一文彻底学会spring循环依赖
概念
循环依赖:顾名思义就是相互存在依赖关系,我们是为了学习源码这里就不太多的啰嗦了, 大家一定有一个比较深入的了解
前提条件
需要知道ioc容器的初始化过程,不然容进去容易找不到相关的方法;
技术储备: java8中的一些特性: lamda表达式, 函数式接口, 并发相关的锁知识
如果想先了解理论请查看Spring循环依赖是如何解决的
我们在哪
循环依赖存在bean初始化时,所以我们今天我们学的ioc容器初始化过程中的一部分,就在非懒加载bean初始化相关部分,位置是在refresh方法中的 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory) 方法完成的包扫描以及bean的初始化
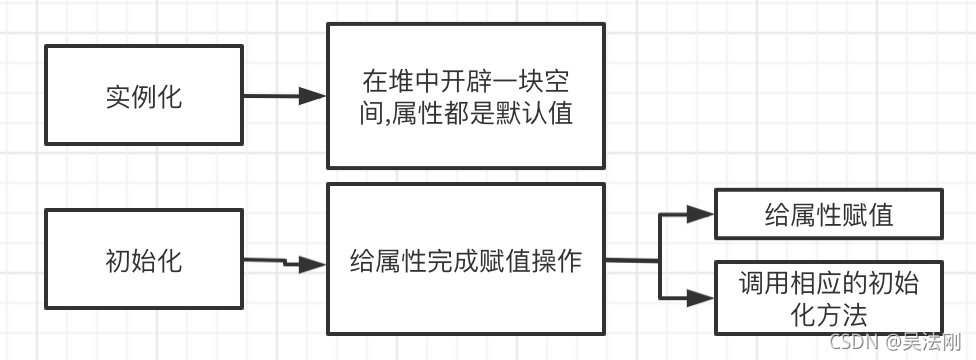
实力化和初始化的概念我们要清楚:
我们今天看的是在ioc这个位置:如下图所示:
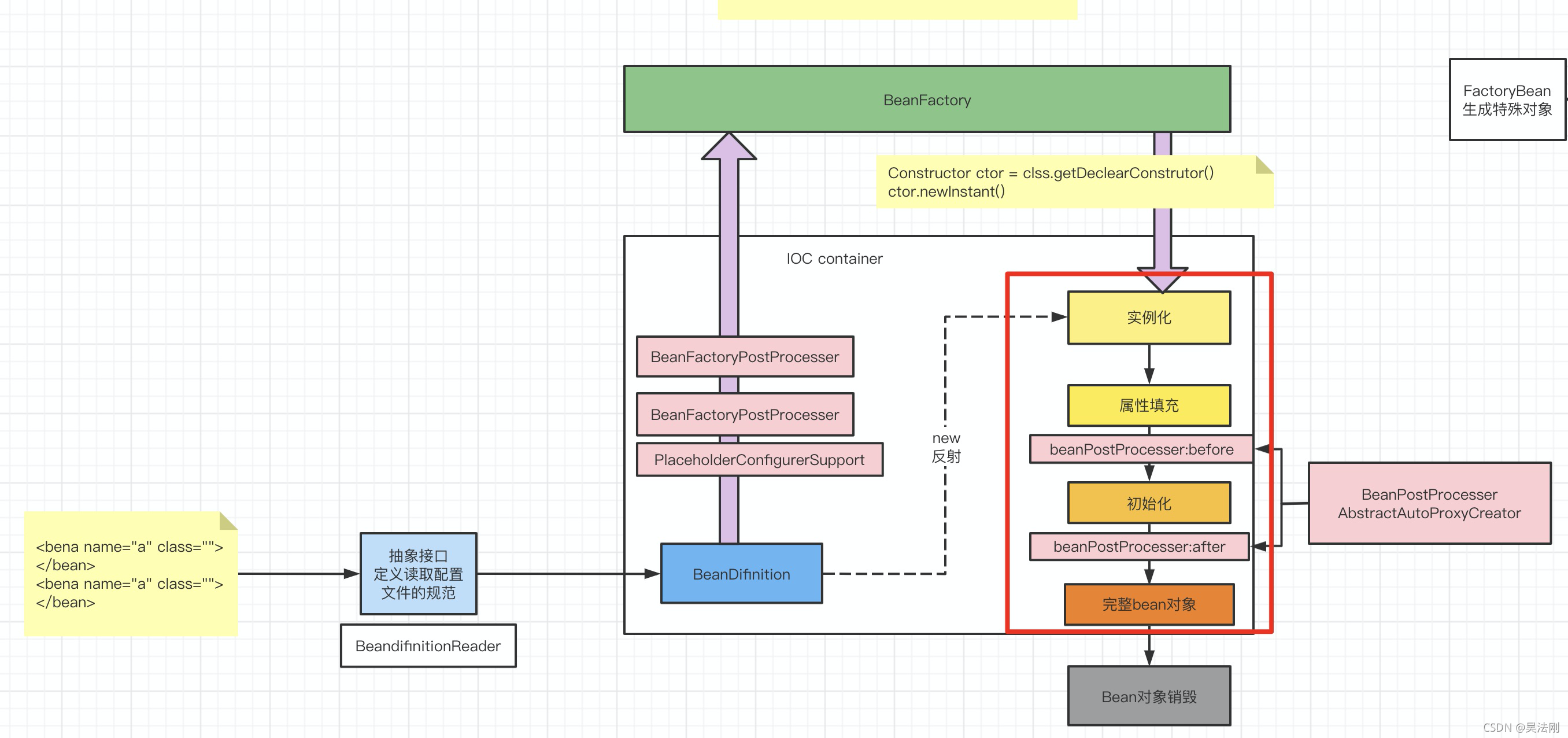
源码分析
我们项目中编写2个类A,B 并且相互依赖,先加载A再加重B 这样约定好方便后面代码里面说:
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
看注解: 初始化非懒加载,单列bean
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
以上代码逻辑如下图:非常简单FactoryBean今天不说等着专门写一篇相关blog
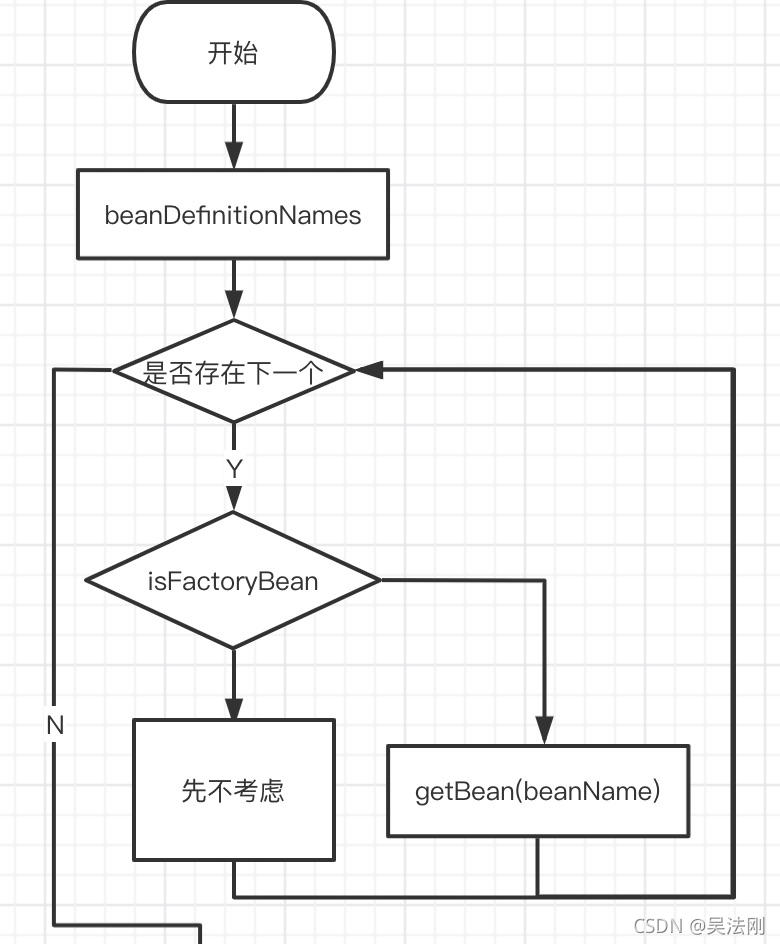
真正的开始 getBean
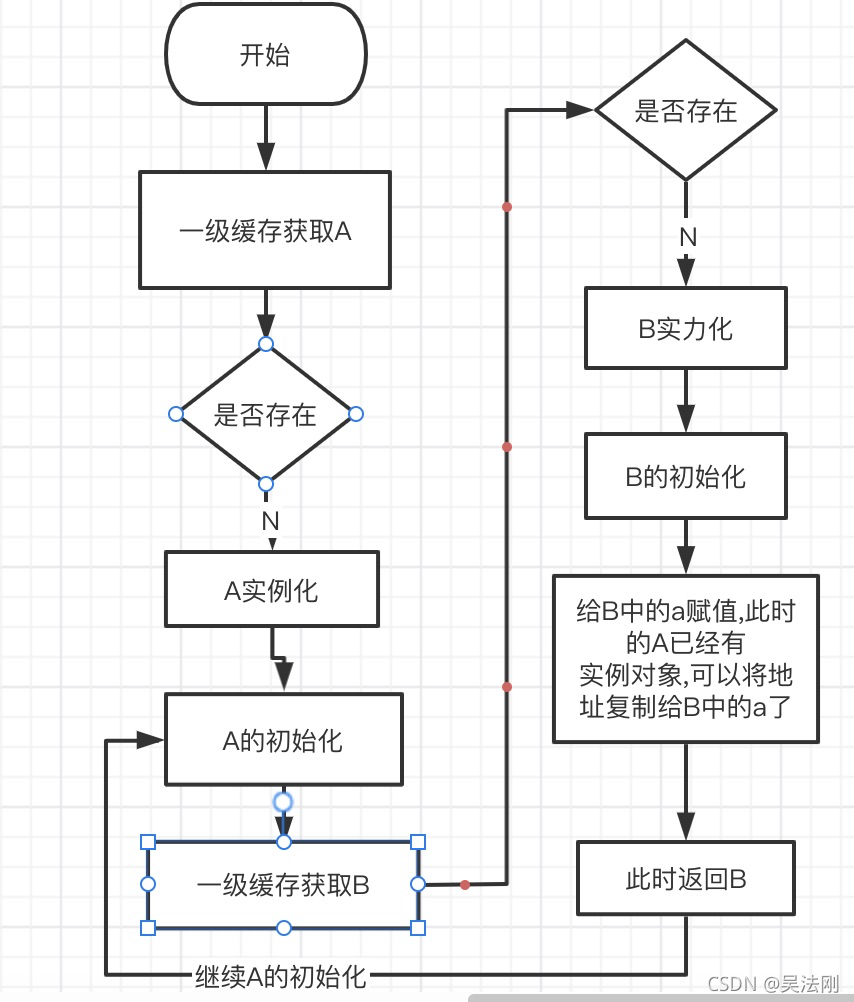
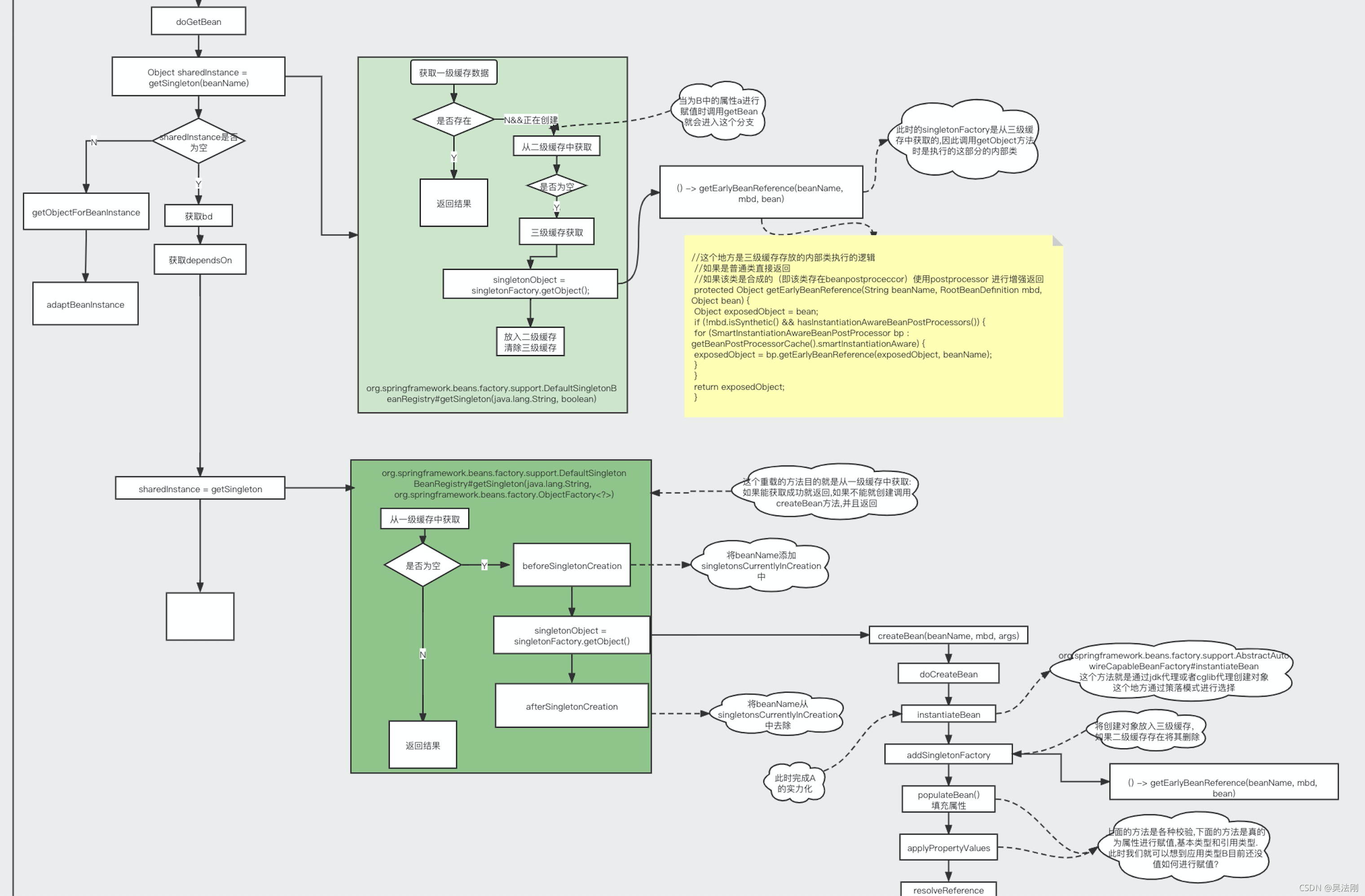
这是一个非常简单的思路流程图,方便理解
AbstractBeanFactory的getBean跟doGetBean方法
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
doGetBean do开头的方法是真正做事的方法将代码进行删减之和我们这次相关代码如下
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object beanInstance;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
}
return adaptBeanInstance(name, beanInstance, requiredType);
}
首先从一级缓存中获取对象:判断是否是否存在,此时缓存中无对行返回一定为空:
接着进行下面的操作:
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
下面这个我们可以久理解为一个参数即可(ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory),只是此参数是一个函数式接口,
() -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
因此该方法的逻辑如下:
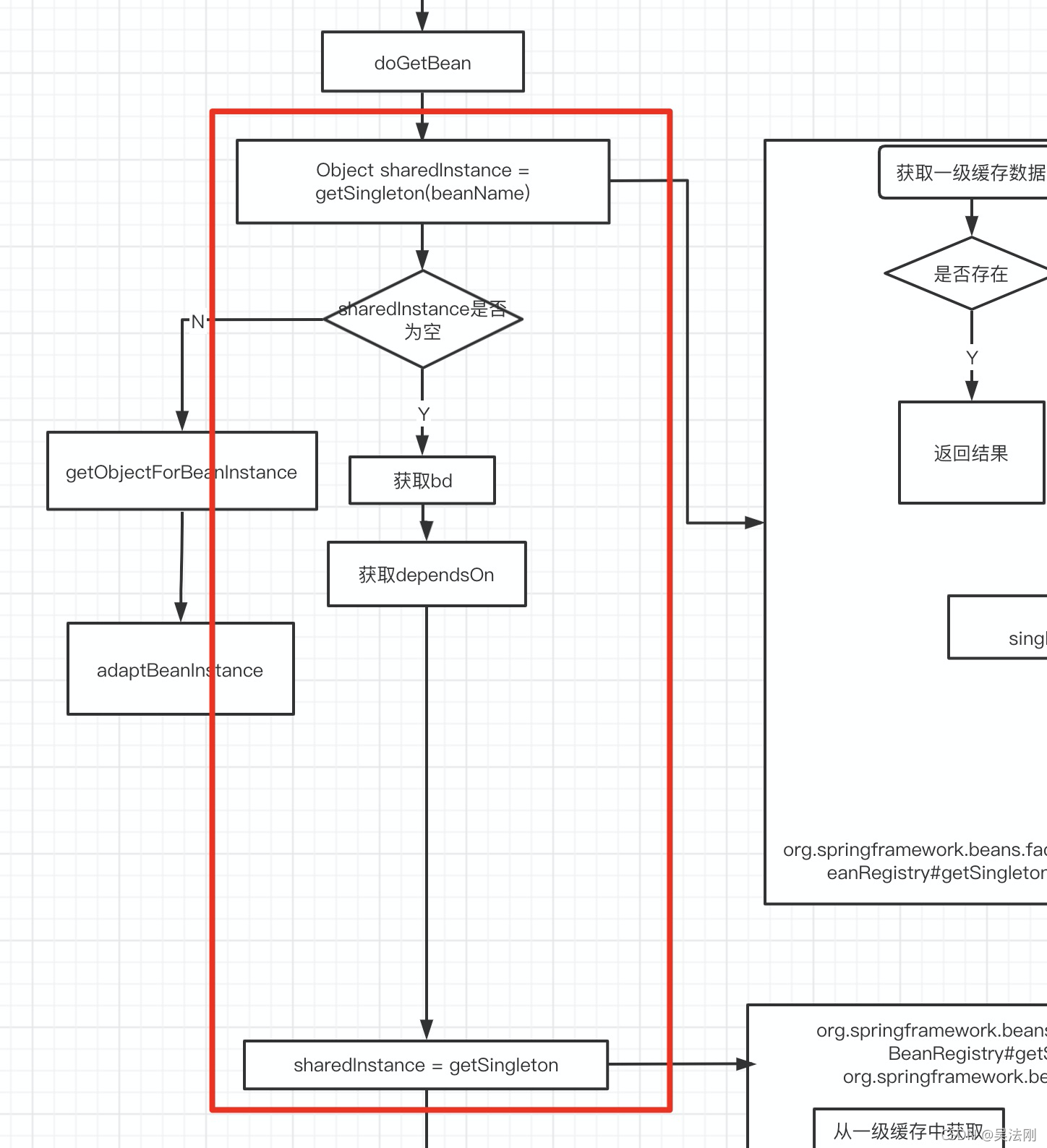
第一次当获取A对象的时候缓存中是空因此进入下面的getSingleton方法
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory)
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
if (this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction) {
throw new BeanCreationNotAllowedException(beanName,
"Singleton bean creation not allowed while singletons of this factory are in destruction " +
"(Do not request a bean from a BeanFactory in a destroy method implementation!)");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Creating shared instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// Has the singleton object implicitly appeared in the meantime ->
// if yes, proceed with it since the exception indicates that state.
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
for (Exception suppressedException : this.suppressedExceptions) {
ex.addRelatedCause(suppressedException);
}
}
throw ex;
}
finally {
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = null;
}
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
if (newSingleton) {
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
该方法逻辑非常简单:
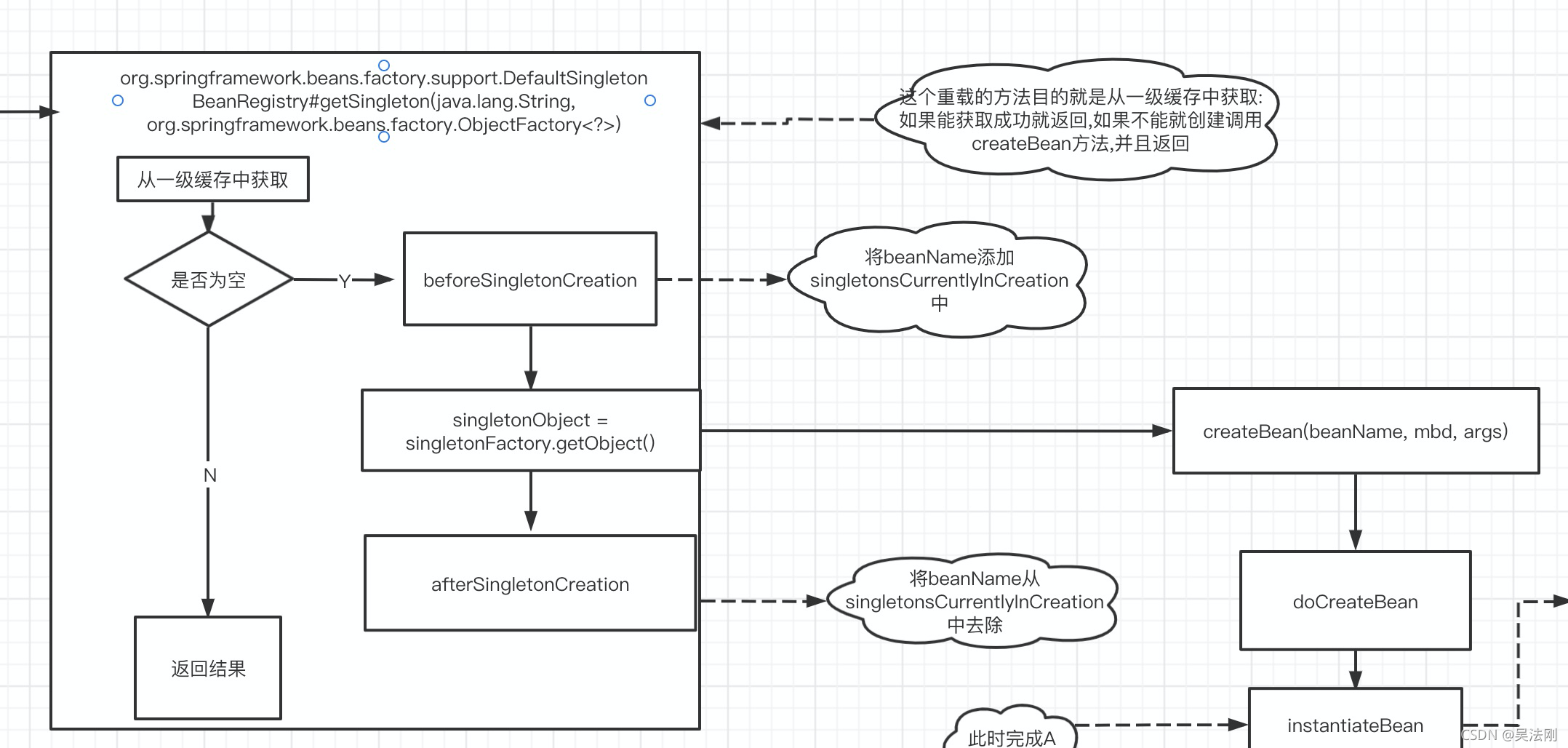
一级缓存中获取不到就调用
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject()
上面以及说了singletonFactory 这个传进来的是一个内部类做的参数因此调用这个就是调用的参数中的createBean方法,此时就是真正的创建方法开始
后面的流程参考 # 实例创建章节
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName)
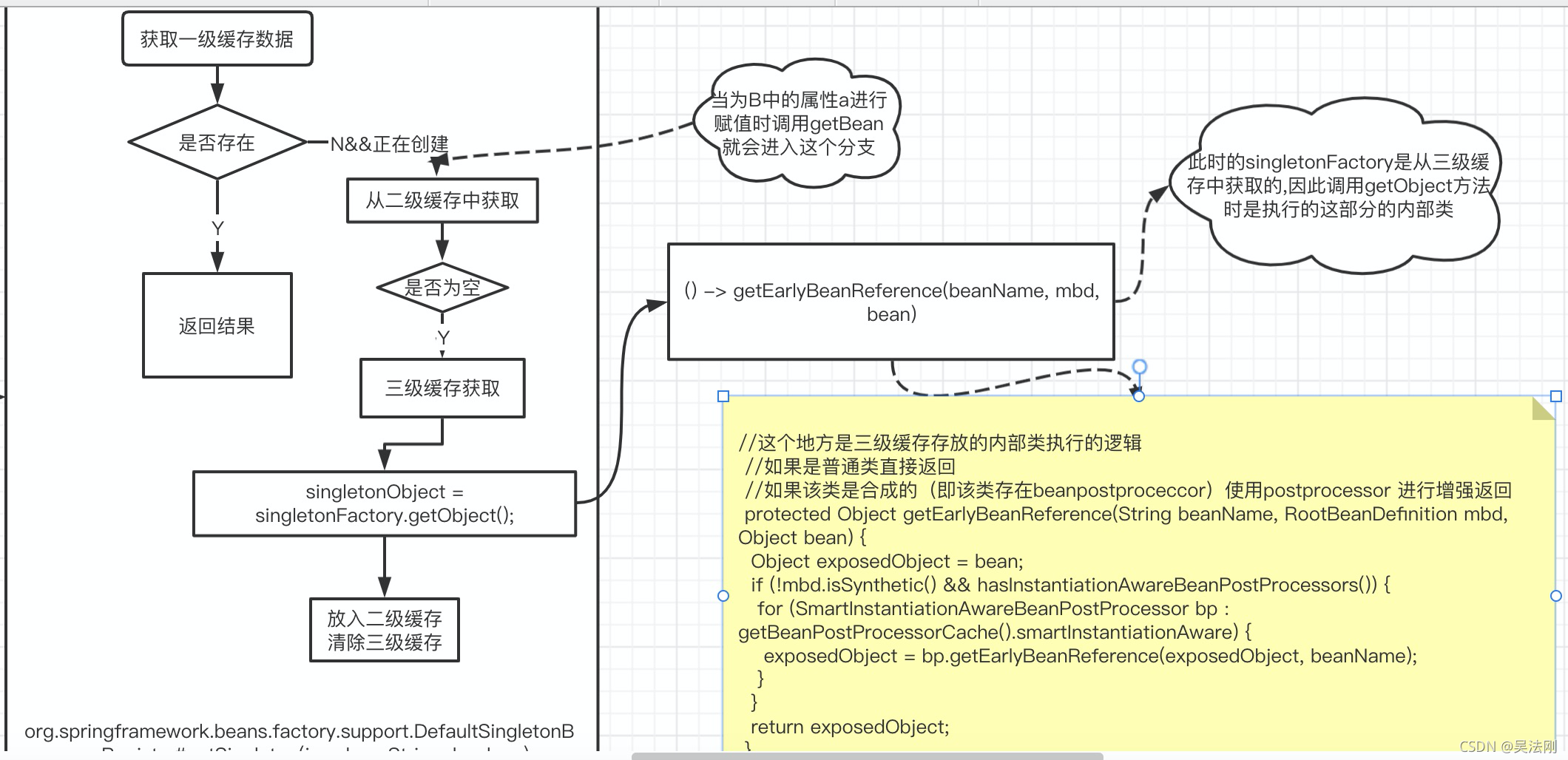
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
//从一级缓存中获取bean
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
//如果没有获取到并且正在创建中进入,正在创建中含义就是:实例化但是没有初始化(earlySingleton)
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
//从二级缓存中获取
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Consistent creation of early reference within full singleton lock
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
//三级缓存中获取,三级缓存中存放的是内部代码块
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
//通过三级缓存中的内部代码块进行创建依赖Bean
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
//将创建的放入二级缓存
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
//删除三级缓存中数据
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
第一次传入A 不存在直接返回null
为A的b属性赋值时获取B 此时也返回null
当为B中的属性a赋值时,此时获取A的对象虽然为空同时isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation 为true因此到if中进行即:从三级缓存中获取;
这个地方也就体现出来三级缓存的真正意义:
我们需要三级缓存的主要意义就在于,你所需要的类有能是简单对象(实力化,初始化)也有可能是需要进行代理的代理对象(有BeanPostProcessor后置处理器),当我们向三级缓存中放置匿名内部类的时候,可以在获取的时候决定到底是简单对象,还是合成对象(即BeanPostProcessor后置处理器),这就是三级缓存在的意义
实例创建
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//实力化
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
//实例化完成,此时属性全部为空
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
//将创建对象放入三级缓存,如果二级缓存存在将其删除
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//初始化 属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
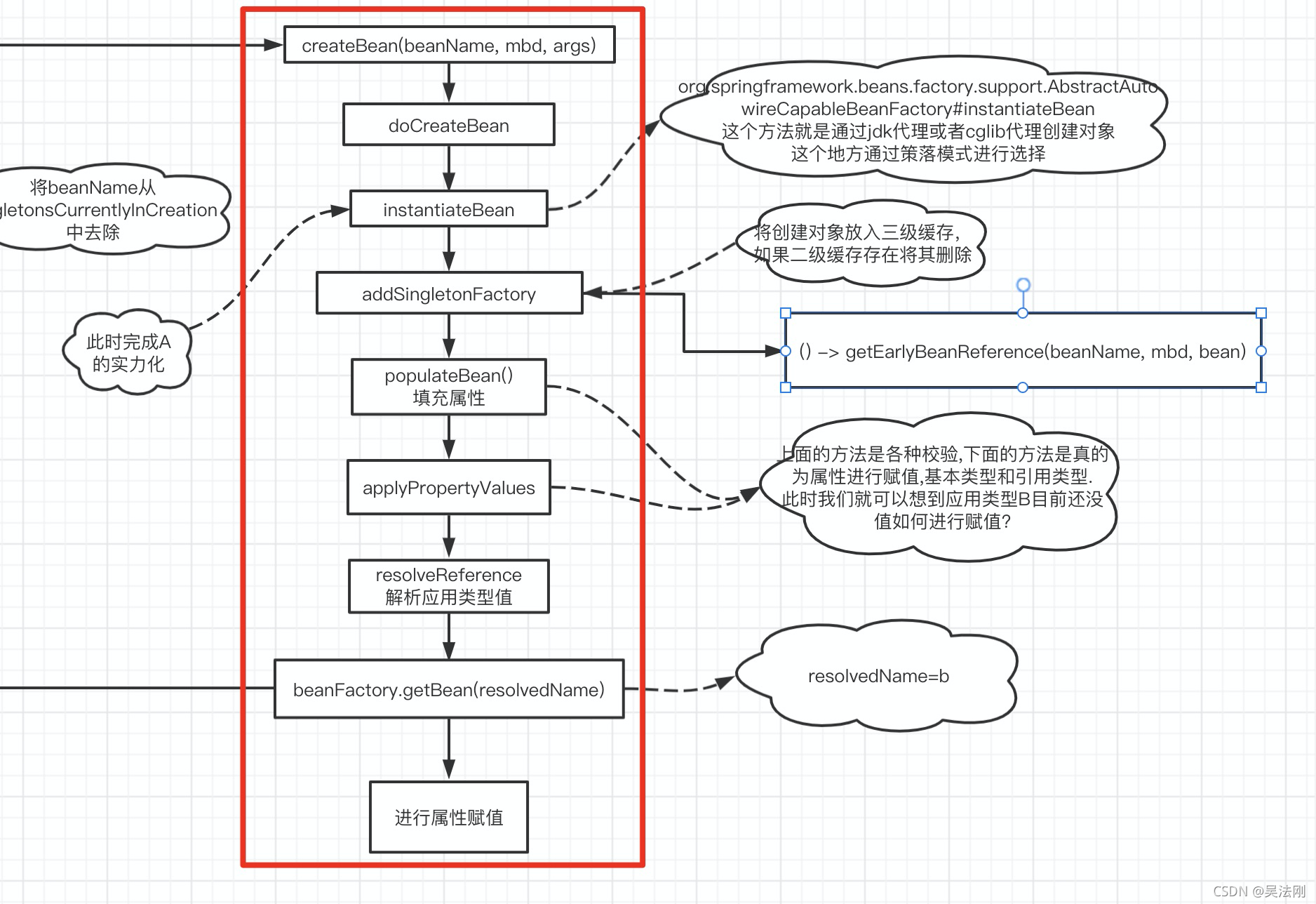
小结
属性注入主要是在populateBean方法中进行的。对于循环依赖,以我们上文中的A中注入了B、B中注入了A为例来说明,假定Spring的加载顺序为先加载A,再加载B。
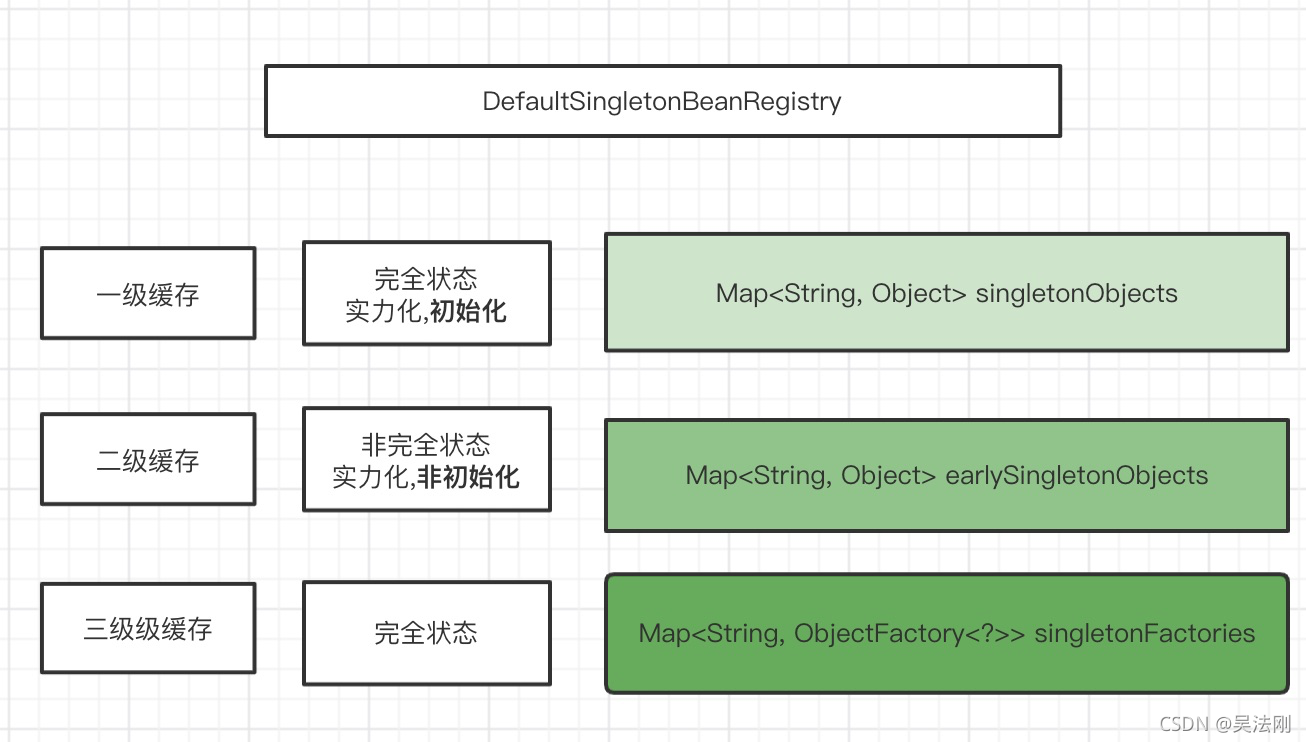
三级缓存
自己根据流程图多debug几次比较好…
面试题
1.spring 循环依赖的解决一定要通过三级缓存吗?
2.一级缓存能不能解决循环依赖问题?
不能,如果只有一级缓存,那么久意味着完全状态和非完全状态都存在,如果此时需要获取某个对象,恰巧获取到非完全兑现,怎么办?可以添加二级缓存
3.二级缓存能不能解决问题?为什么非要使用三级缓存?如果在A类上配置Aop,是否需要生成一个代理对象?
我们需要三级缓存的主要意义就在于,你所需要的类有能是简单对象(实力化,初始化)也有可能是需要进行代理的代理对象,当我们向三级缓存中放置匿名内部类的时候,可以在获取的时候决定到底是简单对象,还是合成对象(即BeanPostProcessor后置处理器),这就是三级缓存在的意义.