Spring Security
以下介绍来自官方文档(博主稍微进行了补充):
Spring Security是一个提供身份验证、授权和针对常见攻击进行保护的框架,对命令式(Servlet)、反应式(Webflux)应用程序都提供了一流的支持,它是保护基于Spring的应用程序的事实标准。
Spring Security为身份验证提供了全面的支持。身份验证是验证尝试访问特定资源的用户的身份的方式。验证用户身份的常用方法是要求用户输入用户名和密码。一旦执行身份验证,就知道其身份并可以执行授权。
Filters
Spring Security的Servlet支持是基于Servlet Filter的,所以了解Filter的作用是有助于理解Spring Security的实现原理。下图显示了单个HTTP请求的处理程序的典型分层。
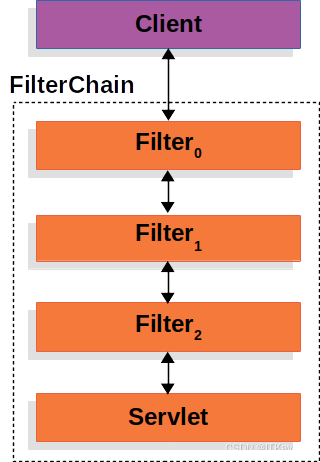
客户端向应用程序发送一个请求,容器创建一个FilterChain,其中包含多个Filter和一个Servlet,这些Filter和Servlet应根据请求URI的路径处理HttpServletRequest。在Spring MVC应用程序中,Servlet是DispatcherServlet的一个实例。最多使用一个Servlet处理单个HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse。但是,可以使用多个Filter来:
-
防止调用下游
Filter或Servlet。在这种情况下,Filter通常会写入HttpServletResponse(比如身份验证不通过,并且不需要再调用下游Filter或Servlet,应设置响应的HTTP状态码,然后返回该响应)。 -
修改被下游
Filter和Servlet使用的HttpServletRequest或HttpServletResponse。
DelegatingFilterProxy
Spring提供了一个名为DelegatingFilterProxy的Filter实现,它允许在Servlet容器的生命周期和Spring的ApplicationContext之间架桥。Servlet容器允许使用自己的标准注册的Filter,但它并不知道Spring定义的bean,DelegatingFilterProxy可以通过标准的Servlet容器机制进行注册,但是将所有工作委托给实现Filter的Spring bean。
下面是一张DelegatingFilterProxy如何融入Filter和FilterChain的结构图。
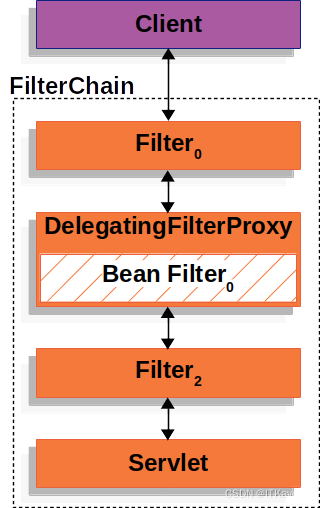
DelegatingFilterProxy从ApplicationContext中查找Bean Filter0,然后调用Bean Filter0。DelegatingFilterProxy的伪代码如下所示。
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) {
// 延迟获取注册为Spring bean的过滤器
// 例如,DelegatingFilterProxy委托中的示例是Bean Filter0的一个实例
Filter delegate = getFilterBean(someBeanName);
// 将工作委托给Spring bean
delegate.doFilter(request, response);
}
DelegatingFilterProxy的另一个好处是它允许延迟查找Filter bean实例。这一点很重要,因为容器需要在启动之前注册Filter。但是,Spring通常使用ContextLoaderListener来加载Spring bean,直到需要注册Filter实例之后才会进行加载。
FilterChainProxy
Spring Security的Servlet支持包含在FilterChainProxy中。FilterChainProxy是Spring Security提供的一种特殊Filter,它允许通过SecurityFilterChain委托给多个Filter实例。由于FilterChainProxy是一个bean,它通常被包装在一个DelegatingFilterProxy中。
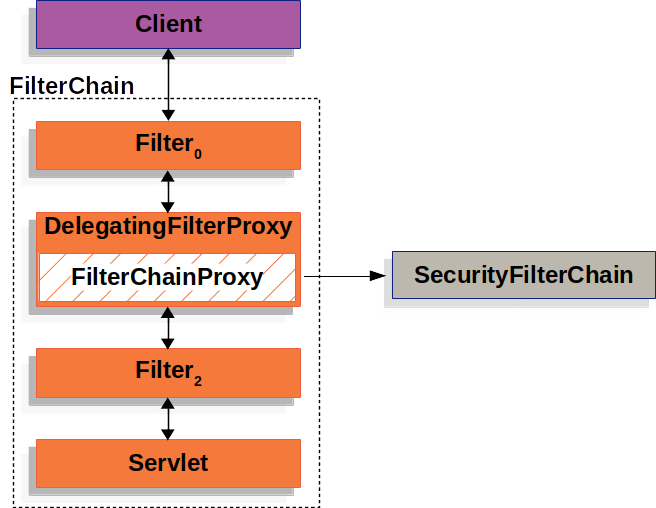
SecurityFilterChain
FilterChainProxy使用SecurityFilterChain确定应为请求调用哪些Security Filter。
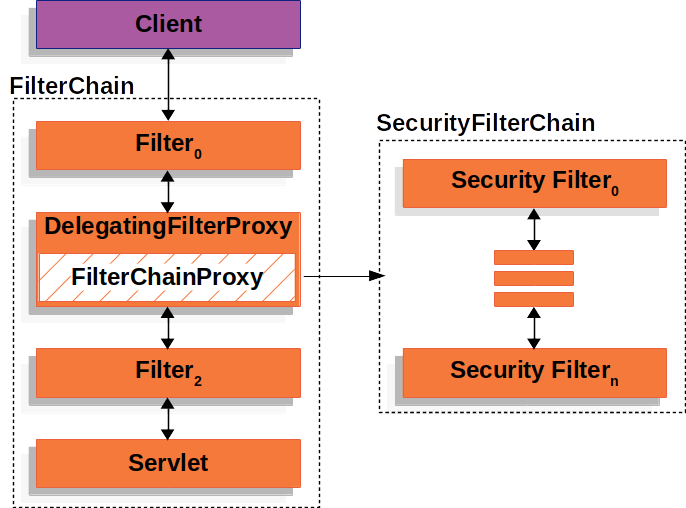
SecurityFilterChain中的Security Filter通常是bean,但它们是在FilterChainProxy中注册的,而不是在DelegatingFilterProxy中注册的。FilterChainProxy为直接向Servlet容器或DelegatingFilterProxy注册Filter提供了许多优势。
首先,它为Spring Security的所有Servlet支持提供了一个起点。因此,如果试图解决Spring Security的Servlet支持问题,那么在FilterChainProxy中添加调试点是一个很好的起点。
其次,由于FilterChainProxy是Spring Security使用的核心,因此它可以执行一些必要的任务。例如,它清除SecurityContext以避免内存泄漏。它还应用Spring Security的HttpFirewall保护应用程序免受某些类型的攻击。
此外,它在确定何时调用SecurityFilterChain提供了更大的灵活性。在Servlet容器中,仅根据URL调用Filter。但是,FilterChainProxy可以通过利用RequestMatcher接口,根据HttpServletRequest中的任何内容确定调用。
事实上,FilterChainProxy可以用来确定应该使用哪个SecurityFilterChain。这允许在应用程序运行时为不同的片提供完全独立的配置。
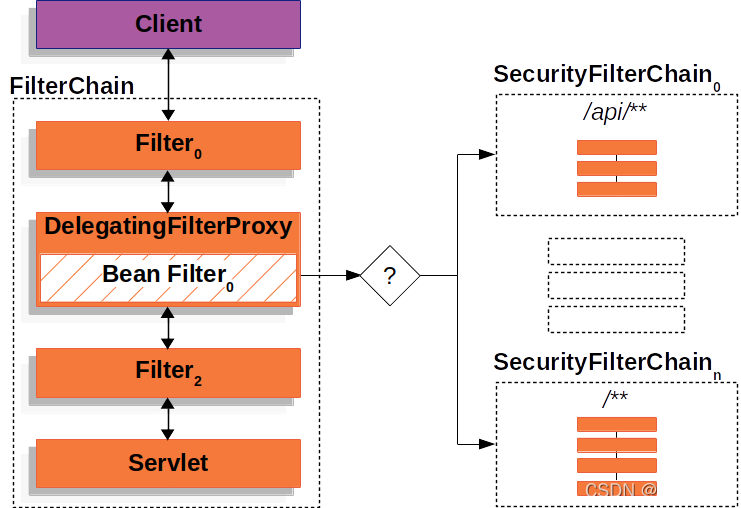
在多个SecurityFilterChain的视图中,FilterChainProxy决定应该使用哪个SecurityFilterChain,将仅调用匹配的第一个SecurityFilterChain。如果请求的URL为/api/messages/,它将首先与SecurityFilterChain0的/api/**模式匹配,因此仅调用SecurityFilterChain0,即使它也与SecurityFilterChainn匹配。如果请求的URL为/messages/,它将与SecurityFilterChain0的/api/**模式不匹配,因此FilterChainProxy将继续尝试每个SecurityFilterChain,SecurityFilterChainn将被调用(假设在这之前没有任何一个SecurityFilterChainn的模式与该请求匹配,SecurityFilterChainn的/**模式匹配该请求)。
Security Filters
Security Filters通过SecurityFilterChain API插入FilterChainProxy。这些Security Filter的顺序可以参考官方文档,数量比较多,这里就不一一列出来了。
每个Security Filter都有各自的功能,博主以后也会介绍这些Security Filter的功能和实现原理。
Handling Security Exceptions
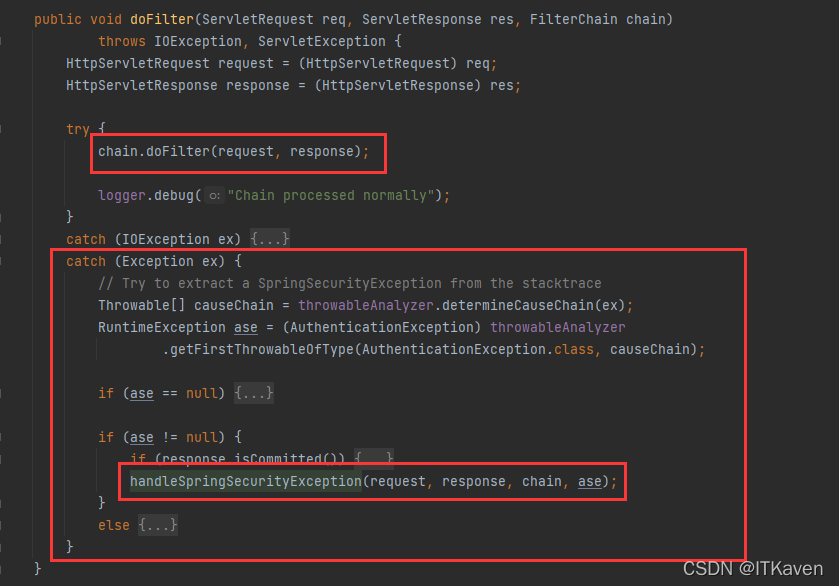
ExceptionTranslationFilter(Security Filter)允许将AccessDeniedException和AuthenticationException转换为HTTP响应。ExceptionTranslationFilter作为Security Filters之一插入到FilterChainProxy中。
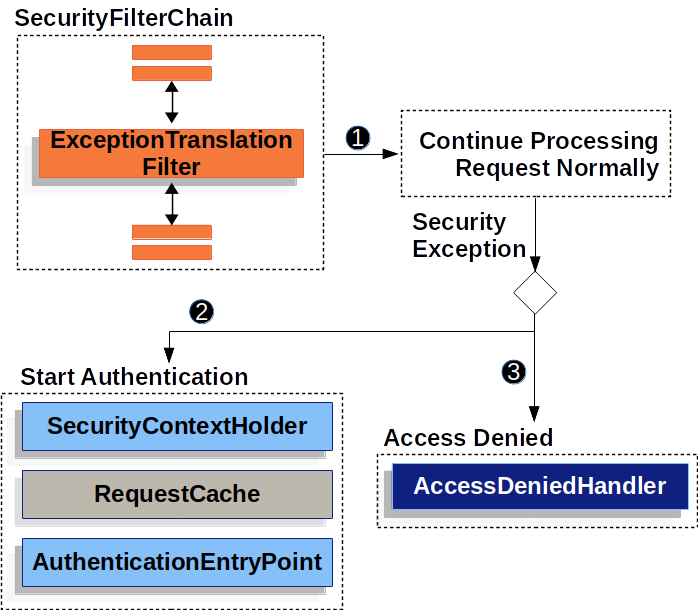
- 首先,
ExceptionTranslationFilter调用FilterChain.doFilter(request, response),即调用应用程序的其余部分(出现异常才执行自己的逻辑)。
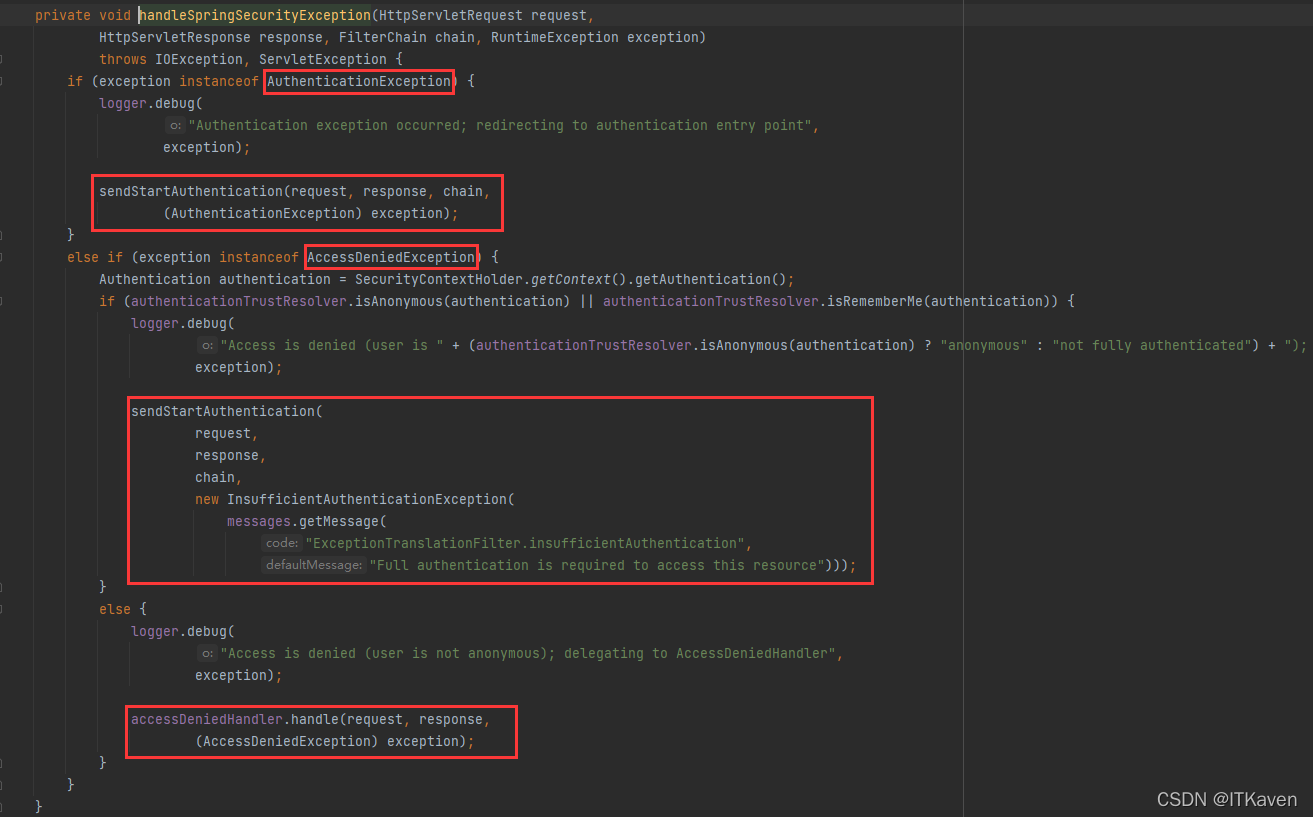
- 如果用户未经身份验证或是身份验证异常,则启动身份验证。
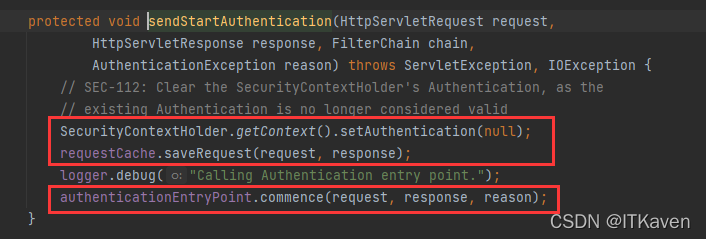
- 清除
SecurityContextHolder的身份验证(SEC-112:清除SecurityContextHolder的身份验证,因为现有身份验证不再有效)。 - 将
HttpServletRequest保存在RequestCache中。当用户成功进行身份验证时,RequestCache用于重现原始请求。 AuthenticationEntryPoint用于从客户端请求凭据。例如,它可能会重定向到登录页面或发送WWW-Authenticate标头。
- 清除
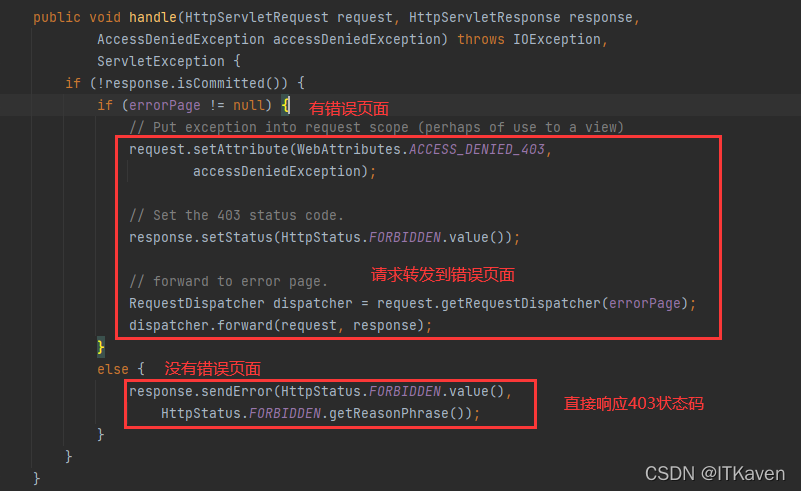
- 否则,如果是
AccessDeniedException,则拒绝访问。调用AccessDeniedHandler来处理拒绝的访问。
Spring Security的介绍就到这里,接下来博主带大家来体验一下Spring Security的便捷。
创建工程
pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.kaven</groupId>
<artifactId>security</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
接口定义:
package com.kaven.security.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: ITKaven
* @Date: 2021/12/25 11:18
* @Blog: https://kaven.blog.csdn.net
* @Leetcode: https://leetcode-cn.com/u/kavenit
* @Notes:
*/
@RestController
public class MessageController {
@GetMapping("/message")
public String getMessage() {
return "hello kaven, this is security";
}
}
启动类:
package com.kaven.security;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @Author: ITKaven
* @Date: 2021/12/25 11:17
* @Blog: https://kaven.blog.csdn.net
* @Leetcode: https://leetcode-cn.com/u/kavenit
* @Notes:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}
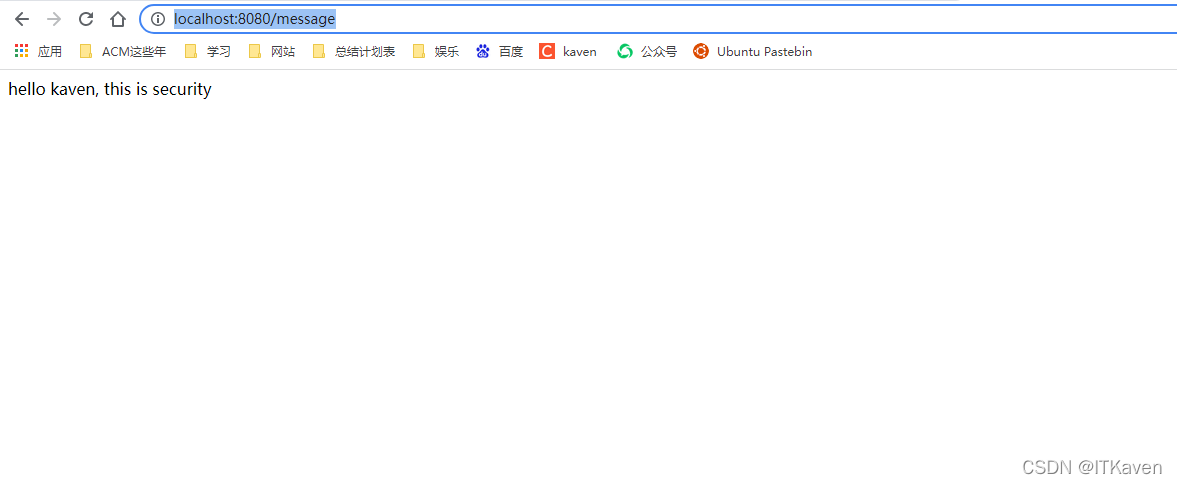
这样一个简单的Spring Boot工程就搭建好了。访问http://localhost:8080/message,就会出现如下图所示的页面:
整合Spring Security
添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
重新启动应用,日志输出和之前有所不同,如下图所示:
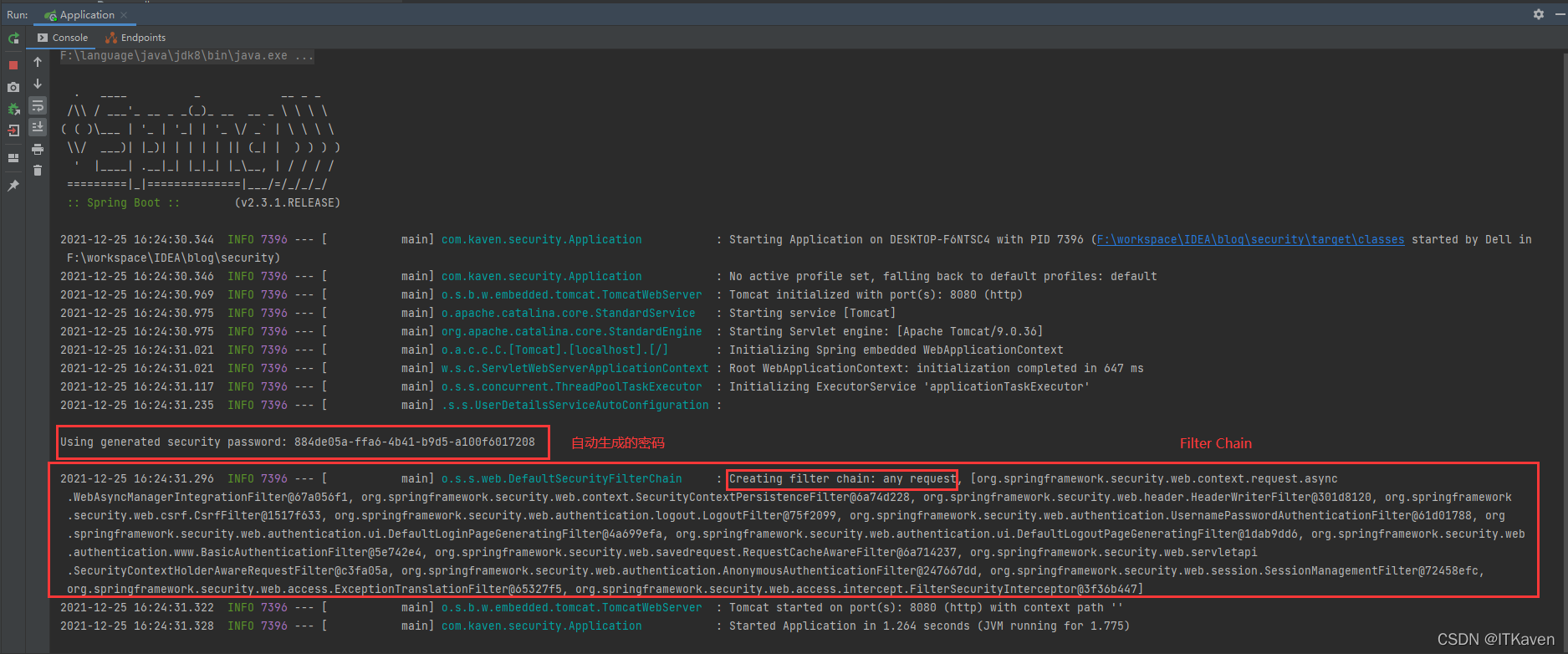
再次访问http://localhost:8080/message,会被重定向到http://localhost:8080/login,需要进行登录才能请求该接口,如下图所示:
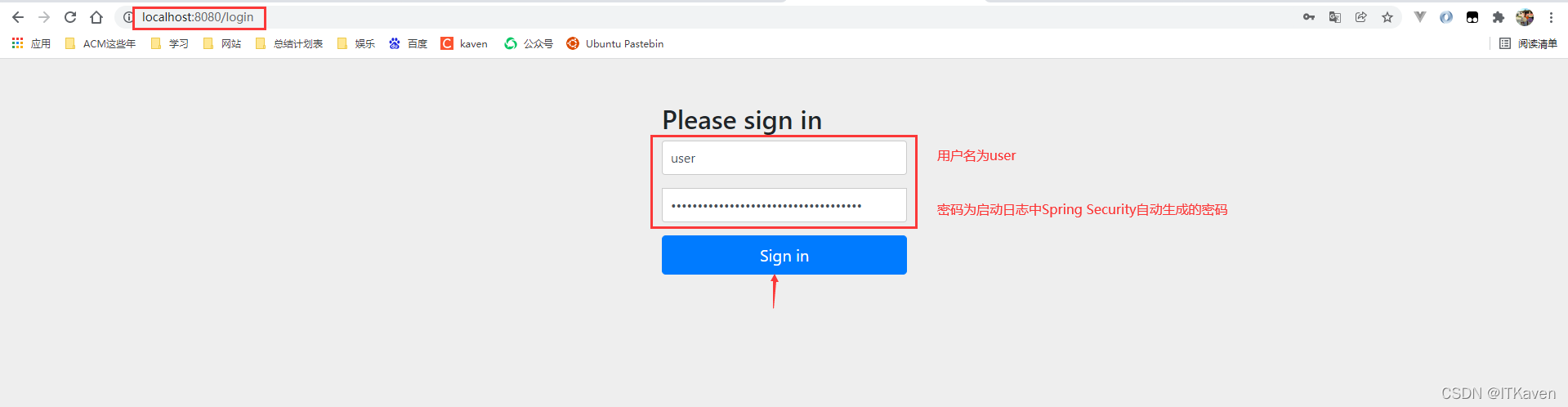
可以在application.yml配置文件中指定登录的用户名、密码以及授予该用户的权限列表:
spring:
security:
user:
name: kaven
password: itkaven
roles:
- "insert"
- "update"
- "delete"
源码与日志分析
为了探究重定向的原因,在application.yml配置文件中加入如下所示的配置:
logging:
level:
org.springframework.security: DEBUG
该配置就是让Spring Security项目的日志输出级别为DEBUG(默认为INFO),可以看见更加详细的日志信息,重新启动应用,再次访问http://localhost:8080/message,可以发现Filter Chain中有15个Filter。
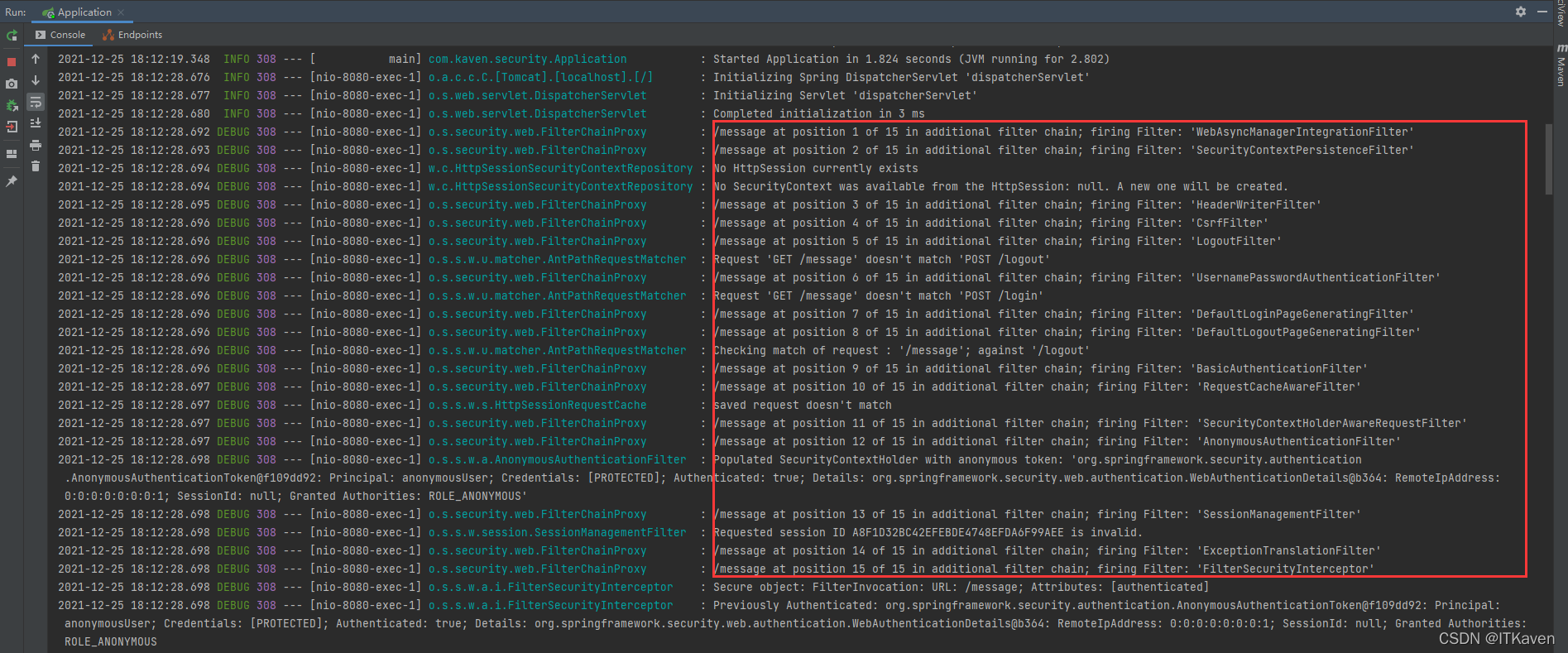
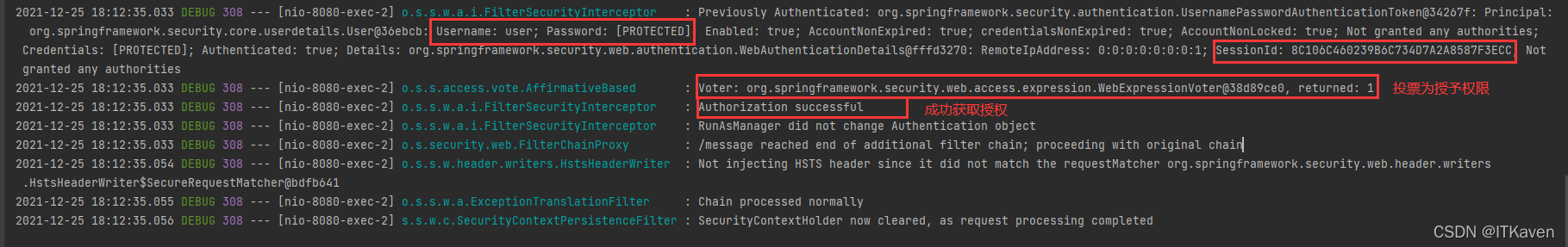
基于投票来决定是否授予访问权限(博主以后会详细介绍),默认情况下,没有赞成票就会抛出异常。
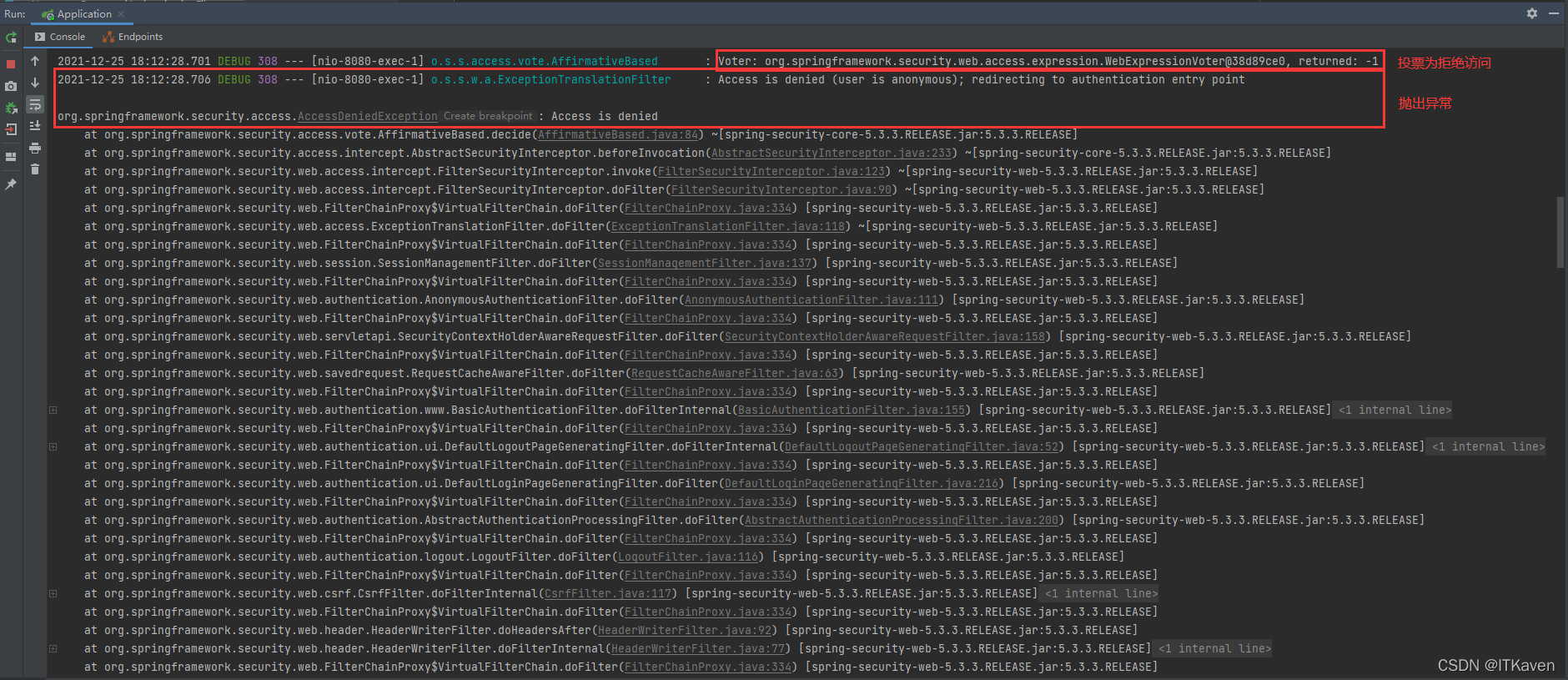
源码:
/**
* 轮询所有配置的AccessDecisionVoter
* 并在任意AccessDecisionVoter投赞成票时授予访问权限
* 仅当存在拒绝票且没有赞成票时才拒绝访问
* 如果每个AccessDecisionVoter都放弃投票
* 则决策将基于allowIfAllAbstainDecisions属性(默认为 false)
*/
public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException {
int deny = 0;
for (AccessDecisionVoter voter : getDecisionVoters()) {
int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configAttributes);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result);
}
switch (result) {
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_GRANTED:
return;
case AccessDecisionVoter.ACCESS_DENIED:
deny++;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (deny > 0) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}
// 每个AccessDecisionVoter都弃权了
checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions();
}
private boolean allowIfAllAbstainDecisions = false;
protected final void checkAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions() {
if (!this.isAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions()) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(messages.getMessage(
"AbstractAccessDecisionManager.accessDenied", "Access is denied"));
}
}
public boolean isAllowIfAllAbstainDecisions() {
return allowIfAllAbstainDecisions;
}
之后会进行重定向(说明执行了ExceptionTranslationFilter的逻辑),如下图所示(会先缓存请求):
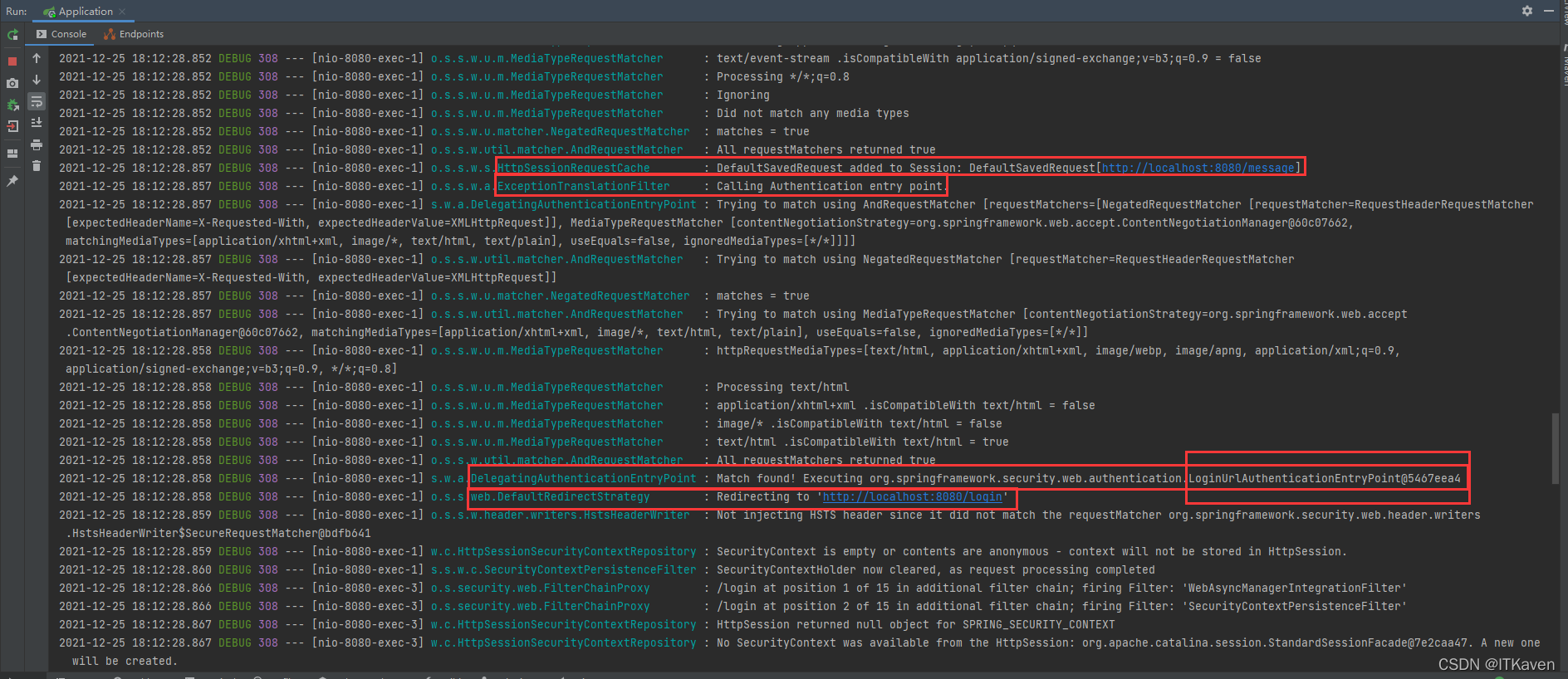
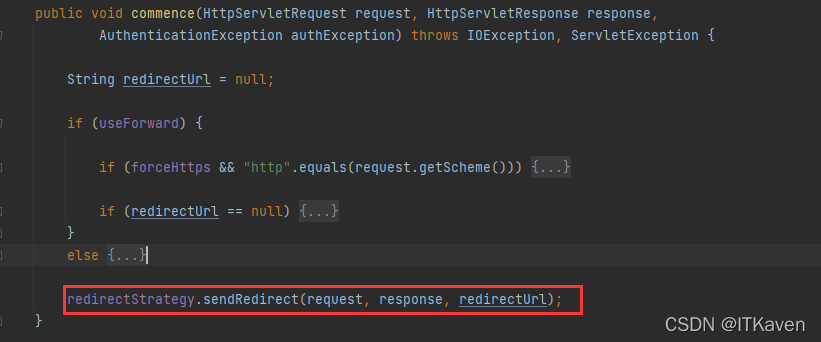
重定向到登录页面(http://localhost:8080/login),LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint相关源码:
/**
* 执行重定向(或转发)到登录表单URL
*/
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
String redirectUrl = null;
if (useForward) {
if (forceHttps && "http".equals(request.getScheme())) {
// 首先将当前请求重定向到HTTPS
// 收到该请求后,将使用登录页面的转发
redirectUrl = buildHttpsRedirectUrlForRequest(request);
}
if (redirectUrl == null) {
String loginForm = determineUrlToUseForThisRequest(request, response,
authException);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Server side forward to: " + loginForm);
}
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(loginForm);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
return;
}
}
else {
// 重定向到登录页面
// 如果forceHttps为真,则使用https
redirectUrl = buildRedirectUrlToLoginPage(request, response, authException);
}
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, redirectUrl);
}
输入正确的用户名和密码后,就会被重定向到http://localhost:8080/message。
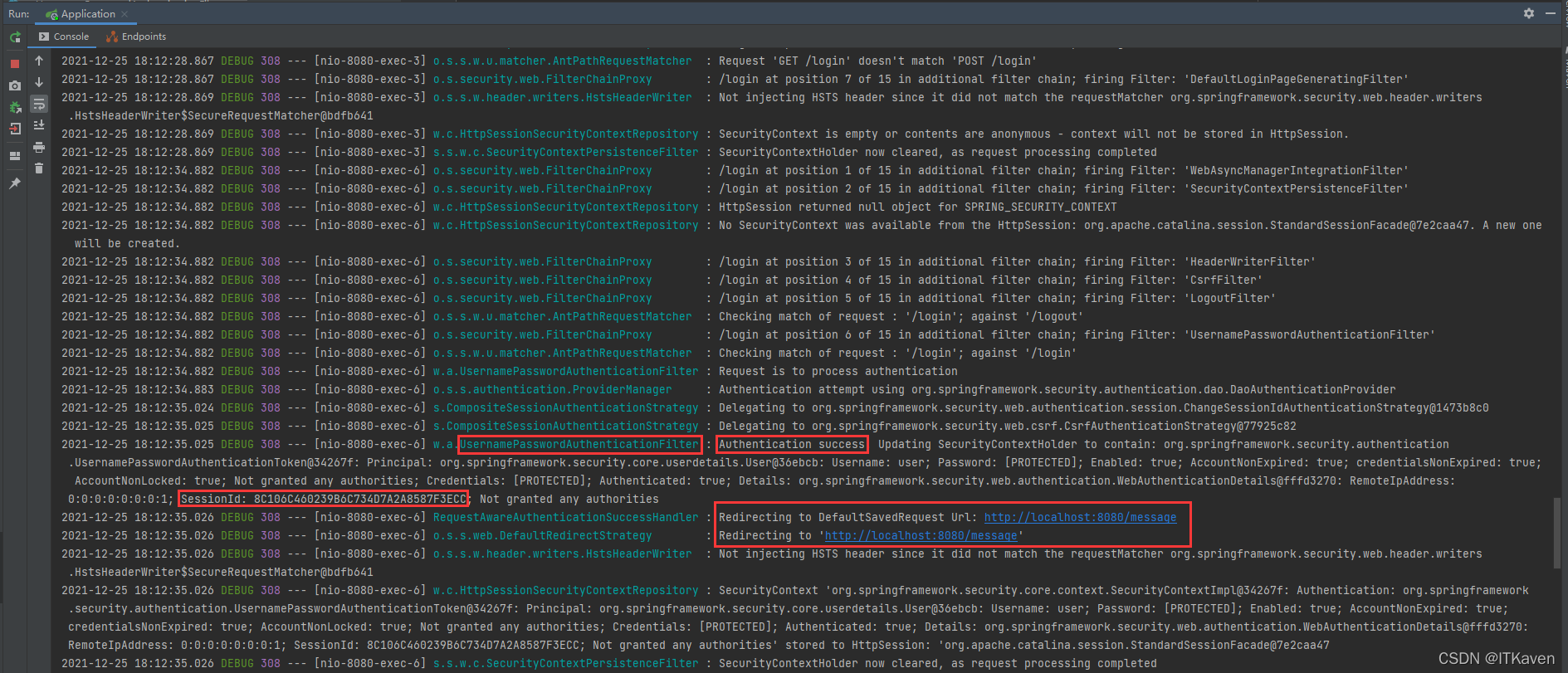
// 执行实际身份验证
// 为经过身份验证的用户返回填充的身份验证令牌,表示身份验证成功
// 如果身份验证过程失败,则抛出AuthenticationException
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
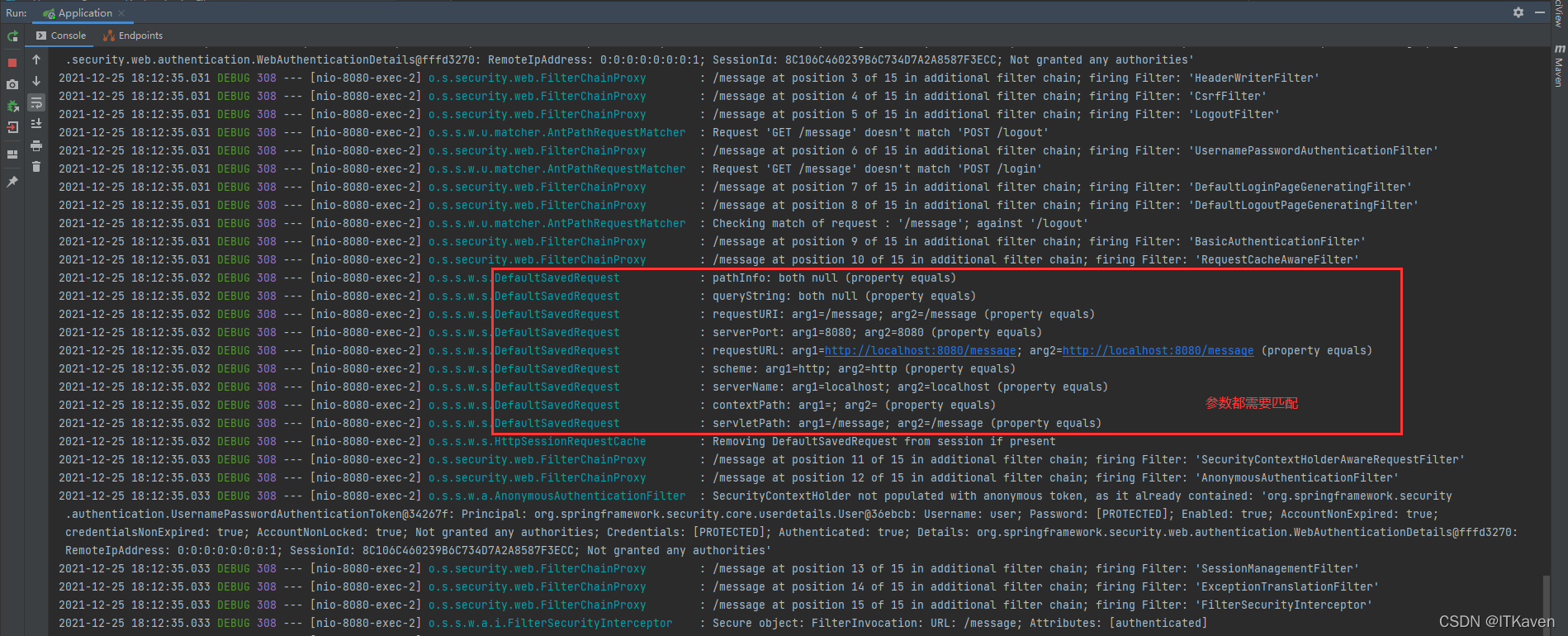
DefaultSavedRequest类被AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter和SavedRequestAwareWrapper用来在认证成功后重现请求。ExceptionTranslationFilter在身份验证异常时存储此类的实例(缓存请求阶段)。当之前的请求与此次重定向的请求完全匹配时,就会成功获取授权,即可以成功访问到该接口。
Spring Security的介绍、初体验以及关于重定向到登录页面的源码与日志分析就介绍到这里,如果博主有说错的地方或者大家有不同的见解,欢迎大家评论补充。