1.算术运算符
1.1基本四则运算符
+ - * / %
1.1.1int / int 结果还是 int, 需要使用 double 来计算.
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
System.out.println(a / b);
// 结果为 0
0不能作除数
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
System.out.println(a / b)

% 表示取余, 不仅仅可以对 int 求模, 也能对 double 来求模
public class TestDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 5.7;
double b = 2.0;
System.out.println(a % b);
}
}

增量赋值运算符
+= -= *= /= %=
public class TestDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
a += 1; // 等价于 a = a + 1
System.out.println(a);
}
}

自增/自减运算符
++ --
public class TestDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = ++a;
System.out.println(b);
int c = a++;
System.out.println(c);
}
}
2.关系运算符
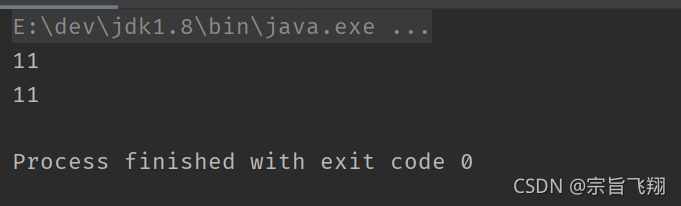
== != < . <= >=
public class TestDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(a == b);
System.out.println(a != b);
System.out.println(a < b);
System.out.println(a > b);
System.out.println(a <= b);
System.out.println(a >= b);
}
}
注意: 关系运算符的表达式返回值都是 boolean 类型.
3.逻辑运算符
&& || !
注意: 逻辑运算符的操作数(操作数往往是关系运算符的结果)和返回值都是 boolean
逻辑与&&
规则: 两个操作数都为 true, 结果为 true, 否则结果为 false.
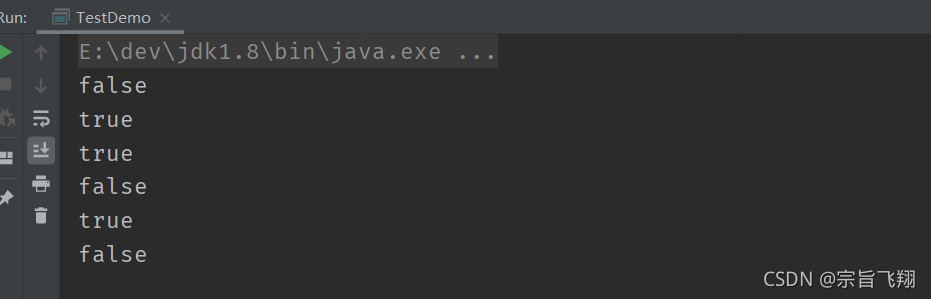
public class TestDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 30;
System.out.println(a < b && b < c);
}
}

3.2逻辑或||
规则: 两个操作数都为 false, 结果为 false, 否则结果为 true.
public class TestDemo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 30;
System.out.println(a < b || b < c);
}
}
3.3逻辑非!
规则: 操作数为 false, 结果为 true,操作数为 true, 结果为 false,操作数只有一个
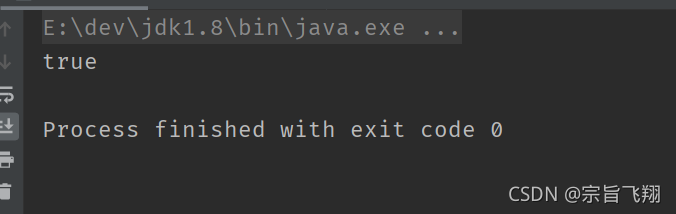
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(!(a < b));
}
}
3.4短路求值
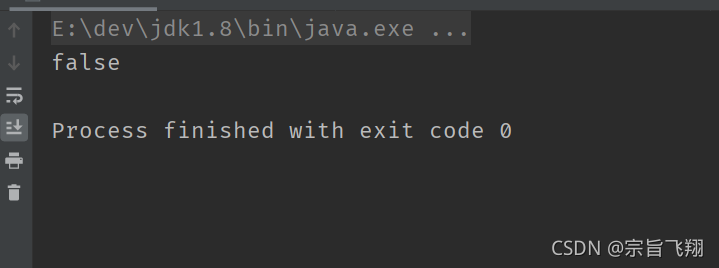
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(10 > 20 && 10 / 0 == 0); // 打印 false
System.out.println(10 < 20 || 10 / 0 == 0); // 打印 true
}
}
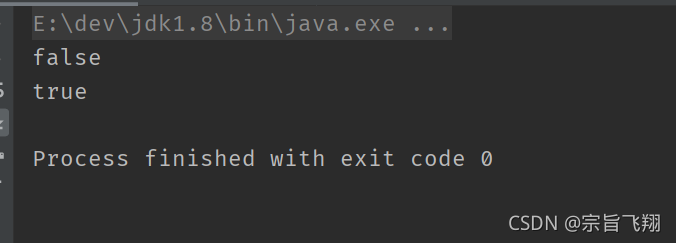
我们都知道, 计算 10 / 0 会导致程序抛出异常. 但是上面的代码却能正常运行, 说明 10 / 0 并没有真正被求值.
结论:
1. 对于 && , 如果左侧表达式值为 false, 则表达式的整体的值一定是 false, 无需计算右侧表达式.
2. 对于 ||, 如果左侧表达式值为 true, 则表达式的整体的值一定是 true, 无需计算右侧表达式.
3.5 & 和 | 不推荐使用
& 和 | 如果操作数为 boolean 的时候, 也表示逻辑运算. 但是和 && 以及 || 相比, 它们不支持短路求值
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(10 > 20 & 10 / 0 == 0); // 程序抛出异常
System.out.println(10 < 20 | 10 / 0 == 0); // 程序抛出异常
}
}

4.位运算符
Java 中对数据的操作的最小单位不是字节, 而是二进制位.
位运算符主要有四个
& | ~ ^
位操作表示 按二进制位运算. 计算机中都是使用二进制来表示数据的(01构成的序列), 按位运算就是在按照二进制位的每一位依次进行计算.
4.1按位与 &
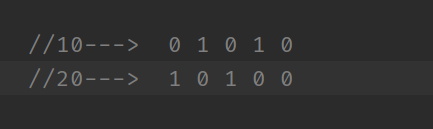
按位与 &: 如果两个二进制位都是 1, 则结果为1,否则结果是0
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
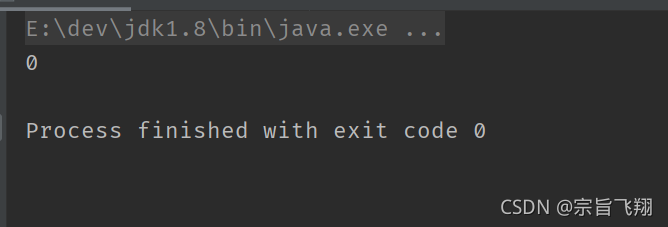
System.out.println(a & b);
}
}
4.2按位或|
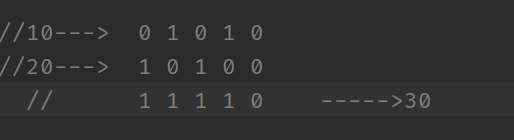
如果两个二进制位都是 0, 则结果为 0, 否则结果为 1.
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) { //10---> 0 1 0 1 0
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println(a | b);
}
}
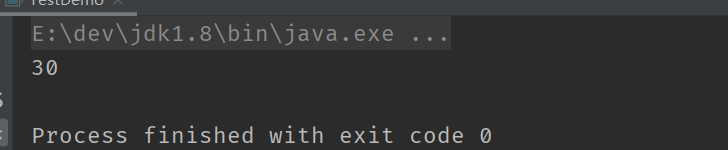
注意: 当 & 和 | 的操作数为整数(int, short, long, byte) 的时候, 表示按位运算, 当操作数为 boolean 的时候, 表示逻辑运算
4.3按位取反~
如果该位为 0 则转为 1, 如果该位为 1 则转为 0
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) { //10---> 0 1 0 1 0
int a = 0xf;
System.out.printf("%x\n", ~a);
}
}
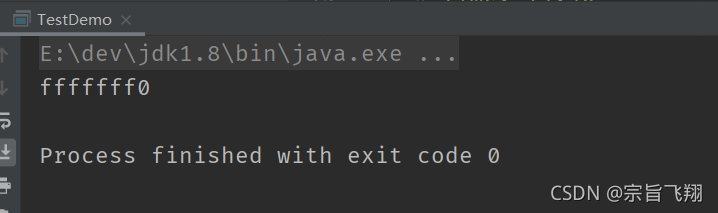
注意:
1. 0x 前缀的数字为十六进制数字. 十六进制可以看成是二进制的简化表示方式. 一个十六进制数字对应 4 个二进
制位.
2. 0xf 表示 10 进制的 15, 也就是二进制的 1111
3. printf 能够格式化输出内容, %x 表示按照十六进制输出.
4. \n 表示换行符
4.4按位异或^
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0x1;
int b = 0x2;
System.out.printf("%x\n", a ^ b);
}
}
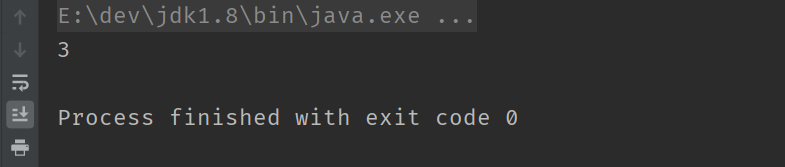
5.移位运算
移位运算符有三个:
<< >> >>>
都是按照二进制位来运算
5.1左移<<:最左侧位不要了,最右侧补0
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0x10;
System.out.printf("%x\n", a << 1);
}
}
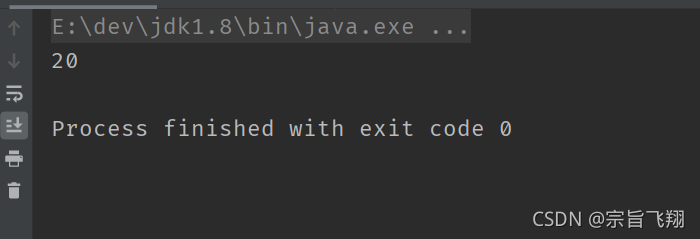
5.2左移<<:最右侧位不要了,最左侧补符号位(正数补0, 负数补1)
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0x10;
System.out.printf("%x\n", a >> 1);
int b = 0xffff0000;
System.out.printf("%x\n", b >> 1);
}
}

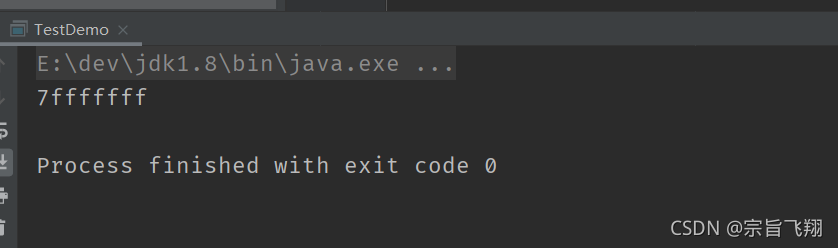
5.3无符号右移 >>>: 最右侧位不要了, 最左侧补 0.
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 0xffffffff;
System.out.printf("%x\n", a >>> 1);
}
}
注意:
- 左移 1 位, 相当于原数字 * 2. 左移 N 位, 相当于原数字 * 2 的N次方.
- 右移 1 位, 相当于原数字 / 2. 右移 N 位, 相当于原数字 / 2 的N次方.
- 由于计算机计算移位效率高于计算乘除, 当某个代码正好乘除 2 的N次方的时候可以用移位运算代替.
- 移动负数位或者移位位数过大都没有意义
6.条件运算符
表达式1 ? 表达式2 : 表达式3
当 表达式1 的值为 true 时, 整个表达式的值为 表达式2 的值; 当 表达式1 的值为 false 时, 整个表达式的值为 表达式3 的值.
也是 Java 中唯一的一个 三目运算符, 是条件判断语句的简化写法.
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 求两个整数的最大值
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int max = a > b ? a : b;
System.out.println(max);
}
}
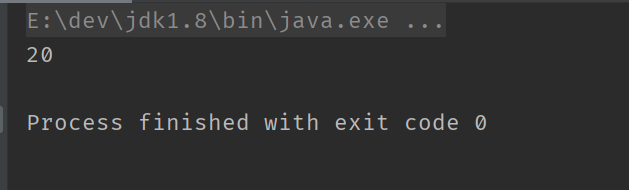
7运算符的优先级
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(1 + 2 * 3);
}
}
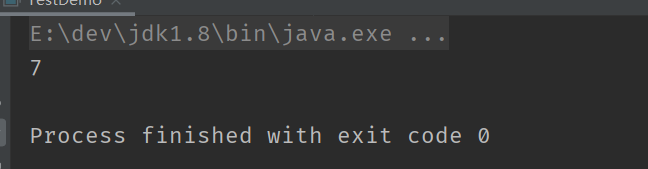
结果为 7, 说明先计算了 2*3 , 再计算 1+
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(10 < 20 && 20 < 30);
}
}
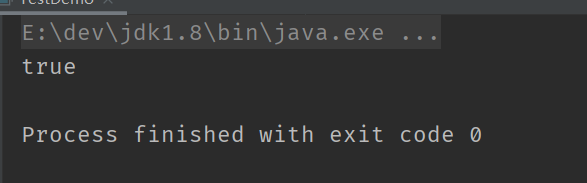
此时明显是先计算的 10 < 20 和 20 < 30, 再计算 &&. 否则 20 && 20 这样的操作是语法上有误的(&& 的操作数只能是boolean).
8 小结
- % 操作再 Java 中也能针对 double 来计算.
- 需要区分清楚 前置自增 和 后置自增之间的区别.
- 由于 Java 是强类型语言, 因此对于类型检查较严格, 因此像 && 之类的运算操作数必须是 boolean.
- 要区分清楚 & 和 | 什么时候是表示按位运算, 什么时候表示逻辑运算.
整体来看, Java 的运算符的基本规则和 C 语言基本一致