Set和Map
一、关于集合的体系结构

- Set是继承自Collection的接口类,Set中只存储了Key。
- Map是一个接口类,该类没有继承自Collection,该类中存储的是<K,V>结构的键值对,并且K一定是唯一的,不
能重复。
二、Map的使用
2.1关于Map.Entry的说明
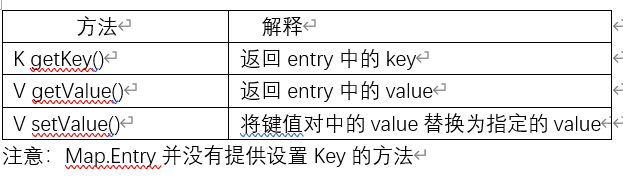
- Map.Entry<K, V> 是Map内部实现的用来存放<key, value>键值对映射关系的内部类,该内部类中主要提供了<key, value>的获取,value的设置以及Key的比较方式。
2.2Map的常用方法说明
-
方法介绍


-
代码演示
public class MapDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
//V put(K key,V value):添加元素
map.put("张无忌","赵敏");
map.put("郭靖","黄蓉");
map.put("杨过","小龙女");
//V remove(Object key):根据键删除键值对元素
System.out.println(map.remove("郭靖"));
System.out.println(map.remove("郭襄"));
//void clear():移除所有的键值对元素
// map.clear();
//boolean containsKey(Object key):判断集合是否包含指定的键
System.out.println(map.containsKey("郭靖"));
System.out.println(map.containsKey("郭襄"));
//boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
//int size():集合的长度,也就是集合中键值对的个数
System.out.println(map.size());
//输出集合对象
System.out.println(map);
}
}
public class MapDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//添加元素
map.put("张无忌", "赵敏");
map.put("郭靖", "黄蓉");
map.put("杨过", "小龙女");
//V get(Object key):根据键获取值
// System.out.println(map.get("张无忌"));
// System.out.println(map.get("张三丰"));
//Set<K> keySet():获取所有键的集合
// Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
// for(String key : keySet) {
// System.out.println(key);
// }
//Collection<V> values():获取所有值的集合
Collection<String> values = map.values();
for(String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
2.3Map需要注意的点
- Map是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap
- Map中存放键值对的Key是唯一的,value是可以重复的
- 在Map中插入键值对时,key可以为空,value也可以为空
- Map中的Key可以全部分离出来,存储到Set中来进行访问(因为Key不能重复)。
- Map中的value可以全部分离出来,存储在Collection的任何一个子集合中(value可能有重复)。
- Map中键值对的Key不能直接修改,value可以修改,如果要修改key,只能先将该key删除掉,然后再来进行
重新插入。
2.4HashMap与TreeMap的比较

三、Set的使用
3.1Set集合概述和特点
- 不可以存储重复元素
- 没有索引,不能使用普通for循环遍历
3.2Set常用方法

3.3Set需要注意的点
- Set是继承自Collection的一个接口类
- Set中只存储了key,并且要求key一定要唯一
- Set的底层是使用Map来实现的,其使用key与Object的一个默认对象作为键值对插入到Map中的
- Set最大的功能就是对集合中的元素进行去重
- 实现Set接口的常用类有TreeSet和HashSet,还有一个LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashSet是在HashSet的基础上维护了一个双向链表来记录元素的插入次序。
- Set中的Key不能修改,如果要修改,先将原来的删除掉,然后再重新插入
- Set中能插入null的key
3.4TreeSet和HashSet的比较

四、相关面试题及编程题
HashMap的相关面试题:List与HashMap相关面试题
- 与运算来做
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int single = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
single ^= num;
}
return single;
}
}
- HashSet来做
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
for(int x:nums){
if(!set.contains(x)){
set.add(x);
}else{
set.remove(x);
}
}
return set.iterator().next();
}
}
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head==null) return null;
Map<Node,Node> map=new HashMap<>();
Node cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
Node list=new Node(cur.val);
map.put(cur,list);
cur=cur.next;
}
cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
map.get(cur).next=map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random=map.get(cur.random);
cur=cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
3.宝石与石头

class Solution {
public int numJewelsInStones(String jewels, String stones) {
Set<Character> set=new HashSet<>();
for(int i=0;i<jewels.length();i++){
set.add(jewels.charAt(i));
}
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<stones.length();i++){
if(set.contains(stones.charAt(i))){
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
4.坏键盘打字

- 解题思路
1.将打印的字符串,转化为大写放入Set中
2.(遍历输入的字符串,如果set中不包含就打印,但是会打印重复的键,所以:)
3.因为打印坏的键不能重复,所以在定义个Set 名为setBroken
打印前如果set和setBroken中都不含该字符在打印,打印完再将打印的字符加入setBroken中
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void fun3(String str1,String str2){
Set <Character> set=new HashSet<>();
for(char ch:str2.toUpperCase().toCharArray()){
set.add(ch);
}
Set <Character> setBroken=new HashSet<>();
for(char ch:str1.toUpperCase().toCharArray()){
if(!set.contains(ch)&&!setBroken.contains(ch)){
System.out.print(ch);
setBroken.add(ch);
}
}
}
public static void main(String [] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextLine()){
String str1=sc.nextLine();
String str2=sc.nextLine();
fun3(str1,str2);
}
}
}
5.前K个高频单词

- 解题思路
1.将world里的字符串放入map中,Map<String,Integer>,并统计String出现的次数
2.找频率最大的字符,所以用小堆PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String,Integer>>
3.跟topK问题一样解
4.遍历Map中的所有Entry,如果新的Emtry的value值大于堆顶的Value(新Entry的频率大),则堆顶元素出堆,新的Entry入
5.如果频率相等考虑String(key)的元素大小,若字母小 堆先出 后入堆
6.因为PriorityQueue是小堆所以 实现Comparator重写compare时是o1.getValue()-o2.getValue();最后当堆不满K个元素出现Value相同时,要进行调整 当(key大的话交换)

class Solution {
public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for(String s: words){
if(map.get(s)==null){
map.put(s,1);
}else{
Integer value=map.get(s);
map.put(s,value+1);
}
}
PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> minHeap=new PriorityQueue<>(k,
new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
if(o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue())==0){
return o2.getKey().compareTo(o1.getKey());
}
return o1.getValue()-o2.getValue();
}
});
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer>me: map.entrySet() ){
if(minHeap.size()<k){
minHeap.offer(me);
}else{
Map.Entry<String,Integer> top=minHeap.peek();
//频率相同
if(top.getValue().compareTo(me.getValue())==0){
//看字母大小 字母小入队
if(top.getKey().compareTo(me.getKey())>0){
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(me);
}
}else if(top.getValue().compareTo(me.getValue())<0){//堆顶元素的值小 堆顶出 me进
minHeap.poll();
minHeap.offer(me);
}
}
}
//将出现频率为前K个的String放入List
List<String> ret=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
Map.Entry<String,Integer> top=minHeap.poll();
ret.add(top.getKey());
}
//弹出来是从小到大 所以要反转
Collections.reverse(ret);
return ret;
}
}


