引言
? ? ? ? 在这个信息化时代,我们如何去处理日益繁杂的文件系统呢?CV?还是文件夹,都不对,作为一个准程序员,我们应该学习如何利用流去处理文件,并且利用流去做一系列的操作,比如数据永久保存,不随着程序进程结束而结束,下面就随我一起进入这美丽的IO流世界吧!

?
目录
目录
一、File类
? ? ? ? 学习IO流,首先我们应该学习一个叫做File的类,什么是File类呢?
????????- Java File(文件)类以抽象的方式代表文件名和目录路径名。该类主要用于文件和目录的创建、文件的查找和文件的删除等。?
????????- 对于File而言,其封装的并不是一个真正存在的文件,仅仅是一个路径名而已。它可以是存在的,也可以是不存在的。将来是要通过具体的操作把这个路径的内容转换为具体存在的
? ? ? ? 既然是类,就有应该有相应的构造方法供我们使用,以下是File类的常用构造方法
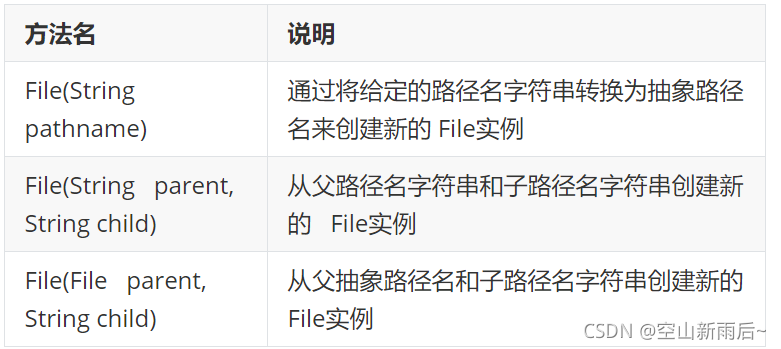
1.1File类的构造方法
????
?代码演示:
????????
public class FileDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//File(String pathname):通过将给定的路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建新的 File实例。
File f1 = new File("E:\\java\\Demo");
System.out.println(f1);
//File(String parent, String child):从父路径名字符串和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。
File f2 = new File("E:\\java","Demo");
System.out.println(f2);
//File(File parent, String child):从父抽象路径名和子路径名字符串创建新的 File实例。
File f3 = new File("E:\\java");
File f4 = new File(f3,"Demo");
System.out.println(f4);
//你甚至还可以这样
String s = "hello";
File f5 = new File("E:\\java",s + ".txt");
System.out.println(f5);
}
}
/*
输出结果
E:\java\Demo
E:\java\Demo
E:\java\Demo
E:\java\hello.txt
*/?除了构造方法,当然还有很多该类提供给我们的方法,
?
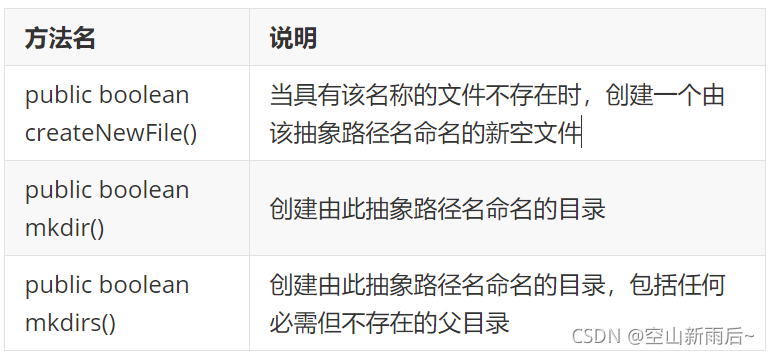
1.2File类创建功能
?? ?方法分类
? ? ? ?
??
?实例代码
?? ??
? ?public class FileDemo02 {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
? ? ? ? //需求1:我要在E:\\itcast目录下创建一个文件java.txt
? ? ? ? File f1 = new File("E:\\itcast\\java.txt");
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f1.createNewFile());
? ? ? ? System.out.println("--------");
?
? ? ? ? //需求2:我要在E:\\itcast目录下创建一个目录JavaSE
? ? ? ? File f2 = new File("E:\\itcast\\JavaSE");
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f2.mkdir());
? ? ? ? System.out.println("--------");
? ? ? ? //需求3:我要在E:\\itcast目录下创建一个多级目录JavaWEB\\HTML
? ? ? ? File f3 = new File("E:\\itcast\\JavaWEB\\HTML");
// ? ? ? ?System.out.println(f3.mkdir());
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f3.mkdirs());
? ? ? ? System.out.println("--------");
? ? ? ? //需求4:我要在E:\\itcast目录下创建一个文件javase.txt
? ? ? ? File f4 = new File("E:\\itcast\\javase.txt");
// ? ? ? ?System.out.println(f4.mkdir());
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f4.createNewFile());
? ? }
}
?? ?注意
?? ??? ?如果文件存在,就不创建文件,并返回false,如果文件不存在,就创建文件,并返回true,创建目录(文件夹)同理
?? ??? ?如果我在创建文件时调用了创建目录的方法,那么会默认创建目录,并且如果我再次创建该同名文件,是不成功的,必须先删除同名目录,才能再次创建文件。
?? ??? ?在创建多级目录时如果调用mkdir()方法,是无法创建成功的
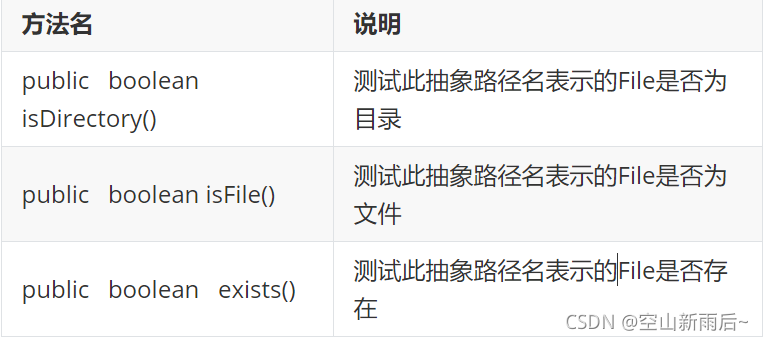
1.3File类判断和获取功能
?? ?判断功能
? ? ? ??
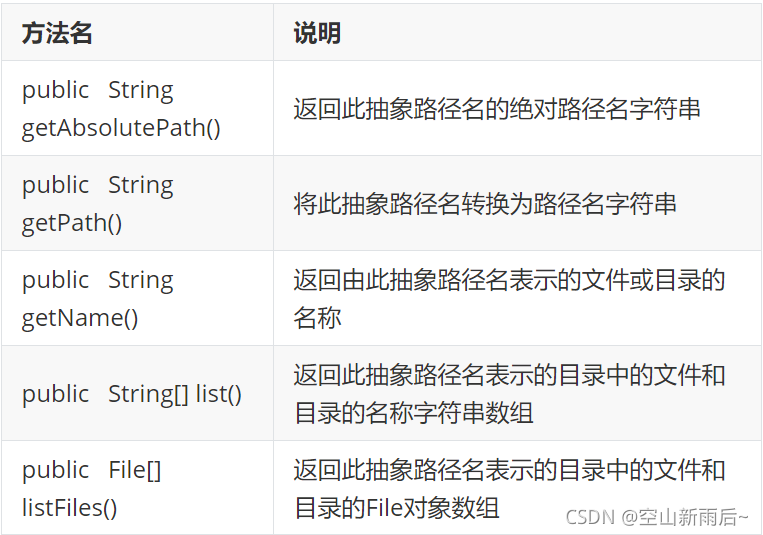
?? ?获取功能
? ? ? ??
?? ?
示例代码
?? ??? ?
public class FileDemo04 {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ? //创建一个File对象
? ? ? ? File f = new File("myFile\\java.txt");
// ? ? ? ?public boolean isDirectory():测试此抽象路径名表示的File是否为目录
// ? ? ? ?public boolean isFile():测试此抽象路径名表示的File是否为文件
// ? ? ? ?public boolean exists():测试此抽象路径名表示的File是否存在
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f.isDirectory());
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f.isFile());
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f.exists());
// ? ? ? ?public String getAbsolutePath():返回此抽象路径名的绝对路径名字符串
// ? ? ? ?public String getPath():将此抽象路径名转换为路径名字符串
// ? ? ? ?public String getName():返回由此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录的名称
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f.getPath());
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f.getName());
? ? ? ? System.out.println("--------");
// ? ? ? ?public String[] list():返回此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录的名称字符串数组
// ? ? ? ?public File[] listFiles():返回此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录的File对象数组
? ? ? ? File f2 = new File("E:\\myfile");
? ? ? ? String[] strArray = f2.list();
? ? ? ? for(String str : strArray) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println(str);
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? System.out.println("--------");
? ? ? ? File[] fileArray = f2.listFiles();
? ? ? ? for(File file : fileArray) {
// ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(file);
// ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(file.getName());
? ? ? ? ? ? if(file.isFile()) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println(file.getName());
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
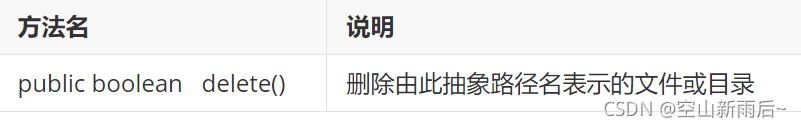
}1.4File类删除功能
?? ?方法分类
?? ??? 
?? ?示例代码
?? ???
?public class FileDemo03 {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// ? ? ? ?File f1 = new File("E:\\itcast\\java.txt");
? ? ? ? //需求1:在当前模块目录下创建java.txt文件
? ? ? ? File f1 = new File("myFile\\java.txt");
// ? ? ? ?System.out.println(f1.createNewFile());
?
? ? ? ? //需求2:删除当前模块目录下的java.txt文件
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f1.delete());
? ? ? ? System.out.println("--------");
? ? ? ? //需求3:在当前模块目录下创建itcast目录
? ? ? ? File f2 = new File("myFile\\itcast");
// ? ? ? ?System.out.println(f2.mkdir());
? ? ? ? //需求4:删除当前模块目录下的itcast目录
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f2.delete());
? ? ? ? System.out.println("--------");
? ? ? ? //需求5:在当前模块下创建一个目录itcast,然后在该目录下创建一个文件java.txt
? ? ? ? File f3 = new File("myFile\\itcast");
// ? ? ? ?System.out.println(f3.mkdir());
? ? ? ? File f4 = new File("myFile\\itcast\\java.txt");
// ? ? ? ?System.out.println(f4.createNewFile());
? ? ? ? //需求6:删除当前模块下的目录itcast
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f4.delete());
? ? ? ? System.out.println(f3.delete());
? ? }
}
?? ?绝对路径和相对路径的区别
?? ??? ?- - 绝对路径:完整的路径名,不需要任何其他信息就可以定位它所表示的文件。例如:E:\itcast\java.txt
?? ??? ? ?- 相对路径:必须使用取自其他路径名的信息进行解释。例如:myFile\\java.txt
?二、IO流
? ? ? ? 学完如何对文件进行处理,我们就可以去了解流,因为文件操作是基础。
2.1、IO流的定义
????????一个流可以理解为一个数据的序列。输入流表示从一个源读取数据,输出流表示向一个目标写数据。Java 为 I/O 提供了强大的而灵活的支持,使其更广泛地应用到文件传输和网络编程中。
2.2、IO 流的分类
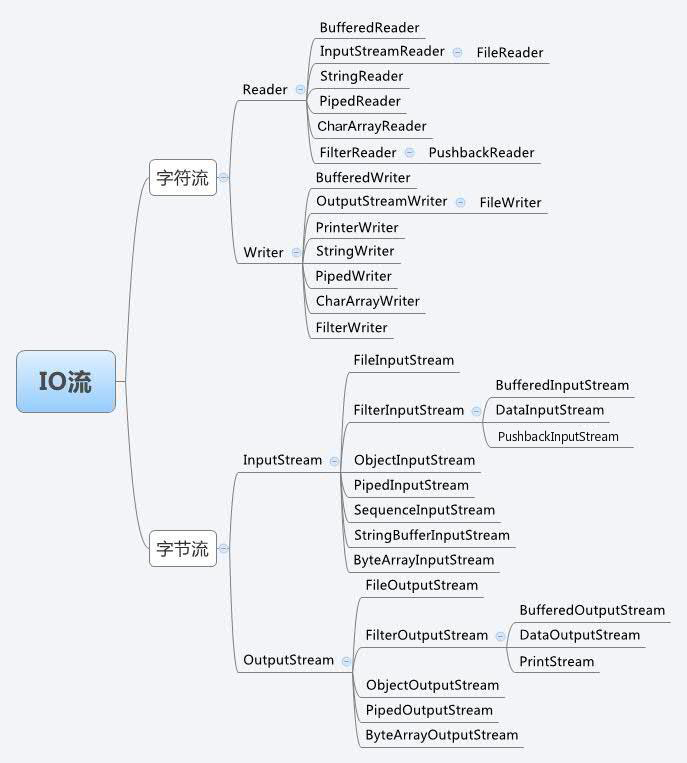
?????????可以看到其内容是十分繁多的,我们暂时只了解字符、字节的输入,输出流,以及他们的缓冲流即可。
2.3.1、字节输入流(FileInputStream)
????????该流用于从文件读取数据,它的对象可以用关键字 new 来创建。有多种构造方法可用来创建对象。可以使用字符串类型的文件名来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件:
InputStream f = new FileInputStream("C:\\java\\hello");????????也可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件。我们首先得使用 File() 方法来创建一个文件对象:
File f = new File("C:\\java\\hello");
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(f);对于该流,java提供了以下方法:
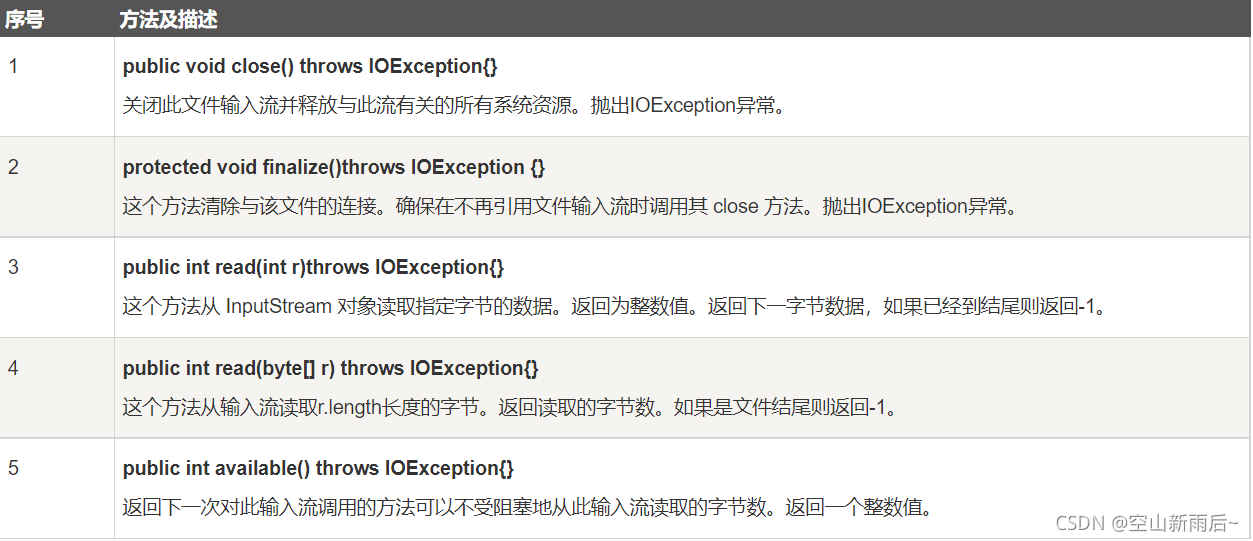
?????????注意:我们创建流,完成相关操作之后,需要close()方法释放资源,一定要做哦!
一次读取一个字节public int read(Int r)throws IOException{}示例代码
public class FileInputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\Java\\08.阶段八之文件IO流\\01_File类&递归&字节流\\案例\\学员练习代码\\myByteStream\\fos.txt");
// byte[] bys = new byte[5];
//第一次读数据
// int get = fis.read(bys);
// System.out.println(get);
// System.out.println(new String(bys));
//
// //第二次读数据
// get = fis.read(bys);
// System.out.println(get);
// System.out.println(new String(bys));
//
//
// //第三次读数据
// get = fis.read(bys);
// System.out.println(get);
// System.out.println(new String(bys));
//标准读取格式,一次读取一个字节
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int get ;
while((get = fis.read(bys)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bys,0,get));
}
//3:释放资源
fis.close();
}
}
一次读取一个字节数组
public class FileInputStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\Java\\08.阶段八之文件IO流\\01_File类&递归&字节流\\案例\\学员练习代码\\myByteStream\\fos.txt");
// int get = fis.read();
// System.out.println(get);
// System.out.println((char)get);
//
// get = fis.read();
// System.out.println(get);
// System.out.println((char)get);
int get;
while((get = fis.read())!= -1) {
System.out.print((char)get);
}
fis.close();
}
}
2.3.2字节输出流:FileOutputStream
? ? ? ? 我们可以从文件中读取数据,那么也可以从文件中写入数据,这个就是我们字节输入流:
????????该类用来创建一个文件并向文件中写数据。如果该流在打开文件进行输出前,目标文件不存在,那么该流会创建该文件。有两个构造方法可以用来创建 FileOutputStream 对象。
????????使用字符串类型的文件名来创建一个输出流对象:
OutputStream f = new FileOutputStream("C:\\java\\hello")????????也可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输出流来写文件。我们首先得使用File()方法来创建一个文件对象:
File f = new File("C:\\java\\hello");
OutputStream fOut = new FileOutputStream(f);?同样,该流的方法:
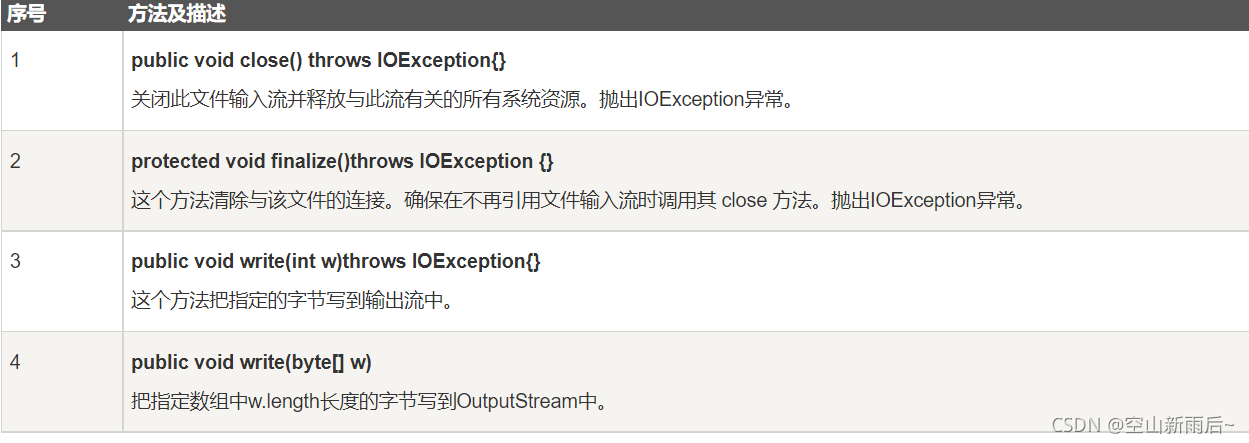
字节流写数据的三种方式:
????????
public class FileOutputStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//FileOutputStream(String name):创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myByteStream\\fos.txt");
//new File(name)
// FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("myByteStream\\fos.txt"));
//FileOutputStream(File file):创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件
// File file = new File("myByteStream\\fos.txt");
// FileOutputStream fos2 = new FileOutputStream(file);
// FileOutputStream fos2 = new FileOutputStream(new File("myByteStream\\fos.txt"));
//void write(int b):将指定的字节写入此文件输出流
// fos.write(97);
// fos.write(98);
// fos.write(99);
// fos.write(100);
// fos.write(101);
// void write(byte[] b):将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此文件输出流
// byte[] bys = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101};
//byte[] getBytes():返回字符串对应的字节数组
byte[] bys = "abcde".getBytes();
// fos.write(bys);
//void write(byte[] b, int off, int len):将 len字节从指定的字节数组开始,从偏移量off开始写入此文件输出流
// fos.write(bys,0,bys.length);
fos.write(bys,1,3);
//释放资源
fos.close();
}
}2.3.3、字节流复制文件的案例
?? ?案例需求
?? ??? ?把“E:\\itcast\\窗里窗外.txt”复制到模块目录下的“窗里窗外.txt”
?? ?实现步骤
?? ??? ?- 复制文本文件,其实就把文本文件的内容从一个文件中读取出来(数据源),然后写入到另一个文件中(目的地)
?? ??? ?- 数据源:
?? ??? ??? ? ???? ?E:\\itcast\\窗里窗外.txt --- 读数据 --- InputStream --- FileInputStream?
?? ??? ?- 目的地:
?? ??? ??? ? ???? ?myByteStream\\窗里窗外.txt --- 写数据 --- OutputStream --- FileOutputStream
?? ?代码实现:
? ?public class CopyTxtDemo {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
? ? ? ? //根据数据源创建字节输入流对象
? ? ? ? FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\itcast\\窗里窗外.txt");
? ? ? ? //根据目的地创建字节输出流对象
? ? ? ? FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myByteStream\\窗里窗外.txt");
? ? ? ? //读写数据,复制文本文件(一次读取一个字节,一次写入一个字节)
? ? ? ? int by;
? ? ? ? while ((by=fis.read())!=-1) {
? ? ? ? ? ? fos.write(by);
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? //释放资源
? ? ? ? fos.close();
? ? ? ? fis.close();
? ? }
}2.4字符流? ? ? ?
????????2.4.1为什么会出现字符流
?? ?字符流的介绍
?? ??? ?由于字节流操作中文不是特别的方便,所以Java就提供字符流
?? ??? ?字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表
?? ?中文的字节存储方式
?? ??? ?用字节流复制文本文件时,文本文件也会有中文,但是没有问题,原因是最终底层操作会自动进行字节拼接成中文,如何识别是中文的呢?
?? ??? ?汉字在存储的时候,无论选择哪种编码存储,第一个字节都是负数
?? ?示例代码
?? ???
?import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
? ? 需求:字节流读文本文件数据
?*/
public class FileInputStreamDemo {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
? ? ? ? FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\Java\\08.阶段八之文件IO流\\02_字符流&字节缓冲流\\案例\\学员练习代码\\myCharStream\\abc.txt");
? ? ? ? int by;
? ? ? ? while ((by = fis.read()) != -1) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.print((char) by);
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? //abc??-??
? ? ? ? //输出乱码的原因是因为中文的编码方式有两种:
// ? ? ? ? ? ?GBK编码格式一个中文字符会占用两个字节
// ? ? ? ? ? ?UTF-8编码格式会占用三个字节,
// ? ? ? ? ? ?而我们用循环输出是一个字节一个字节的读,因此会导致字节分离,读出乱码,而通过复制文本文件是因为系统自动帮我们拼接了字节,
? ? ? ? String s = "sss";
? ? ? ? String ss = "中国";
? ? ? ? byte[] bys = ss.getBytes("GBK");//[-42, -48, -71, -6]
? ? ? ? byte[] bydd = ss.getBytes("UTF-8");//[-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67]
? ? ? ? System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bydd));
? ? ? ? fis.close();
? ? }
}????????当我们使用指定编码集时要注意,写入是什么编码,读取也要什么编码,否则可能会出现乱码问题,idea工具默认编码是UTF-8,各位用的其他编辑器也需要注意哦。
? ? ? ? 2.4.2、编码表
?? ?????????什么是字符集:?是一个系统支持的所有字符的集合,包括各国家文字、标点符号、图形符号、数字等
?? ??? ?计算机要准确的存储和识别各种字符集符号,就需要进行字符编码,一套字符集必然至少有一套字符编码。常见字符集有ASCII字符集、GBXXX字符集、Unicode字符集等
?? ?常见的字符集
?? ??? ?- ASCII字符集:
?? ??? ??? ?ASCII:是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,用于显示现代英语,主要包括控制字符(回车键、退格、换行键等)和可显示字符(英文大小写字符、阿拉伯数字和西文符号) ,基本的ASCII字符集,使用7位表示一个字符,共128字符。ASCII的扩展字符集使用8位表示一个字符,共256字符,方便支持欧洲常用字符。是一个系统支持的所有字符的集合,包括各国家文字、标点符号、图形符号、数字等
?? ??? ?- GBXXX字符集:
?? ??? ??? ? ?GBK:最常用的中文码表。是在GB2312标准基础上的扩展规范,使用了双字节编码方案,共收录了21003个汉字,完全兼容GB2312标准,同时支持繁体汉字以及日韩汉字等
?? ??? ?- Unicode字符集:
?? ??? ??? ? ?UTF-8编码:可以用来表示Unicode标准中任意字符,它是电子邮件、网页及其他存储或传送文字的应用 中,优先采用的编码。互联网工程工作小组(IETF)要求所有互联网协议都必须支持UTF-8编码。它使用一至四个字节为每个字符编码
?? ??? ? ?编码规则:?
?? ??? ??? ? ? ?128个US-ASCII字符,只需一个字节编码
?? ??? ??? ? ? ?拉丁文等字符,需要二个字节编码
?? ??? ??? ? ? ?大部分常用字(含中文),使用三个字节编码
?? ??? ??? ? ? ?其他极少使用的Unicode辅助字符,使用四字节编码
2.4.3、字符串中的编码解码问题
?? ?相关方法
?? ??? ?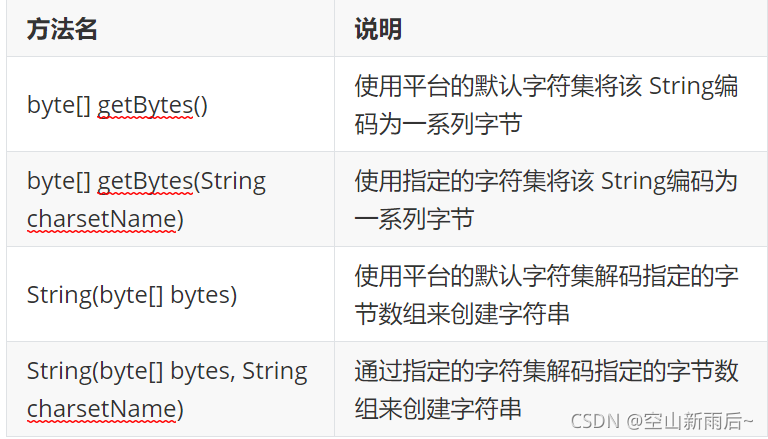 ?? ?代码演示? ?
?? ?代码演示? ?
?
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
? ? 编码:
? ? ? ? byte[] getBytes():使用平台的默认字符集将该 String编码为一系列字节,将结果存储到新的字节数组中
? ? ? ? byte[] getBytes(String charsetName):使用指定的字符集将该 String编码为一系列字节,将结果存储到新的字节数组中
? ? 解码:
? ? ? ? String(byte[] bytes):通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的字节数组来构造新的 String
? ? ? ? String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName):通过指定的字符集解码指定的字节数组来构造新的 String
?*/
public class StringDemo {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
? ? ? ? //定义一个字符串
? ? ? ? String s = "中国";
? ? ? ? //默认编码
? ? ? ? byte[] bys = s.getBytes();
? ? ? ? System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bys));
? ? ? ? //指定字符集编码
? ? ? ? byte[] bysU = s.getBytes("UTF-8");
? ? ? ? System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bysU));
? ? ? ? byte[] bysG = s.getBytes("GBK");
? ? ? ? System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bysG));
? ? ? ? //默认解码
? ? ? ? String ss = new String(bys);
? ? ? ? System.out.println(ss);
? ? ? ? //指定字符集解码
? ? ? ? String sU = new String(bysU, "UTF-8");
? ? ? ? System.out.println(sU);
? ? ? ? String sG = new String(bysG, "GBK");
? ? ? ? System.out.println(sG);
? ? ? ? //格式不匹配的情况
? ? ? ? String sss = new String(bysG);
? ? ? ? System.out.println(sss);
? ? ? ? String s1 = new String(bys, "GBK");
? ? ? ? System.out.println(s1);
? ? }
}
2.4.4、字符流中的编码解码问题
?字符流中的编码解码问题相关的两个类
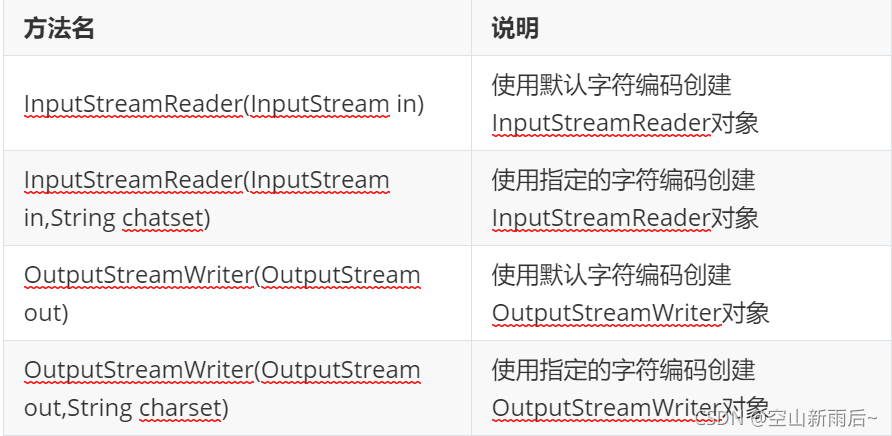
?? ??? ?- InputStreamReader:是从字节流到字符流的桥梁
?? ??? ??? ? ???? ?它读取字节,并使用指定的编码将其解码为字符
?? ??? ??? ? ???? ?它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台的默认字符集
?? ??? ?- OutputStreamWriter:是从字符流到字节流的桥梁
?? ??? ??? ? ???? ?是从字符流到字节流的桥梁,使用指定的编码将写入的字符编码为字节
?? ??? ??? ? ???? ?它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台的默认字符集
?? ?构造方法
?? ??? ?
?? ?示例代码
?? ???
public class ConversionStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt"));
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt"),"GBK");
osw.write("中国");
osw.close();
//InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt"));
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt"),"GBK");
//一次读取一个字符数据
int ch;
while ((ch=isr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
isr.close();
}
}2.4.5、字符流写数据的5种方式
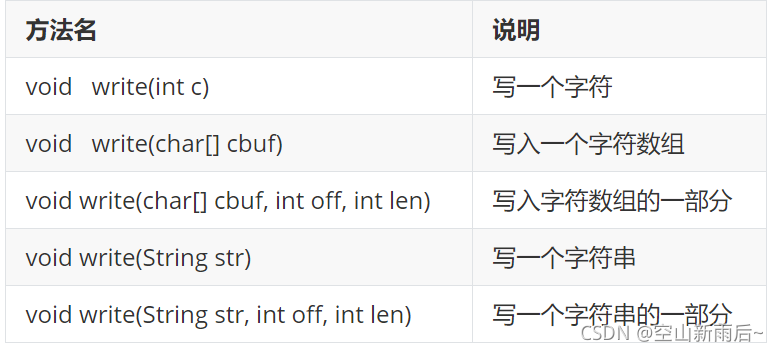
?? ?方法介绍
?? ??? ?
?? ?刷新和关闭的方法
?? ??? 
?? ?代码演示
?? ???
?public class OutputStreamWriterDemo {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
? ? ? ? OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt"));
? ? ? ? //void write(int c):写一个字符
// ? ? ? ?osw.write(97);
// ? ? ? ?osw.write(98);
// ? ? ? ?osw.write(99);
? ? ? ? //void writ(char[] cbuf):写入一个字符数组
? ? ? ? char[] chs = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'};
// ? ? ? ?osw.write(chs);
? ? ? ? //void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len):写入字符数组的一部分
// ? ? ? ?osw.write(chs, 0, chs.length);
// ? ? ? ?osw.write(chs, 1, 3);
? ? ? ? //void write(String str):写一个字符串
// ? ? ? ?osw.write("abcde");
? ? ? ? //void write(String str, int off, int len):写一个字符串的一部分
// ? ? ? ?osw.write("abcde", 0, "abcde".length());
? ? ? ? osw.write("abcde", 1, 3);
? ? ? ? //释放资源
? ? ? ? osw.close();
? ? }
}2.4.6、字符流读数据的两种方式
?? ?方法介绍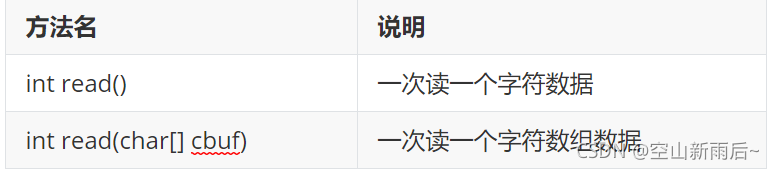 ?? ?代码演示
?? ?代码演示
?? ???
?public class InputStreamReaderDemo {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
? ?
? ? ? ? InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("myCharStream\\ConversionStreamDemo.java"));
? ? ? ? //int read():一次读一个字符数据
// ? ? ? ?int ch;
// ? ? ? ?while ((ch=isr.read())!=-1) {
// ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print((char)ch);
// ? ? ? ?}
? ? ? ? //int read(char[] cbuf):一次读一个字符数组数据
? ? ? ? char[] chs = new char[1024];
? ? ? ? int len;
? ? ? ? while ((len = isr.read(chs)) != -1) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.print(new String(chs, 0, len));
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? //释放资源
? ? ? ? isr.close();
? ? }
}2.5、字节缓冲流
字节缓冲流介绍
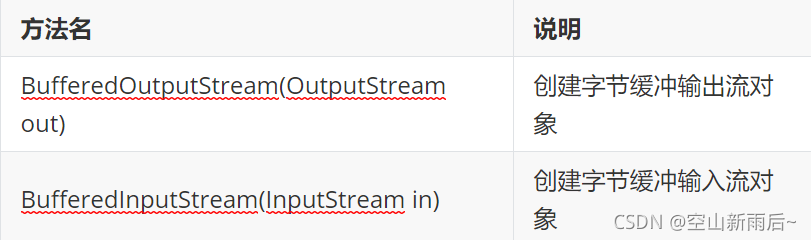
?? ??? ??? ?- BufferOutputStream:该类实现缓冲输出流。 通过设置这样的输出流,应用程序可以向底层输出流写入字节,而不必为写入的每个字节导致底层系统的调用
?? ??? ??? ?- BufferedInputStream:创建BufferedInputStream将创建一个内部缓冲区数组。 当从流中读取或跳过字节时,内部缓冲区将根据需要从所包含的输入流中重新填充,一次很多字节
?
?构造方法
? ? ? ? ? ??
?? ??? ?示例代码
?? ??? ???
?public class BufferStreamDemo {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
? ? ? ? //字节缓冲输出流:BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
?
? ? ? ? BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new ?? ??? ??? ??? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? FileOutputStream("myByteStream\\bos.txt"));
? ? ? ? //写数据
? ? ? ? bos.write("hello\r\n".getBytes());
? ? ? ? bos.write("world\r\n".getBytes());
? ? ? ? //释放资源
? ? ? ? bos.close();
? ? ? ? //字节缓冲输入流:BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
? ? ? ? BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?FileInputStream("myByteStream\\bos.txt"));
? ? ? ? //一次读取一个字节数据
// ? ? ? ?int by;
// ? ? ? ?while ((by=bis.read())!=-1) {
// ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print((char)by);
// ? ? ? ?}
? ? ? ? //一次读取一个字节数组数据
? ? ? ? byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
? ? ? ? int len;
? ? ? ? while ((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.print(new String(bys,0,len));
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? //释放资源
? ? ? ? bis.close();
? ? }
}?2.6字符缓冲流
? ? ? ? ?字符串缓冲流介绍
?? ??? ?- BufferedWriter:将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲字符,以提供单个字符,数组和字符串的高效写入,可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以接受默认大小。默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途
?? ??? ?
?? ??? ?- BufferedReader:从字符输入流读取文本,缓冲字符,以提供字符,数组和行的高效读取,可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以使用默认大小。 默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途
??

?? ?构造方法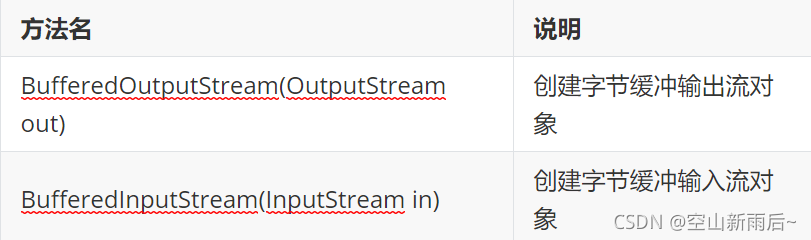 ?? ?代码演示
?? ?代码演示
?? ???
?public class BufferedStreamDemo01 {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
? ? ? ? //BufferedWriter(Writer out)
? ? ? ? BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?FileWriter("myCharStream\\bw.txt"));
? ? ? ? bw.write("hello\r\n");
? ? ? ? bw.write("world\r\n");
? ? ? ? bw.close();
?
? ? ? ? //BufferedReader(Reader in)
? ? ? ? BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? FileReader("myCharStream\\bw.txt"));
? ? ? ? //一次读取一个字符数据
// ? ? ? ?int ch;
// ? ? ? ?while ((ch=br.read())!=-1) {
// ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print((char)ch);
// ? ? ? ?}
? ? ? ? //一次读取一个字符数组数据
? ? ? ? char[] chs = new char[1024];
? ? ? ? int len;
? ? ? ? while ((len=br.read(chs))!=-1) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.print(new String(chs,0,len));
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? br.close();
? ? }
}结语
? ? ? ? 今天就跟大家分享到这里啦,快来一起快乐的用IO流吧,下期会跟大家分享一些细节问题哦,敬请期待。

?