Lombok 一个充满争议性的插件,不能否认它的神奇,大量的让我们偷懒了,不过在减少代码量的同时,当某一个模块使用 Lombok 后,其余依赖此模块的其他代码都需要引入 Lombok 依赖。实际应用时酌情使用
简介
Project Lombok is a java library that automatically plugs into your editor and build tools, spicing up your java.
Never write another getter or equals method again, with one annotation your class has a fully featured builder, Automate your logging variables, and much more.
Lombok 是一种 Java 实用工具,可用来帮助开发人员消除 Java 的冗长,尤其是对于简单的 Java 对象(POJO)。它通过注释实现这一目的。通过在开发环境中实现 Lombok,开发人员可以节省构建诸如 hashCode() 和 equals() 这样的方法以及以往用来分类各种 accessor 和 mutator 的大量时间。
安装
IDEA 安装 Lombok 插件
1、Setting → Plugin,搜索 Lombok 安装即可
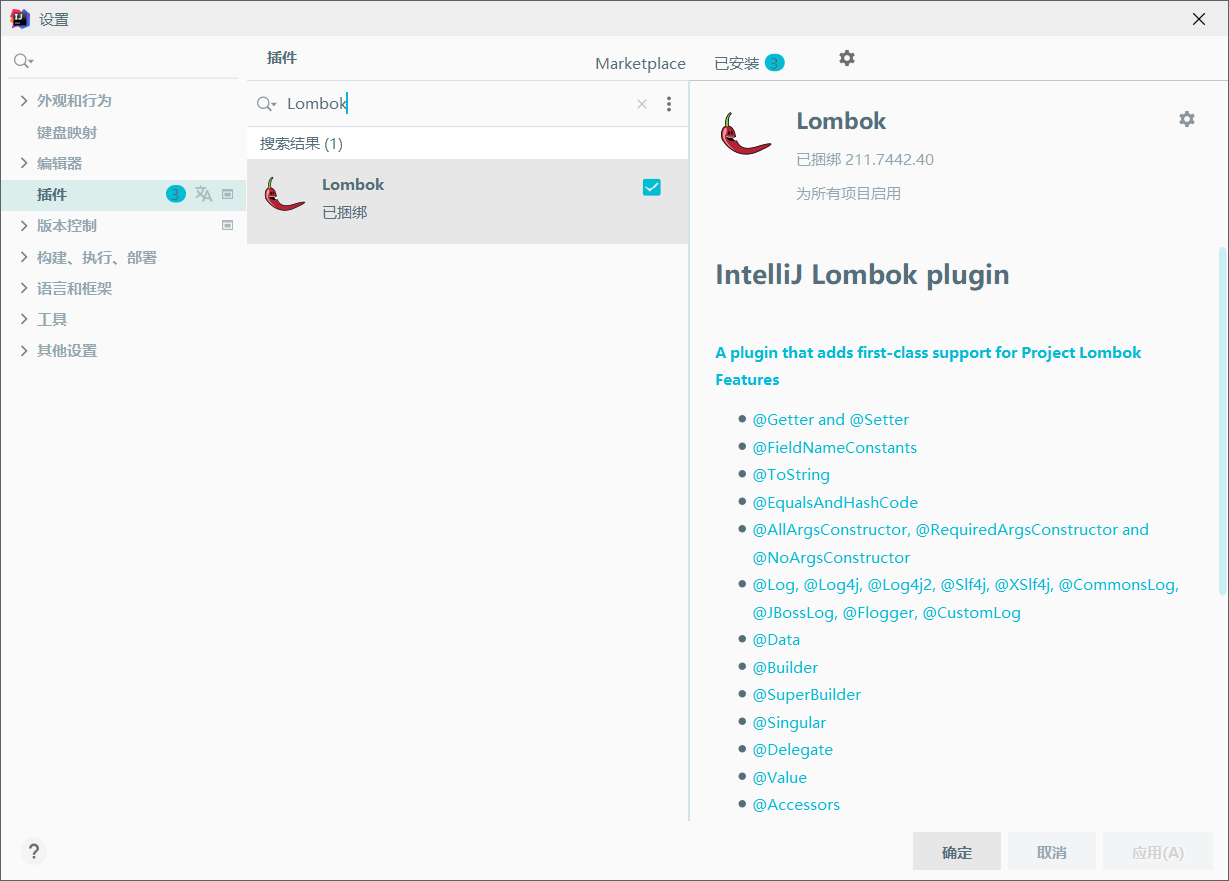
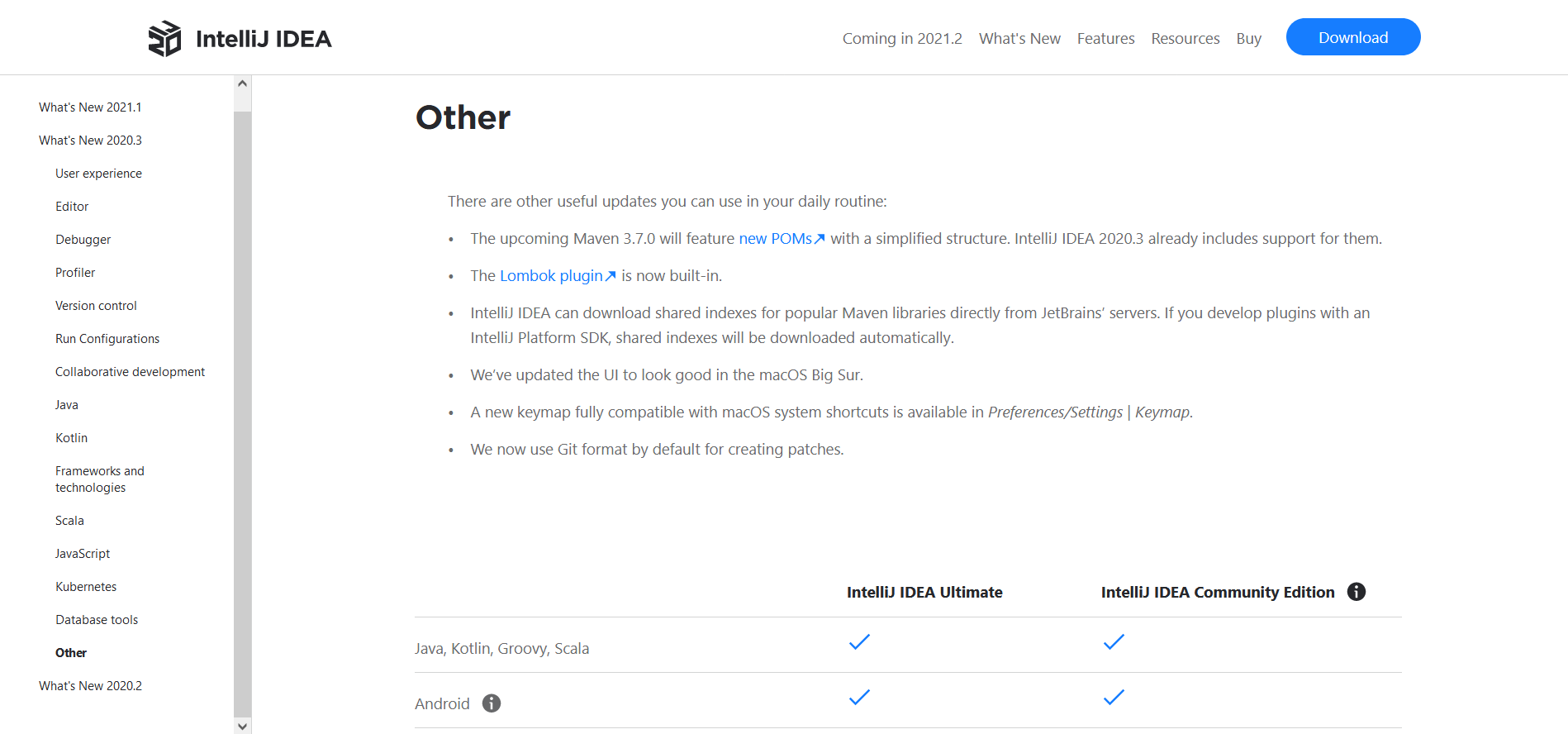
IDEA 2020.3 版本开始已经内置 Lombok 插件,
2、导入 Lombok 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
Eclipse 安装 Lombok 插件
1、官网下载 jar 包:https://projectlombok.org/download
2、双击 lombak.jar 包
3、点击 Install / Update
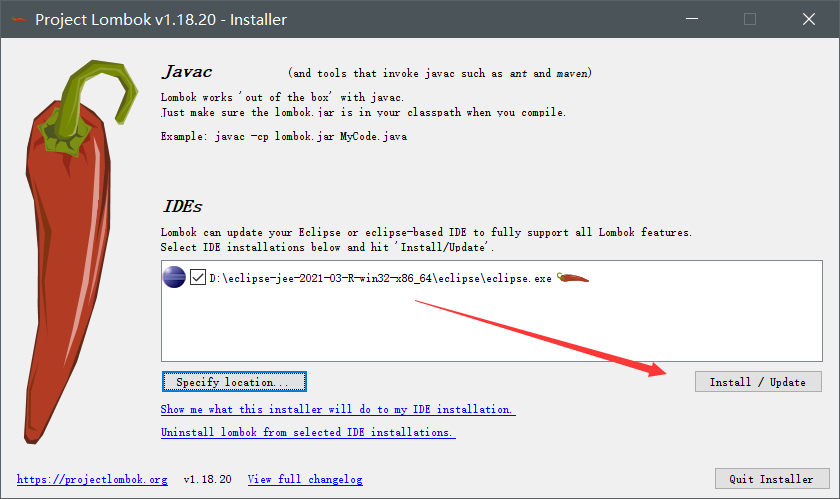
4、点击Quit Installer,完成安装

5、安装完成之后,确认 eclipse 安装路径下是否多了一个 lombok.jar 包,并且配置文件 eclipse.ini 中是否添加了如下内容:
-javaagent:D:\eclipse-jee-2021-03-R-win32-x86_64\eclipse\lombok.jar
Lombok 常用注解说明
@NonNull
@Cleanup
@Getter and @Setter
@AllArgsConstructor
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
@Data
@NonNull
用在成员方法或者构造方法的参数前面,会自动产生一个关于此参数的非空检查,如果参数为空,则抛出一个空指针异常
import lombok.NonNull;
public class NonNullExample extends Something {
private String name;
public NonNullExample(@NonNull Person person) {
this.name = person.getName();
}
}
相当于
import lombok.NonNull;
public class NonNullExample extends Something {
private String name;
public NonNullExample(@NonNull Person person) {
if (person == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("person is marked @NonNull but is null");
}
this.name = person.getName();
}
}
@Cleanup
用在变量前面,可以保证此变量代表的资源会被自动关闭,默认是调用资源的close()方法
import lombok.Cleanup;
import java.io.*;
public class CleanupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
@Cleanup InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
@Cleanup OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);
byte[] b = new byte[10000];
while (true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) break;
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
}
}
相当于
import java.io.*;
public class CleanupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
try {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);
try {
byte[] b = new byte[10000];
while (true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) break;
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
} finally {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
} finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
}
}
}
@Getter and @Setter
在成员变量前面,相当于为成员变量生成对应的 get 和 set 方法,还可以为生成的方法指定访问修饰符,默认为public
在类上,可以为此类里的所有非静态成员变量生成对应的 get 和 set 方法。
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
public class GetterSetterExample {
@Getter
@Setter
private int age;
@Setter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
private String name;
}
相当于
public class GetterSetterExample {
private int age;
private String name;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
protected void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
@AllArgsConstructor / @NoArgsConstructor
在类上使用,为该类产生全参构造方法和无参构造方法
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
}
相当于
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name, String password) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
}
@ToString
在类上使用,生成 toString() 方法
- @ToString.Exclude 排除指定字段
- @ToString.Include 包含指定字段
import lombok.ToString;
@ToString
public class User {
@ToString.Exclude
private int id;
private String name;
}
相当于
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public User() {
}
public String toString() {
return "User(name=" + this.name + ")";
}
}
@EqualsAndHashCode
生成 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法,以及 canEqual() 方法用来判断某个对象是否是当前类的实例,生成方法时只会使用类中的 非静态 和 非transient 成员变量
- @EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude 排除指定字段
- @EqualsAndHashCode.Include 包含指定字段
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
}
相当于
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public User() {
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
} else {
User other = (User)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else if (this.id != other.id) {
return false;
} else {
Object this$name = this.name;
Object other$name = other.name;
if (this$name == null) {
if (other$name != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof User;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
int result = result * 59 + this.id;
Object $name = this.name;
result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
return result;
}
}
@Data
包含了 @Getter and @Setter 、@ToString、@EqualsAndHashCode、@NoArgsConstructor
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
}
相当于
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public User() {
}
public int getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
} else {
User other = (User)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else if (this.getId() != other.getId()) {
return false;
} else {
Object this$name = this.getName();
Object other$name = other.getName();
if (this$name == null) {
if (other$name != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof User;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
int result = result * 59 + this.getId();
Object $name = this.getName();
result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
return "User(id=" + this.getId() + ", name=" + this.getName() + ")";
}
}