文章目录
Spring Cloud学习笔记总目录:总目录
Spring Cloud Config
- spring cloud config是
为微服务架构中的各个服务提供集中化的外部配置支持的组件 - 分为服务端和客户端两个部分,服务端也叫
分布式配置中心(Config Server),是一个独立的微服务应用,用来保存配置信息(默认使用Git存储),客户端(Config Client)则就是通过指定的配置中心来获取配置内容
使用Spring Cloud Config的好处
集中管理公用配置信息动态的配置更新,切换配置环境(开发、测试、生产),实时同步到所有服务- 配置信息以
REST接口形式暴露
bootstrap.yml是什么
- 简单的说,application.yml是各个服务各自的配置,而bootstrap.yml则是系统级的、公用的,具有
最高优先级 - 必须要将Config Client服务的配置文件命名为bootstrap.yml
如何动态刷新配置到各个client
- 加入actuator行为监控图形化的pom依赖
暴露监控端点,让服务器中心检测到- controller层加
@RefreshScope - 需要运维工程师发送一个
post请求(如:curl -X POST http://localhost:3355/actuator/refresh)到需要刷新配置的微服务,就不用重启了
但是很麻烦,需要向每个微服务单独发请求,有没有一种广播通知,可以让我们只用发送一次广播就处处生效呢?这就是后文的Bus
@RefreshScope注解
@RestController
@RefreshScope
public class ConfigClientController
{
@Value("${config.info}")
private String configInfo;
@GetMapping("/configInfo")
public String getConfigInfo()
{
return configInfo;
}
}
Config Server的配置
关键依赖
<!--添加消息总线RabbitMQ支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 图形监控 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 启动类加
@EnableConfigServer - 其中有些是关于Bus的配置
server:
port: 3344
spring:
application:
name: cloud-config-center #注册进Eureka服务器的微服务名
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: git@github.com:zzyybs/springcloud-config.git #GitHub上面的git仓库名字
search-paths:
- springcloud-config # 类似于根目录
label: master # 读取的分支
# rabbitmq相关配置 Bus要用
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
#服务注册到eureka地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
# rabbitmq相关配置,暴露bus刷新配置的端点
management:
endpoints: #暴露bus刷新配置的端点
web:
exposure:
include: 'bus-refresh'
Config Client的配置
关键依赖
<!--添加消息总线RabbitMQ支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 注意配置文件名叫bootstrap.yml
server:
port: 3355
spring:
application:
name: config-client
cloud:
# Config客户端配置
config:
label: master # 分支名称
name: config # 配置文件名称
profile: dev # 读取后缀名称 上述3个综合:master分支上config-dev.yml的配置文件被读取http://config-3344.com:3344/master/config-dev.yml
uri: http://localhost:3344 # config server的地址
#rabbitmq相关配置 15672是Web管理界面的端口;5672是MQ访问的端口
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
#服务注册到eureka地址
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka
# 暴露监控端点
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
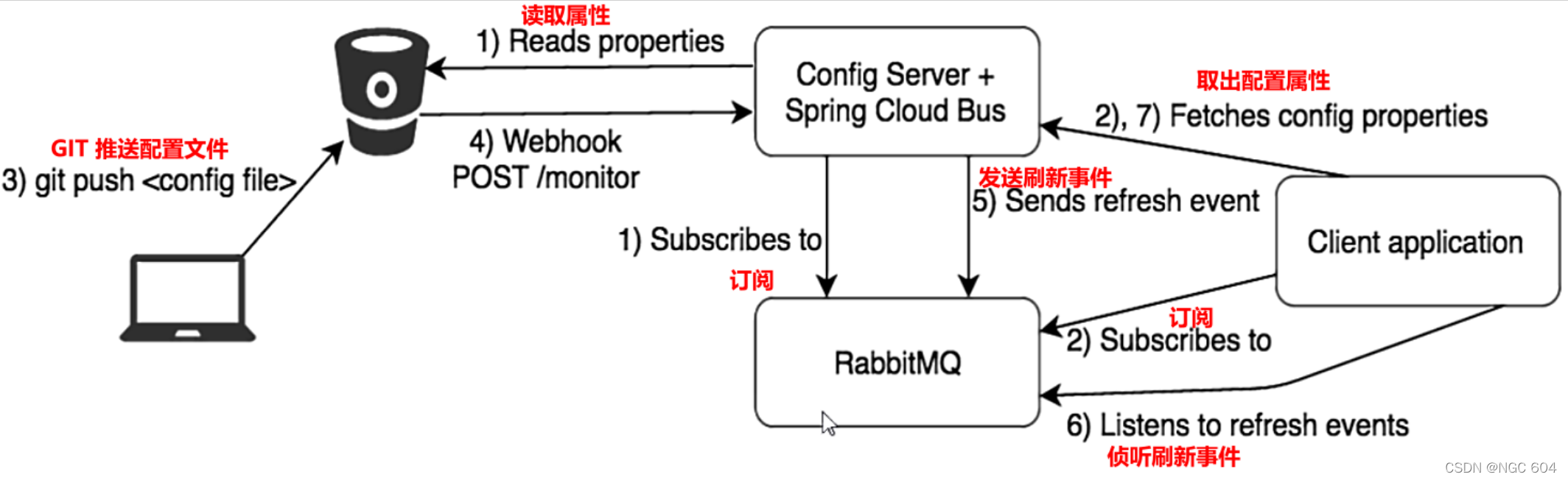
Spring Cloud Bus
- 简单的说就是在微服务架构的系统中构建了一个共用的消息主题,该主题中产生的消息会被订阅了它的所有微服务实例监听、消费
- 基本原理:所有Config Client实例都监听MQ中同一个
topic(默认叫springCloudBus),当数据更新的时候,实例就会自动更新自己的配置 - Spring Cloud Bus配合Spring Cloud Config可以实现配置的动态刷新,Spring Cloud Bus目前只支持RabbitMQ和Kafka
两种设计思想
- 利用消息总线触发一个
客户端/bus/refresh,由该客户端刷新所有客户端的配置 - 利用消息总线触发一个
服务端ConfigServer 的 /bus/refresh 端点,由Server刷新所有客户端的配置(更加推荐)
方案1不适合的原因如下:
打破了微服务的职责单一性,因为微服务本身是业务模块,它本不应该承担配置刷新职责- 破坏了微服务各节点的对等性
- 有一定的局限性。例如,微服务在迁移时,它的网络地址常常会发生变化,此时如果想要做到自动刷新,那就会增加更多的修改
主要添加的配置(简单说,前文都有)
- bus-amqp的依赖
- mq的配置
- 暴露 Bus 刷新配置的端点
最后只需要发送一个post请求(curl -X POST "http://localhost:3344/actuator/bus-refresh")到Config Server,就可以实现配置文件的动态刷新广播
动态刷新定点通知
- 上文配置的是广播,假设想要实现定点通知,只需要更改一下post请求:http://localhost:配置中心的端口号/actuator/bus-refresh/{destination}
- 其中destination是指定的
微服务名+端口,如:config-client:3355 - /bus-refresh 请求不再发送到具体的服务实例上,而是发给 config server 并通过 destination 参数类指定需要更新配置的服务或实例
总结