1.什么是 JdbcTemplate
Spring 框架对 JDBC 进行封装,使用 JdbcTemplate 方便实现对数据库操作
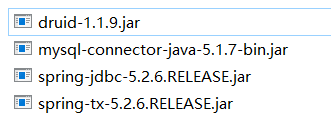
2.导入需要的jar包
这是实现JdbcTemplate操作需要的jar包
3.编写代码
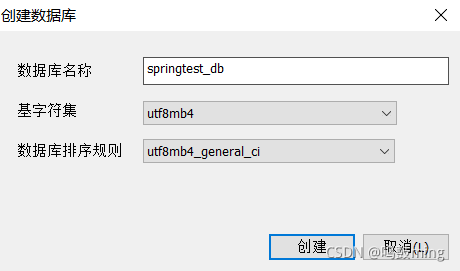
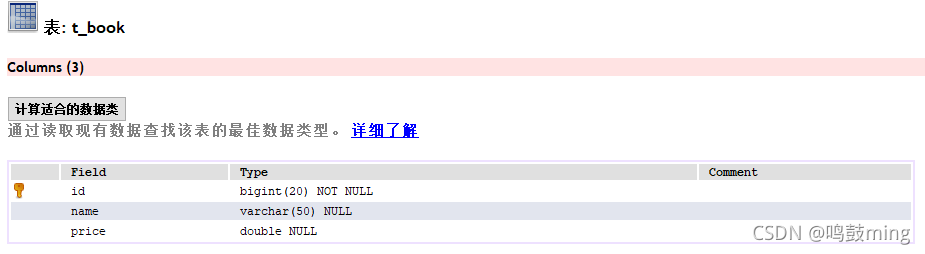
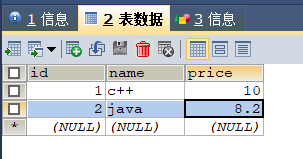
1.创建数据库
2.编写java代码
配置文件bean1.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.limi"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 1.在 spring 配置文件配置数据库连接池-->
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_springtest" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
</bean>
<!--2.配置 JdbcTemplate 对象,注入 DataSource-->
<!-- JdbcTemplate 对象 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--注入 dataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
BookService
package com.limi.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//获取书的数量
public int getBookCount(){
String sql ="select count(*) from t_book";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
return count;
}
}
测试类MyTest
package com.limi.test;
import com.limi.service.BookService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
//1.加载bean的xml文件, 以src为根目录
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
//2.获取配置的对象, 参数1:bean的id值, 参数2: 类名.class
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
//3.使用对象
System.out.println("书的数量="+bookService.getBookCount());
}
}
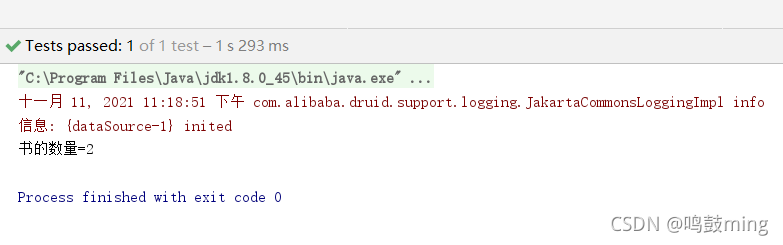
3.测试结果