并发编程系列之什么是并发协同?
1、什么是并发协同?
多个线程并发,协作来完成一件任务的过程。因为任务处理的需要,需控制某些线程等待另外一些线程执行完成任务的某些部分,然后继续执行。
2、并发协同实现方式
- 基于synchronized以及Object的wait notify notifyAll监视器方法的方式
- 基于Lock以及 Condition的await singal方法的等待通知方式
- 基于Java并发包中提供的其它协同的api,比如CountDownLatch方式
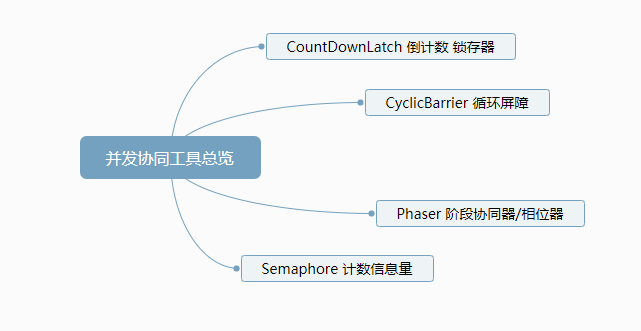
3、JUC并发协同工具类总览
jdk的juc包中除提供了用于专门处理1并发协同的工具类,主要有CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier、Phaser、Semaphore
4、CountDownLatch倒计数锁存器
- CountDownLatch倒计数锁存器
用途:用于协同控制一个或多个线程等待在其他线程中执行的一组操作完成,然后再继续执行 - CountDownLatch用法
- 构造方法:CountDownLatch(int count),count指定等待的条件数(任务数、操作数),不可再更改
- 等待方法:await(),阻塞等待线程直到count减少为0,count为0时,不会阻塞,继续执行
- boolean await(long timeout,TimeUnit unit):可以设置超时时间的await方法,返回true表示等待条件到达;false表示条件未来到达,但超时了
- long getCount():获取当前计数值,常用于调试或者测试
CountDownLatch注意事项:只可使用一次,不能重复使用,计数变为0之后,就不可再用
- CountDownLatch适用场景
- 等待多个条件完成,
countDownLatch(N)这个多个条件可以是:等待N个线程、等待N个操作、等待某操作的N次执行 - 用于并发测试,等待多个线程一起出发
例子:等待n个线程执行完成,再一起执行
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class CountDownLatchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final CountDownLatch cdl = new CountDownLatch(1);
int concurrency = 100;
final Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < concurrency; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10_000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "准备就绪");
// 让并发线程都等待发出信号
try {
cdl.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始工作");
}).start();
}
System.out.println("******************** 发出开始信号***********");
cdl.countDown();
}
}
执行,发现结果不符合我们的要求,虽然也是多个线程等待,再一起无序执行:
******************** 发出开始信号***********
Thread-22准备就绪
Thread-22开始工作
Thread-45准备就绪
Thread-45开始工作
...
因为CountDownLatch不能重用,所以再新加一个CountDownLatch协同N个线程:
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
public class StartTogerCountdownLatchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final CountDownLatch cdl = new CountDownLatch(1);
int concurrency = 100;
final CountDownLatch cdln = new CountDownLatch(concurrency);
final Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0;i < concurrency; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10_000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 准备就绪");
// 调用countDown()报告完成任务
cdln.countDown();
// 让所有线程都等待发出信号
try {
cdl.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 开始工作");
}).start();
}
//等待准备完成
cdln.await();
System.out.println("******************** 发出开始信号***********");
cdl.countDown();
}
}
等待N个线程准备就绪,然后一个总的CountDownLatch发出信号量,所有线程一起执行
...
Thread-11 准备就绪
Thread-14 准备就绪
Thread-53 准备就绪
Thread-91 准备就绪
******************** 发出开始信号***********
Thread-97 开始工作
Thread-57 开始工作
...
5、CyclicBarrier循环屏障
-
CyclicBarrier循环屏障定义
定义:协同指定数目的线程,让这些线程都在这个屏障前等待,直到所有的线程都到这个屏障前,再一起继续执行。线程执行完成后,这个屏障可以再次使用,因此被称之为循环屏障。 -
CyclicBarrier用法以及原理
- 构造方法,
CyclicBarrier(int parties):parties指定有多少个部分(线程)参与,称之为参与数。 - 构造方法,
CyclicBarrier(int parties,Runnable barrierAction):barrierAction,所有参与者都到达屏障时执行一次的命令。在一组线程中最后一个线程到达之后(但在释放所有线程之前),在该线程中执行改命令,该命令只在每个屏障点运行一次。若要在继续执行所有线程之前更新共享状态,此屏障操作很有用。 int await() throws InterruptedException,BrowkenBarrierException:线程执行过程会调用await()方法,表明自己已经到达屏障,该线程自己阻塞,等待其它线程也到达屏障;当所有线程都到达屏障,也即线程等待数等于参与数,则释放所有线程,让它们继续执行。返回值int表示到达当前线程的索引号,注意索引号是从parties-1开始减为0。BrokenBarrierException,屏障被破坏异常,当调用await时,或等待过程中屏障被破坏,则会抛出BrokenBarrierException。int await(long timeout,TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException,BrokenBarrierException,TimeoutException:等待指定时长,如到了时间还不能释放,则将抛出TimeoutExceptionint getNumberWaiting(): 获取当前在屏障处的线程数boolean isBroken(): 判断屏障是否被破坏void reset():重置屏障为初始化状态。如果当前有线程正在等待,则这些线程将被释放并抛出BrokenBarrierException
- 构造方法,
-
CyclicBarrier使用注意事项
- 一定要确保有足够多的参与者线程,否则会一直阻塞在屏障处。
- 在线程池中使用要注意,确保线程池的线程数大于等于参与数。
-
CyclicBarrier适用场景
- 线程等待一起执行
- 多次等待一起执行
-
CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier对比
- CountDownLatch是一部分线程等待另外一部分线程来唤醒
- CyclicBarrier是参与线程彼此等待,都到达了,再一起执行
- CountDownLatch不可以循环引用,CyclicBarrier可以循环使用
-
场景:多阶段等待一起出发
案例:公司组织周末旅游活动,大家各自从家出发到公司集合,大家都到了之后,出发到公司各自游玩,然后在公园门口集合,再去餐厅就餐,大家都到了就开始用餐。使用并非编程模拟场景。
参与者不变,多次彼此等待。正好可用CyclicBarrier的循环使用特性
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
public class CyclicBarrierExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int concurrency = 100;
final CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(concurrency , ()->{
System.out.println("*****************准备完成!************");
});
final Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0 ; i < concurrency; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10_000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "准备就绪");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(
Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 开始工作....");
}).start();
}
}
}
控制台打印:
...
Thread-12准备就绪
Thread-58准备就绪
Thread-75准备就绪
Thread-25准备就绪
*****************准备完成!************
Thread-25 开始工作....
Thread-89 开始工作....
Thread-34 开始工作....
...
6、相位器Phaser
jdk7中增加了一个用于多阶段同步控制的工具类,它包含了CyclicBarrier和CountDownLatch的相关功能,比它们更强大灵活。
对Phaser阶段协同器的理解,Phaser适用于多个线程协作的任务,分为多个阶段,每个阶段都可以有任意个参与者,线程可以随时注册并参与某个阶段;当一个阶段中所有任务都成功完成后,Phaser的onAdvance()被调用,然后Phaser释放等待线程,自动进入下个阶段。如此循环,直到Phaser不再包含任何参与者。
Phaser API说明:
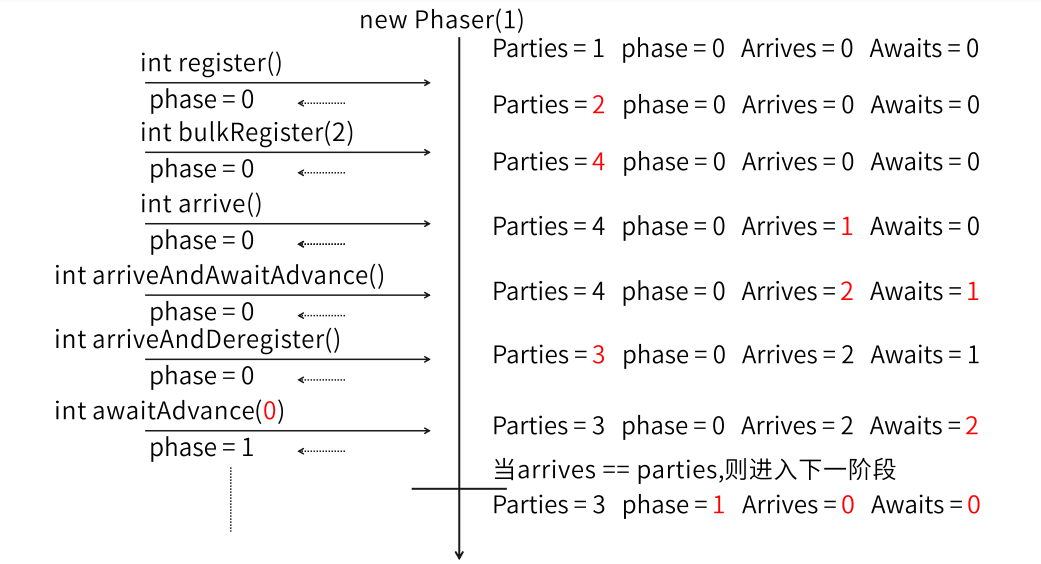
-
构造方法
Phaser():参与任务数0Phaser(int parties):指定初始参与任务数Phaser(Phaser parent):指定parent阶段器, 子对象作为一个整体加入parent对象,当子对象中没有参与者时,会自动从parent对象解除注册Phaser(Phaser parent , int parties):集成上面两个方法的
-
增减参与任务数方法
int register():增加一个数,返回当前阶段号int bulkRegister(int parties):增加指定个数,返回当前阶段号int arriveAndDeregister():减少一个任务数,返回当前阶段号
-
到达等待方法
int arrive():到达,任务完成,返回当前阶段号int arriveAndAwaitAdvance():到达后等待其他任务到达,返回到达阶段号int awaitAdvance(int phase):在指定阶段等待(必须是当前阶段才有效)int awaitAdvanceInterruptibly(int phase)int awaitAdvanceInterruptibly(int phase , long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
-
阶段到达触发动作
protected boolean onAdvance(int Phase , int registeredParties):类似于CyclicBarrier的触发命令,通过重写该方法来增加阶段到达动作
-
其它api
void forceTermination():强制结束boolean isTerMinated():判断是否结束void getPhase():获取当前阶段号
-
注意事项 : 单个Phaser实例允许的注册任务数的上限是65535,如果参与任务数超过,可以用父子Phaser树的方式
场景:公司组织郊游活动,大家各自从家出发到公司集合,大家都到了后,出发到公园各自游玩,然后在公园门口集合,再去餐厅就餐,大家都到了就开始用餐。有的员工白天有事,选择晚上的聚餐,有的员工则晚上有事,只参加白天的活动。编程模拟实现。
- 第一阶段,到公司集合5人,任务数为5,去公园游玩。
- 第二阶段,到公园门口集合,有2人因为晚上有事,自行从公园回家;则3人去餐厅,这是减少参与数,任务数变为3
- 第三阶段,餐厅集合,有另外4人参加聚餐,这是增加参与数,任务数变为7
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Phaser;
public class MultipleStartTogetherPhserDemo {
Random rd = new Random();
int bound = 5000;
public void step1Task() throws InterruptedException {
// 经过一段时间后,到达公司
Thread.sleep(rd.nextInt(bound));
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】" + "到达公司!");
}
public void step2Task() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】" + "出发去公园玩...");
// 玩了一段时间后,到公园门口集合
Thread.sleep(rd.nextInt(bound));
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】" + "完成公园游玩!");
}
public void step3Task() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】" + "出发去餐厅...");
// 玩了一段时间后,到公园门口集合
Thread.sleep(rd.nextInt(bound));
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】" + "到达餐厅!");
}
public void step4Task() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】" + "开始用餐...");
// 玩了一段时间后,到公园门口集合
Thread.sleep(rd.nextInt(bound));
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】" + "回家了!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建阶段协同器对象,重写了onAdvance方法,增加阶段到达处理逻辑
final Phaser ph = new Phaser() {
protected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) {
int staffs = registeredParties - 1;
switch (phase) {
case 0:
System.out.println("大家都到公司了,出发去公园!人数:" + staffs);
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("大家都到公园大门,出发去餐厅!人数:" + staffs);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("大家都到餐厅了,开始用餐!人数:" + staffs);
break;
}
// 判断是否只剩主线程一个参与者,是,则返回true,阶段协同器终止。
return registeredParties == 1;
}
};
// 增加一个任务数,用来让主线程全程参与
ph.register();
final MultipleStartTogetherPhserDemo job = new MultipleStartTogetherPhserDemo();
// 让3个全程参与的线程加入
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// 增加参与任务数
ph.register();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
job.step1Task();
ph.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
job.step2Task();
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】"
+ "到达公园大门集合");
ph.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
job.step3Task();
ph.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
job.step4Task();
// 完成了,注销离开
ph.arriveAndDeregister();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
// 让两个不参加聚餐的员工加入
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
// 增加参与任务数
ph.register();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
job.step1Task();
ph.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
job.step2Task();
System.out.println(
"员工【" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "】"
+ "回家了!");
// 完成了,注销离开
ph.arriveAndDeregister();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
while (!ph.isTerminated()) {
int phaser = ph.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
if (phaser == 2) { // 到了去餐厅的阶段,让只参加晚上聚餐的人加入
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
// 增加参与任务数
ph.register();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
job.step3Task();
ph.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();
job.step4Task();
// 完成了,注销离开
ph.arriveAndDeregister();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
}
}
7、Semaphore计数信号量
-
Semaphore计数信号量定义
理解:就是要给令牌池,可获取信号量(令牌或者许可)、放入信号量。常用于控制并发的线程数,也可用于池类资源的访问控制。 -
构造方法
Semaphore(int permits):指定初始许可数Semaphore(int permits , boolean fair):指定是否公平模式
-
尝试获取许可
boolean tryAcquire(long timeout , TimeUnit unit)boolean tryAcquire(int permits)boolean tryAcquire(int permits, long timeout , TimeUnit unit)
-
获取许可
void acquire() throws InterruptedException;:获取1个许可,可中断void acquire(int permits) throws InterruptedException;:获取指定数量的许可,可中断void acquireUninterruptibly():获取1个许可,不可中断void acquireUninterruptibly(int permits)int drainPermits():获取当前所有可用的
-
放入许可
void release():放入1个void release(int permits):放入多个
-
其它API
boolean isFair()int availablePermitsboolean hasQueuedThreads()int getQueueLength()Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads()
场景:一个共享汽车场地有10辆汽车,但是有20个人需要借车,一辆汽车只能被一个人租赁,只有使用还车之后,其他人才能继续使用租赁
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
/**
* <pre>
* Semaphore example
* </pre>
*
* <pre>
* @author mazq
* 修改记录
* 修改后版本: 修改人: 修改日期: 2021/11/30 14:16 修改内容:
* </pre>
*/
public class SemaphoreExample {
// 公平模式
private Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(10, true);
private final Random random = new Random();
public void userCar() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "需要用车");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取许可
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "租车成功,等待了:" +(System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(10_000));
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
} finally {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "还车了!");
// 释放许可
semaphore.release();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Random ran = new Random();
final SemaphoreExample semaphoreExample = new SemaphoreExample();
for (int i = 0; i < 20 ; i++) {
new Thread(()-> {
try {
Thread.sleep(ran.nextInt(5_000));
semaphoreExample.userCar();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
Thread-8需要用车
Thread-8租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-1需要用车
Thread-1租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-12需要用车
Thread-12租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-6需要用车
Thread-6租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-13需要用车
Thread-13租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-15需要用车
Thread-15租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-19需要用车
Thread-19租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-5需要用车
Thread-5租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-18需要用车
Thread-18租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-0需要用车
Thread-0租车成功,等待了:0
Thread-7需要用车
Thread-11需要用车
Thread-10需要用车
Thread-13还车了!
Thread-7租车成功,等待了:461
Thread-14需要用车
Thread-2需要用车
Thread-3需要用车
Thread-4需要用车
Thread-15还车了!
Thread-11租车成功,等待了:1291
Thread-0还车了!
Thread-10租车成功,等待了:1601
Thread-9需要用车
Thread-10还车了!
Thread-14租车成功,等待了:2008
Thread-17需要用车
Thread-16需要用车
Thread-11还车了!
Thread-2租车成功,等待了:2858
Thread-6还车了!
Thread-3租车成功,等待了:2513
Thread-8还车了!
Thread-4租车成功,等待了:3218
Thread-7还车了!
Thread-9租车成功,等待了:2420
Thread-12还车了!
Thread-17租车成功,等待了:3266
Thread-3还车了!
Thread-16租车成功,等待了:3329
Thread-19还车了!
Thread-1还车了!
Thread-17还车了!
Thread-5还车了!
Thread-4还车了!
Thread-18还车了!
Thread-2还车了!
Thread-14还车了!
Thread-9还车了!
Thread-16还车了!
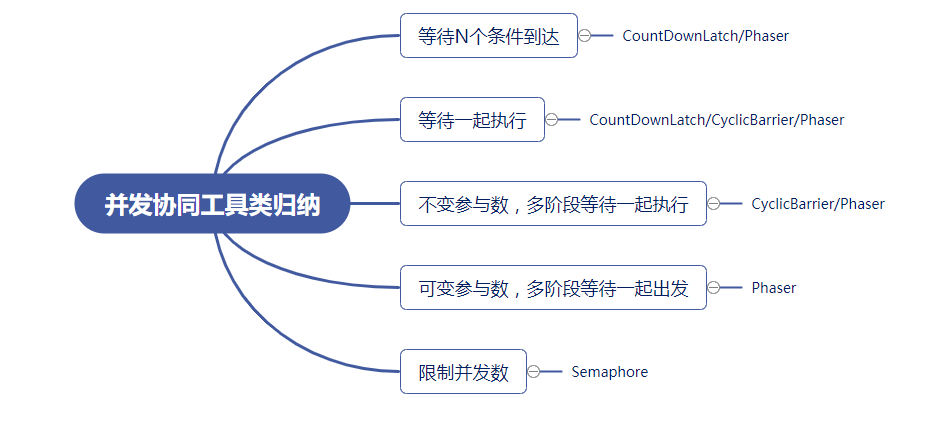
8、并发协同工具类归纳