一、集合
1.什么是集合
? ? 1、集合类存放于java.util包中。
? ? 2、集合类型主要有3种:set(集)、list(列表)和map(映射)。
? ? 3、集合存放的都是对象的引用,而非对象本身。所以我们称集合中的对象就是集合中对象的引用。
? ? 简单来讲:集合就是一个放数据的容器,准确的说是放数据对象引用的容器。
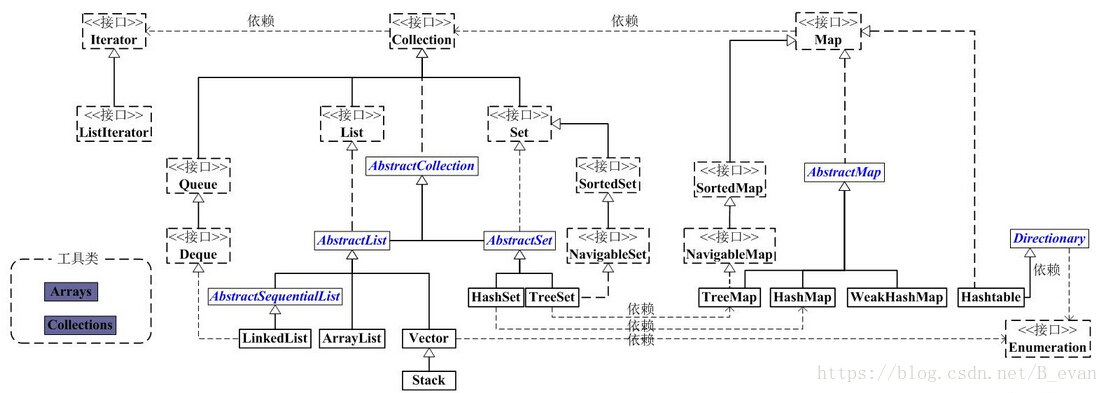
2.集合的关系
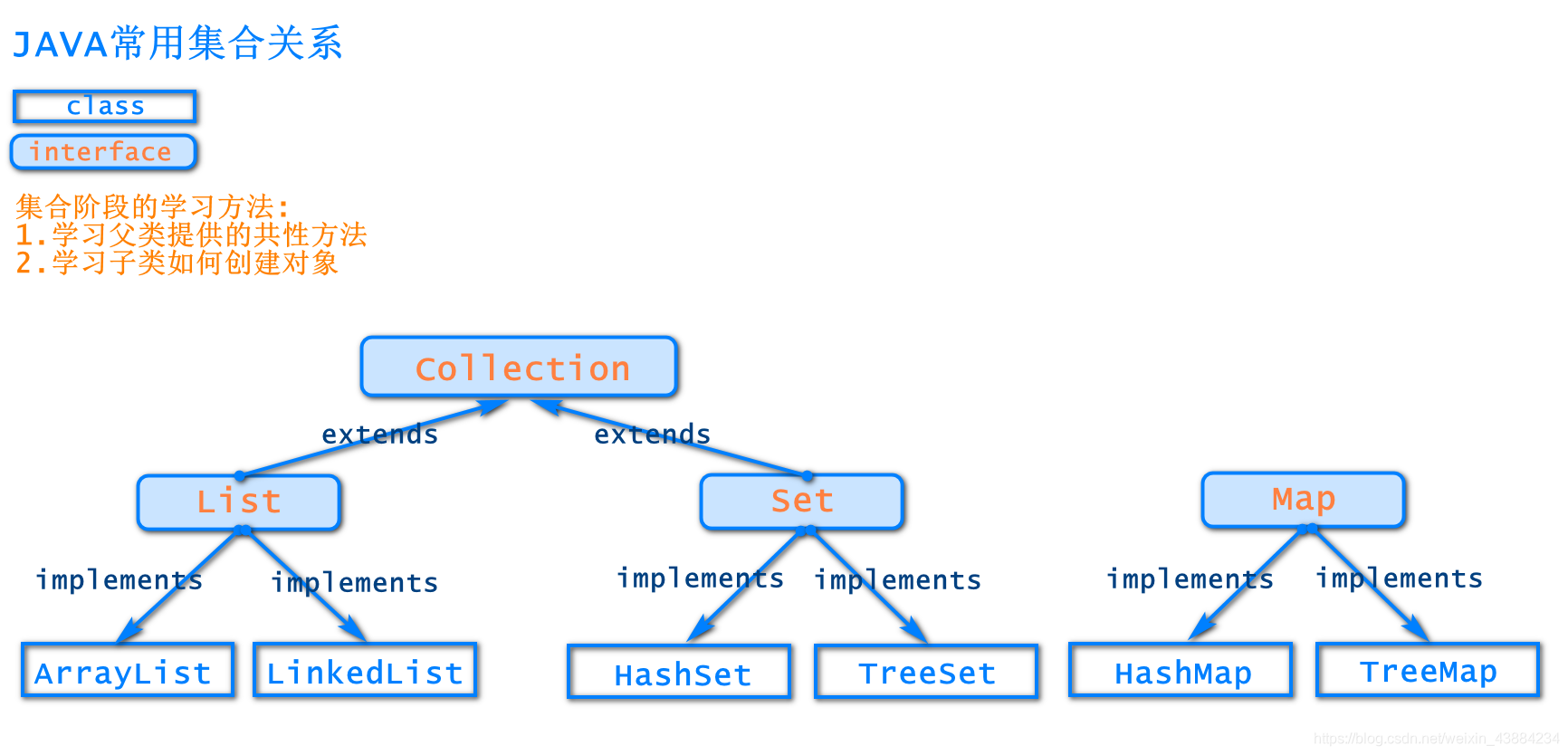
?
?
3.集合的继承结构
Collection接口
4.Collection接口介绍
Collection c = new ArrayList();
Iterator it = c.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object ob = it.next();
}public class TestCollection {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建Collection对象
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<>();
//2.向集合添加元素
collection.add(123);
collection.add(234);
collection.add(345);
//3.打印集合中的内容
System.out.println(collection);
//4集合的常用方法测试
//4.1清空集合
collection.clear();
//4.2获取对象的哈希码值
System.out.println(collection.hashCode());
//4.3打印集合的具体元素
System.out.println(collection.toString());
//4.4判断集合对象中是否有指定元素
System.out.println(collection.equals(200));
//4.5判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
//4.6移除集合中的指定元素
System.out.println(collection.remove(200));
//4.7返回元素的个数
System.out.println(collection.size());
//4.8将指定的集合转为数组object
Object[] objects = collection.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(objects));
//5.操作集合与集合之间的常用方法
//5.1创建Collection对象
Collection<Integer> collection2 = new ArrayList<>();
//5.2向集合添加元素
collection2.add(111);
collection2.add(222);
collection2.add(333);
//5.3把集合2 添加到 集合1 中
System.out.println(collection.containsAll(collection2));
//5.4查看是否包含指定元素
System.out.println(collection.contains(123));
//5.5删除集合1中的集合2的所有元素
System.out.println(collection.removeAll(collection2));
//5.6取集合的公共元素
System.out.println(collection.retainAll(collection2));
//6.遍历集合
//6.1增强for变量
for (Integer integer : collection) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
//6.2迭代器变量
Iterator<Integer> iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}四、多线程
1.进程 线程 多线程
????????核心概念:
- 线程就是独立的执行路径
- 在程序运行时,即使没有自己创建线程,后台也会有多个线程
- main()称之为主线程,为系统的入口,用于执行整个程序
- 在一个进程中,如果开辟了多个线程,线程的运行有调度器安排调度也就是cpu,调度器是与操作系统紧密相关的,先后顺序是不能人为的干预的
- 对同一份资源操作时,会存在资源抢夺问题,需要加入并发控制
- 线程会带来额外的开销,如cpu调度时间,并发控制开销
- 每个线程在自己的工作内存交互,内存控制不当会造成数据不一致
2.三种创建方式
1.继承Thread类(重点)
- 自定义线程类继承Thread类
- 重写run()方法,编写线程执行方法
- 创建线程对象,调用start()方法启动线程
- 启动线程不是立即执行,而是调度器进行分配后执行(分配时间片和执行顺序)
public class TestThread1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread1 = new MyThread();
MyThread myThread2 = new MyThread();
MyThread myThread3 = new MyThread();
//启动线程
myThread1.start();
myThread2.start();
myThread3.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("这是主线程:"+i);
}
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(i+"----"+getName());
}
}
}2.实现Runnable接口 (重点)
- 定义MyRunnable类实现Runnable接口
- 实现run()方法,编写线程执行体
- 创建线程对象,调用start()方法启动线程
- 推荐使用Runnable对象,因为java单继承的局限性
public class TestRunnable1 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程:"+i+" "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建接口的实现类对象
TestRunnable1 t1 = new TestRunnable1();
TestRunnable1 t2 = new TestRunnable1();
TestRunnable1 t3 = new TestRunnable1();
//创建线程的对象,通过线程对象来开启我们的线程,代理
new Thread(t1).start();
new Thread(t2).start();
new Thread(t3).start();
//另一个参数可以设置线程的名字
new Thread(t1,"小名").start();
new Thread(t2,"小黄").start();
new Thread(t3,"小红").start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程:"+i);
}
}
}买票练习:
public class TestRunnable2 implements Runnable{
private int mp = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if (mp <= 0)break;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+mp--+"票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestRunnable2 testRunnable21 = new TestRunnable2();
//出现并发问题
//问题1:产生了重卖的现象:同一张票卖了多个人
//问题2:产生了超卖的现象:超出了规定的票数100,出现了0 -1 -2这样的票
new Thread(testRunnable21,"xiaoming----").start();
new Thread(testRunnable21,"xiaozhang----").start();
new Thread(testRunnable21,"xiaomi-----").start();
}
}3.实现Callable接口(了解)
- 实现Callable接口,需要返回值类型
- 重写call方法,需要抛出异常
- 创建目标对象
- 创建执行服务:ExecutorService ser = Excutors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
- 提交执行:Future<Boolean> result1 = ser.submit(1);
- 获取结果:boolean r1 = result1.get();
- 关闭服务:ser.shutdownNow();
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
static int i = 10;
String ck;
public TestCallable() {}
public TestCallable(String ck) {
this.ck = ck;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
while (true){
if (i==0)break;
System.out.println(ck +"卖了"+i--+"了");
}
return i;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
TestCallable testCallable1 = new TestCallable("窗口1");
TestCallable testCallable2 = new TestCallable("窗口2");
TestCallable testCallable3 = new TestCallable("窗口3");
TestCallable testCallable4 = new TestCallable("窗口4");
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
Future<Integer> submit1 = service.submit(testCallable1);
Future<Integer> submit2 = service.submit(testCallable2);
Future<Integer> submit3 = service.submit(testCallable3);
Future<Integer> submit4 = service.submit(testCallable4);
Integer integer1 = submit1.get();
Integer integer2 = submit2.get();
Integer integer3 = submit3.get();
Integer integer4 = submit4.get();
service.shutdownNow();
}3.线程的方法
1.停止线程
- 不推荐使用JDK提供的stop()、destroy()方法。
- 推荐线程自己停止下来
- 建议使用一个标志位进行终止变量
package cn.tedu.review;
public class TestStop implements Runnable{
static boolean flag = true;
public void stop(){
this.flag = false;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while(flag){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---"+i++);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop testStop = new TestStop();
new Thread(testStop,"小张").start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
if (i == 9) {
testStop.stop();
System.out.println("线程结束了");
}
}
}
}
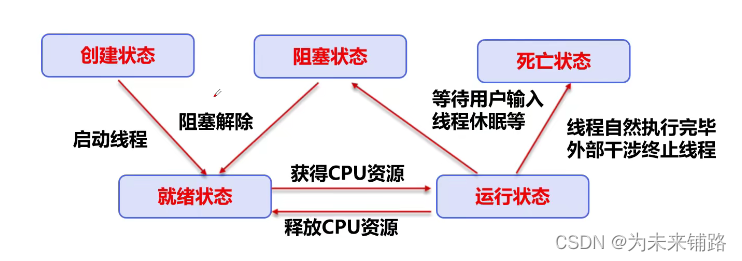
2.线程休眠
- sleep指定当前线程
- sleep存在异常InterruptedException
- sleep时间达到后线程进入就绪状态
- sleep可以模拟网络延迟时,倒计时等
- 每个对象都有一个锁,sleep不会释放锁
3.线程礼让
- 礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
- 将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态
- 让CPU重新调度,礼让不一定成功看cpu心情!!
- yield()
4.Join
- Join合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其它的线程阻塞
- 可以想象成插队
- 不建议使用,防止线程阻塞
5.线程状态观测
? ? ? ? Thread.State
6.线程优先级
Java提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度器按照优先级决定应该调度哪个线程执行
线程的优先级用数字表示? 1-10
getPriority()? 获取优先级
setPriority(int i)改变优先级
7.守护线程
- 线程分为用户线程和守护线程
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- setDaemon(boolean true);
4.线程的状态
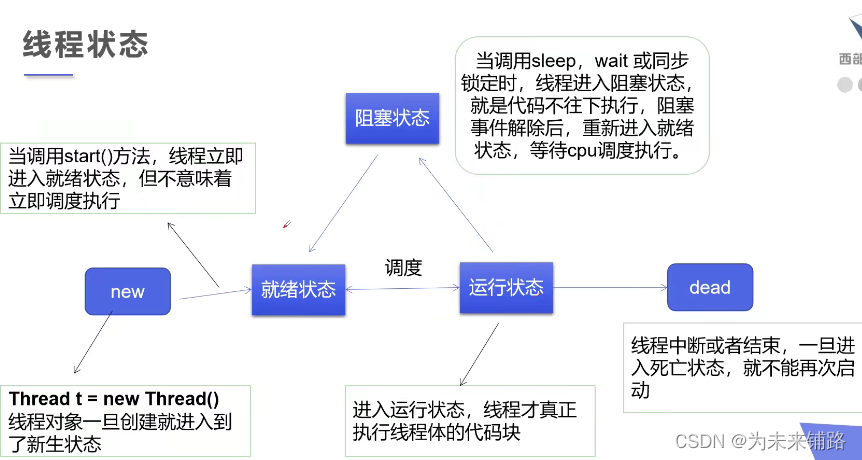
?
?5.线程同步
在多线程程序中 + 有共享数据 + 多条语句操作共享数据
同步:体现了排队的效果,同一时刻只能有一个线程独占资源,其他没有权力的线程排队。
坏处就是效率低,不过保证了安全
异步:体现了多线程抢占资源的效果,线程间互相不等待,互相抢夺资源,坏处就是安全隐患,效率要高一些。
十、单例设计模式
1.什么是设计模式?
设计模式(Design pattern)是一套被反复使用、多数人知晓的、经过分类编目的、代码设计经验的总结。(百度解释)
其实设计模式是人们实践的产物,在初期的开发过程中好多人发现再进行重复的代码书写,那些开发大牛们就不断总结、抽取最终得到了大家的认可于是就产生了设计模式,其实设计模式的种类可以分为23种左右,今天主要和大家一起学习一下单例设计模式,因为这种设计模式是使用的最多的设计模式。
2.为什么会有单例设计模式?
可以保证一个类在内存中的对象的唯一性,在一些常用的工具类、线程池、缓存,数据库,账户登录系统、配置文件等程序中可能只允许我们创建一个对象,一方面如果创建多个对象可能引起程序的错误,另一方面创建多个对象也造成资源的浪费。在这种基础之上单例设计模式就产生了因为使用单例能够保证整个应用中有且只有一个实例,
3.单例模式的设计思想
(1)不允许其他程序用new对象。
? ? 因为new就是开辟新的空间,在这里更改数据只是更改的所创建的对象的数据,如果可以new的话,每一次new都产生一个对象,这样肯定保证不了对象的唯一性。
(2)在该类中创建对象
? ?因为不允许其他程序new对象,所以这里的对象需要在本类中new出来
(3)对外提供一个可以让其他程序获取该对象的方法
? ?因为对象是在本类中创建的,所以需要提供一个方法让其它的类获取这个对象。
那么这三步怎么用代码实现呢?将上述三步转换成代码描述是这样的
(1)私有化该类的构造函数
(2)通过new在本类中创建一个本类对象
(3)定义一个公有的方法,将在该类中所创建的对象返回
单例模式的写法
????????
目录
十一、反射
1.反射的概念
????????JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
要想解剖一个类,必须先要获取到该类的字节码文件对象。而解剖使用的就是Class类中的方法.所以先要获取到每一个字节码文件对应的Class类型的对象.
反射就是把java类中的各种成分映射成一个个的Java对象
Class对象的由来是将class文件读入内存,并为之创建一个Class对象。
2.为什么要是有反射
类不是你创建的,是你同事或者直接是第三方公司,此时你要或得这个类的底层功能调用,就需要反射技术实现。有点抽象
3.反射的使用
1.获取Class对象的三种方式
//第一种 【常用】
Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;
//第二种
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("cn.tedu.cn.Student");
//第三种
Class<? extends Student> aClass1 = new Student().getClass();2.获取类对象
System.out.println("==============获取类对象==============");
System.out.println(studentClass);
System.out.println(aClass);
System.out.println(aClass1);
System.out.println("==============获取当前字节码对象的名字==============");
System.out.println(studentClass.getName());
System.out.println("==============获取类的类名==============");
System.out.println(studentClass.getSimpleName());
System.out.println("==============获取类对应的包名==============");
System.out.println(studentClass.getPackage());
System.out.println("==============获取类对应的包名对象再获取包的名字==============");
System.out.println(studentClass.getPackage().getName());3.通过字节码对象获取类的成员方法
public void eat2(){
//1.获取字节码对象
Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;
//2.通过字节码对象获取目标类中的成员方法们
Method[] methods = studentClass.getMethods();
//3.通过高效for循环遍历数组,拿到每一个方法对象
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
System.out.println("==============通过方法对象获取方法名==============");
System.out.println(method.getName());
System.out.println("==============通过对象获取方法所有参数==============");
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(parameterTypes));
System.out.println("=============================================");
}
}4.通过字节码对象获取类的构造方法
@Test
public void eat3(){
//1.获取字节码对象
Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;
//2.通过字节码对象获取目标类Student的构造方法们
Constructor<?>[] constructors = studentClass.getConstructors();
//3.通过高效for循环遍历数组
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
System.out.println("==============获取构造方法的名字==============");
System.out.println(constructor.getName());
System.out.println("==============构造函数对象获取构造函数的参数类型==============");
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = constructor.getParameterTypes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(parameterTypes));
System.out.println("=============================================");
}
}5.通过反射获取构造方法并使用
/*
* 通过Class对象可以获取某个类中的:构造方法、成员变量、成员方法;并访问成员;
*
* 1.获取构造方法:
* 1).批量的方法:
* public Constructor[] getConstructors():所有"公有的"构造方法
public Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors():获取所有的构造方法(包括私有、受保护、默认、公有)
* 2).获取单个的方法,并调用:
* public Constructor getConstructor(Class... parameterTypes):获取单个的"公有的"构造方法:
* public Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(Class... parameterTypes):获取"某个构造方法"可以是私有的,或受保护、默认、公有;
*
* 调用构造方法:
* Constructor-->newInstance(Object... initargs)
*/
@Test
public void eat4() throws Exception {
//1.加载Class对象
Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;
//2.获取所有公有构造方法
System.out.println("**********************所有公有构造方法*********************************");
Constructor<?>[] constructors = studentClass.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
System.out.println("************所有的构造方法(包括:私有、受保护、默认、公有)***************");
Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = studentClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> declaredConstructor : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(declaredConstructor);
}
System.out.println("*****************获取公有、无参的构造方法*******************************");
Constructor<Student> constructor = studentClass.getConstructor(null);
System.out.println(constructor);
//调用构造方法
Object obj = constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println("******************获取私有构造方法,并调用*******************************");
Constructor<Student> declaredConstructor = studentClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class,char.class);
//暴力访问(忽略掉访问修饰符)
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
//调用构造方法
obj = declaredConstructor.newInstance("事实上",12,'男');
System.out.print(obj);
}后台输出:
**********************所有公有构造方法*********************************
public cn.tedu.cn.Student()
public cn.tedu.cn.Student(java.lang.String,int,char)
************所有的构造方法(包括:私有、受保护、默认、公有)***************
public cn.tedu.cn.Student()
public cn.tedu.cn.Student(java.lang.String,int,char)
*****************获取公有、无参的构造方法*******************************
public cn.tedu.cn.Student()
******************获取私有构造方法,并调用*******************************
public cn.tedu.cn.Student(java.lang.String,int,char)
Student{string='事实上', age=12, sex=男}
6.获取成员变量并调用
@Test
public void eat5() throws Exception {
/*
* 获取成员变量并调用:
*
* 1.批量的
* 1).Field[] getFields():获取所有的"公有字段"
* 2).Field[] getDeclaredFields():获取所有字段,包括:私有、受保护、默认、公有;
* 2.获取单个的:
* 1).public Field getField(String fieldName):获取某个"公有的"字段;
* 2).public Field getDeclaredField(String fieldName):获取某个字段(可以是私有的)
*
* 设置字段的值:
* Field --> public void set(Object obj,Object value):
* 参数说明:
* 1.obj:要设置的字段所在的对象;
* 2.value:要为字段设置的值;
*
*/
//1.获取Class对象
Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;
//2.获取字段
System.out.println("************获取所有公有的字段********************");
Field[] fields = studentClass.getFields();
for(Field f : fields){
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println("************获取所有的字段(包括私有、受保护、默认的)********************");
Field[] declaredFields = studentClass.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field f : declaredFields){
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println("*************获取公有字段**并调用***********************************");
Field field = studentClass.getField("string");
//获取一个对象 getConstructor()公共类函数.newInstance()创建一个新的实例化
Object obj = studentClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
//为字段设置值
field.set(obj, "刘德华");//为Student对象中的string属性赋值--》stu.string = "刘德华"
//验证
System.out.println(field.get(obj));
System.out.println("**************获取私有字段****并调用********************************");
Field phoneNum = studentClass.getDeclaredField("sex");
//触发无参构造利用反射创建对象
Student student = studentClass.newInstance();
phoneNum.setAccessible(true);//暴力反射,解除私有限定
phoneNum.set(student, '男');
System.out.print(phoneNum.get(student));
}后台输出:
************获取所有公有的字段********************
public java.lang.String cn.tedu.cn.Student.string
************获取所有的字段(包括私有、受保护、默认的)********************
public java.lang.String cn.tedu.cn.Student.string
private int cn.tedu.cn.Student.age
private char cn.tedu.cn.Student.sex
*************获取公有字段**并调用***********************************
刘德华
**************获取私有字段****并调用********************************
男
7.获取成员方法并调用
@Test
public void eat7() throws Exception {
/*
* 获取成员方法并调用:
*
* 1.批量的:
* public Method[] getMethods():获取所有"公有方法";(包含了父类的方法也包含Object类)
* public Method[] getDeclaredMethods():获取所有的成员方法,包括私有的(不包括继承的)
* 2.获取单个的:
* public Method getMethod(String name,Class<?>... parameterTypes):
* 参数:
* name : 方法名;
* Class ... : 形参的Class类型对象
* public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name,Class<?>... parameterTypes)
*
* 调用方法:
* Method --> public Object invoke(Object obj,Object... args):
* 参数说明:
* obj : 要调用方法的对象;
* args:调用方式时所传递的实参;
*/
//1.获取Class对象
Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;
//2.获取所有公有方法
System.out.println("***************获取所有的”公有“方法*******************");
Method[] methodArray = studentClass.getMethods();
for(Method m : methodArray){
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println("***************获取所有的方法,包括私有的*******************");
methodArray = studentClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for(Method m : methodArray){
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println("***************获取公有的show1()方法*******************");
Method m = studentClass.getMethod("show1", String.class);
//实例化一个Student对象
Object obj = studentClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
m.invoke(obj, "刘德华");
System.out.println("***************获取私有的show1()方法******************");
m = studentClass.getDeclaredMethod("show1", int.class);
Constructor<Student> constructor = studentClass.getConstructor();
Student student = constructor.newInstance();
m.setAccessible(true);//解除私有限定
m.invoke(student, 20);//需要两个参数,一个是要调用的对象(获取有反射),一个是实参
}后台输出:
***************获取所有的”公有“方法*******************
public java.lang.String cn.tedu.cn.Student.getString()
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.show1(int)
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.show1(java.lang.String)
public int cn.tedu.cn.Student.getAge()
public char cn.tedu.cn.Student.getSex()
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.setString(java.lang.String)
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.setSex(char)
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.setAge(int)
public java.lang.String cn.tedu.cn.Student.toString()
public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)
public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()
public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()
public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()
public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()
***************获取所有的方法,包括私有的*******************
public java.lang.String cn.tedu.cn.Student.getString()
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.show1(int)
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.show1(java.lang.String)
public int cn.tedu.cn.Student.getAge()
public char cn.tedu.cn.Student.getSex()
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.setString(java.lang.String)
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.setSex(char)
public void cn.tedu.cn.Student.setAge(int)
public java.lang.String cn.tedu.cn.Student.toString()
***************获取公有的show1()方法*******************
刘德华
***************获取私有的show4()方法******************
20