1.MQ的基本概念
1.1消息队列MQ
????????MQ全称为Message Queue,消息队列是应用程序和应用程序之间的通信方法。
????????为什么使用MQ?在项目中,可将一些无需即时返回且耗时的操作提取出来,进行异步处理,而这种异步处理的方式大大的节省了服务器的请求响应时间,从而提高了系统的吞吐量。
????????开发中消息队列通常有如下应用场景: 1、任务异步处理,将不需要同步处理的并且耗时长的操作由消息队列通知消息接收方进行异步处理。提高了应用程序的响应时间;2、应用程序解耦合,MQ相当于一个中介,生产方通过MQ与消费方交互,它将应用程序进行解耦合。
1.2AMQP和JMS
????????MQ是消息通信的模型;实现MQ的大致有两种主流方式:AMQP、JMS。
1.2.1AMQP
1.2.2JMS
????????JMS即Java消息服务(JavaMessage Service)应用程序接口,是一个Java平台中关于面向消息中间件(MOM)的API,用于在两个应用程序之间,或分布式系统中发送消息,进行异步通信。
1.2.3AMQP与JMS区别
- JMS是定义了统一的接口,来对消息操作进行统一;AMQP是通过规定协议来统一数据交互的格式;
- JMS限定了必须使用Java语言;AMQP只是协议,不规定实现方式,因此是跨语言的;
- JMS规定了两种消息模式;而AMQP的消息模式更加丰富。
1.3消息队列产品
- ActiveMQ:基于JMS;
- ZeroMQ:基于C语言开发;
- RabbitMQ:基于AMQP协议,erlang语言开发,稳定性好;
- RocketMQ:基于JMS,阿里巴巴产品;
- Kafka:类似MQ的产品;分布式消息系统,高吞吐量;
1.4RabbitMQ

2.RabbitMQ的安装和配置
2.1安装说明
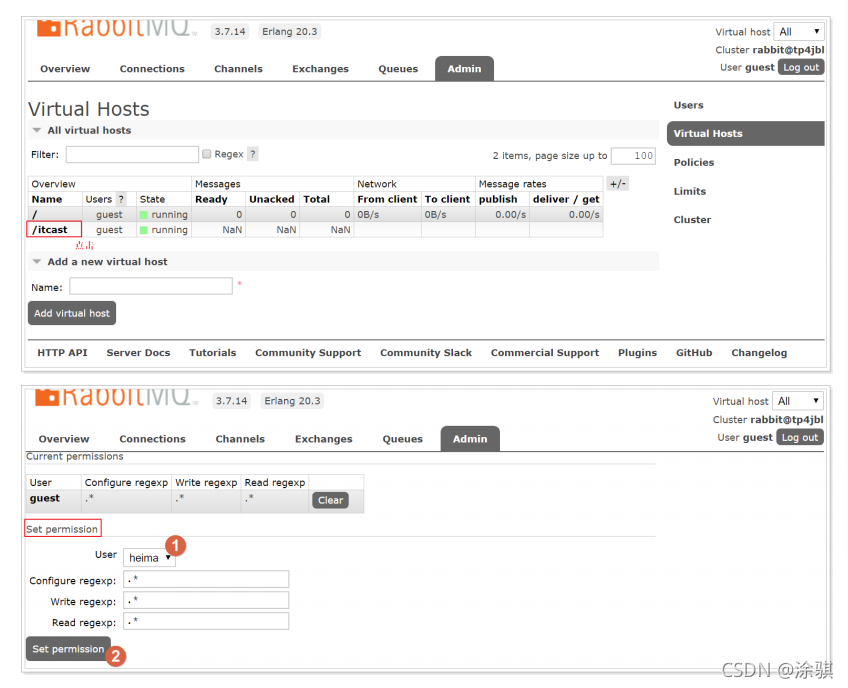
2.2用户以及Virtual Hosts配置
2.2.1用户角色

角色说明:
2.2.2Virtual Hosts配置

?????????2.设置Virtual Hosts权限
3.RabbitMQ快速入门
3.1搭建工程示例
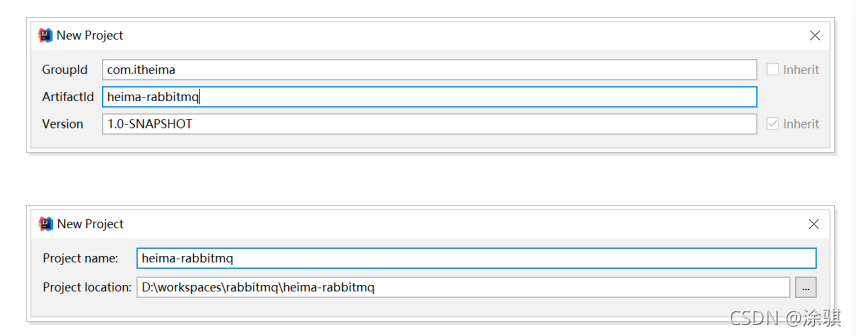
3.1.1创建工程
?
3.1.2. 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.6.0</version>
</dependency>3.2编写生产者
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class Producer {
static final String QUEUE_NAME = "simple_queue";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建连接工厂
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
//主机地址;默认为 localhost
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");
//连接端口;默认为 5672
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
//虚拟主机名称;默认为 /
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("/itcast");
//连接用户名;默认为guest
connectionFactory.setUsername("heima");
//连接密码;默认为guest
connectionFactory.setPassword("heima");
//创建连接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);
// 要发送的信息
String message = "你好;小兔子!";
/*** 参数1:交换机名称,如果没有指定则使用默认Default Exchage * 参数2:路由key,简单模式可以传递队列名称 * 参数3:消息其它属性 * 参数4:消息内容 */
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message);
// 关闭资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
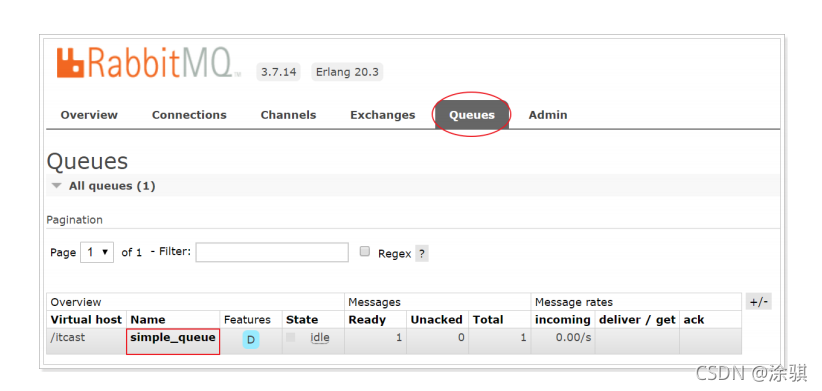
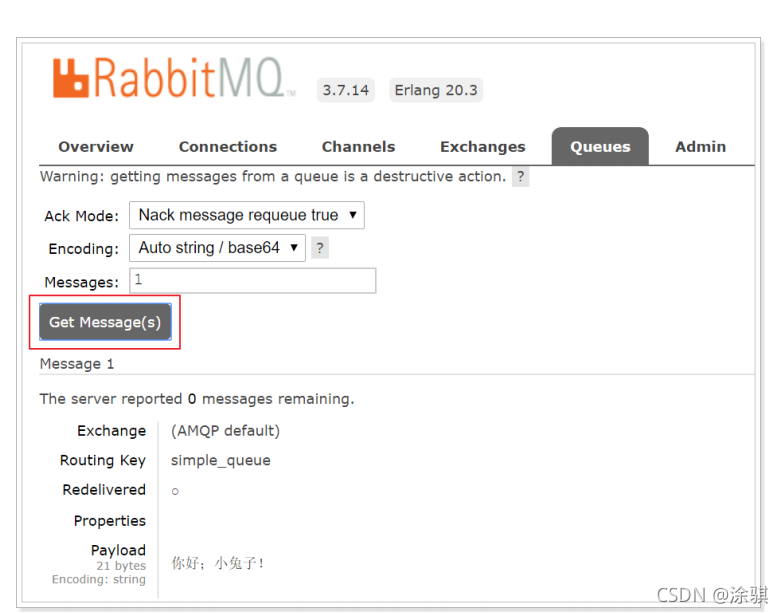
}? ? ? ?在执行上述的消息发送之后;可以登录rabbitMQ的管理控制台,可以发现队列和其消息:
 ?
?
?
3.3编写消费者
????????抽取创建connection的工具类com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class ConnectionUtil {
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
//创建连接工厂
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
//主机地址;默认为 localhost
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");
//连接端口;默认为 5672
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
//虚拟主机名称;默认为 /
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("/itcast");
//连接用户名;默认为guest
connectionFactory.setUsername("heima");
//连接密码;默认为guest
connectionFactory.setPassword("heima");
//创建连接
return connectionFactory.newConnection();
}
}import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列
* 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);
//创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定
* * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送)
* * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
//消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf-8"));
}
};
//监听消息
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */
channel.basicConsume(Producer.QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer);
//不关闭资源,应该一直监听消息 //channel.close(); //connection.close();
//
}
}
}3.4小结
????????上述的入门案例中中其实使用的是如下的简单模式:
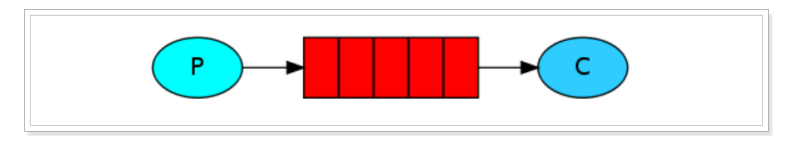 ?
?
- P:生产者,也就是要发送消息的程序
- C:消费者:消息的接受者,会一直等待消息到来。
- queue:消息队列,图中红色部分。类似一个邮箱,可以缓存消息;生产者向其中投递消息,消费者从其中取 出消息。
在rabbitMQ中消息者是一定要到某个消息队列中去获取消息的 。
4.RabbitMQ的工作模式
4.1Work queues工作队列模式
4.1.1模式说明
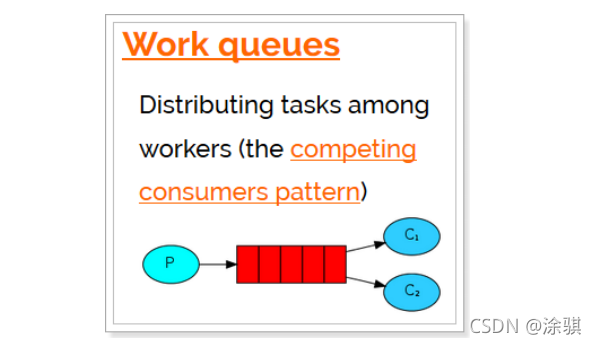
?????????Work Queues 与入门程序的 简单模式 相比,多了一个或一些消费端,多个消费端共同消费同一个队列中的消息。
????????应用场景:对于 任务过重或任务较多情况使用工作队列可以提高任务处理的速度。
4.1.2代码
????????Work Queues 与入门程序的 简单模式 的代码是几乎一样的;可以完全复制,并复制多一个消费者进行多个消费者同时消费消息的测试。
? ? ? ? 生产者
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
public class Producer {
static final String QUEUE_NAME = "work_queue";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建连接
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
// 发送信息
String message = "你好;小兔子!work模式--" + i;
/*** 参数1:交换机名称,如果没有指定则使用默认Default Exchage * 参数2:路由key,简单模式可以传递队列名称 * 参数3:消息其它属性 * 参数4:消息内容 */
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message);
}
// 关闭资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
????????消费者1
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);
//一次只能接收并处理一个消息
channel.basicQos(1);
//创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
try {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
//消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("消费者1-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf- 8"));
Thread.sleep(1000);
//确认消息
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
//监听消息
/*** 参数1:队列名称
* 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认
* 参数3:消息接收到后回调
*/
channel.basicConsume(Producer.QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
}
}????????消费者2
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数
*
*/
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);
//一次只能接收并处理一个消息
channel.basicQos(1);
// 创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
try {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
// 消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("消费者2-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf- 8"));
Thread.sleep(1000);
//确认消息
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
//监听消息 /*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */
channel.basicConsume(Producer.QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
}
}
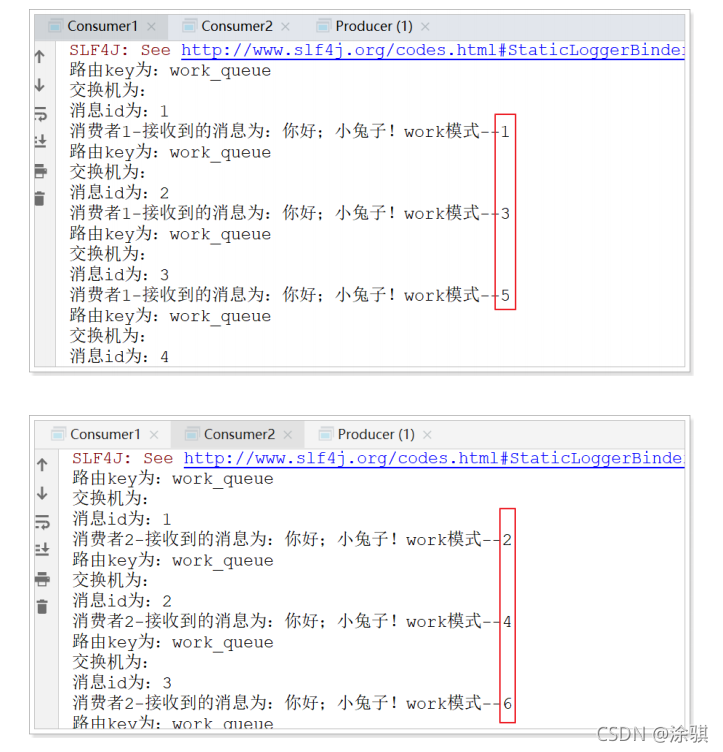
4.1.3测试
????????启动两个消费者,然后再启动生产者发送消息;到IDEA的两个消费者对应的控制台查看是否竞争性的接收到消息。
?
4.1.4小结
????????在一个队列中如果有多个消费者,那么消费者之间对于同一个消息的关系是竞争的关系。
4.2订阅模式类型
????????订阅模式示例图:
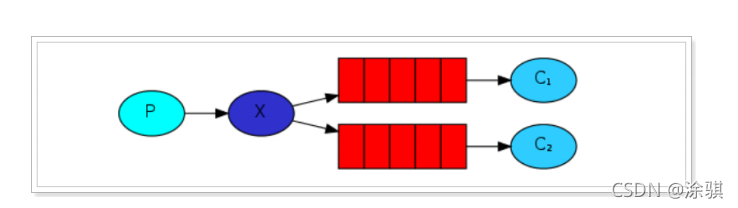
?????????前面2个案例中,只有3个角色:
- P:生产者,也就是要发送消息的程序
- C:消费者:消息的接受者,会一直等待消息到来。
- queue:消息队列,图中红色部分
- P:生产者,也就是要发送消息的程序,但是不再发送到队列中,而是发给X(交换机);
- C:消费者,消息的接受者,会一直等待消息到来;
- Queue:消息队列,接收消息、缓存消息;
- Exchange:交换机,图中的X。一方面,接收生产者发送的消息。另一方面,知道如何处理消息,例如递交给某个特别队列、递交给所有队列、或是将消息丢弃。到底如何操作,取决于Exchange的类型。Exchange有常见以下3种类型:
- Fanout:广播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列;
- Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key 的队列;
- Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式) 的队列。
????????Exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息,不具备存储消息的能力,因此如果没有任何队列与Exchange绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那么消息会丢失!
4.3Publish/Subscribe发布与订阅模式
4.3.1模式说明
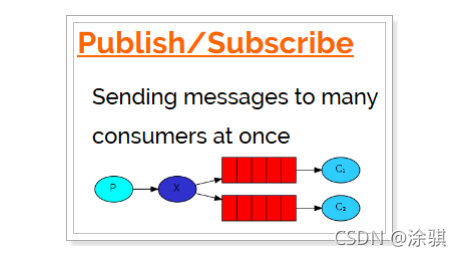
????????发布订阅模式: 1、每个消费者监听自己的队列。 2、生产者将消息发给broker,由交换机将消息转发到绑定此交换的每个队列,每个绑定交换机的队列都将接收 到消息。
4.3.2代码
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
/*** 发布与订阅使用的交换机类型为:fanout */
public class Producer {
//交换机名称
static final String FANOUT_EXCHAGE = "fanout_exchange";
//队列名称
static final String FANOUT_QUEUE_1 = "fanout_queue_1";
//队列名称
static final String FANOUT_QUEUE_2 = "fanout_queue_2";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建连接
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/*** 声明交换机 * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:交换机类型,fanout、topic、direct、headers */
channel.exchangeDeclare(FANOUT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT);
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(FANOUT_QUEUE_1, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(FANOUT_QUEUE_2, true, false, false, null);
//队列绑定交换机
channel.queueBind(FANOUT_QUEUE_1, FANOUT_EXCHAGE, "");
channel.queueBind(FANOUT_QUEUE_2, FANOUT_EXCHAGE, "");
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// 发送信息
String message = "你好;小兔子!发布订阅模式--" + i;
/*** 参数1:交换机名称,如果没有指定则使用默认Default Exchage * 参数2:路由key,简单模式可以传递队列名称 * 参数3:消息其它属性 * 参数4:消息内容 */
channel.basicPublish(FANOUT_EXCHAGE, "", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message);
}
// 关闭资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.FANOUT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT);
// 声明(创建)队列 /*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数*/
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_1, true, false, false, null);
//队列绑定交换机
channel.queueBind(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_1, Producer.FANOUT_EXCHAGE, "");
//创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
//消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("消费者1-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf- 8"));
}
};
//监听消息 /*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */
channel.basicConsume(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_1, true, consumer);
}
}import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.FANOUT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT);
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数*/
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_2, true, false, false, null);
//队列绑定交换机
channel.queueBind(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_2, Producer.FANOUT_EXCHAGE, "");
//创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
//消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("消费者1-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf- 8"));
}
};
//监听消息 /*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */
channel.basicConsume(Producer.FANOUT_QUEUE_2, true, consumer);
}
}4.3.3测试
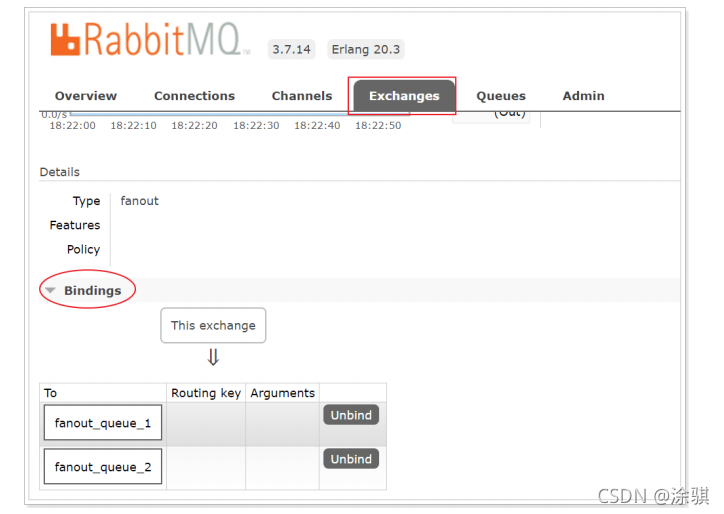
???????启动所有消费者,然后使用生产者发送消息;在每个消费者对应的控制台可以查看到生产者发送的所有消息;到达广播的效果。在执行完测试代码后,其实到RabbitMQ的管理后台找到 Exchanges 选项卡,点击 fanout_exchange 的交换机,可以查看到如下的绑定:
?
?
4.3.4小结
????????交换机需要与队列进行绑定,绑定之后;一个消息可以被多个消费者都收到。
- 工作队列模式不用定义交换机,而发布/订阅模式需要定义交换机。
- 发布/订阅模式的生产方是面向交换机发送消息,工作队列模式的生产方是面向队列发送消息(底层使用默认交换机)。
- 发布/订阅模式需要设置队列和交换机的绑定,工作队列模式不需要设置,实际上工作队列模式会将队列绑定到默认的交换机 。
4.4Routing路由模式
4.4.1模式说明
- 队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个 RoutingKey (路由key);
- 消息的发送方在 向 Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的 RoutingKey ;
- Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的 Routing Key 进行判断,只有队列的Routingkey 与消息的 Routing key 完全一致,才会接收到消息。
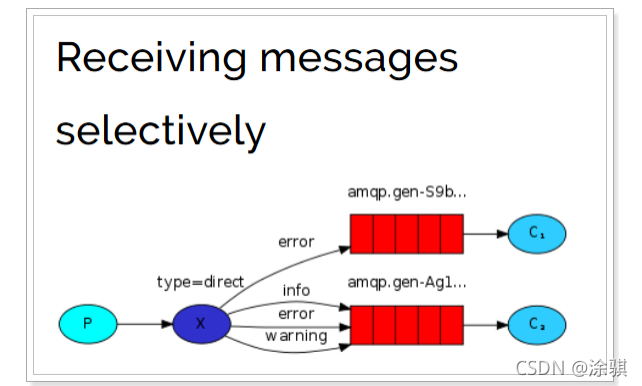
?图解:
- P:生产者,向Exchange发送消息,发送消息时,会指定一个routing key;
- X:Exchange(交换机),接收生产者的消息,然后把消息递交给 与routing key完全匹配的队列;
- C1:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key 为 error 的消息;
- C2:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key 为 info、error、warning 的消息。
4.4.2代码
????????在编码上与 Publish/Subscribe发布与订阅模式 的区别是交换机的类型为:Direct,还有队列绑定交换机的时候需要指定routing key。
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType; 1234
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
/*** 路由模式的交换机类型为:direct */
public class Producer {
//交换机名称
static final String DIRECT_EXCHAGE = "direct_exchange";
//队列名称
static final String DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT = "direct_queue_insert";
//队列名称
static final String DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE = "direct_queue_update";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建连接
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/*** 声明交换机 * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:交换机类型,fanout、topic、direct、headers */
channel.exchangeDeclare(DIRECT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, true, false, false, null);
//队列绑定交换机
channel.queueBind(DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "insert");
channel.queueBind(DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "update");
// 发送信息
String message = "新增了商品。路由模式;routing key 为 insert ";
/*** 参数1:交换机名称,如果没有指定则使用默认Default Exchage * 参数2:路由key,简单模式可以传递队列名称 * 参数3:消息其它属性 * 参数4:消息内容*/
channel.basicPublish(DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "insert", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message);
// 发送信息
message = "修改了商品。路由模式;routing key 为 update";
/*** 参数1:交换机名称,如果没有指定则使用默认Default Exchage * 参数2:路由key,简单模式可以传递队列名称 * 参数3:消息其它属性 * 参数4:消息内容 */
channel.basicPublish(DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "update", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message);
// 关闭资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.DIRECT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, true, false, false, null);
//队列绑定交换机
channel.queueBind(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, Producer.DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "insert");
//创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
//消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("消费者1-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf- 8"));
}
};
//监听消息
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */
channel.basicConsume(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_INSERT, true, consumer);
}
}消费者2
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.DIRECT_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT);
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, true, false, false, null);
//队列绑定交换机
channel.queueBind(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, Producer.DIRECT_EXCHAGE, "update");
//创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
//消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("消费者2-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf- 8"));
}
};
//监听消息
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */
channel.basicConsume(Producer.DIRECT_QUEUE_UPDATE, true, consumer);
}
}4.4.3测试

?
4.4.4小结
????????Routing模式要求队列在绑定交换机时要指定routing key,消息会转发到符合routing key的队列。
4.5Topics通配符模式
4.5.1模式说明
????????Topic 类型与 Direct 相比,都是可以根据 RoutingKey 把消息路由到不同的队列。只不过 Topic 类型 Exchange 可以让队列在绑定 Routing key 的时候使用通配符!Routingkey 一般都是有一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以”.”分割,例如: item.insert。
- # :匹配一个或多个词;
- * :匹配不多不少恰好1个词。
- item.# :能够匹配 item.insert.abc 或者 item.insert
- item.* :只能匹配 item.insert
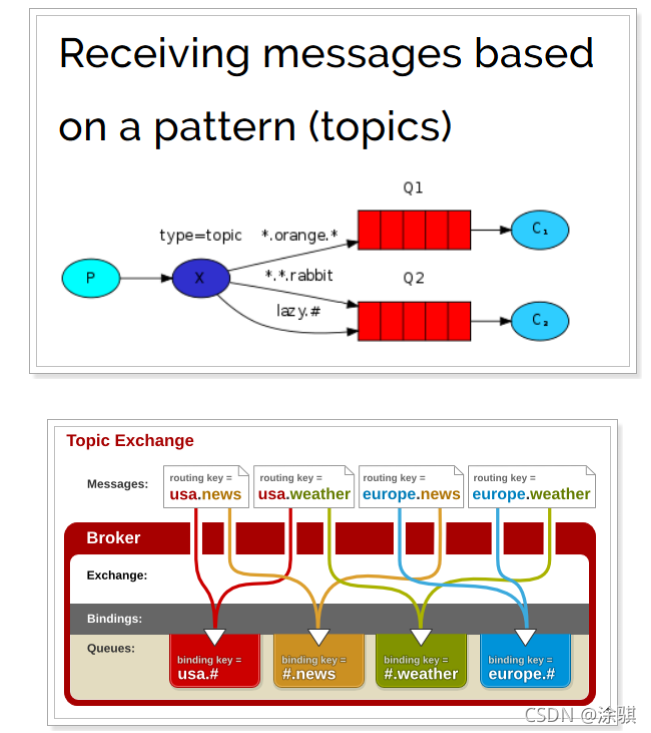
?????????图解:
- 红色Queue:绑定的是 usa.# ,因此凡是以 usa. 开头的 routing key 都会被匹配到;
- 黄色Queue:绑定的是 #.news ,因此凡是以 .news 结尾的 routing key 都会被匹配。
4.5.2代码
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
/*** 通配符Topic的交换机类型为:topic */
public class Producer {
//交换机名称
static final String TOPIC_EXCHAGE = "topic_exchange";
//队列名称
static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_1 = "topic_queue_1";
//队列名称
static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_2 = "topic_queue_2";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建连接
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/*** 声明交换机 * 参数1:交换机名称 * 参数2:交换机类型,fanout、topic、topic、headers */
channel.exchangeDeclare(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC);
// 发送信息
String message = "新增了商品。Topic模式;routing key 为 item.insert ";
channel.basicPublish(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.inssert", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message);
// 发送信息
message = "修改了商品。Topic模式;routing key 为 item.update";
channel.basicPublish(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.update", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message);
// 发送信息
message = "删除了商品。Topic模式;routing key 为 item.delete";
channel.basicPublish(TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.delete", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println("已发送消息:" + message);
// 关闭资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC);
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否定义持久化队列 * 参数3:是否独占本次连接 * 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列 * 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_1, true, false, false, null);
//队列绑定交换机
channel.queueBind(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_1, Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.update");
channel.queueBind(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_1, Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.delete");
//创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定 * envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送) * properties 属性信息 * body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
//消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("消费者1-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf- 8"));
}
};
/*** 参数1:队列名称 * 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认 * 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */
channel.basicConsume(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_1, true, consumer);
}
}import com.itheima.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 创建频道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC);
// 声明(创建)队列
/*** 参数1:队列名称
* 参数2:是否定义持久化队列
* 参数3:是否独占本次连接
* 参数4:是否在不使用的时候自动删除队列
* 参数5:队列其它参数 */
channel.queueDeclare(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_2, true, false, false, null);
//队列绑定交换机
channel.queueBind(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_2, Producer.TOPIC_EXCHAGE, "item.*");
// 创建消费者;并设置消息处理
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
/*** consumerTag 消息者标签,在channel.basicConsume时候可以指定
* envelope 消息包的内容,可从中获取消息id,消息routingkey,交换机,消息和重传标志 (收到消息失败后是否需要重新发送)
* properties 属性信息
* body 消息 */
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
//路由key
System.out.println("路由key为:" + envelope.getRoutingKey());
//交换机
System.out.println("交换机为:" + envelope.getExchange());
//消息id
System.out.println("消息id为:" + envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//收到的消息
System.out.println("消费者2-接收到的消息为:" + new String(body, "utf- 8"));
}
};
//监听消息
/*** 参数1:队列名称
* 参数2:是否自动确认,设置为true为表示消息接收到自动向mq回复接收到了,mq接收到回复会删除消 息,设置为false则需要手动确认
* 参数3:消息接收到后回调 */
channel.basicConsume(Producer.TOPIC_QUEUE_2, true, consumer);
}
}
4.5.3测试

?
4.5.4小结
????????Topic主题模式可以实现 Publish/Subscribe发布与订阅模式 和 Routing路由模式 的功能;只是Topic在配置routingkey 的时候可以使用通配符,显得更加灵活。
4.6模式总结
5.SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ
5.1简介
????????在Spring项目中,可以使用Spring-Rabbit去操作RabbitMQ https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-amqp 尤其是在spring boot项目中只需要引入对应的amqp启动器依赖即可,方便的使用RabbitTemplate发送消息,使用注解接收消息。
????????一般在开发过程中:
5.2搭建生产者工程
5.2.1创建工程
创建生产者工程springboot-rabbitmq-producer
5.2.2添加依赖
修改pom.xml文件内容为如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>5.2.3启动类
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProducerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProducerApplication.class);
}
}5.2.4配置RabbitMQ
配置文件:创建application.yml,内容如下:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host:
localhost
port: 5672
virtual-host: /itcast
username: heima
password: heima????????绑定交换机和队列:创建RabbitMQ队列与交换机绑定的配置类com.itheima.rabbitmq.confifig.RabbitMQConfifig
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
//交换机名称
public static final String ITEM_TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "item_topic_exchange";
// 队列名称
public static final String ITEM_QUEUE = "item_queue";
//声明交换机
@Bean("itemTopicExchange")
public Exchange topicExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.topicExchange(ITEM_TOPIC_EXCHANGE).durable(true).build();
}
//声明队列
@Bean("itemQueue")
public Queue itemQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(ITEM_QUEUE).build();
}
//绑定队列和交换机
@Bean
public Binding itemQueueExchange(@Qualifier("itemQueue") Queue queue, @Qualifier("itemTopicExchange") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("item.#").noargs();
}
}
5.3搭建消费者工程
5.3.1创建工程
5.3.2添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>5.3.3启动类
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication .class);
}
}5.3.4配置RabbitMQ
????????配置文件:创建application.yml,内容如下:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host:
localhost
port: 5672
virtual-host: /itcast
username: heima
password: heima? ? ? ?
5.3.5消息监听处理类
????????编写消息监听器com.itheima.rabbitmq.listener.MyListener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyListener {
/*** 监听某个队列的消息 * @param message 接收到的消息 */
@RabbitListener(queues = "item_queue")
public void myListener1(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者接收到的消息为:" + message);
}
}5.4测试
import com.itheima.rabbitmq.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class RabbitMQTest {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void test() {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitMQConfig.ITEM_TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "item.insert", "商品新增,routing key 为item.insert");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitMQConfig.ITEM_TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "item.update", "商品修改,routing key 为item.update");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitMQConfig.ITEM_TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "item.delete", "商品删除,routing key 为item.delete");
}
}先运行上述测试程序(交换机和队列才能先被声明和绑定),然后启动消费者;在消费者工程springboot-rabbitmq-consumer中控制台查看是否接收到对应消息。
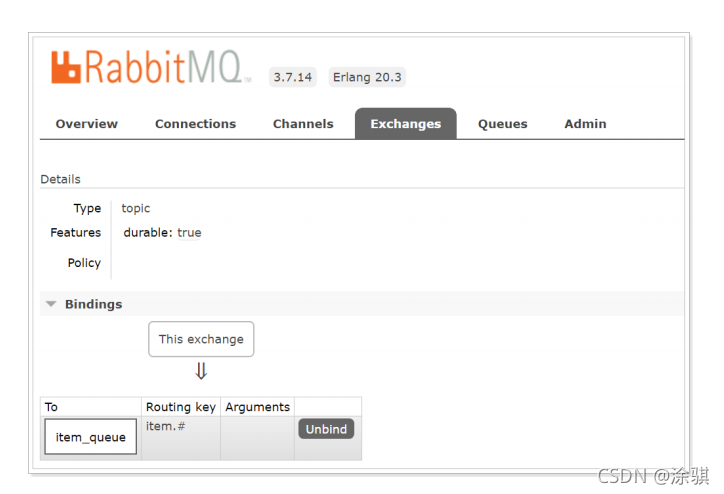
????????另外;也可以在RabbitMQ的管理控制台中查看到交换机与队列的绑定:
?