1. 分布式锁之Redisson
? Redisson是一个在Redis的基础上实现的Java驻内存数据网格(In-Memory Data Grid)。它不仅提供了一系列的分布式的Java常用对象,还提供了许多分布式服务。其中包括(BitSet, Set, Multimap, SortedSet, Map, List, Queue, BlockingQueue, Deque, BlockingDeque, Semaphore, Lock, AtomicLong, CountDownLatch, Publish / Subscribe, Bloom filter, Remote service, Spring cache, Executor service, Live Object service, Scheduler service) Redisson提供了使用Redis的最简单和最便捷的方法。Redisson的宗旨是促进使用者对Redis的关注分离(Separation of Concern),从而让使用者能够将精力更集中地放在处理业务逻辑上。

官方文档地址:https://github.com/redisson/redisson/wiki
1.1. 快速入门
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.11.2</version>
</dependency>
2.添加配置
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
Config config = new Config();
// 可以用"rediss://"来启用SSL连接
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://172.16.116.100:6379");
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
3.代码实现
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Override
public void testLock() {
RLock lock = this.redissonClient.getLock("lock"); // 只要锁的名称相同就是同一把锁
lock.lock(); // 加锁
// 查询redis中的num值
String value = this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("num");
// 没有该值return
if (StringUtils.isBlank(value)) {
return;
}
// 有值就转成成int
int num = Integer.parseInt(value);
// 把redis中的num值+1
this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("num", String.valueOf(++num));
lock.unlock(); // 解锁
}
使用ab压力测试,查看redis内容:

1.2. 可重入锁(Reentrant Lock)
基于Redis的Redisson分布式可重入锁RLock Java对象实现了java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock接口。
大家都知道,如果负责储存这个分布式锁的Redisson节点宕机以后,而且这个锁正好处于锁住的状态时,这个锁会出现锁死的状态。为了避免这种情况的发生,Redisson内部提供了一个监控锁的看门狗,它的作用是在Redisson实例被关闭前,不断的延长锁的有效期。默认情况下,看门狗的检查锁的超时时间是30秒钟,也可以通过修改Config.lockWatchdogTimeout来另行指定。
另外Redisson还通过加锁的方法提供了leaseTime的参数来指定加锁的时间。超过这个时间后锁便自动解开了。
快速入门使用的就是可重入锁。也是最常使用的锁。
最常见的使用:
RLock lock = redisson.getLock("anyLock");
// 最常使用
lock.lock();
// 加锁以后10秒钟自动解锁
// 无需调用unlock方法手动解锁
lock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 尝试加锁,最多等待100秒,上锁以后10秒自动解锁
boolean res = lock.tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (res) {
try {
...
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
改造程序:

重启后在浏览器测试:

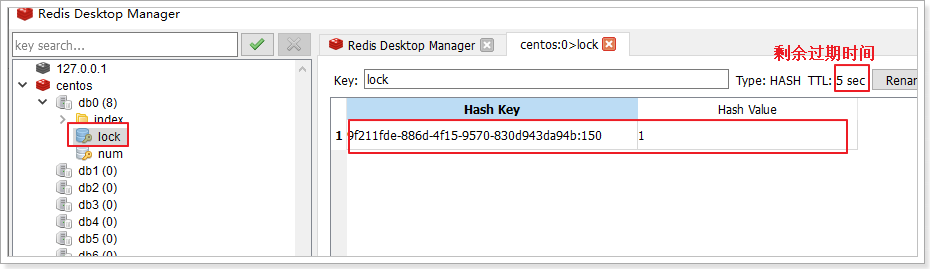
在这10s期间,可以在redis客户端看到lock锁的内容:
1.3. 读写锁(ReadWriteLock)
基于Redis的Redisson分布式可重入读写锁RReadWriteLock Java对象实现了java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock接口。其中读锁和写锁都继承了RLock接口。
分布式可重入读写锁允许同时有多个读锁和一个写锁处于加锁状态。
RReadWriteLock rwlock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("anyRWLock");
// 最常见的使用方法
rwlock.readLock().lock();
// 或
rwlock.writeLock().lock();
// 10秒钟以后自动解锁
// 无需调用unlock方法手动解锁
rwlock.readLock().lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 或
rwlock.writeLock().lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 尝试加锁,最多等待100秒,上锁以后10秒自动解锁
boolean res = rwlock.readLock().tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 或
boolean res = rwlock.writeLock().tryLock(100, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
...
lock.unlock();
IndexController中的两个方法:
@GetMapping("read")
public ResponseVo<String> read(){
String msg = indexService.readLock();
return ResponseVo.ok(msg);
}
@GetMapping("write")
public ResponseVo<String> write(){
String msg = indexService.writeLock();
return ResponseVo.ok(msg);
}
IndexService接口方法:注意保证锁的名称一致,才能使用同一把锁
public String readLock() {
// 初始化读写锁
RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redissonClient.getReadWriteLock("readwriteLock");
RLock rLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); // 获取读锁
rLock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 加10s锁
String msg = this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("msg");
//rLock.unlock(); // 解锁
return msg;
}
public String writeLock() {
// 初始化读写锁
RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redissonClient.getReadWriteLock("readwriteLock");
RLock rLock = readWriteLock.writeLock(); // 获取写锁
rLock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 加10s锁
this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("msg", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
//rLock.unlock(); // 解锁
return "成功写入了内容。。。。。。";
}
打开开两个浏览器窗口测试:
-
同时访问写:一个写完之后,等待一会儿(约10s),另一个写开始
-
同时访问读:不用等待
-
先写后读:读要等待(约10s)写完成
-
先读后写:写要等待(约10s)读完成
1.4. 信号量(Semaphore)和闭锁(CountDownLatch)
基于Redis的Redisson的分布式信号量(Semaphore)Java对象RSemaphore采用了与java.util.concurrent.Semaphore相似的接口和用法。
RSemaphore semaphore = redisson.getSemaphore("semaphore");
semaphore.acquire();
//或
semaphore.acquire(23);
semaphore.tryAcquire();
semaphore.tryAcquire(23, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 释放资源
semaphore.release();
基于Redisson的Redisson分布式闭锁(CountDownLatch)Java对象RCountDownLatch采用了与java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch相似的接口和用法。
RCountDownLatch latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("anyCountDownLatch");
latch.trySetCount(1);
latch.await();
// 在其他线程或其他JVM里
RCountDownLatch latch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("anyCountDownLatch");
latch.countDown();
需要两个线程,一个等待。一个计数countDown
演示代码
IndexController:
/**
* 等待
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("latch")
public ResponseVo<Object> countDownLatch(){
String msg = indexService.latch();
return ResponseVo.ok(msg);
}
/**
* 计数
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("out")
public ResponseVo<Object> out(){
String msg = indexService.countDown();
return ResponseVo.ok(msg);
}
IndexService:
public String latch() {
RCountDownLatch countDownLatch = this.redissonClient.getCountDownLatch("countdown");
try {
countDownLatch.trySetCount(6);
countDownLatch.await();
return "关门了。。。。。";
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public String countDown() {
RCountDownLatch countDownLatch = this.redissonClient.getCountDownLatch("countdown");
countDownLatch.countDown();
return "出来了一个人。。。";
}
重启测试,打开两个页面:当第二个请求执行6次之后,第一个请求才会执行。

2. 分布式锁 + AOP实现缓存
随着业务中缓存及分布式锁的加入,业务代码变的复杂起来,除了需要考虑业务逻辑本身,还要考虑缓存及分布式锁的问题,增加了程序员的工作量及开发难度。而缓存的玩法套路特别类似于事务,而声明式事务就是用了aop的思想实现的。

- 以 @Transactional 注解为植入点的切点,这样才能知道@Transactional注解标注的方法需要被代理。
- @Transactional注解的切面逻辑类似于@Around
模拟事务,缓存可以这样实现:
- 自定义缓存注解@GmallCache(类似于事务@Transactional)
- 编写切面类,使用环绕通知实现缓存的逻辑封装
定义一个注解:GmallCache
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface GmallCache {
/**
* 缓存的前缀
* @return
*/
String prefix() default "";
/**
* 设置缓存的有效时间
* 单位:分钟
* @return
*/
int timeout() default 5;
/**
* 防止雪崩设置的随机值范围
* @return
*/
int random() default 5;
/**
* 防止击穿,分布式锁的key
* @return
*/
String lock() default "lock";
}
定义一个切面类加强注解:
@Aspect
@Component
public class GmallCacheAspect {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
/**
* joinPoint.getArgs(); 获取方法参数
* joinPoint.getTarget().getClass(); 获取目标类
* @param joinPoint
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Around("@annotation(com.atguigu.gmall.index.config.GmallCache)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 获取切点方法的签名
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();
// 获取方法对象
Method method = signature.getMethod();
// 获取方法上指定注解的对象
GmallCache annotation = method.getAnnotation(GmallCache.class);
// 获取注解中的前缀
String prefix = annotation.prefix();
// 获取方法的参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
String param = Arrays.asList(args).toString();
// 获取方法的返回值类型
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
// 拦截前代码块:判断缓存中有没有
String json = this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(prefix + param);
// 判断缓存中的数据是否为空
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(json)){
return JSON.parseObject(json, returnType);
}
// 没有,加分布式锁
String lock = annotation.lock();
RLock rLock = this.redissonClient.getLock(lock + param);
rLock.lock();
// 判断缓存中有没有,有直接返回(加锁的过程中,别的请求可能已经把数据放入缓存)
String json2 = this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(prefix + param);
// 判断缓存中的数据是否为空
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(json2)){
rLock.unlock();
return JSON.parseObject(json2, returnType);
}
// 执行目标方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed(joinPoint.getArgs());
// 拦截后代码块:放入缓存 释放分布锁
int timeout = annotation.timeout();
int random = annotation.random();
this.redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(prefix + param, JSON.toJSONString(result), timeout + new Random().nextInt(random), TimeUnit.MINUTES);
rLock.unlock();
return result;
}
}
具体使用
在IndexServiceImpl的querySubCategories方法中使用注解,完成数据缓存功能:
@GmallCache(prefix = "index:category:", timeout = 14400, random = 3600, lock = "lock")
public List<CategoryEntity> queryLvl2CategoriesWithSub(Long pid) {
ResponseVo<List<CategoryEntity>> listResp = this.gmallPmsFeign.querySubCategory(pid);
List<CategoryEntity> categoryVOS = listResp.getData();
return categoryVOS;
}
该方法的实现只需要考虑业务逻辑本身,使用注解即可完成缓存功能。
测试:
