21天养成好习惯_第十七天
今天主要学习Java的常用类(基础没学好, 现在得补课…),之后还得学集合,IO流… [有些知识点作者也有点迷糊, 期待各位大佬斧正]
1. 成员内部类:在一个类的内部在定义一个完整的类
- 编译之后可以生成独立的字节码文件
- 内部类可直接访问外部类的私有成员 , 而不破坏封装
- 可为外部类提供必要的内部功能组件
- 创建内部类对象时 , 必须依赖外部类对象
- 当内部类和外部类重名属性时, 会先访问内部类属性
- 成员内部类不能定义静态成员,但可以定义静态常量 (static final) (好像有问题, 我现在的java版本是java17 可能这个版本已经可以定义static变量了)
代码测试:
package BUPALAOYE;
public class test1 {
private String str = "Outer";
public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
public void show3(){
System.out.println(test1_1.str2);
System.out.println(test1_1.str3);
}
public class test1_1{
private String str = "Inner";
private static final String str2 = "中国";
private static String str3 = "中国2";
public void show(){
System.out.println(str);
}
public void show4(){
System.out.println(test1_1.str2);
System.out.println(test1_1.str3);
}
public void show2(){
//若内部类属性和外部类属性相同 , 则优先取内部类属性,
//若想用外部类属性可用, 类名.this.属性 获取
//内部类不可定义static属性,但可以定义static final属性 -- 可能与新版本不一样
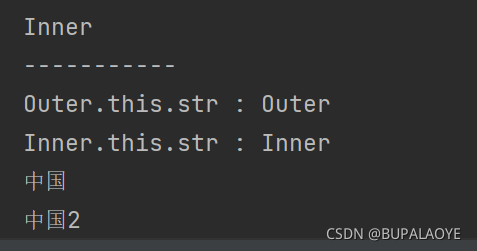
System.out.println("Outer.this.str : " + test1.this.str);
System.out.println("Inner.this.str : " + this.str);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法1.先创建外部类,再利用外部类的new操作创建内部类
//方法2. 或者一步到位
// test1 t1 = new test1();
// test1_1 t1_1 = t1.new test1_1();
// t1_1.show();
test1_1 t2 = new test1().new test1_1();
t2.show(); //str为赋值, 默认是null
System.out.println("-----------");
t2.show2();
t2.show4();
}
}
运行结果:
2. 静态内部类
直接看代码
package BUPALAOYE;
//外部类
//只有内部类可以用static修饰, 外部类不可以用static修饰
public class test2 {
private String name = "xxx";
private int age = 18;
//静态内部类,和外部类相同
static class Inner{
private String addr = "三海";
private static int count = 110;
private void show_Inner(){
//怎么调用外部类的属性
//1.先创建外部类对象
//2. 再调用外部类对象的属性
test2 Outer = new test2();
System.out.println(Outer.name);
System.out.println(Outer.age);
//调用内部类属性
System.out.println(addr + count);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//直接创建静态内部类对象(注意再这里并没有创建外部类对象,而是直接创建内部类对象)
test2.Inner inner = new test2.Inner();
//调用对象
inner.show_Inner();
}
}
运行结果:
3.局部内部类
package BUPALAOYE;
//局部内部类, 定义再外部类方法中, 作用范围和创建对象范围仅限与当前方法
public class test3 {
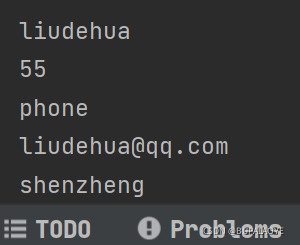
private String name = "liudehua";
public int age = 55;
public void show(){
//定义局部变量, 方法运行结束(因为jdk1.8自动会为其添加final),内存不释放
String addr = "shenzheng";
//局部内部类,注意不能添加任何访问修饰符
class Inner {
private String phone = "phone";
public String email = "liudehua@qq.com";
public void show2(){
//访问外部类的属性
System.out.println(test3.this.name);
System.out.println(test3.this.age);
//访问局部内部类的属性
System.out.println(this.phone);
System.out.println(this.email);
//访问方法的局部变量 (jdk1.8自动添加final)
System.out.println(addr);
}
}
//在方法里创建局部内部类对象
Inner inner = new Inner(); //方法结束,内存并不释放
inner.show2();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test3 test3 = new test3();
test3.show();
}
}
运行结果:
匿名内部类(没有类名的局部内部类) , 一切特征都与局部内部类相同 , 且必须继承一个父类或者实现一个接口.
package BUPALAOYE;
public class test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用一个接口 '接住' 匿名内部类,这样就可以借助接口调用一个类的方法
Usb usb = new Usb() {
@Override
public void server() {
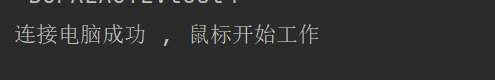
System.out.println("连接电脑成功 , 鼠标开始工作");
}
};
usb.server();
}
}
其中Usb接口直接自己写一下好了(也简单)
运行结果:
其他知识Java的注解和反射
代码验证:
public class test1 {
private String str;
public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
public class test1_1{
public void show(){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法1.先创建外部类,再利用外部类的new操作创建内部类
//方法2. 或者一步到位
test1 t1 = new test1();
test1_1 t1_1 = t1.new test1_1();
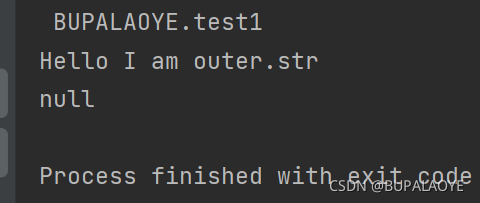
t1.setStr("Hello I am outer.str");
t1_1.show();
test1_1 t2 = new test1().new test1_1();
t2.show(); //str为赋值, 默认是null
}
}
运行结果:
注解(Annotation)与注释的区别
注释只是给人看的, 机器不会看
注解是给人和机器看的
三大注解:
- @Override 重写的注解
- @Deprecated 不推荐使用的方法,
- @SuppressWarings注解 作用:用于抑制编译器产生警告信息