pojo
package com.kuang.pojo;
public class Hello {
private String str;
public String getStr() {
return str;
}
public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hello{" +
"str='" + str + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd ">
<!--使用spring来创建对象,在spring这些都成为Bean-->
<bean id="hello" class="com.kuang.pojo.Hello">
<property name="str" value="Spring"/>
</bean>
</beans>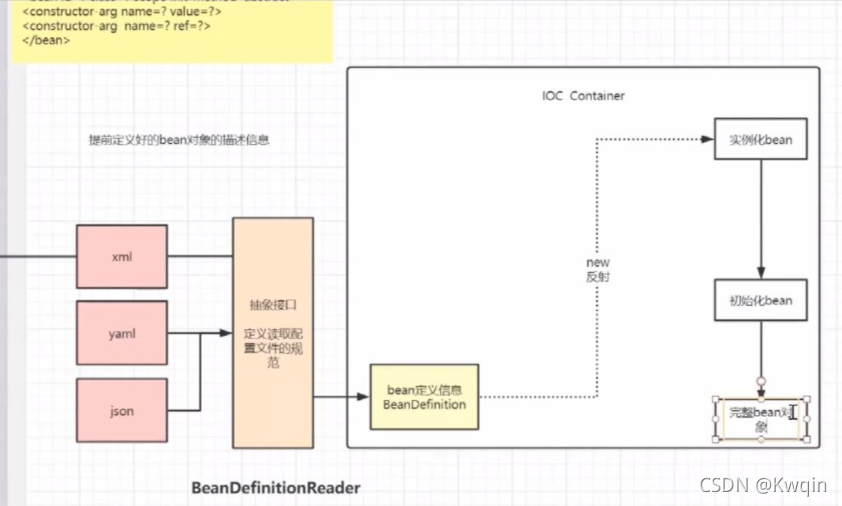

接口 BeanDefinitionReader
描述信息
Simple interface for bean definition readers.
* Specifies load methods with Resource and String location parameters.
bean 定义阅读器的简单界面。 使用 Resource 和 String 位置参数指定加载方法
接口 BeanDefinition
A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values, constructor argument values, and further information supplied by concrete implementations.
This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a BeanFactoryPostProcessor such as PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer to introspect and modify property values and other bean metadata.
?BeanDefinition 描述了一个 bean 实例,它具有属性值、构造函数参数值以及由具体实现提供的更多信息。
这只是一个最小的接口:主要目的是允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor例如PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer内省和修改属性值和其他 bean 元数据总之:就是BeanDefinition 是用来获取xml中bean对象的信息
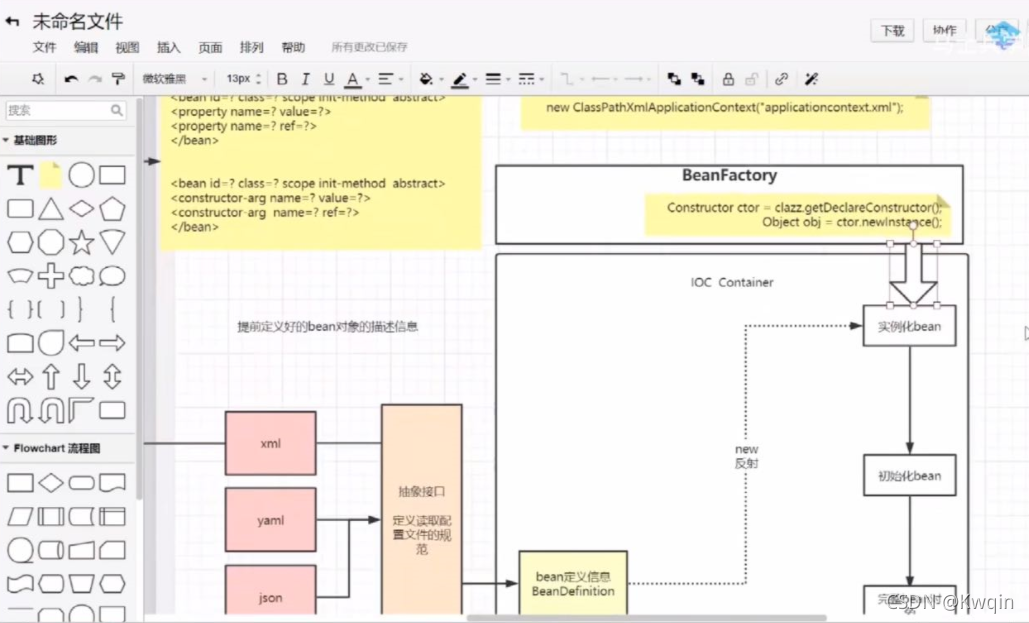
接口 BeanFactory
描述信息:
The root interface for accessing a Spring bean container?
BeanFactory用反射实例化bean ?
?接口PostProcessor
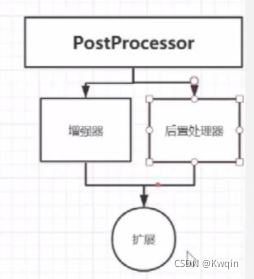
?PostProcessor也叫作增强器或者后置处理器,其目的是为了扩展,就是因为spring的扩展性好,因此它的生态好,扩展出了springboot和springcloud
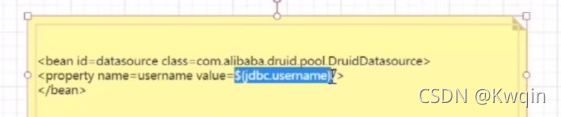
如何解析$符,让其把对应的值传给BeanFactory呢?
就是通过这个BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现的,
?接口实现类是 PlaceholderConfigurerSupport 当然还有很多实现类,功能都不一样
public abstract class PlaceholderConfigurerSupport extends PropertyResourceConfigurer
? ? ? implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware {
?这个实现类是用来用来解析下面这个格式的
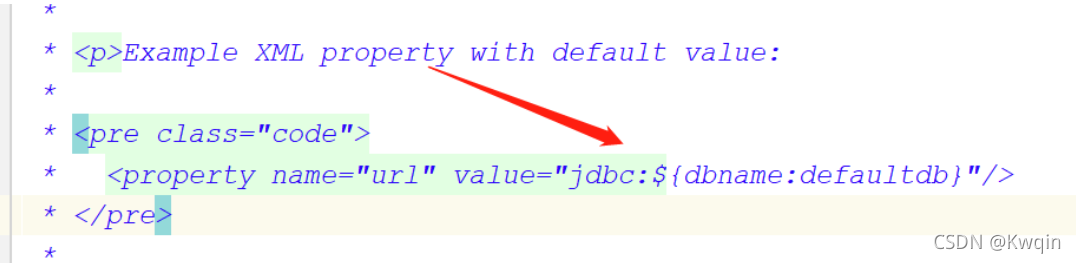
从他的功能描述可以看出来
?Abstract base class for property resource configurers that resolve placeholders
* in bean definition property values. Implementations <em>pull</em> values from a
* properties file or other {@linkplain org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource
* property source} into bean definitions.
*
接口BeanPostProcessor
?里面两个方法;
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;作用是在初始化bean前后对bean的信息进行操作
 ?接着进入源码环节,看看初始化配置文件的时候发生了啥?
?接着进入源码环节,看看初始化配置文件的时候发生了啥?
debug一下

?配置文件信息;

中间有些不那么重要的就忽略啦
1设置配置文件位置:方便后面的读取工作

?2然后进入refresh方法
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}3点进去 prepareRefresh();
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
/**
* <p>Replace any stub property sources with actual instances.
* @see org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource.StubPropertySource
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils#initServletPropertySources
*/
protected void initPropertySources() {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}总结下,此方法就是设置一些环境,初始化属性资源,获取环境对象,创建一系列集合
4走完refresh方法就要开始创建工厂啦
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}一定是会创建一个新的工厂
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); 加载配置文件
加载前
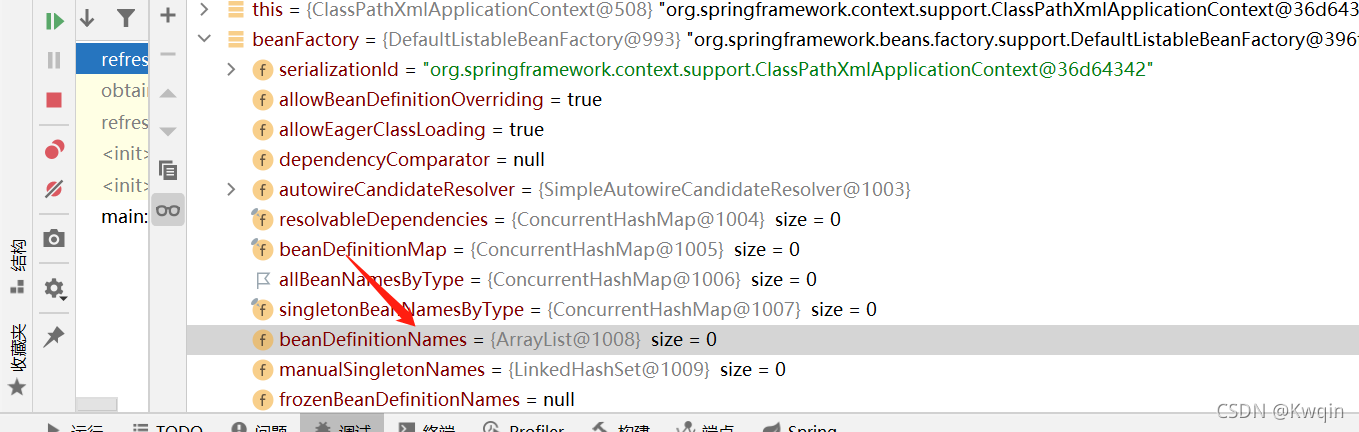
?加载后

这样就拿到了所以Bean的名字
5.接着执行prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
为什么要执行这步呢,因为在创建完工厂很多值都没被初始化,可以看到下面属性一堆的0和true,这个方法就是用来给这些属性赋值的
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}?看了下注释,简要概括就是配置工厂的标准上下文特征;
6执行postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);点进去发现方法是空的,是为了方便扩展而写的一个方法
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}
7invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.?
调用在上下文中注册为 bean 的工厂处理器。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);?
/**
* Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* <p>Must be called before singleton instantiation.
*/
实例化并调用所有已注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor bean
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}BeanFactoryPostProcessor做一系列事情,比如解析$表达式来替换值
8registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
注册拦截 bean 创建的 bean 处理器。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);9initMessageSource();
initMessageSource(); 国际化处理的时候用
10initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
为此上下文初始化事件多播器。 用于发布监听器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
11onRefresh();
空的,不鸟他
12.registerListeners();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners(); ? ? //注册监听器?
13.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
实例化所有剩余的(非延迟初始化)单例
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);利用反射实例化所有剩余的(非延迟初始化)单例,然后对属性值进行填充
套娃里面发现有这三玩意:
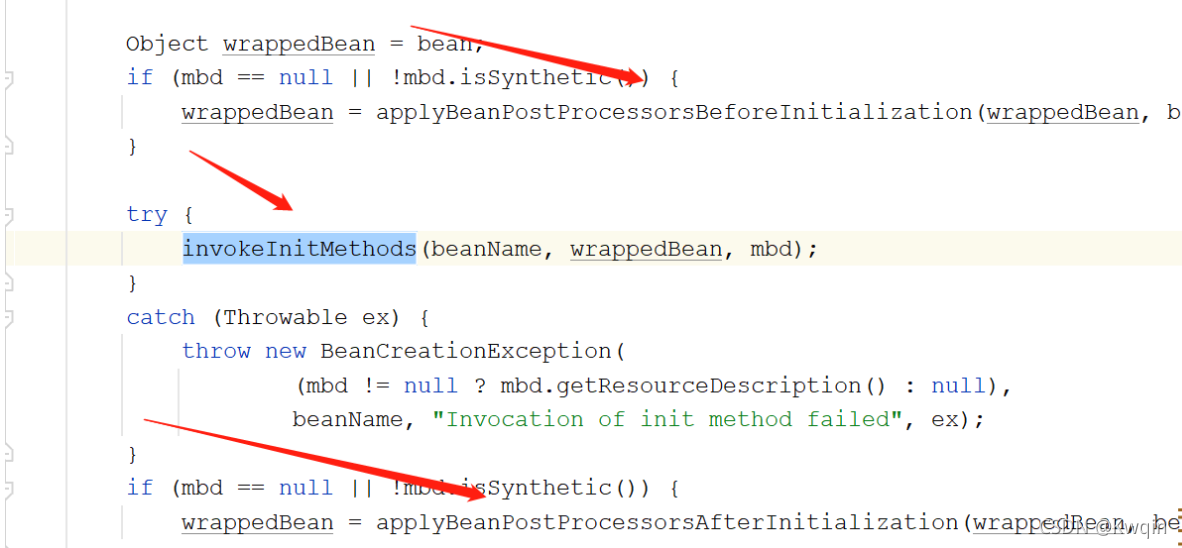
对应这些 用来做扩展
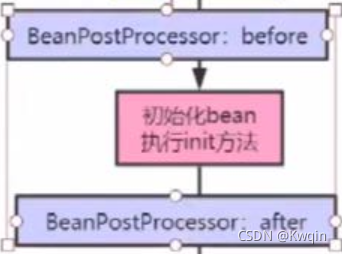
总结一下就是说:
?获取环境对象,创建集合 创建工厂 加载配置文件,拿到bean对象名字,配置工厂标准上下文参数,调用处理器来辅助工厂实例化,注册监听器,反射实例化对象,接着对属性进行填充。