springboot2
1.相比于springboot 1.0 版本,JDK需要1.8以上,maven 3.3以上。
2.新特性有主要有响应式编程,通过异步数据流的方式,占用少量线程和资源,来实现高吞吐量,高并发。
3.优点:
① 快速构建一个生产spring 应用
②内嵌web服务器可以打成直接运行
③构建项目,不用担心依赖冲突
④与第三方中间件整个,简化我们的开发
⑤提供生产级别的监控,健康检查,及动态化部署
⑥支持无xml等配置文件,纯代码
springboot 是整个spring技术站的一站式框架,是spring技术站开发的脚手架.
4.springboot 广泛运营于微服务应用的开发过程中,微服务就是把单体的应用拆分成几个小洞相对独立的服务,之间通过轻量的通讯(http) 来互相调用,独立部署,微服务部署主要的困难有:
① 远程调用②服务发现③负载均衡④服务容错⑤配置管理⑥服务监控⑦链路追踪⑧日志管理 等
解决办法: springboot + springcloud
5.云原生带来的挑战
①服务自愈②弹性扩展③服务隔离④自动化部署⑤灰度发布⑥流量治理…
6. springboot 基本知识
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
引入的这个父工程的主要作用就是帮我们定义好要使用的第三方的版本号,避免产生冲突
当然如果我们可以修改springboot已经定义好的版本号,例如
<properties>
<mysql.version>我们自己的版本</mysql.version>
</properties>
第三方的没有在springboot parent 工程定义的依赖,版本号需要我们自己标注
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
以上是springboot 的一个maven插件.可以帮助我们把项目打包
7.springboot 的自动配置
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true) 该注解标注的类指明是一个配置类,类似于spring 容器中bean.xml ,本身会被加载到spring 容器当中, 该类中的方法上加上@bean 注解就是加入一个类加入到spring容器中
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true)
public class ConfigContain {
@Bean
public User user(Cat cat){
User user = new User();
user.setAge(17);
user.setName("lisi");
return user;
}
}
proxyBeanMethods = true 默认true ,意思是该配置类下的组件,在互相引用时,会先配置spring容器中是否存在需要的,有的话就用容器中的,可以保证跟容器中的一致,proxyBeanMethods = false ,组件在互相引用的时候,每次都是新创建的,非容器中对象. 优点就是不需要判断容器中是否存在,相对会快一点. @bean 标注的方法的参数,会优先在spring容器中查,
1.首先先了解几个常见的注解
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = talkweb.**)
public class MyConfig {
…
}
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MyConfig.class)
两个注解通常一起使用, 表示把 Myconfig 组件加入到spring 容器,并把相应的配置与前缀talkweb.* 配置类的属相一起绑定
@ConfigurationProperties 也可以和 @Component 配置使用达到一样的效果 ,前者更加灵活
@import 给容器中导入指定组件
@ImportResource(“classpath:beans.xml”) 直接原生spring 的配置文件(例如: beans.xml)的形式,给容器中加入组件
@conditional 有很多衍生的注解,都是用来按条件来控制组件往容器中的注入
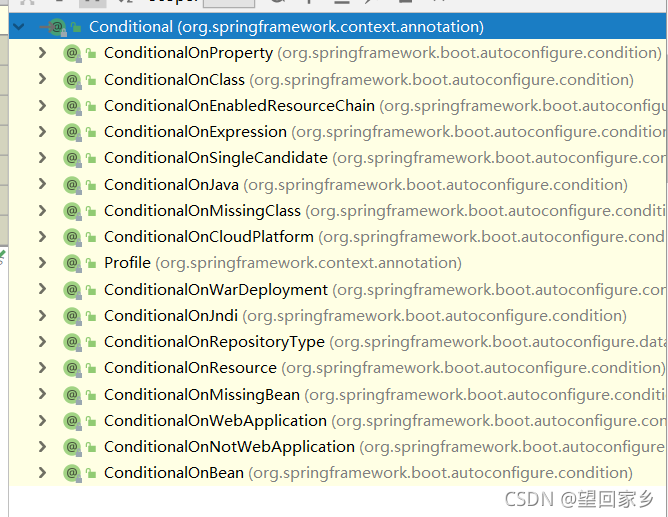
例如@ConditionalOnClass @ConditionalOnMissingClass
前者如果容器中有存在的符合要求的类型的组件,则对应的类或者方法就生效.
后者表示 容器中没有该类型的组件时才会生效.
springboot 自动配置按需加载就是大量使用到这些注解
2. springboot 自动配置 原理源码:
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@SpringBootConfiguration 声明是个配置类
@ComponentScan 要扫描的包,默认当前类所在包及子包
@EnableAutoConfiguration 重点
@AutoConfigurationPackage
**@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)**
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames() 批量导入我们当前主程序所在的包及子包 默认当前类所在包及子包 加载到容器中
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = “META-INF/spring.factories”;
通过源码发现springboot 启动的时候会加载我们这个位置下的文件
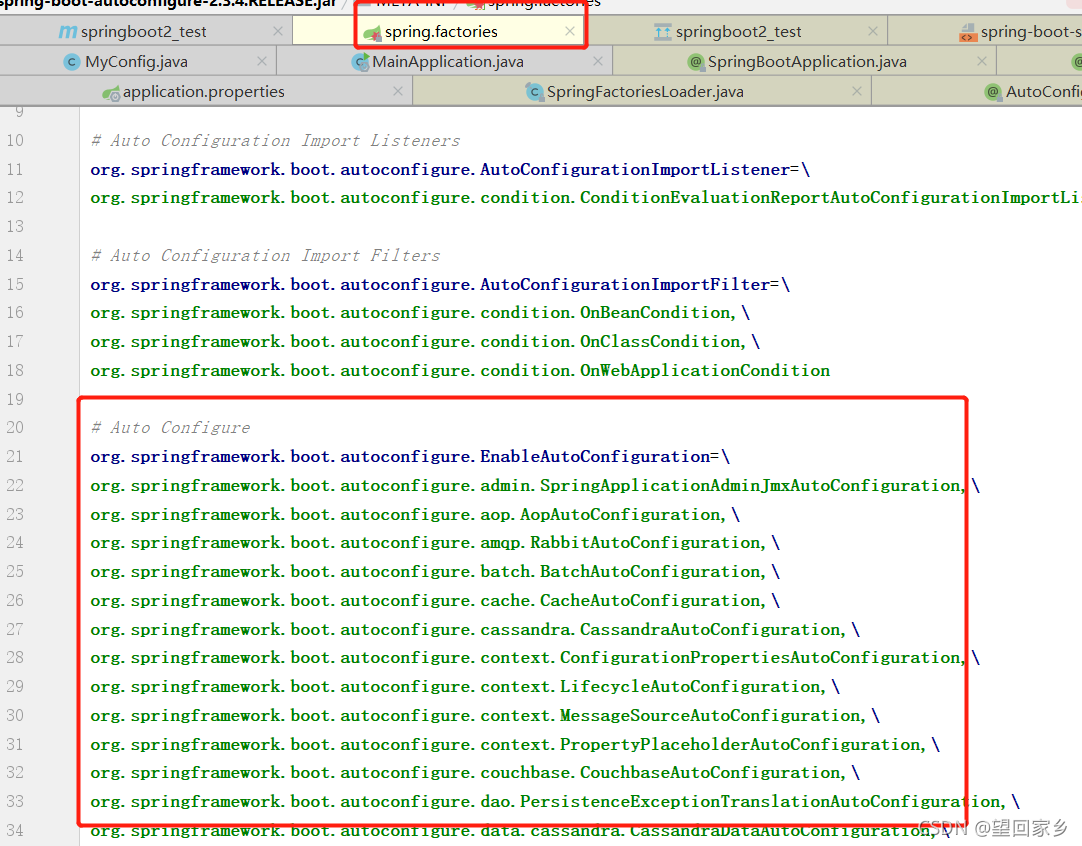
这个里边有我们springboot 写死的要加载的组件127个,但是不一定这127个组件不一定会生效,会根据条件按需加载.
演示我们springmvc 在项目加载的时候springboot 帮我们自动配置的代码
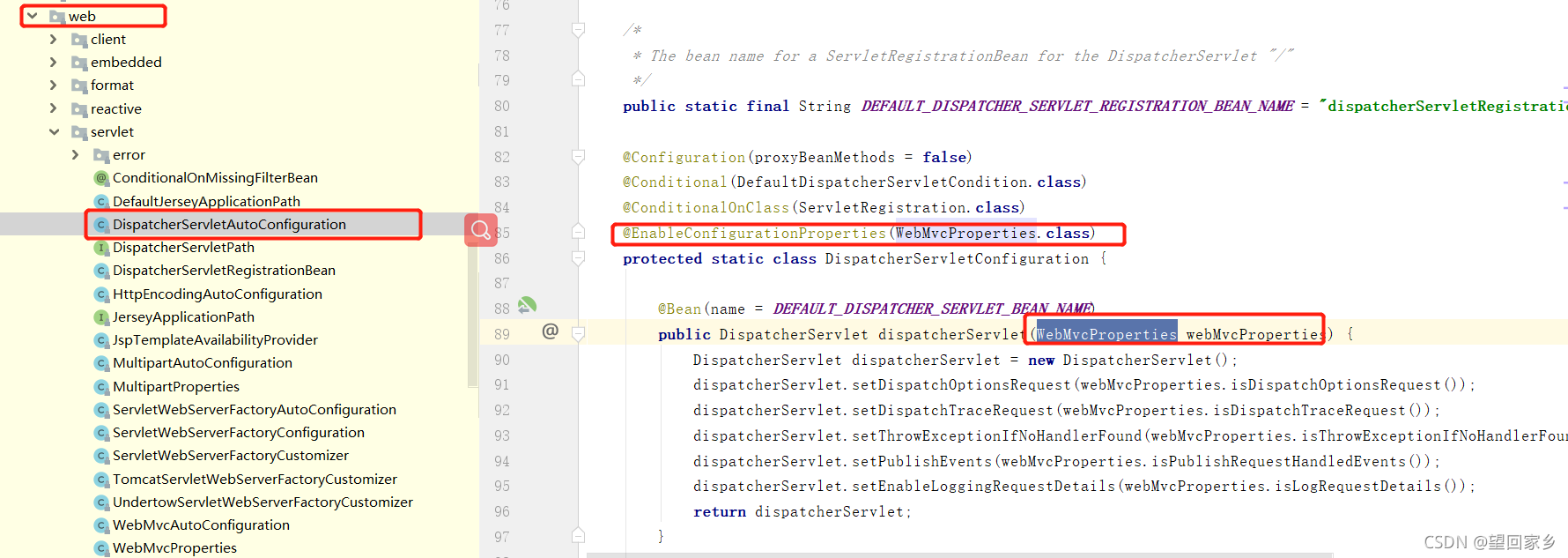
通过这样,把配置跟WebMvcProperties .class 绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.mvc")
public class WebMvcProperties {
所有我们可以直接找对对应的前缀的配置,直接修改或者通过@bean 自己配置我们需要的组件,会覆盖到springboot 帮我们自动注入的
也可以在spring官网上查看每个自动配置的默认值,及用途.
8.springboot 的一些常用开发工具
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
一个是lombok 快速帮我们生成实体类的get/set 方法等
一个是热部署(实际是检测到有变化,自动重启)
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
配置我们的yml 配置文件的自动识别