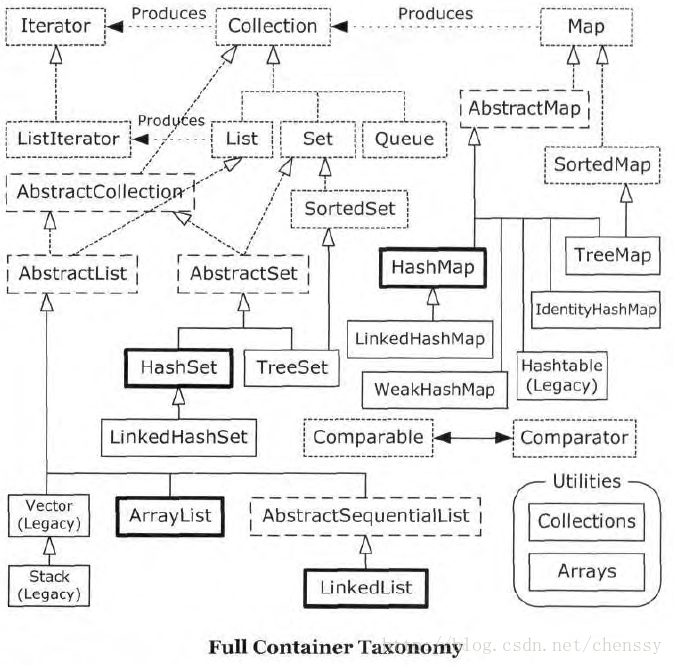
Java 提供的 集合类都在 Java.utils 包下,其中包含了很多 List, Set, Map, Queue… 它们的关系如下面这张类图所示:
?可以看到,Java 集合主要分为两类:Collection 和 Map. 而 Collection 又继承了 Iterable< E > 接口,Iterable 接口内只有一个 iterator 方法,返回一个 Iterator 迭代器:
public interface Iterable<T> {
? ? /**
? ? * Returns an {@link Iterator} for the elements in this object.
? ? *
? ? * @return An {@code Iterator} instance.
? ? */
? ? Iterator<T> iterator();
}
本篇文章将介绍 Iterator 迭代器。 在介绍 Iterator 之前不得不提一下被它替代的 Enumeration< E >:
Enumeration< E >
public interface Enumeration<E> {
/**
?* Returns whether this {@code Enumeration} has more elements.
?*
?* @return {@code true} if there are more elements, {@code false} otherwise.
?* @see #nextElement
?*/
? ? public boolean hasMoreElements();
/**
?* Returns the next element in this {@code Enumeration}.
?*
?* @return the next element..
?* @throws NoSuchElementException
?* if there are no more elements.
?* @see #hasMoreElements
?*/
? ? public E nextElement();
}
Enumeration 是一个很古老的迭代器,有两个方法:
hasMoreElements() //是否还有元素
nextElement() //返回下一个元素
Enumeration 的实现类会生成一系列子元素,比如 StringTokenizer;通过Enumeration 的上述
两个方法可以用来遍历它实现类的元素,比如这样:
? ? //StringTokenizer : 切割, Breaks a string into tokens; new code should probably use {@link String#split}.
? ? Enumeration enumeration = new StringTokenizer("A-B-C", "-");
? ? while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()){
? ? ? ? System.out.println(enumeration.nextElement());
? ? }
运行结果:

Enumeration 接口早在 JDK 1.0 时就推出了,当时比较早的容器比如 Hashtable, Vector 都使用它
作为遍历工具。
那 Enumeration 为什么会被废弃呢?
根据官方文档:
NOTE: The functionality of this interface is duplicated by the Iterator interface. In addition, Iterator
adds an optional remove operation, and has shorter method names. New implementations
should consider using Iterator in preference to Enumeration.
可以大胆猜一下,应该是当初设计没有考虑全,只有两个方法,而且名字还太长了 - -。 后来在
JDK 1.2 推出了 Iterator 替代它的功能。虽然 Enumeration 在 JDK 1.5 后增加了泛型的应用,依旧
大势已去。
Iterator
Iterator 是一个集合上的迭代器,用来替代 Enumeration 进行遍历、迭代。
它 和 Enumeration 有什么不同呢?
根据官方文档:
Iterators differ from enumerations in two ways:Iterators allow the caller to remove elements from
the underlying collection during the iteration with well-defined semantics.Method names have
been improved.
哈哈首先是名字缩短了,看来大家都懒得输入那么长的方法名。 其次是 允许调用者在遍历过程中
语法正确地删除元素。
注意这个 [语法正确],事实上我们在使用 Iterator 对容器进行迭代时如果修改容器 可能会报
ConcurrentModificationException 的错。官方称这种情况下的迭代器是 fail-fast 迭代器。
fail-fast 与 ConcurrentModificationException
以 ArrayList 为例,在调用迭代器的 next,remove 方法时:
?public E next() {
? ? ? ? if (expectedModCount == modCount) {
? ? ? ? ? ? try {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? E result = get(pos + 1);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? lastPosition = ++pos;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? return result;
? ? ? ? ? ? } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? throw new NoSuchElementException();
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
? ? }
? ? public void remove() {
? ? ? ? if (this.lastPosition == -1) {
? ? ? ? ? ? throw new IllegalStateException();
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? if (expectedModCount != modCount) {
? ? ? ? ? ? throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? try {
? ? ? ? ? ? AbstractList.this.remove(lastPosition);
? ? ? ? } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
? ? ? ? ? ? throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? expectedModCount = modCount;
? ? ? ? if (pos == lastPosition) {
? ? ? ? ? ? pos--;
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? lastPosition = -1;
? ? }
可以看到在调用迭代器的 next,remove 方法时都会比较 expectedModCount 和 modCount 是
否相等,如果不相等就会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException ,也就是成为了 fail-fast。
而 modCount 在 add, clear, remove 时都会被修改:
public boolean add(E object) {
? ? //...
? ? modCount++;
? ? return true;
}
public void clear() {
? ? if (size != 0) {
? ? ? ? //...
? ? ? ? modCount++;
? ? }
}
public boolean remove(Object object) {
? ? Object[] a = array;
? ? int s = size;
? ? if (object != null) {
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? if (object.equals(a[i])) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? //...
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? modCount++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? return true;
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? }
? ? } else {
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? if (a[i] == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? //...
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? modCount++;
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? return true;
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
? ? return false;
}
因此我们知道了 fail-fast 即 ConcurrentModificationException 出现的原因,怎么解决呢?
方法一:
用 CopyOnWriteArrayList,ConcurrentHashMap 替换 ArrayList, HashMap,它们的功能和
名字一样,在写入时会创建一个 copy,然后在这个 copy 版本上进行修改操作,这样就不会影响
原来的迭代。不过坏处就是浪费内存。
方法二:
使用 Collections.synchronizedList 加 同步锁,不过这样有点粗暴。
可能得方法三(待考究,目前我还没搞清楚):
在学习 ListView 中的观察者模式 时,我注意到 DataSetObservable 的 notifyChanged 方法中
有如下注释:
public void notifyChanged() {
? ? synchronized(mObservers) {
? ? ? ? // since onChanged() is implemented by the app, it could do anything, including
? ? ? ? // removing itself from {@link mObservers} - and that could cause problems if
? ? ? ? // an iterator is used on the ArrayList {@link mObservers}.
? ? ? ? // to avoid such problems, just march thru the list in the reverse order.
? ? ? ? for (int i = mObservers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
? ? ? ? ? ? mObservers.get(i).onChanged();
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
}
to avoid such problems, just march thru the list in the reverse order
为了避免影响 ArrayList 迭代,倒序处理。 待考究,目前我还没搞清楚。
不过意外的发现了,原来 for-each 的循环内部也是使用了 Iterator 来遍历Collection,它也调用了 Iterator.next(),所以在修改元素时会检查(元素的)变化并抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
在从任何 Collection中删除对象时总要使用 Iterator 的remove 方法, for-each 循环只是标准 Iterator 代码标准用法之上的一种语法糖(syntactic sugar)而已。
差点忘了 Iterator 的使用
所有 Collection 的子类都有 iterator() 方法来获得 Iterator,通过 Iterator 的标准操作方法,可以让我们不必关心具体集合的类型,从而避免向客户端暴露出集合的内部结构。
不使用 Iterator 遍历集合是这样的:
? ? for(int i=0; i<集合的大小;i++){ ?
? ? ? ? // ...?
? ? }?
使用 Iterator 遍历集合是这样的:
? ? Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
? ? while (iterator.hasNext()){
? ? ? ? System.out.println(iterator.next());
? ? }
对比而言,后者客户端代码与具体集合类型耦合性弱,复用性更强。缺点就是无法获取指定的元素,只能挨个遍历。
Thanks
?
?