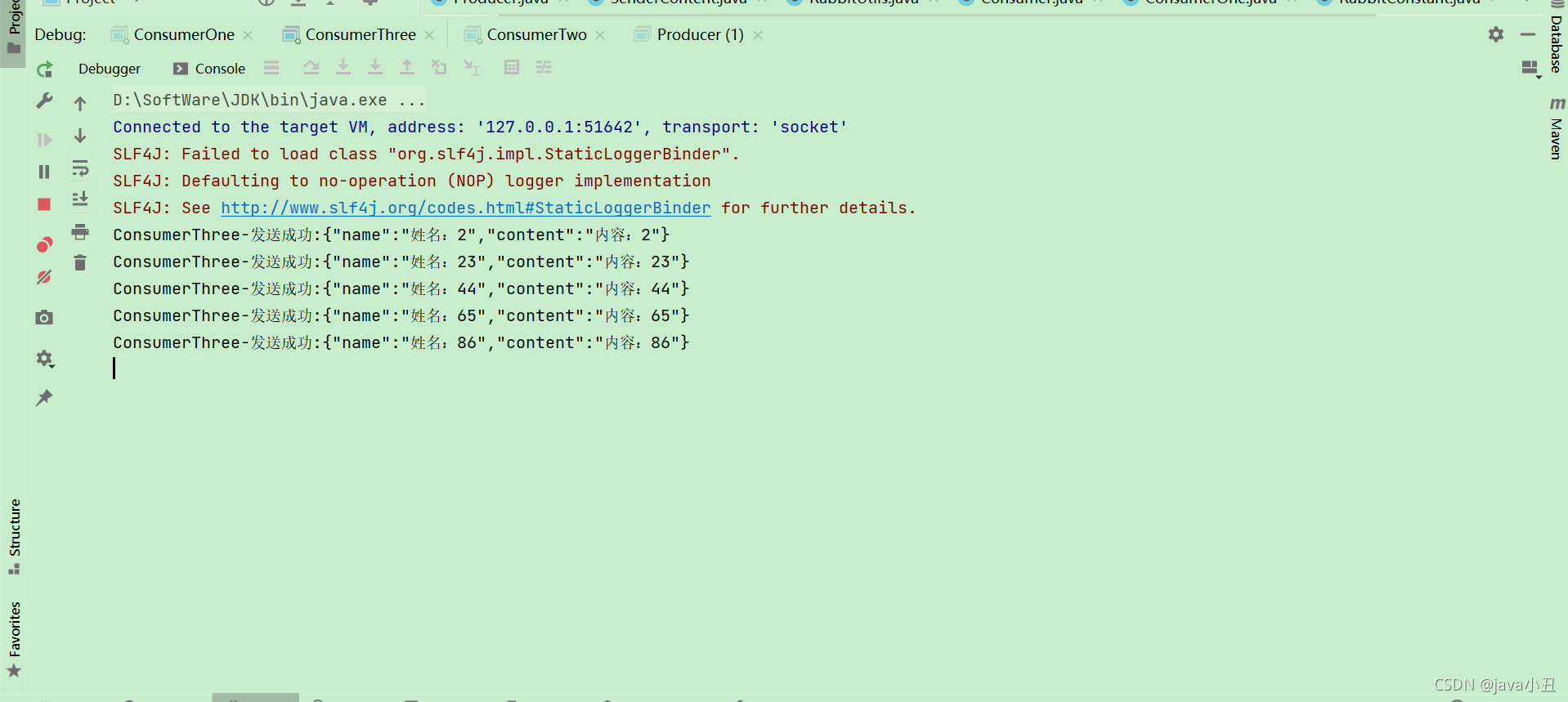
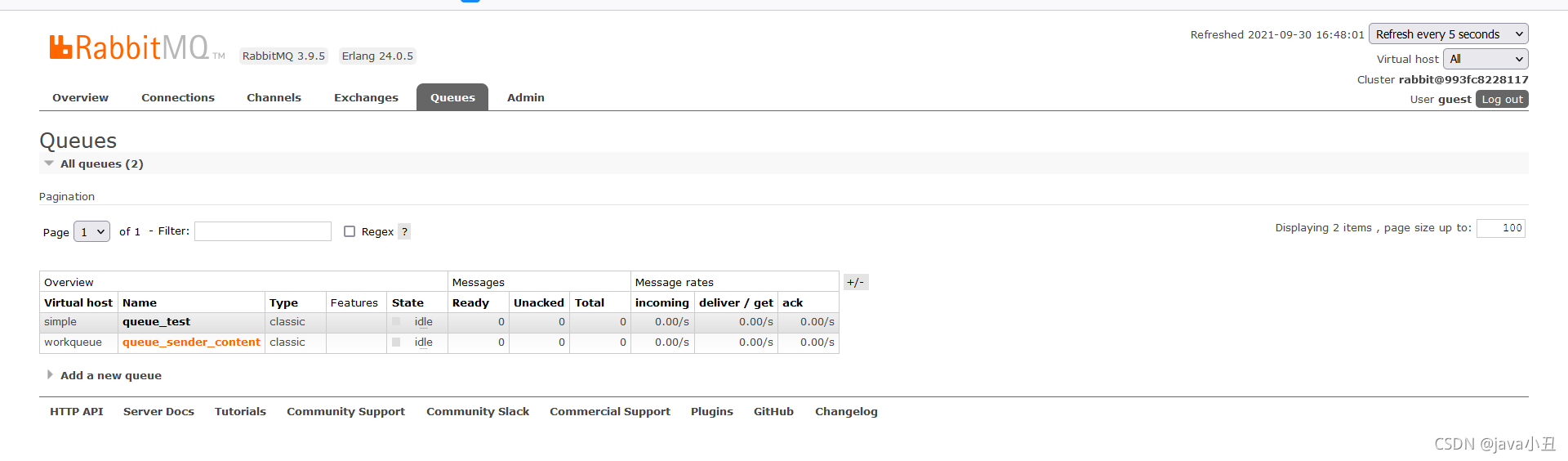
可以看出消费者一消费的最多,消费者三消费的最少,因为代码中设置了这个
channel.basicQos(1);//处理完一个取一个
消费者处理完一个消息后(确认后),在从队列中获取一个新的。
Pub/Sub 订阅模式 :
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
 创建一个交换机:这里用广播模式作为交换机的类型用来演示
创建一个交换机:这里用广播模式作为交换机的类型用来演示
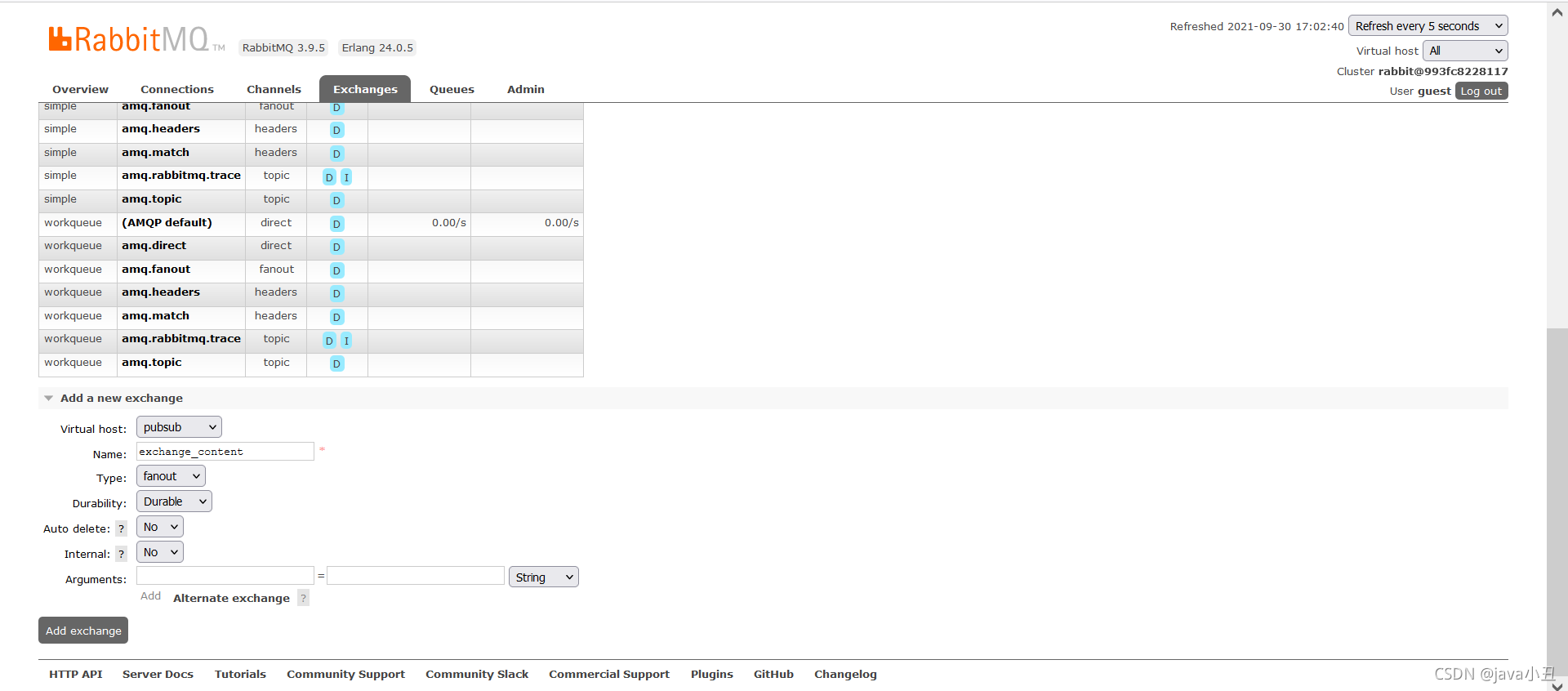
修改工具类的虚拟机

生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 发布者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//键盘输入
String input = new Scanner(System.in).next();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//第一个参数交换机名字 其他参数和之前的一样
channel.basicPublish(RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT,"" , null , input.getBytes());
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者一:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者1
*/
public class ConsumerOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取TCP长连接
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//获取虚拟连接
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列信息
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key(暂时用不到)
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT, "");
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者一收到信息:" + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者二:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者2
*/
public class ConsumerTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取TCP长连接
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//获取虚拟连接
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列信息
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key(暂时用不到)
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT, "");
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者二收到信息:" + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
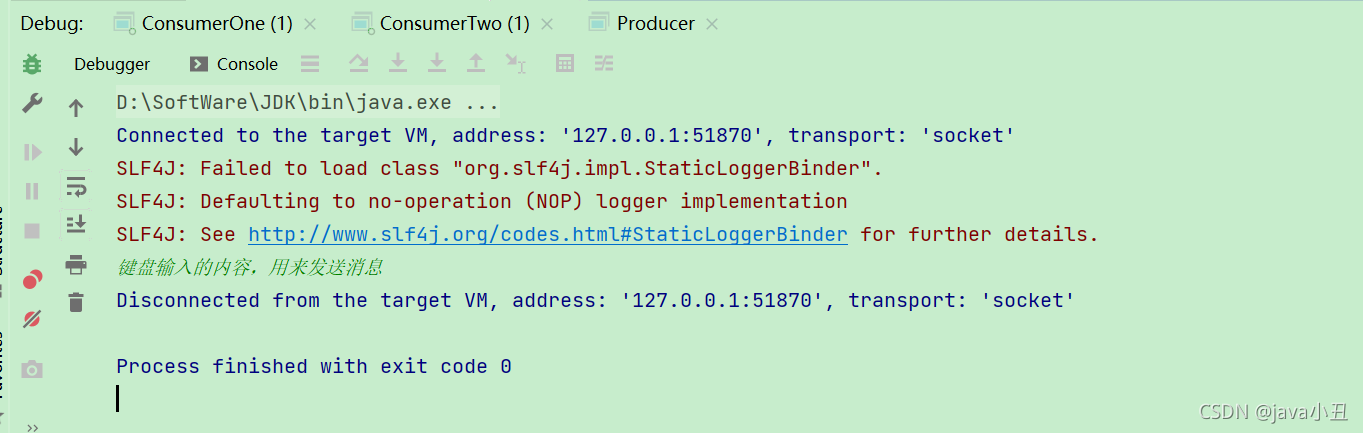
演示效果:

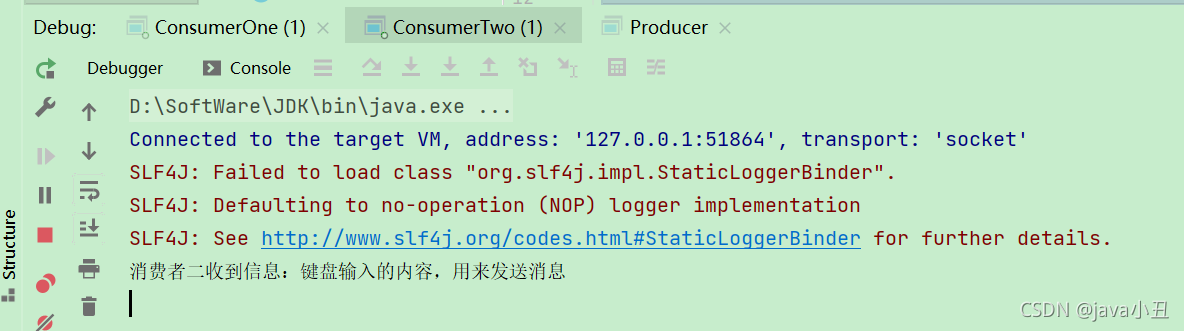
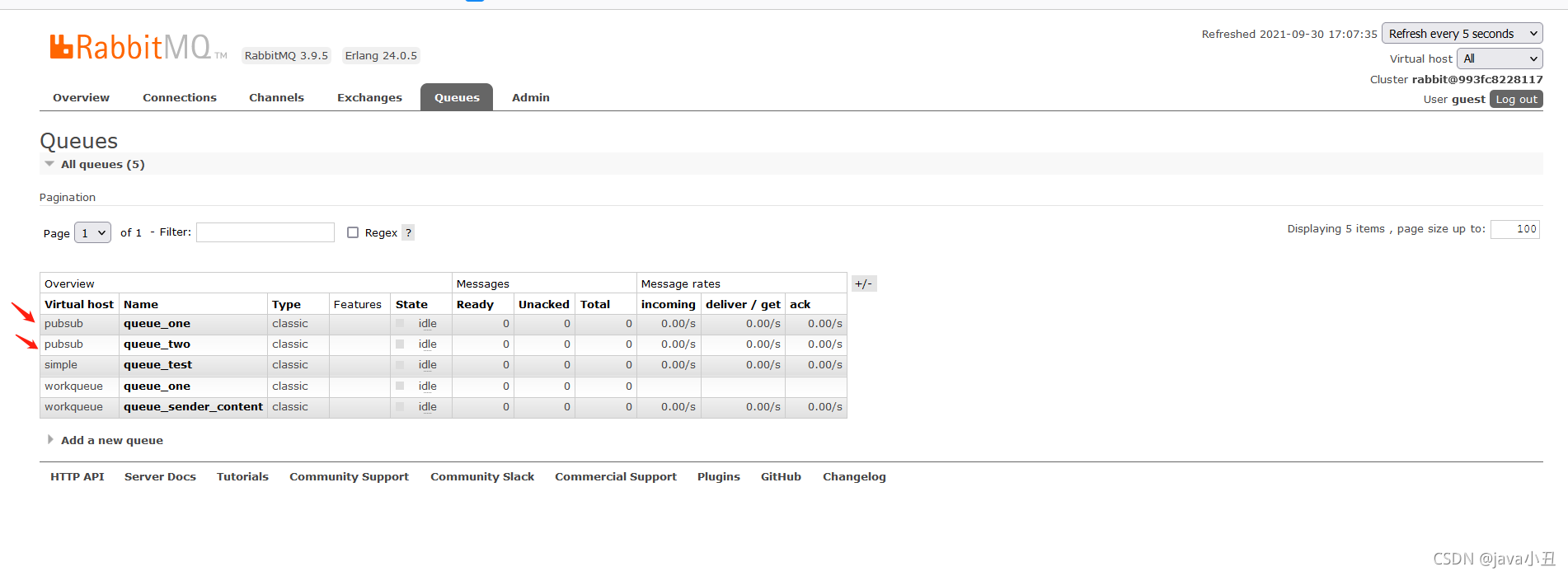
Routing 路由模式:
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
 修改工具类的虚拟机
修改工具类的虚拟机

创建交换机:这里的交换机type类型一定要改成routing模式,如果还是广播模式的fanout的话,跟上面发布和订阅模式出现的效果会是一样的。
错误实例:
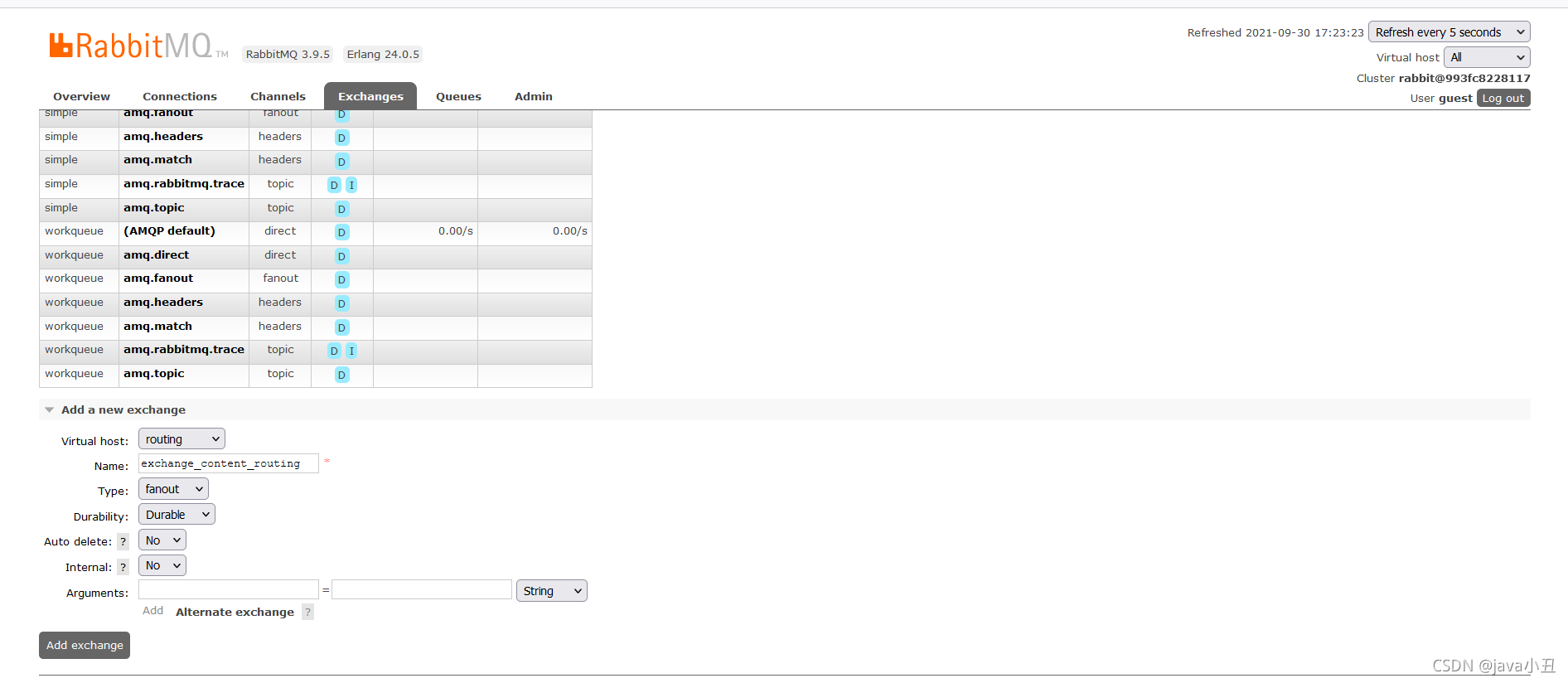 正确的实例:
正确的实例:
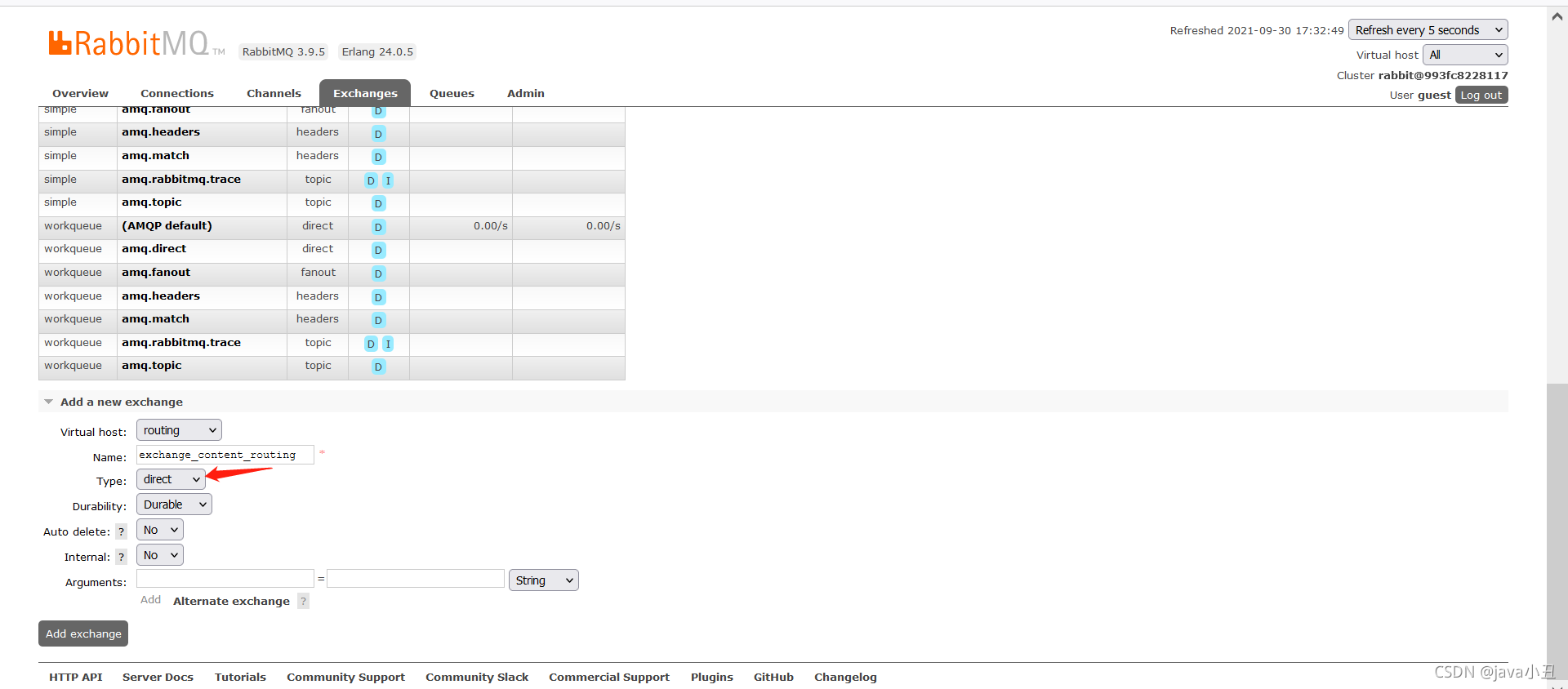 生产者:
生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 发布者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map area = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
area.put("routing.one.a.20201127", "中国湖南长沙20201127私密数据");
area.put("routing.one.d.20201128", "中国河北石家庄20201128私密数据");
area.put("routing.two.b.20201127", "中国湖北武汉20201127私密数据");
area.put("routing.two.e.20201128", "中国湖北武汉20201128私密数据");
area.put("routing.three.c.20201127", "中国湖南株洲20201128私密数据");
area.put("routing.three.f.20201128", "中国河南郑州20201128私密数据");
area.put("us.one.a.20201127", "美国加州洛杉矶20201127私密数据");
area.put("us.two.b.20201128", "美国加州洛杉矶20201128私密数据");
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> itr = area.entrySet().iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> me = itr.next();
//第一个参数交换机名字 第二个参数作为 消息的routing key
channel.basicPublish(RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING,me.getKey() , null , me.getValue().getBytes());
}
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者一:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者1
*/
public class ConsumerOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING, "routing.one.a.20201127");
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING, "us.one.a.20201127");
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1收到信息:" + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者二:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者2
*/
public class ConsumerTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING, "routing.one.d.20201128");
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING, "routing.two.e.20201128");
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2收到信息:" + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
效果:
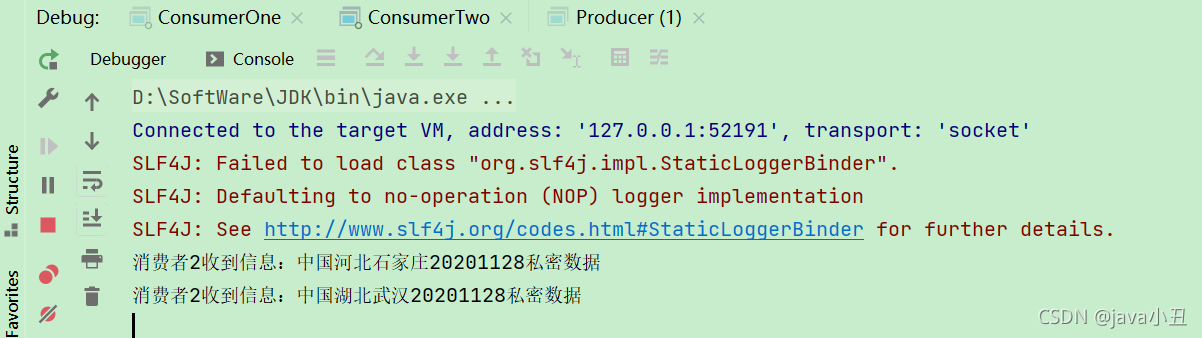
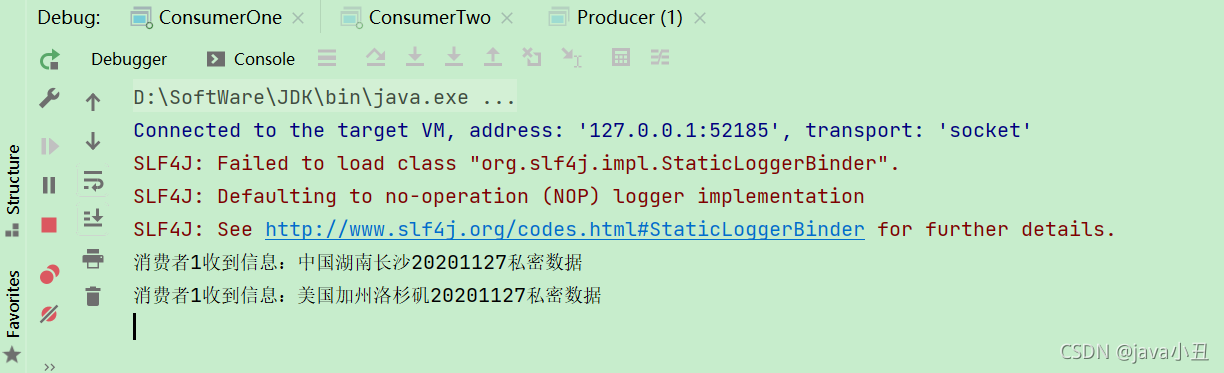
 路由模式需要消费者指定路由key
路由模式需要消费者指定路由key
Topics 通配符模式:
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
 修改工具类的虚拟机
修改工具类的虚拟机

创建交互机,类型为topic
 生产者:
生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 发布者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map area = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
area.put("routing.one.a.20201127", "中国湖南长沙20201127私密数据");
area.put("routing.one.d.20201128", "中国河北石家庄20201128私密数据");
area.put("routing.two.b.20201127", "中国湖北武汉20201127私密数据");
area.put("routing.two.e.20201128", "中国湖北武汉20201128私密数据");
area.put("routing.three.c.20201127", "中国湖南株洲20201128私密数据");
area.put("routing.three.f.20201128", "中国河南郑州20201128私密数据");
area.put("us.one.a.20201127", "美国加州洛杉矶20201127私密数据");
area.put("us.two.b.20201128", "美国加州洛杉矶20201128私密数据");
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> itr = area.entrySet().iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> me = itr.next();
//第一个参数交换机名字 第二个参数作为 消息的routing key
channel.basicPublish(RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_TOPIC,me.getKey() , null , me.getValue().getBytes());
}
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者一:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者1
*/
public class ConsumerOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_TOPIC, "*.*.*.20201127");
// channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_TOPIC, "us.two.b.20201128");
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1收到信息:" + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者二:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者2
*/
public class ConsumerTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取TCP长连接
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//获取虚拟连接
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列信息
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, false, false, false, null);
//指定队列与交换机以及routing key之间的关系
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_TOPIC, "us.#");
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2收到信息:" + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
效果:
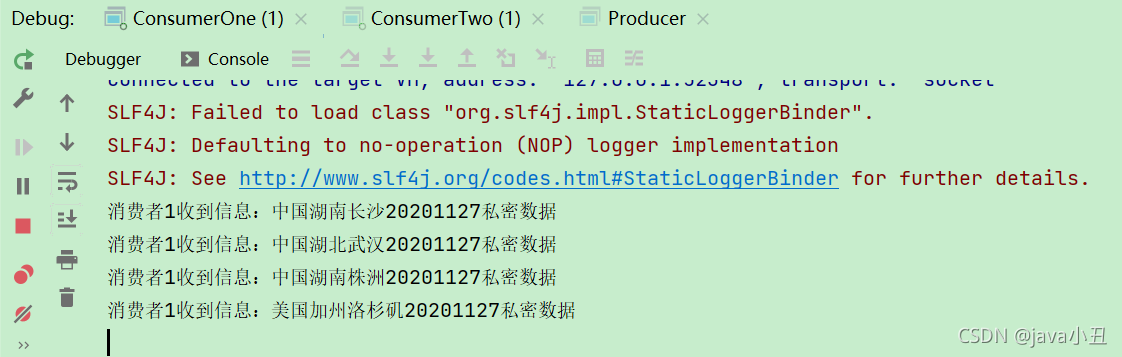
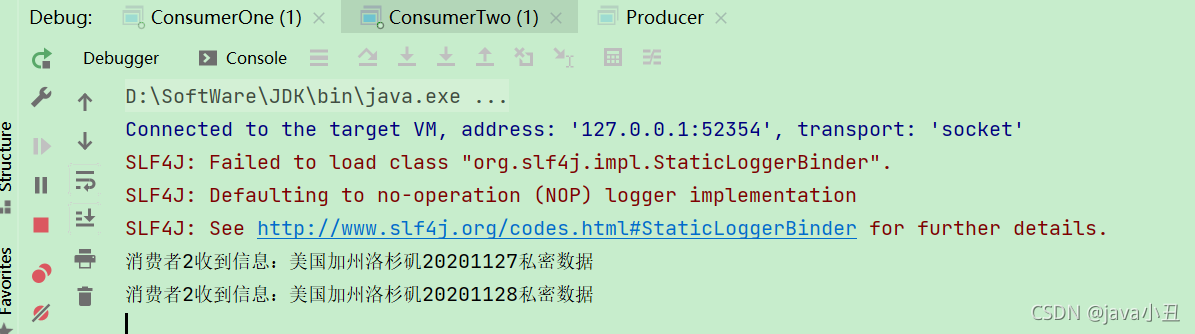
说明:如果想切换模式进行测试,只需要修改工具类中的虚拟机即可。前面的命名都是一样的,就是为了在这个时候体现出每个虚拟机都是隔离的,所以那么key是一样的也没关系。
二、消息确认机制:confirm状态和return状态
一、confirm状态和return状态理论
confirm状态:表示生产者将消息投递到Broker时产生的状态,会出现二种情况:
- ack:表示已经被Broker签收
- nack:表示表示已经被Broker拒收,原因可能有队列满了,限流,IO异常…
return状态:表示生产者将消息投递到Broker,被Broker签收,但是没有对应的队列进行投递,将消息回退给生产者的状态。
说明:这二种状态都只和生产者有关,于消费者没关系。
二、confirm状态和return状态代码
沿用之前的topic虚拟机,就不在创建新的虚拟机了
创建一个交换机:
 生产者:
生产者:
package com.liao.rabbitmq.confirm;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 发布者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map area = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
area.put("routing.one.a.20211001", "中国长沙20211001私密数据");
area.put("routing.two.b.20211001", "中国武汉20211001私密数据");
area.put("routing.three.c.20211001", "中国株洲20211001私密数据");
area.put("routing.one.d.20211002", "中国石家庄20211002私密数据");
area.put("routing.two.e.20211002", "中国武汉20211002私密数据");
area.put("routing.three.f.20211002", "中国郑州20211002私密数据");
area.put("routing.error.f.aaa", "未成功投递的私密数据");
area.put("us.one.a.20211001", "美国洛杉矶20211001私密数据");
area.put("us.two.b.20211002", "美国洛杉矶20211002私密数据");
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//开启confirm监听模式
channel.confirmSelect();
channel.addConfirmListener(new ConfirmListener() {
public void handleAck(long l, boolean b) throws IOException {
//第二个参数代表接收的数据是否为批量接收,一般我们用不到。
System.out.println("消息已被Broker接收,Tag:" + l );
}
public void handleNack(long l, boolean b) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消息已被Broker拒收,Tag:" + l);
}
});
channel.addReturnListener(new ReturnCallback() {
public void handle(Return r) {
System.err.println("===========================");
System.err.println("Return编码:" + r.getReplyCode() + "-Return描述:" + r.getReplyText());
System.err.println("交换机:" + r.getExchange() + "-路由key:" + r.getRoutingKey() );
System.err.println("Return主题:" + new String(r.getBody()));
System.err.println("===========================");
}
});
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> itr = area.entrySet().iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> me = itr.next();
//Routing key 第二个参数相当于数据筛选的条件
//第三个参数为:mandatory true代表如果消息无法正常投递则return回生产者,如果false,则直接将消息放弃。
channel.basicPublish(RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_TOPIC_CONFIRM,me.getKey() ,true, null , me.getValue().getBytes());
}
//如果关闭则无法进行监听,因此此处不需要关闭
/*channel.close();
connection.close();*/
}
}
消费者一:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者1
*/
public class ConsumerOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_TOPIC_CONFIRM, "*.*.*.20211001");
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者1收到信息:" + new String(body));
//channel.basicNack的三个参数
//第一个参数:long deliveryTag:唯一标识 ID。
//第二个参数:boolean multiple:是否批处理,当该参数为 true 时,则可以一次性确认 delivery_tag 小于等于传入值的所有消息。
//第三个参数:boolean requeue:如果 requeue 参数设置为 true,则 RabbitMQ 会重新将这条消息存入队列,以便发送给下一个订阅的消费者; 如果 requeue 参数设置为 false,则 RabbitMQ 立即会还把消息从队列中移除,而不会把它发送给新的消费者。
// channel.basicNack(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false,false);
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者二:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 消费者2
*/
public class ConsumerTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取TCP长连接
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//获取虚拟连接
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列信息
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, false, false, false, null);
//指定队列与交换机以及routing key之间的关系
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_TOPIC_CONFIRM, "us.#");
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("消费者2收到信息:" + new String(body));
// channel.basicNack(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false,false);
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
演示效果:
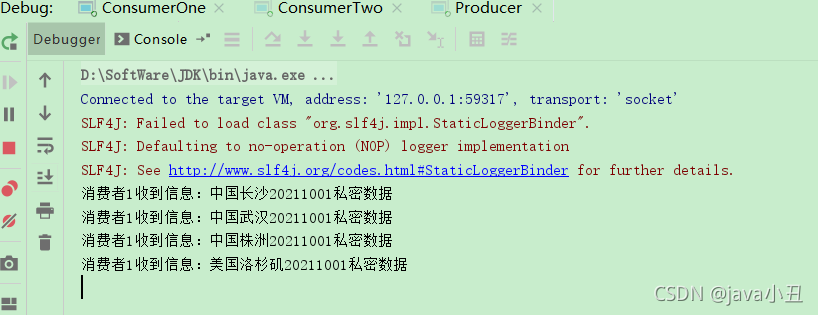
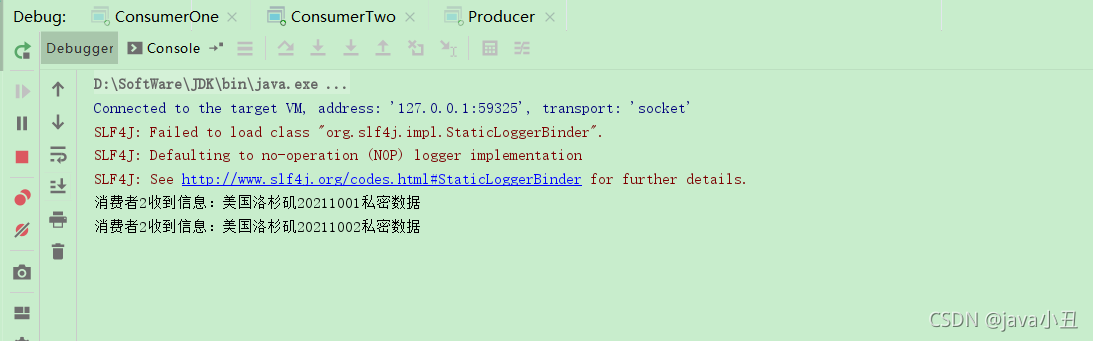
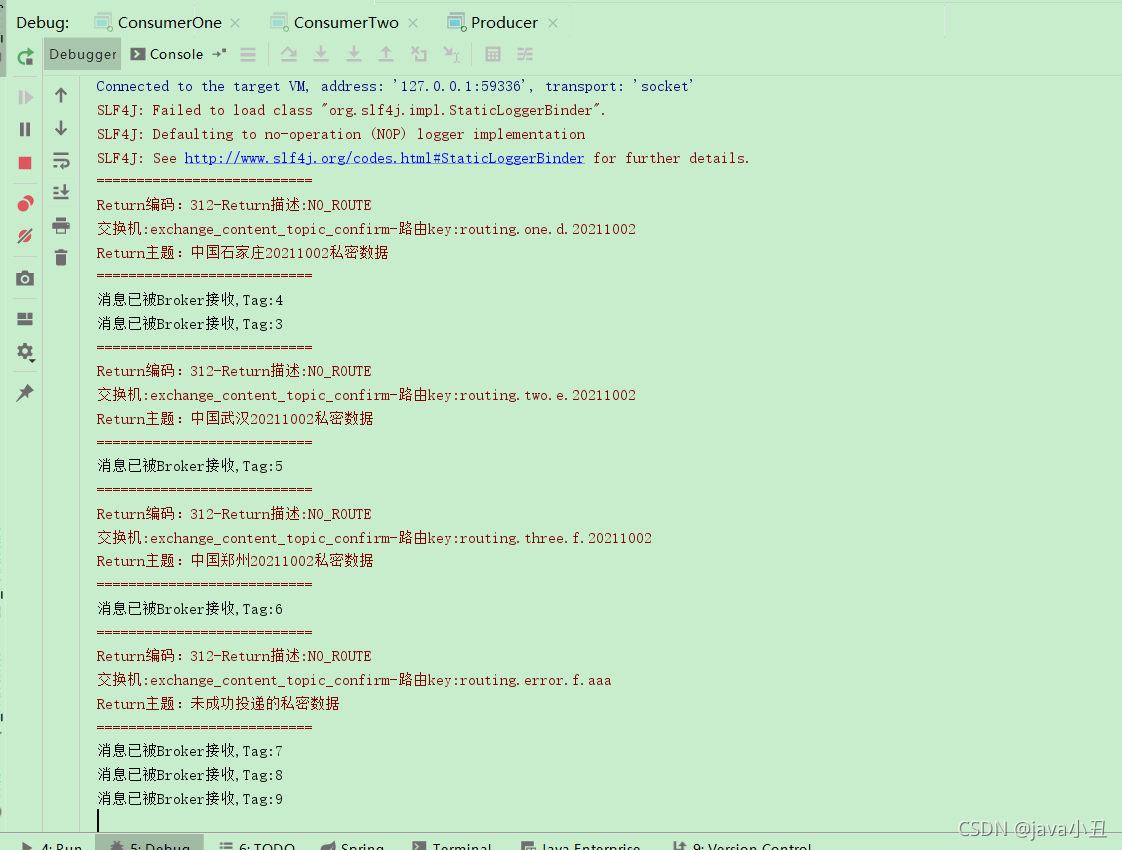 可以看到打印return都是key中没有20211001后缀或者没有us前缀的数据
可以看到打印return都是key中没有20211001后缀或者没有us前缀的数据
总结
提示:这里对文章进行总结:
例如:以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文介绍了RabbitMQ的基本概念,以及6种工作模式,消息确认机制,并且通过简单的Demo演示对RabbitMQ的理论进行强化理解,理论与实践相结合,帮助大家快速理解。