- 从maven变成boot
1 继承 只有继承了boot的父级项目才是springboot项目
2 依赖启动器
3 手动编写启动类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.bjsxt.springbootnewstyle</groupId>
<artifactId>springbootnewhaha</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!--必须要继承父工程-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<!--一定要注入springboot的启动器 所谓的启动器就是一些jar包的集合 springboot框架将jar分类成
不同的启动器,使用哪个启动器就代表导入了哪些jar包,springboot一共提供了44中启动器,
spring-boot-starter-web 支持了全栈式的开发,包含了jar包有tomcat,springmvc等,
-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
========================
@Controller
public class Mvc {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> show(){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("张三","18");
return map;
}
}
================================
@SpringBootApplication //启动类的第一点加注解
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
//在main方法中调用springapplication类中的run方法启动boot框架,参数是启动类的class和main方法中的参数
}
}
================================
<!--可以指定jdk的版本号-->
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
====================================
<!--这是一个打包插件 如果项目没有这个插件,那么在打包时候是不会把boot中依赖的jar打包到项目中的-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
-
注意关于编写启动器的位置
启动器存放的位置:启动器可以controller类位于同一个包下,或者启动器高于controller。但不能把启动器放到平级的其他包中,或是子包。防止启动器扫描不到其他类, -
启动类
springboot框架内嵌了tomcat,所以不需要用容器来启动项目,而是用启动类来启动框架了,
启动类的作用是启动boot框架,是基于main方法运行的,
启动类在启动的时候会做注解扫描包含@controller,@Service @Repository ,扫描位置为同包或是子包下的注解, -
启动器starter
boot框架将功能场景进行了分类,做成了不同的启动器,项目中引入了启动器后相关的依赖会导入进来,在jar包管理上非常方便,
springboot提供了44中启动器: -
配置文件
springboot框架可以设置全局配置文件,名字为application的全局文件,支持两种格式properteis和yaml格式; -
配置文件存放的位置
1当前项目的根目录下;
2当前目录下的config目录中;
3项目中的resources其实就是classpath的根路径;
4 项目中的resources中的config目录中;
注意优先加载properties文件 -
配置文件中的占位符
1 "${}"是占位符,可以获取方法中的值 random.int
2 可以获取配置文件中的键的值,根据键获取值; -
springboot的核心注解
1 @springbootApplication
是标识为启动类,这个注解是相当于多个注解组成而成,@configuration + @EnableAutoConfiguration+ComponentScan 的组合,
2 @SpringbootConfiguration
是@configuration注解的子注解,功能是一样的,标注这个类是配置类,会自动扫描并实例化运行里面的方法,注意 SpringbootConfiguration是boot框架的注解,@configuration是spring中的注解,
3 @configuration
这个注解是代表注解类,通过bean对象的操作代替spring中的xml配置文件,
4 @EnableAutoconfiguration
这个注解是springboot中的自动装配注解,能够根据你添加的jar依赖自动配置你的spring应用,是@AutoconfigurationPackage和@import注解的组成,
5 @AutoconfigurationPackage
这个注解会自动扫描包下所有加了注解的类实例化出bean对象,(@controlle,@service,@configuration)
6 @Import
直接导入普通的类,导入实现了ImportSelector接口的类,
7 @ComponentScan
组件扫描,自动发现和装配bean对象,
8 @ConfigurationPropertiesScan
将扫描@configurationProperties注解类自动装载bean对象, -
Springboot项目中常用的注解
1 @RestController
是一个组合注解 @Controller+@ResponsBody,该类下的方法return返回的就是字符串,无法返回jsp,html,无法配置视图解析器,
@Controller注解是代表是一个接口控制类,该类下的所有方法return可以是jsp,html,object,可以和视图解析器配合使用,
@ResponseBody 作用是该类下所有的api接口返回的数据都是以json字符串的形式来返回,如果返回的String,则仍是String,
2 @RequestMapping()
该注解是spring mvc中的注解,是用来处理请求地址映射的注解,属性有:
value:指定请求的地址路径
path:指定请求的地址路径
method:指定请求的方法类型;get|post|put|delete
params:必须包含某些参数;
@Controller
public class Mvc {
@RequestMapping(path ="/hello",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> show(){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("张三","18");
return map;
}
@RequestMapping(value ="/java",method = RequestMethod.GET,params = "name=\"李四\"")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> showJava(){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("李四","28");
return map;
}
}
请求路径:
http://localhost:8080/java?name=“李四”
http://localhost:8080/hello
3 @GetMapping
等于@RequestMapping(method=RequestMethod.GET);
- springboot整合Servlet
方式一通过注解来实现Servlet组件注册
/**Springboot整合Servlet技术方式一
* 创建一个servlet之后要在xml中配置servelt 场景如下:
* <servlet>
* <servlet-name>FirstServlet</servlet-name>
* <servlet-class>com.bjsxt.servlet.FirstServlet</servlet-class>
* </servlet>
* <servlet-mapping>
* <servlet-name>FirstServlet</servlet-name>
* <url-pattern>/first</url-pattern>
* </servlet-mapping>
* 以上就是以前的方式来配置servelt,但是使用boot之后直接一个注解就搞定了
* 下面就是通过注解来实现servlet组件注册
* */
@WebServlet(name = "FirstServlet",urlPatterns = "/first")
public class FirstServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("webServlet启动了");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
=====================================
@SpringBootApplication
@ServletComponentScan //在启动时会扫描@webServlet注解并实例化 Component组件
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
}
}
方式二通过方法来实例化Servlet组件
package com.bjsxt;
@SpringBootApplication
//@ServletComponentScan //在启动时会扫描@webServlet注解并实例化 Component组件
public class Appa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(com.bjsxt.App.class,args);
}
/** 用方法来实例化出Servlet组件
* 方法名字自定义,返回值是ServletRegistrationBean
* 记得给方法加上@bean就行
* */
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean getServlet(){
//第一步先new出Servlet对象
FirstServlet firstServlet = new FirstServlet();
//创建一个ServletRegistrationBean对象 参数是Servlet对象
ServletRegistrationBean servletBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(firstServlet);
//添加一个url路径
servletBean.addUrlMappings("/firstServlet");
return servletBean;
}
}
- Springboot整合filter
方式一,使用注解来注册filter
package com.bjsxt.filter;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.logging.LogRecord;
/** Springboot整合Filter方式一过滤器
* 首先说明过滤器是Servlet中的一个组件,不是javaEE平台技术,
* 作用是:从客户端向服务器端发送请求进行过滤,或是对服务器返回响应进行处理,
* 创建类继承Filter接口实现三个抽象方法,
* init():初始化方法,在实例化后调用完成初始化动作,
* doFilter():拦截请求或是处理响应方法,实现预处理,
* destroy():销毁filter之前调用,一般用于资源释放,
* <filter>
* <filter-name>FirstFilter</filter-name>
* <filter-class>com.bjsxt.filter.FirstFilter</filter-class>
* </filter>
* <filter-mapping>
* <filter-name>FirstFilter</filter-name>
* <url-pattern>/filter</url-pattern>
* </filter-mapping>
*
*
* */
/*@WebFilter(filterName = "FirstFilter",urlPatterns = {"*.do","*.jsp"})*/
@WebFilter(filterName = "FirstFilter",urlPatterns = "/filter")
public class FirstFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("进入Filter");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
System.out.println("离开Filter");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
====================================
@SpringBootApplication
@ServletComponentScan //在启动时会扫描@webFilter注解并实例化 Component组件
public class Appa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(com.bjsxt.Appa.class,args);
}
}
- Springboot配置listener
Servlet中的监听器:用来监听web应用中某些对象的创建,销毁,增删改等动作触发监听器,
监听器的分类:
1ServletContext对象监听器和属性监听器 实现ServletContextListener接口,
2 HttpSession对象生命周期监听器和属性监听器
3 ServletRequest对象生命周期监听器和属性操作监听器
/** springboot整合listener
* 方式一 通过注解扫描完成listener组件注册,
* <listener>
* <listener-class>com.bjsxt.listener.Listenerdemo</listener-class>
* </listener>
* 现在只需要添加一个注解就可以了
* */
@WebListener//配置监听器
public class Listenerdemo implements ServletContextListener {
//ServletContext对象创建后会触发该监听器
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("listener开始工作了???");
}
//ServletContext对象在销毁之后会触发该监听器
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
}
}
==============================
@SpringBootApplication
@ServletComponentScan //在启动时会扫描@WebListener注解并实例化 Component组件
public class Appa {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(com.bjsxt.Appa.class,args);
}
}
- Springboot访问静态资源
访问静态的位置有
1 Springboot从classpath/static目录下
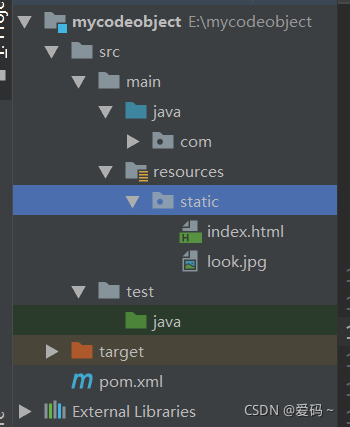
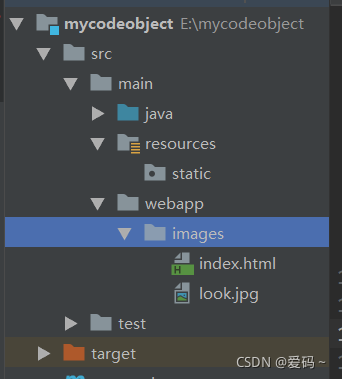
2 从ServletContext根目录下
在src/main/webapp 创建一个webapp目录,这个根目录作为存放静态资源的位置,其实boot框架也是从tomcat中的webapp目录下找资源,
- springboot上传文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>实现文件上传</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--表单上传文件方法必须是post enctype编码方式 是设置提交数据的格式
multipart/form-data是代表上传二进制文件-->
<form action="/fileuploadController" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file"/>
<input type="submit" value="ok"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
package com.bjsxt.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import javax.servlet.annotation.MultipartConfig;
import java.io.File;
/** 实现文件上传*/
@Controller
public class FileUploadController {
//文件上传
@PostMapping("/fileuploadController")
@ResponseBody
//这个参数名字必须和form表单的名字一样
public String fileUpload(MultipartFile file) throws Exception{
//获取原始文件的名字
System.out.println(file.getOriginalFilename());
//将上传的文件转移到指定位置
file.transferTo(new File("E:/"+file.getOriginalFilename()));
return "上传成功!";
}
}
============================
#配置单个上传文件的大小限制
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=3MB
#配置一次请求上传多个文件的总容量大小限制
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=20MB
配置文件application.properties设置