
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口是BeanPostProcessor的子接口,通过接口字面意思翻译该接口的作用是感知Bean实例话的处理器。实际上该接口的作用也是确实如此。
接口
该源码来自 spring 5.1.2.RELEASE 版本,先来看下接口的源代码:
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
@Deprecated
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}
}
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| postProcessBeforeInitialization | BeanPostProcessor接口中的方法,在Bean的自定义初始化方法之前执行 |
| postProcessAfterInitialization | BeanPostProcessor接口中的方法 在Bean的自定义初始化方法执行完成之后执行 |
| postProcessBeforeInstantiation | 自身方法,是最先执行的方法,它在目标对象实例化之前调用,该方法的返回值类型是Object,我们可以返回任何类型的值。由于这个时候目标对象还未实例化,所以这个返回值可以用来代替原本该生成的目标对象的实例(比如代理对象)。如果该方法的返回值代替原本该生成的目标对象,后续只有postProcessAfterInitialization方法会调用,其它方法不再调用;否则按照正常的流程走 |
| postProcessAfterInstantiation | 在目标对象实例化之后调用,这个时候对象已经被实例化,但是该实例的属性还未被设置,都是null。因为它的返回值是决定要不要调用postProcessPropertyValues方法的其中一个因素(因为还有一个因素是mbd.getDependencyCheck());如果该方法返回false,并且不需要check,那么postProcessPropertyValues就会被忽略不执行;如果返回true,postProcessPropertyValues就会被执行 |
| postProcessProperties | 对属性值进行修改,如果postProcessAfterInstantiation方法返回false,该方法可能不会被调用。可以在该方法内对属性值进行修改 |
| postProcessPropertyValues | 该方法废弃,同 postProcessProperties |
注意两个单词
| 单词 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Instantiation | 表示实例化,对象还未生成 |
| Initialization | 表示初始化,对象已经生成 |
举例说明
- 创建接口实现类
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
/**
* BeanPostProcessor接口中的方法
* 在Bean的自定义初始化方法之前执行
* Bean对象已经存在了
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(">>postProcessBeforeInitialization");
return bean;
}
/**
* BeanPostProcessor接口中的方法
* 在Bean的自定义初始化方法执行完成之后执行
* Bean对象已经存在了
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("<<postProcessAfterInitialization");
return bean;
}
/**
* InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor中自定义的方法
* 在方法实例化之前执行 Bean对象还没有
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("--->postProcessBeforeInstantiation");
return null;
}
/**
* InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor中自定义的方法
* 在方法实例化之后执行 Bean对象已经创建出来了
*/
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("<---postProcessAfterInstantiation");
return true;
}
/**
* InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor中自定义的方法
* 可以用来修改Bean中属性的内容
*/
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("<---postProcessProperties--->");
return pvs;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("<---postProcessPropertyValues--->");
return pvs;
}
}
- 创建目标类
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String beanName;
public User(){
System.out.println("User 被实例化");
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("设置:"+name);
this.name = name;
}
public String getBeanName() {
return beanName;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
this.beanName = beanName;
}
public void start(){
System.out.println("自定义初始化的方法....");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", beanName=" + beanName + "]";
}
}
- 测试
@Configuration
public class InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorBootstrap.class, args);
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
@Bean
public User user() {
return new User();
}
@Bean
public MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor myInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
return new MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor();
}
}
- 结果
--->postProcessBeforeInstantiation
User 被实例化
<---postProcessAfterInstantiation
<---postProcessProperties--->
>>postProcessBeforeInitialization
自定义初始化的方法....
<<postProcessAfterInitialization
通过输出结果,我们可以看到几个方法的执行顺序,而且五个方法都执行了,那么每个方法的返回结果对其他方法有什么影响没有呢,接下来分别看下这几个方法。
分析相关方法
- postProcessBeforeInstantiation
该方法返回的结果如果为null,后面的方法都正常执行了,但是如果该方法返回了实例对象了呢?我们来看下
/**
* InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor中自定义的方法
* 在方法实例化之前执行 Bean对象还没有
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("--->postProcessBeforeInstantiation");
// 利用cglib动态代理生成对象返回
if (beanClass == User.class) {
Enhancer e = new Enhancer();
e.setSuperclass(beanClass);
e.setCallback((MethodInterceptor) (obj, method, objects, methodProxy) -> {
System.out.println("目标方法执行前:" + method + "\n");
Object object = methodProxy.invokeSuper(obj, objects);
System.out.println("目标方法执行后:" + method + "\n");
return object;
});
User user = (User) e.create();
// 返回代理类
return user;
}
return null;
}
测试输出结果:
--->postProcessBeforeInstantiation
User 被实例化
<<postProcessAfterInitialization
通过数据结果我们发现,postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法返回实例对象后跳过了对象的初始化操作,直接执行了postProcessAfterInitialization(该方法在自定义初始化方法执行完成之后执行),跳过了postProcessAfterInstantiation,postProcessPropertyValues以及自定义的初始化方法(start方法),为什么会这样呢?我们要来查看下源代码。
在AbstractBeanFactory中的对InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor实现该接口的BeanPostProcessor 设置了标志
@Override
public void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {
Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null");
// Remove from old position, if any
this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor);
// Track whether it is instantiation/destruction aware
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
this.hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true;
}
// Add to end of list
this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);
}
在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中有个createBean方法
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException {
// ... 省略
try {
// Give BeanPostProcessors a chance to return a proxy instead of the target bean instance.
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
// ... 省略
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);这行代码之后之后根据bean判断如果不为空null就直接返回了,而不执行doCreateBean()方法了,而该方法是创建Bean对象的方法
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
// //如果beforeInstantiationResolved还没有设置或者是false(说明还没有需要在实例化前执行的操作)
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
// 判断是否有注册过InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor类型的bean
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
// 直接执行自定义初始化完成后的方法,跳过了其他几个方法
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
//只要有一个result不为null;后面的所有 后置处理器的方法就不执行了,直接返回(所以执行顺序很重要)
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
//如果返回null;后面的所有 后置处理器的方法就不执行,直接返回(所以执行顺序很重要)
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}
画个图说明下:
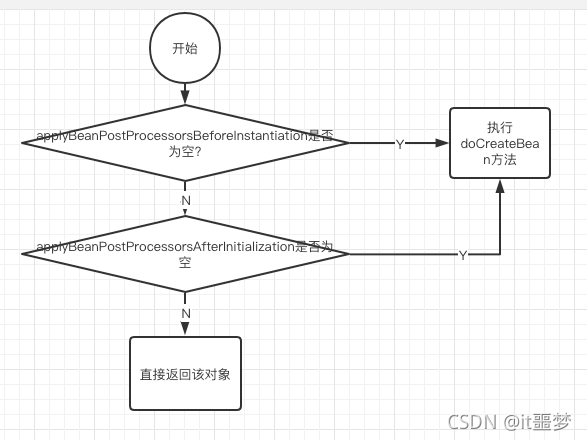
2. postProcessAfterInstantiation
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 此处执行 postProcessAfterInstantiation方法
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
// postProcessAfterInstantiation 返回true与false决定
// continueWithPropertyPopulation
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
// postProcessAfterInstantiation false
// continueWithPropertyPopulation 就为false 然后该方法就结束了!!!
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
// 调用 postProcessPropertyValues方法
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
// 真正设置属性的方法。
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
这个postProcessAfterInstantiation返回值要注意,因为它的返回值是决定要不要调用postProcessPropertyValues方法的其中一个因素(因为还有一个因素是mbd.getDependencyCheck());如果该方法返回false,并且不需要check,那么postProcessPropertyValues就会被忽略不执行;如果返true,postProcessPropertyValues就会被执行
- postProcessPropertyValues
在populateBean方法中我们已经看到了postProcessPropertyValues执行的位置了。我们来看下postProcessPropertyValues的效果
/**
* InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor中自定义的方法 可以用来修改Bean中属性的内容
*/
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean,
String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("<---postProcessPropertyValues--->");
if(bean instanceof User){
PropertyValue value = pvs.getPropertyValue("name");
System.out.println("修改前name的值是:"+value.getValue());
value.setConvertedValue("bobo");
}
return pvs;
}